Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Unit Plan 1 2018-2019
Загружено:
Nancy CárdenasОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Unit Plan 1 2018-2019
Загружено:
Nancy CárdenasАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
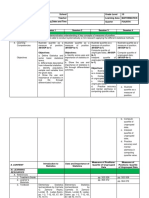
ILUSTRE MUNICIPIO DEL DISTRITO METROPOLITANO DE QUITO
SECRETARÍA DE EDUCACIÓN Y CULTURA SCHOOL YEAR
UNIDAD EDUCATIVA MUNICIPAL “SEBASTIÁN DE BENALCÁZAR” 2018--‐2019
UNIT PLANNING BY SKILLS AND PERFORMANCE CRITERIA
1. INFORMATIVE DATA:
TEACHER Nancy AREA: English GRADE/COURSE: SECOND BGU CLASS: ABCD
Cárdenas
UNIT TEXTBOOK : CONTENTS In this unit students learn O.EFL 5.1
NUMBER: how: Encounter socio-cultural aspects of their own and other countries in a
1 Unit Title:
Perfect tenses review Speculate about lifestyles thoughtful and inquisitive manner, maturely, and openly experiencing
BREAKING (affirmative, negative, yes/no in the past.
other cultures and languages from the secure standpoint of their own
NEWS question with short / long
Express opinion and national and cultural identity.
answers, Wh- Questions,
Tag questions) possibility about past
Passive voice (affirmative, events. O.EFL 5.2
negative, yes/no question Describe people, objects Draw on this established propensity for curiosity and tolerance towards
with short / long answers, and events. different cultures to comprehend the role of diversity in building an
Wh- Questions, Tag intercultural and multinational society.
questions)
Phrasal verbs 20 O.EFL 5.3
Transition words
Access greater flexibility of mind, creativity, enhanced linguistic
intelligence, and critical thinking skills through an appreciation of
linguistic differences. Enjoy an enriched perspective of their own L1 and
of language use for communication and learning.
PERIODS: 1 STARTING October ENDING WEEK: November
WEEK:
2. UNIT PLAN
SKILLS AND PERFORMANCE CRITERIA TO BE DEVELOPED: EVALUATION CRITERIA:
Oral Communication:(Listening and Speaking)
EFL 5.2.4 CE.EFL.5.1.
Follow oral directions in classroom activities and projects and provide Display an understanding of the integrity of different cultures by sharing experiences and by participating in class
directions to peers in selected interactions. activities and discussions in a way that shows empathy and respect for others.
EFL 5.2.6 CE.EFL.5.2.
Demonstrate an ability to discuss culture by analyzing cultural products and referents from Ecuador and other countries
while making informed choices about and taking action on issues of prejudice and discrimination.
Use new words and expressions which occur in conversations in the
personal and educational domains, and make use of such terms and
expressions wherever appropriate and necessary. CE.EFL.5.6.
Listening for Information: Deal with practical, everyday communication demands in familiar social and academic
Reading contexts, including following directions in class activities and identifying main ideas in other curricular subjects when
given sufficient support.
EFL 5.3.1 CE.EFL.5.7.
Production – Accuracy and Intelligibility: Use appropriate vocabulary and language in a variety of oral interactions for a
Find specific predictable information in short, simple texts in a range
range of audiences and level-appropriate purposes.
of age- and level-appropriate topics. (Example: biographies, news
articles, narratives, memoirs and personal accounts, formal letters
and emails, etc.) CE.EFL.5.10.
Find specific information and identify the main points in simple, straightforward texts on subjects of personal interest or
Writing familiar academic topics while making informed decisions about one’s own reaction to the text.
CE.EFL.5.15.
Plan and produce well-constructed informational texts by applying the writing process and while demonstrating an ability
EFL 5.4.7 to justify one’s position on an argument through carefully selected information and appropriate language, tone and
evidence.
Use the process of prewriting, drafting, revising, peer editing and
CE.EFL.5.19.
proofreading (i.e., “the writing process”) to produce well-constructed
informational texts.
Engage in collaborative activities through a variety of student groupings in order to solve problems and reflect on literary
texts, and produce criteria for evaluating the effectiveness of the group.
Language through the Arts
EFL 5.5.7
Collaboratively produce criteria for evaluating literary texts and the
effectiveness of group work.
METHODOGICAL RESOURCES: PERFORMANCE INDICATORS: ACTIVITIES TECHNIQUES/INSTRUMENTS:
STRATEGIES:
Cycle 1
Communication and Cultural New Curriculum EFL for Superior Communication and Cultural Awareness Warm up;Ss might ask to find out about classmates (brainstorm
Awareness BGU questions) what do you think of matchmaking? Does it work? and write
Interchange 3 fourth Edition I.EFL.5.1.1. Learners can demonstrate an un- on the board their ideas.
Writing a weekly journal entry derstanding of the integrity of different cultures Ss complete the mind map using their background knowledege
about a cross-cultural by sharing experiences and by participating in Ss answer the following questions and elicit ideas:
experience. class activities and discussions in a way that What do you think women look for most in a partner?
Flash Cards shows empathy and respect for others. (I.3, What are some important differences between men and women?
Oral Communication:(Listening S.1, S.2, J.1, J.3) Ss look at the picture displayed at the screen and they describe it.
and Speaking) Photocopiable Sheets Ss are encouraged to make guesses.
Listening to a set of instructions I.EFL.5.2.1. Learners can exhibit an ability to Ss. Answer the following questions by listening the audio:
and putting them in order. Crosswords discuss culture by analyzing cultural products 1. What is Kim problem?
and referents from Ecuador and other 2. Who does Chris suggest?
Listening to and following class Strategies Templates countries while making informed choices 3. How will Kim meet Chris friend?
commands. about and taking action on issues of prejudice Ss practice the conversation in pairs.
and discrimination. (I.1, I.2, S.2, J.1, J.3) Listening for opinions; listening to descriptions of people; making
inferences.
Singing songs that practice
Oral Communication: Listening and Ss divide the class into teams. Each team brainstorm positive and
helpful language.
Speaking) negative adjectives to describe personalities.
Ss. Set a time limit of three minutes. Call on different Ss from each
Giving learner’s language
I.EFL.5.6.1. Learners can deal with practical, team to write adjectives into 2 columns on the board.
prompts to use during
everyday communication demands in familiar Ss will listen to descriptions of three people. After listening to each
pair/group work. (Example:
social and academic contexts, such as conversation. They decide if the general feeling is positive or negative
What do you think? I
following directions in class activities and and tell reasons to the class.
agree/disagree. I think we need
identifying main ideas in other curricular Then, Ss talk about an ideal friend in pairs. Ss write the first draft of
to…, It’s your turn, etc.)
subjects when given sufficient support. (I.1, their paragraph focusing in three areas: 1. Content 2. Organization 3.
I.3, S.1) Grammar. They work in class and as a homework.
Playing games that practice
Ss model the conversation using the vocabulary learned in the website
classroom language, turn-
I.EFL.5.7.1. Learners can communicate then they create their own conversation performing in front of the class.
taking, being polite, etc.
clearly and effectively by using appropriate practice online
vocabulary and language in a variety of oral http://www.cambridge.org/interchangearcade/
Reading Video online:
Reading a short text and interactions for a range of audiences and
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WhSzXFQb3qc
showing comprehension by level-appropriate purposes. (I.2, I.3, J.2) Audio online:
completing the accompanying http://www.cambridge.org/interchange/audioprogram/#a4
graphic organizer. (Example: Reading
learners read about Cycle 2
archeological ruins and I.EFL. 5.10.1. Learners can find specific in- Ss look at the pictures and discuss the questions and review the
complete a Venn diagram, etc.) common complaints :
formation and identify the main points in
simple, straightforward texts on subjects of What is happening?
Reading a text on a familiar How do you think the teachers and students feel?
personal interest or familiar academic topics
content area subject and Would this annoy you? Why?
while making informed decisions about one’s
answering information ques- Ss will hear 8 common complaints. They are displayed on the screen
own reaction to the text. (I.1, I.2, S.2)
tions. (Example: learners read but displayed in the wrong order. Then ss listen and number the
about foodborne illnesses and Writing complaints in the order they hear them. Play the audio program. Then
then write three ways to prevent I.EFL.5.15.1. Learners can plan and produce Ss open their worksheets and check their own answers.
them, etc.) Ss elaborate paragraphs using expressions of compliments and also
well-constructed informational texts by
applying the writing process and while add the phrases it embarrasses me …………..
Reading a text and answering It bothers me……
demonstrating an ability to justify one’s
information questions. It upsets me……..
position on an argument through carefully
selected information and appropriate lan- I hate it……..
guage, tone and evidence. (I.2, I.3, I.4, S.3,
Choosing from a list of words to J.1) Ss find some examples of sentences that begin with the word it in the
complete gaps from a reading. chart displayed and copied in their digital books.
Language through the Arts Then they use the samples in their sentences.
Reading a paragraph about a Ss are encouraged to use some of the phrases on the board and give
familiar content area subject I.EFL.5.19.1. Learners can engage in collabo- their opinions, they will share with their partners and in front of the class.
and then correcting incorrect rative activities through a variety of student Ss will predict what kind of information they will read in the article. Then
sentences. (Example: In groupings in order to solve problems and re- Ss read the article silently, Ss should read the article without stopping
northern India, the monsoon flect on literary texts, and produce criteria for to ask questions or use a dictionary. back through the text and circle
season lasts for six months evaluating the effectiveness of the group. (I.1, words they can´t guess from the context
every year - three, etc.) I.2, S.2, S.3, S.4, J.3, J.4) Then, tell students to go back through the text and circle words they
can´t guess from context. Ss work in pairs to figure it out unfamiliar
Writing vocabulary and finally teacher explains any remaining new vocabulary.
Completing an online graphic The teacher explains based on the article the task and Ss decide what
organizer in order to help plan a is true and what is false. The ss reread the article individually and
piece of writing. answer the questions. Then ss compare the answers in pairs, ss show
their partners where answers are in the article. Teacher goes over
Reading a text and using a answers with the class.
checklist to talk about how it is
organized. (Example: Is there a OPTION Ss write a poem for a friend or loved one Ss fill in this
title? Does it have an opening framework: You are…..
sentence?, etc.) Someone who…..
Someone…………….
Recording synonyms and Someone who…….
antonyms of words in the And that is why…….
margins of reading texts. I care for you.
For more practice the ss have to complete the activities in the
Writing new words and phrases workbook 4 ‘ 6
in a vocabulary notebook and Lab guide Exercises 5 -6
then writing a text using three Video activity book unit 1.
words from your vocabulary
notebook. Writing about a best friend.
“Friends again – Forever”
Exchanging writing in pairs in Reading a narrative about friendship.
order to make suggestions Video online:
about things that could be https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WhSzXFQb3qc
improved.
Audio online:
http://www.cambridge.org/interchange/audioprogram/#a4
Language through the Arts
Evaluating and assessing the Practice online:
effectiveness of group work by http://www.cambridge.org/interchangearcade/
answering a set of questions.
(Example: Who always Answers:
participates? Who gets the http://assets.cambridge.org/052160/2254/sample/0521602254ws.pdf
things the group needs? Who
asks good questions?, etc.)
Selecting desirable behaviors
for group work from a list and
reaching a consensus as a
group for the three most
important.
Writing a checklist in pairs to
use to evaluate another group’s
project.
Discussing rules and norms for
a group project before the
project begins. (Example: Don’t
interrupt others, Do your work
on time, Don’t make negative
remarks, etc.)
3. ADAPTED CURRICULUM:
SPECIFICATION OF EDUCATIONAL NEEDS: SPECIFICATION OF THE ADAPTED MATERIAL TO BE APPLIED:
Teachers who work with students with special needs learn how Quizzes, Test, Written Lessons will be taken with a less level of difficulty
identify disabilities in order to design personalized plans based on
assessment results and empirical data. Thus, they should modify the
objectives and indicators in accordance with those results, and adapt
the corresponding activities.
4. CROSS CURRICULUM:
CLIL: SCIENCE: TRANSVERSAL AXES:
https://www.examenglish.com/FCE/fce_reading_and_use_of Intercultural awareness, tolerance, respect, multiculturalism,
_english_part1.htm responsibility, solidarity, responsibility, honesty, respect, love, peace,
justice, innovation, etc.
5. QAP/QAC:
PREPARED BY: REVISED BY: APPROVED BY:
Teacher: Nancy Cárdenas Coordinator: Estefania Perez Principal: Dra. Marcia Barros
Signature: Signature: Signature:
Date October 2018 Date October 2018 Date October 2018
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- RecipeДокумент2 страницыRecipeNancy CárdenasОценок пока нет
- Annual Plan 2Документ22 страницыAnnual Plan 2Nancy CárdenasОценок пока нет
- Jornal Wheel 2Документ4 страницыJornal Wheel 2Nancy CárdenasОценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- I Interviewed CeoДокумент5 страницI Interviewed CeoNancy CárdenasОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Fair LadyДокумент2 страницыFair LadyNancy CárdenasОценок пока нет
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- I Interviewed CeoДокумент5 страницI Interviewed CeoNancy CárdenasОценок пока нет
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Planificacion Segundos 2015Документ11 страницPlanificacion Segundos 2015Nancy CárdenasОценок пока нет
- Villa Beach TourismДокумент5 страницVilla Beach TourismNancy CárdenasОценок пока нет
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Información Enseña Inglés Caribe 2015Документ3 страницыInformación Enseña Inglés Caribe 2015Nancy CárdenasОценок пока нет
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- MethodologyДокумент1 страницаMethodologyNancy CárdenasОценок пока нет
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Chapter 2 Answer SheetДокумент3 страницыChapter 2 Answer SheetsharjaОценок пока нет
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Grammar-Voc Test 3 2Nd Bachillerato BДокумент4 страницыGrammar-Voc Test 3 2Nd Bachillerato BSonia Chamorro BeltranОценок пока нет
- What Not To Put in A Literature ReviewДокумент6 страницWhat Not To Put in A Literature Revieweubvhsvkg100% (1)
- CT20213800256 ApplicationДокумент5 страницCT20213800256 ApplicationGAMING LABОценок пока нет
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- 2019 Brigada-Eskwela-Action-PlanДокумент7 страниц2019 Brigada-Eskwela-Action-PlanMercedita Balgos67% (3)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Overweight Students of GANHS SHS On The Efficacy of The Ketogenic Diet"Документ2 страницыOverweight Students of GANHS SHS On The Efficacy of The Ketogenic Diet"Red Meigen ImportanteОценок пока нет
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- ĐỀ THAM KHẢO SỐ 1Документ6 страницĐỀ THAM KHẢO SỐ 1Lê Hồng LoanОценок пока нет
- USMLE StepДокумент1 страницаUSMLE StepAscend KannanОценок пока нет
- History of Simbahan Ni Teodorico IncorporatedДокумент12 страницHistory of Simbahan Ni Teodorico IncorporatedAileen CañonesОценок пока нет
- CIML005 DICT Oct21 Sem Teaching Plan (CPAM-C) Term BДокумент4 страницыCIML005 DICT Oct21 Sem Teaching Plan (CPAM-C) Term BAnson SooОценок пока нет
- Narrative On ELLNДокумент2 страницыNarrative On ELLNrachelle baggao100% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Abeles-Political Anthropology New Challenges, New Aims PDFДокумент14 страницAbeles-Political Anthropology New Challenges, New Aims PDFJosh MaiyoОценок пока нет
- Case of BundocДокумент5 страницCase of Bundocjunar dacallosОценок пока нет
- Informative Speech Outline LatestДокумент4 страницыInformative Speech Outline LatestAzlan KinGshah II100% (2)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- 11 Reasons Why Quo Warranto Decision On Sereno Was CorrectДокумент3 страницы11 Reasons Why Quo Warranto Decision On Sereno Was CorrectMelvin PernezОценок пока нет
- If You Are A ScientistДокумент2 страницыIf You Are A ScientistCkysha TumpagОценок пока нет
- ARRANGED HEALTH - PEACE.VALUES Catch Up FridaysДокумент44 страницыARRANGED HEALTH - PEACE.VALUES Catch Up FridaysVegilla Sinlao Ann Jeeh100% (1)
- Analisis Beban Kerja Mental Mahasiswa Saat PerkuliДокумент8 страницAnalisis Beban Kerja Mental Mahasiswa Saat PerkuliAdiyatma Ghazian PratamaОценок пока нет
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (120)
- Earth Science Syllabus PDFДокумент4 страницыEarth Science Syllabus PDFthanksforshopinОценок пока нет
- Exercise 3 Predator Prey EcologyДокумент2 страницыExercise 3 Predator Prey EcologyRenielle RebadomiaОценок пока нет
- Interpersonal Relationships and Adaptation of Paramedical Foreign Students in Southwestern University-PhinmaДокумент3 страницыInterpersonal Relationships and Adaptation of Paramedical Foreign Students in Southwestern University-PhinmaAimee-Sara ShuaibОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan Basketball King of The Court 1Документ7 страницLesson Plan Basketball King of The Court 1api-528361125Оценок пока нет
- Dự Án Đề Thi Thử Tốt Nghiệp Thpt Qg 2021 - phân Loại Theo Dạng Bài - thầy Lương (Dr Salary)Документ68 страницDự Án Đề Thi Thử Tốt Nghiệp Thpt Qg 2021 - phân Loại Theo Dạng Bài - thầy Lương (Dr Salary)Thư MinhОценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент593 страницыUntitledSuzan ShanОценок пока нет
- G10 DLL Fourth-QuarterДокумент110 страницG10 DLL Fourth-QuarterJAYSON100% (3)
- Final Coaching Prof Ed June 2022Документ29 страницFinal Coaching Prof Ed June 2022Mark Paul Dumoran Nitafan100% (3)
- Meet and Greet: (Grade 6 - Honesty)Документ20 страницMeet and Greet: (Grade 6 - Honesty)mark anthony ordonioОценок пока нет
- 15 March 2021Документ3 страницы15 March 2021chs076 Maria AlkiftiahОценок пока нет
- Special Report: Survey of Ph.D. Programs in ChemistryДокумент6 страницSpecial Report: Survey of Ph.D. Programs in ChemistryPablo de TarsoОценок пока нет
- Government Policies On Small Scale Business, Its Impact On Nigeria Cooperative DevelopmentДокумент47 страницGovernment Policies On Small Scale Business, Its Impact On Nigeria Cooperative DevelopmentJeezОценок пока нет