Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
BTS, BSC, MSC Details: February 2016
Загружено:
Frenzy Duana AcboОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
BTS, BSC, MSC Details: February 2016
Загружено:
Frenzy Duana AcboАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.
net/publication/295819666
BTS, BSC, MSC details
Presentation · February 2016
DOI: 10.13140/RG.2.1.2075.6241
CITATIONS READS
0 53,010
2 authors, including:
Nizar Zarka
Higher Institute for Applied Sciences and Technology
73 PUBLICATIONS 80 CITATIONS
SEE PROFILE
Some of the authors of this publication are also working on these related projects:
Fast Rule-line Removal using Integral Images and Support Vector Machines View project
Incorporating Appearance and Edge Features for Vehicle Detection in the Blind-spot Area View project
All content following this page was uploaded by Nizar Zarka on 24 February 2016.
The user has requested enhancement of the downloaded file.
Higher Institute for Applied Science and Technology
Telecommunication department
Fifth year
2015-2016
BTS, BSC, MSC details
Raghda Khadoor
Supervisor: Dr. Nizar Zarka
Feb 2016
Raghda Khadoor & Dr. Nizar Zarka
OUTLINE
GSM architecture
BTS
BSC
MSC
Raghda Khadoor & Dr. Nizar Zarka
GSM architecture
the GSM network architecture consists of different elements that all
interact together to form the overall GSM system. These include
elements like the base-station, BSC, MSC, AuC, HLR, VLR, etc.
Raghda Khadoor & Dr. Nizar Zarka
Base Transceiver Station (BTS):
The BTS used in a GSM network comprises the radio
transmitter receivers.
The BTS is the defining element for each cell.
The BTS communicates with the mobiles and the
interface between the two is known as the Um interface
with its associated protocols.
Raghda Khadoor & Dr. Nizar Zarka
BTS architecture
Raghda Khadoor & Dr. Nizar Zarka
Linking units transmitter and receiver with different
location cells
Raghda Khadoor & Dr. Nizar Zarka
Base Station Controller (BSC):
The BSC forms the next stage back into the GSM
network.
It controls a group of BTSs, and is often co-located
with one of the BTSs in its group.
It manages the radio resources and controls items
such as handover within the group of BTSs,
allocates channels and the like.
It communicates with the BTSs over what is termed
the Abis interface.
Raghda Khadoor & Dr. Nizar Zarka
BSC architecture
Raghda Khadoor & Dr. Nizar Zarka
Mobile Switching services Centre (MSC)
The main element within the core network area of the
overall GSM network architecture is the Mobile
switching Services Centre (MSC).It provides registration,
authentication, call location, inter-MSC handovers and
call routing to a mobile subscriber.
It also provides an interface to the PSTN so that calls
can be routed from the mobile network to a phone
connected to a landline.
Interfaces to other MSCs are provided to enable calls to
be made to mobiles on different networks.
Raghda Khadoor & Dr. Nizar Zarka
MSC architecture
Raghda Khadoor & Dr. Nizar Zarka
HLR
This database contains all the administrative information about each
subscriber along with their last known location.
VLR :
This contains selected information from the HLR that
enables the selected services for the individual
subscriber to be provided. The VLR can be
implemented as a separate entity, but it is commonly
realised as an integral part of the MSC, rather than a
separate entity. In this way access is made faster and
more convenient.
Raghda Khadoor & Dr. Nizar Zarka
Authentication Centre (AuC)
The AuC is a protected database that contains the secret key also
contained in the user's SIM card. It is used for authentication and for
ciphering on the radio channel.
Equipment Identity Register (EIR)
The EIR is the entity that decides whether a given mobile equipment
may be allowed onto the network. Each mobile equipment has a
number known as the International Mobile Equipment Identity
Raghda Khadoor & Dr. Nizar Zarka
Thank you
Raghda Khadoor & Dr. Nizar Zarka
View publication stats
Вам также может понравиться
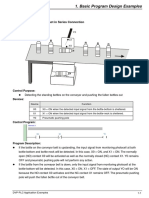
- Basic PLC Program Design ExamplesДокумент169 страницBasic PLC Program Design ExamplesAlexCanenciaОценок пока нет
- SHS Applied - English For Academic and Professional Purposes CG PDFДокумент6 страницSHS Applied - English For Academic and Professional Purposes CG PDFGiancarla Maria Lorenzo Dingle100% (2)
- 04c Process Map Templates-V2.0 PDFДокумент17 страниц04c Process Map Templates-V2.0 PDFAlfredo FloresОценок пока нет
- Preparation: ERICSSON Node B Commissioning and IntegrationДокумент37 страницPreparation: ERICSSON Node B Commissioning and IntegrationBSCОценок пока нет
- A00 281Документ67 страницA00 281Venkata Lakshmi Burla100% (2)
- Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN) Systems Architecture and DesignОт EverandOpen Radio Access Network (O-RAN) Systems Architecture and DesignОценок пока нет
- 4G LTE Mobile Broadband OverviewДокумент64 страницы4G LTE Mobile Broadband OverviewsitanjungОценок пока нет
- Intelligent Routing Metric For Wireless Body Area NetworksДокумент7 страницIntelligent Routing Metric For Wireless Body Area NetworksEditor IJRITCCОценок пока нет
- SAP APO PPDS For Automotive PDFДокумент92 страницыSAP APO PPDS For Automotive PDFOshun Tang100% (6)
- Overview and Design of VXLAN: November 2016Документ7 страницOverview and Design of VXLAN: November 2016Eh PhotographyОценок пока нет
- Bts BSC MscdetailsДокумент14 страницBts BSC Mscdetailsjay shambhoОценок пока нет
- Bts BSC MSC DetailsДокумент14 страницBts BSC MSC Detailsjanej9271Оценок пока нет
- Bts BSC MSC DetailsДокумент13 страницBts BSC MSC DetailsWaheed KhanОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Wireless Sensor Networks: January 2015Документ34 страницыIntroduction To Wireless Sensor Networks: January 2015Surya PrabhaОценок пока нет
- Wireless Body Area Network_ an Overview and Various ApplicationsДокумент16 страницWireless Body Area Network_ an Overview and Various ApplicationsRajesh PОценок пока нет
- RadДокумент12 страницRadForever ForeverОценок пока нет
- A On Summer Vocational Training: Bharat Sanchar Nigam LimitedДокумент20 страницA On Summer Vocational Training: Bharat Sanchar Nigam LimitedMohammad ShoebОценок пока нет
- GSM Hardware Architecture Seminar ReportДокумент13 страницGSM Hardware Architecture Seminar ReportNIKHIL ASОценок пока нет
- A Broad Assessment of Data Migration Practice in Network Communication IndustriesДокумент6 страницA Broad Assessment of Data Migration Practice in Network Communication IndustriesInternational Journal of Engineering and TechniquesОценок пока нет
- Performance Evaluation of Aodv Protocol For Energy Consumption and Qos in Ieee 802.15.4 Based Wireless Sensor Network Using Qualnet SimulatorДокумент11 страницPerformance Evaluation of Aodv Protocol For Energy Consumption and Qos in Ieee 802.15.4 Based Wireless Sensor Network Using Qualnet Simulatorambie tubeОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Wireless Sensor Networks: January 2015Документ34 страницыIntroduction To Wireless Sensor Networks: January 2015Hadjer mОценок пока нет
- WGU IT - Capstone - Proposal-Excellent-CWДокумент18 страницWGU IT - Capstone - Proposal-Excellent-CWT.c. FlattОценок пока нет
- Ieee Iccic PaperДокумент6 страницIeee Iccic PaperBharathОценок пока нет
- Secure Routing in Wireless Sensor Networks Using WEAP ProtocolДокумент7 страницSecure Routing in Wireless Sensor Networks Using WEAP ProtocolShakeel RanaОценок пока нет
- Location Management in Cellular Mobile Networks: IEEE Potentials February 2014Документ16 страницLocation Management in Cellular Mobile Networks: IEEE Potentials February 2014Vũ Trọng LinhОценок пока нет
- MW PDFДокумент9 страницMW PDFtemesgenОценок пока нет
- SDN and Network Slicing Model for Mobile Core NetworksДокумент14 страницSDN and Network Slicing Model for Mobile Core Networkssamaa adelОценок пока нет
- PAPER5Документ6 страницPAPER5Caio CruzОценок пока нет
- Research Papers On WbanДокумент4 страницыResearch Papers On Wbanafeaoebid100% (1)
- Software Defined Cognitive Radio Network Framework: Design and EvaluationДокумент9 страницSoftware Defined Cognitive Radio Network Framework: Design and EvaluationPhong NguyenОценок пока нет
- Wireless Sensor Networks ApplicationДокумент23 страницыWireless Sensor Networks Applicationrock geminiОценок пока нет
- Information Security in Self-Organized NetworkДокумент12 страницInformation Security in Self-Organized NetworkPriyanka RaniОценок пока нет
- Seminar Individual AssignmentДокумент15 страницSeminar Individual AssignmentRobel AsfawОценок пока нет
- Wireless SCADAДокумент3 страницыWireless SCADAEditor IJTSRDОценок пока нет
- CETPA-Wireless TelecomTrainingДокумент2 страницыCETPA-Wireless TelecomTrainingmohd faizanОценок пока нет
- Taxonomy For Wireless Sensor Networks Services Characterisation and ClassificationДокумент4 страницыTaxonomy For Wireless Sensor Networks Services Characterisation and ClassificationAnitha McОценок пока нет
- Agent Based Qos Provisioning For NGMN (Lte) : Prof.D.Jayaramaiah,, A.Prasanth, A.Viswanatha Reddy, DR - Anirban BasuДокумент11 страницAgent Based Qos Provisioning For NGMN (Lte) : Prof.D.Jayaramaiah,, A.Prasanth, A.Viswanatha Reddy, DR - Anirban Basuأبو أيوب تافيلالتОценок пока нет
- Ieee Research Papers On Wireless Network SecurityДокумент6 страницIeee Research Papers On Wireless Network SecuritynepwuhrhfОценок пока нет
- CSC 472E Cat Wireless Sensor NetworksДокумент12 страницCSC 472E Cat Wireless Sensor NetworksEzra KenyanyaОценок пока нет
- Wireless Security An OverviewДокумент16 страницWireless Security An OverviewMervis EncelanОценок пока нет
- 1312 - BDD Tdma Mac - JBMДокумент11 страниц1312 - BDD Tdma Mac - JBMTola AlegbeleyeОценок пока нет
- HCL Industrial Training ReportДокумент40 страницHCL Industrial Training ReportBirjesh KumarОценок пока нет
- Wireless Network Cloud: Architecture and System RequirementsДокумент12 страницWireless Network Cloud: Architecture and System Requirementspeppas4643Оценок пока нет
- Juniper Multiplay GlossaryДокумент13 страницJuniper Multiplay GlossarydjbartuОценок пока нет
- Cisco Mobility Services Engine - Context Aware Mobility Solution Deployment GuideДокумент87 страницCisco Mobility Services Engine - Context Aware Mobility Solution Deployment GuideWardono StОценок пока нет
- WP Ims Migrating HLR HssДокумент5 страницWP Ims Migrating HLR HssJames KiddОценок пока нет
- Bahra University: Global System For Mobile CommunicationДокумент7 страницBahra University: Global System For Mobile Communicationajay palsraОценок пока нет
- Quality of Service of Routing Protocols in Wireless Sensor Networks: A ReviewДокумент26 страницQuality of Service of Routing Protocols in Wireless Sensor Networks: A ReviewlupsumetroОценок пока нет
- GSM Control Channels With RTL-SDR and GNU RadioДокумент5 страницGSM Control Channels With RTL-SDR and GNU RadioImen DjebliОценок пока нет
- 2024 Localization in Wireless Sensors NetworkДокумент51 страница2024 Localization in Wireless Sensors NetworknithyadheviОценок пока нет
- Simulation of MIH Across Heterogenous Wireless Network Using NS2Документ53 страницыSimulation of MIH Across Heterogenous Wireless Network Using NS2nasmasnasОценок пока нет
- Template For Submissions To Scientific ReportsДокумент9 страницTemplate For Submissions To Scientific ReportsMohamed YaCine LaidaniОценок пока нет
- Thesis Report On Ad Hoc NetworkДокумент6 страницThesis Report On Ad Hoc Networkqpftgehig100% (2)
- Dynamic Routing For Data Integrity and Delay Differentiated Services in Wireless Sensor NetworksДокумент4 страницыDynamic Routing For Data Integrity and Delay Differentiated Services in Wireless Sensor NetworksKumara SОценок пока нет
- Performance Analysis of Delay in Wireless Sensor Networks: Jayashree C. Pasalkar Vivek S. DeshpandeДокумент4 страницыPerformance Analysis of Delay in Wireless Sensor Networks: Jayashree C. Pasalkar Vivek S. Deshpandeteferi kassaОценок пока нет
- 4-15the Mobile GlossaryДокумент0 страниц4-15the Mobile GlossaryRIZKY RIFKYОценок пока нет
- Ijesat 2012 02 Si 01 07Документ4 страницыIjesat 2012 02 Si 01 07Ijesat JournalОценок пока нет
- 3 ThreeДокумент4 страницы3 ThreeAlexanderOmorokunwaОценок пока нет
- Middleware ArchitectureДокумент7 страницMiddleware ArchitectureUmaОценок пока нет
- Trust Based Scheme For Iot Enabled Wireless Sensor NetworksДокумент20 страницTrust Based Scheme For Iot Enabled Wireless Sensor NetworksS G ShivaPrasad YadavОценок пока нет
- Mtap S 24 04432Документ13 страницMtap S 24 04432R. B.Оценок пока нет
- Bandwidth RecyclingДокумент4 страницыBandwidth RecyclingMahesh BabuОценок пока нет
- Sarjet 31 31-41Документ12 страницSarjet 31 31-41mohamed balОценок пока нет
- SW 3/22/2010 CCNA3 Chap 7 Study Answers 1Документ6 страницSW 3/22/2010 CCNA3 Chap 7 Study Answers 1Hien TauОценок пока нет
- Network Components Et DevicesДокумент4 страницыNetwork Components Et DevicesAbdourahmane KaneОценок пока нет
- Project Mesa: Broadband Obility For Mergency and Afety PplicationsДокумент29 страницProject Mesa: Broadband Obility For Mergency and Afety PplicationsdominezОценок пока нет
- Annex - Improved Case Studies PDFДокумент2 страницыAnnex - Improved Case Studies PDFFrenzy Duana AcboОценок пока нет
- Annex - Improved Case StudiesДокумент2 страницыAnnex - Improved Case StudiesFrenzy Duana AcboОценок пока нет
- Who Is Rodrigo Duterte?Документ2 страницыWho Is Rodrigo Duterte?Frenzy Duana AcboОценок пока нет
- Bts BSC MSC DetailsДокумент14 страницBts BSC MSC DetailsFrenzy Duana AcboОценок пока нет
- SHS Applied - Research 2 CG PDFДокумент6 страницSHS Applied - Research 2 CG PDFJakie UbinaОценок пока нет
- Technical CommunicationДокумент6 страницTechnical CommunicationRashmi SharmaОценок пока нет
- 2830 D EN 20130318 RM Drystar 5302Документ238 страниц2830 D EN 20130318 RM Drystar 5302agfadsОценок пока нет
- Session 5 Structure of ProgramДокумент8 страницSession 5 Structure of ProgramGandavadi VenkateshОценок пока нет
- Robinson, Julia Bowman PDFДокумент4 страницыRobinson, Julia Bowman PDFcreeshaОценок пока нет
- TriangleДокумент2 страницыTriangleapi-3812198Оценок пока нет
- Java Programming Course Objectives and OutcomesДокумент2 страницыJava Programming Course Objectives and OutcomesSEELAM LAXMAREDDYОценок пока нет
- TSR Hall Ticket NptelДокумент1 страницаTSR Hall Ticket NptelIndrani KotamrajuОценок пока нет
- Nur Syahirah Binti Mohamad Shah B031610082Документ21 страницаNur Syahirah Binti Mohamad Shah B031610082Hilfa TweetОценок пока нет
- Improving Domino and DB2 Performance: Document Version 1Документ24 страницыImproving Domino and DB2 Performance: Document Version 1grangenioОценок пока нет
- As 1199.0-2003 Sampling Procedures For Inspection by Attributes Introduction To The ISO 2859 Attribute SampliДокумент10 страницAs 1199.0-2003 Sampling Procedures For Inspection by Attributes Introduction To The ISO 2859 Attribute SampliSAI Global - APACОценок пока нет
- Fast Parallel CRC & DBI CalculationДокумент4 страницыFast Parallel CRC & DBI CalculationEdmund LeongОценок пока нет
- SSC Aptitude Tier 1 Sample PaperДокумент14 страницSSC Aptitude Tier 1 Sample PaperAbhinish SwaroopОценок пока нет
- HIPI: Computer Vision at Large Scale: Chris Sweeny Liu LiuДокумент17 страницHIPI: Computer Vision at Large Scale: Chris Sweeny Liu LiuLiu LiuОценок пока нет
- ITE 1812 - Mathematics For IT Assignment 01: AnswerДокумент4 страницыITE 1812 - Mathematics For IT Assignment 01: AnswerWarunaОценок пока нет
- E-GP System User Manual - Authorized Officer UserДокумент85 страницE-GP System User Manual - Authorized Officer Usermy09Оценок пока нет
- Examples and Theorems in Analysis: WalkerДокумент3 страницыExamples and Theorems in Analysis: WalkerKiran DeepОценок пока нет
- 3D Graphics TransformationsДокумент22 страницы3D Graphics Transformationsmiryalalokesh123_971Оценок пока нет
- INTERNET, INTRANET & EXTRANET COMPAREDДокумент66 страницINTERNET, INTRANET & EXTRANET COMPAREDCharish CabeltesОценок пока нет
- Survey of Different Database SsoftwaresДокумент17 страницSurvey of Different Database Ssoftwareslocal man100% (1)
- Vba To VB - Net XLL Add in With Excel DnaДокумент51 страницаVba To VB - Net XLL Add in With Excel DnaRadhesh P ShenoyОценок пока нет
- Learn To Use: Your Hands-On GuideДокумент43 страницыLearn To Use: Your Hands-On Guidewendel100% (1)
- pcsc1 v2.01.0 PDFДокумент30 страницpcsc1 v2.01.0 PDFmg5049Оценок пока нет
- PM EquipmentДокумент16 страницPM Equipmentsiva prasadОценок пока нет
- Windows 7 Cheat SheetДокумент4 страницыWindows 7 Cheat SheetAndrey FadinОценок пока нет
- Salesforce Certified Platform Developer I: Certification Exam GuideДокумент14 страницSalesforce Certified Platform Developer I: Certification Exam GuidejuaniruegasОценок пока нет