Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Unit 1
Загружено:
pankaj12345katreИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Unit 1
Загружено:
pankaj12345katreАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
UNIT-I
A] Theory Question Bank
Remembering
Understanding
Applying
Analyzing
Evaluating
Creating
Q. Attainment of
Description Marks
No CO PO BL GA
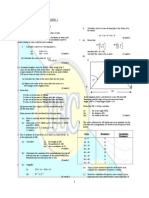
1 What is transformation? Explain the terms 8 CO1 a
translation, rotation, scaling and reflection. Write
their transformation matrix also.
2 A triangle have vertices (5,5), ( 10,5), (7,9) is 8 CO1 b
translated by 5 units in x direction, then it is rotate
by 300 in clockwise and then it is scaled by 3 units in
y direction. Determine the final position of triangle.
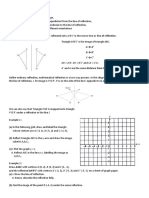
3 Find the reflection matrix for 10 CO1 b
(a) Line passing through origin and make 300 with y-
axis is clockwise direction.
(b) Line passing through origin and make 450 with y-
axis is anticlockwise direction.
4 Write 3-D transformation matrix for rotation about 6 CO1 a
x,y,z, axis.
5 What arer the advantages of homogenous 8 CO1 b
coordinate system? Find out the transform
coordinates of a plain triangular lamina having the
vertices (3,-1), (4,-1), (2,1) rotate through 900 about
the origin in counter clockwise direction.
6 Find the over all transformation matrix for the 8 CO1 b
reflection of a triangular lamina about the line
2y=x+2
7 Perform a 600 rotation of a triangle with vertices 8 CO1 b
A(0,0), B(1,1), C(5,2).
(a) About the origin
(b) About (-1,-1)
8 Explain the following terms related to three- 6 CO1 b
dimensional transformation and show the final
position graphically in each case.
(a) Translation
(b) Rotation
9 For the points P1(1,1), P2(3,1), P3(4,2), P4(2,3) that 10 CO1 b
defined a 2-D polygon, develop a single
concatenated transformation matrix that:
(a) Reflects about line x=0,
(b) Translated by-1 in both x and y direction
(c) Rotates about the z-axis by 180 degree.
Using the matrix, determine the new
coordinates.
10 A rectangle formed by four points PQRS 10 CO1 b
whose coordinates are
P(50,50),Q(100,50),R(100,80),S(50,80).Find
the new coordinates of the
rectangle in reduced size using scaling
factors S
X= 0.5 and S
Y= 0.6
11 Find the refection matrix when the axis of 6 CO1 b
reflection is line y = 3x+2.
12 The two end points of a line segment have 6 CO1 b
coordinates (1,3) and (3,6). If this is
to be scaled to twice its present size, write
the transformation matrix and the
coordinates of the new end points.
13 What is geometric transformation? Explain 6 CO1 a
Translation , rotation, scaling with
respect to 2D
14 What is transformation of geometry? With 6 CO1 a
suitable figure and matrix discuss
following transformation.
(i) Scaling (ii) Reflection (iii)Rotation
15 With help of suitable example explain 2D 6 CO1 a
Transformation (i) Translation and (ii)
Reflection
16 A scaling factor of 2 is applied in the Y 10 CO1 b
direction while no scaling is applied in the
X direction to the line whose two end
points are at coordinates (1, 3) and (3,6).
The line is to be rotated subsequently
through 300, in the counter clockwise
direction. Determine the necessary
transformation matrix for the operation
and the new
coordinates of the end points.
17 The vertices of a triangle are situated at 10 CO1 b
points (15, 30), (25, 35) and (5, 45). Find
the coordinates of the vertices if the
triangle is first rotated 100' counter
clockwise direction about the origin and
then scaled to twice its size.
18 What is the need for concatenation of 6 CO1 a
transformations? Explain what care should
be taken in such cases.
19 Explain the concept of obtaining a 6 CO1 a
reflection about an arbitrary line starting
from the plain reflection about an axis.
How do you obtain the orthographic
projections of 3D geometric data base?
20 What is Composite Transformation? 4 CO1 a
21 Name the different Two Dimensional 4 CO1 a
Geometric Transformation and explain any
two of them.
22 What is Geometric Transformation? Find 8 CO1 b
the Reflection matrix when the axis of
reflection is given by y=5x.Also determine
the reflection of point (7,5) about this axis.
23 A scaling factor of 2 is applied in the Y 8 CO1 b
direction while no scaling is applied in the
X direction to the line whose two end
points are at coordinates (1, 3) and (3,6).
The line is to be rotated subsequently
through 300, in the counter clockwise
direction. Determine the necessary
transformation matrix for the operation
and the new coordinates of the end points.
24 The vertices of a triangle are situated at 8 CO1 b
points (15, 30), (25, 35) and (5, 45). Find
the coordinates of the vertices if the
triangle is first rotated 100 counter
clockwise direction about the origin and
then scaled to twice its size
25 What is the need for concatenation of 6 CO1 a
transformations? Explain what care should
be taken in such cases.
26 Explain the concept of obtaining a 6 CO1 b
reflection about an arbitrary line starting
from the plain reflection about an axis.
How do you obtain the orthographic
projections of 3D geometric data base?
27 What is a projection? Explain different 6 CO1 b
types of projections?
28 Explain how rotation about an arbitrary 6 CO1 a
point obtained.
29 Explain homogenous transformation for 6 CO1 a
3D?
30 Explain isometric projection. 4 CO1 a
31 Explain various applications of computer 4 CO1 b
graphics.
32 The vertices of the triangle are (8,1), (7,3), 8 CO1 b
& (6,2). Find a) the reflection about X-axis,
and b) the reflection about the line Y = -X.
33 A Point P is rotated by 45 [deg] about an 10 CO1 b
axis which is represented by the vector k =
[0.5 0.866 0.707]T passing through origin.
Find the transformation matrix and
calculate its determinant?
47. Given a point P(2, 4, 8). Find the
transformed point P* if P is translated by d
= 3i – 4j – 5k and then scaled uniformly by
S = 1.5?
34 A point is rotated about the Z-axis by two 10 CO1 b
successive angles θ1 and θ2. Show that
this is equivalent to rotating the point
about the same axis once with any angle θ
= θ1 + θ2.
49. Write the various steps to find
reflection matrix when the axis of reflection
is line y = ½(x + 4). The position vectors
(2,4,1), (4, 6, 1) and (2, 6, 1) describe the
vertices of triangle A, B, C. Just mention
the steps involved(no need to do
calculations).
(Hint : translate -2 in Y-direction rotate
by –tan-1(1/2) reflect the triangle
through x-axis transformed position is
then rotated and translated back to the
original orientation.)
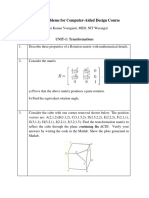
Icons Graduate Attributes
Applying Knowledge
Problem Analysis
Design and Development
Investigation of Problem
Modern Tool Usage
Engineer and Society
Environment Sustainability
Ethics
Individual and Teamwork
Communication
Project Management and Finance
Lifelong Learning
Blooms Taxonomy
Remembering
Understanding
Applying
Analyzing
Evaluating
Creating
Вам также может понравиться
- ProjectManager Project Closure Template NDДокумент11 страницProjectManager Project Closure Template NDVocika MusixОценок пока нет
- Topic - 17 TransformationsДокумент88 страницTopic - 17 TransformationsJorifОценок пока нет
- June 1988 - June 1997 Maths Paper 2Документ38 страницJune 1988 - June 1997 Maths Paper 2Jerilee SoCute Watts0% (1)
- Proven Perimeter Protection: Single-Platform SimplicityДокумент6 страницProven Perimeter Protection: Single-Platform SimplicitytecksanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 解析几何(AMC10)Документ18 страницChapter 2 解析几何(AMC10)Xuemei zhangОценок пока нет
- Manual Cantar Electronic Dibal VD-310Документ34 страницыManual Cantar Electronic Dibal VD-310Prima VD50% (2)
- Image Processing Lab ManualДокумент10 страницImage Processing Lab ManualDeepa SОценок пока нет
- SAP QM Calibration MethodДокумент3 страницыSAP QM Calibration MethodvrkattulaОценок пока нет
- Business Statistics: Communicating With Numbers: by Sanjiv Jaggia and Alison KellyДокумент33 страницыBusiness Statistics: Communicating With Numbers: by Sanjiv Jaggia and Alison KellySinta DewiОценок пока нет
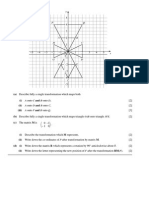
- Transformations - Practice Problems For CADДокумент6 страницTransformations - Practice Problems For CADbinduОценок пока нет
- Computer Graphics Question BankДокумент4 страницыComputer Graphics Question BankEr Sachin ShandilyaОценок пока нет
- Winsem2021-22 Eee4027 Eth Vl2021220501288 Model Question Paper Practice QP Rc-2022Документ3 страницыWinsem2021-22 Eee4027 Eth Vl2021220501288 Model Question Paper Practice QP Rc-2022Nathan ShankarОценок пока нет
- Teaching Notes On Transformation-1Документ40 страницTeaching Notes On Transformation-1kaykampamba9Оценок пока нет
- Affine Transformation - Test 1Документ2 страницыAffine Transformation - Test 1Devanshi MehtaОценок пока нет
- TRANSFORMATIONДокумент58 страницTRANSFORMATIONJavariaОценок пока нет
- LinearTransformations PDFДокумент8 страницLinearTransformations PDFCorneliusОценок пока нет
- Computer GraphicsДокумент2 страницыComputer Graphicsliza50% (2)
- Matrices and Transformations QДокумент5 страницMatrices and Transformations Qwambuieccra79Оценок пока нет
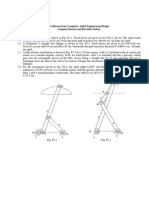
- ME G611: Computer Aided Analysis & Design: Fig. 1: Original Unit Square With Superimposed Two of The Transformed VerticesДокумент1 страницаME G611: Computer Aided Analysis & Design: Fig. 1: Original Unit Square With Superimposed Two of The Transformed VerticesVipul AgrawalОценок пока нет
- Topic: FE - AxisymmetricДокумент3 страницыTopic: FE - AxisymmetricKaushik MukherjeeОценок пока нет
- Caed ProblemsДокумент20 страницCaed ProblemsPardeepОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 Transformations of The Euclidean PlaneДокумент14 страницChapter 5 Transformations of The Euclidean PlaneLitoy ArquizaОценок пока нет
- Cad Assignment #3Документ3 страницыCad Assignment #3Johnson123_45670% (2)
- Worksheet 7Документ2 страницыWorksheet 7Waqar AhmedОценок пока нет
- Computer Graphics Using Open GL, 3 Edition F. S. Hill, Jr. and S. KelleyДокумент49 страницComputer Graphics Using Open GL, 3 Edition F. S. Hill, Jr. and S. KelleyAbrahamОценок пока нет
- Form 4 59 Matrices and TransformationДокумент23 страницыForm 4 59 Matrices and Transformationiminathi ndlovuОценок пока нет
- Transformations: Nur Akma BT Makhtar D20081032217Документ17 страницTransformations: Nur Akma BT Makhtar D20081032217WaniAimiОценок пока нет
- Worksheet 2 - TransformationДокумент19 страницWorksheet 2 - TransformationShnia RodneyОценок пока нет
- Assignment 2Документ1 страницаAssignment 2mrvenkateshОценок пока нет
- Assignment 4 Geometric TransformationsДокумент2 страницыAssignment 4 Geometric TransformationsKrish100% (1)
- Yisak Abu MathisДокумент14 страницYisak Abu MathisYisak AbuОценок пока нет
- Matrix TransformДокумент8 страницMatrix TransformJ Christopher ClementОценок пока нет
- Class NoteДокумент18 страницClass NoteNafis AhmedОценок пока нет
- Transformations: BTEOTSSSBAT Solve Problems Involving Reflection, Rotation, Translation and EnlargementДокумент23 страницыTransformations: BTEOTSSSBAT Solve Problems Involving Reflection, Rotation, Translation and EnlargementmangimanОценок пока нет
- Review For Vector Answers: Check Your Answers Algebraically Using Position VectorsДокумент4 страницыReview For Vector Answers: Check Your Answers Algebraically Using Position VectorsJanel EdwardsОценок пока нет
- Midterm Exam: Solutions: D. Transformations (25 Points)Документ2 страницыMidterm Exam: Solutions: D. Transformations (25 Points)masyuki2002Оценок пока нет
- Transformations Review 2Документ3 страницыTransformations Review 2api-293228282Оценок пока нет
- Homework 1Документ1 страницаHomework 1Eko Budi SatriyoОценок пока нет
- Unit2 5.2.1 and 5.2.2Документ44 страницыUnit2 5.2.1 and 5.2.2Mrs. LaraОценок пока нет
- Homework 1Документ4 страницыHomework 1Sigit Eka Duwi TamaОценок пока нет
- Review Test 4Документ6 страницReview Test 4Bedgemana GadgenОценок пока нет
- TransformationДокумент4 страницыTransformationuththaramala calderaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 11Документ20 страницChapter 11api-171445363Оценок пока нет
- MCS-053 4Документ3 страницыMCS-053 4Sumit Waitforit RanaОценок пока нет
- Xercise: Jee ProblemsДокумент2 страницыXercise: Jee ProblemspandaОценок пока нет
- 3673 Tut 03Документ1 страница3673 Tut 03Kuroko BasukeNОценок пока нет
- Computational GeometryДокумент2 страницыComputational Geometryneelpaigude8Оценок пока нет
- Computer Graphics Question BankNewДокумент5 страницComputer Graphics Question BankNewvishaljain263933% (3)
- Maths 2 Fit1244 Chapter 4Документ10 страницMaths 2 Fit1244 Chapter 4Saran Raj RetnamОценок пока нет
- Transformations PDFДокумент20 страницTransformations PDFjayeshpОценок пока нет
- SutodhДокумент2 страницыSutodhRushabh PatelОценок пока нет
- P4 Graphs TransformationsДокумент38 страницP4 Graphs TransformationsRNGtypicalОценок пока нет
- 2017 H2 Prelim (Graphs and Transformations)Документ21 страница2017 H2 Prelim (Graphs and Transformations)toh tim lamОценок пока нет
- CAD CAM Question BankДокумент2 страницыCAD CAM Question BankrsdeshmukhОценок пока нет
- 3.2 Reflection: AB A'B', BC B'C' and CA C'A'. A' and A Are The Same Distance From The MirrorДокумент8 страниц3.2 Reflection: AB A'B', BC B'C' and CA C'A'. A' and A Are The Same Distance From The MirrorZ AliОценок пока нет
- For More Study Material & Test Papers: Manoj Chauhan Sir (Iit-Delhi) Ex. Sr. Faculty (Bansal Classes)Документ5 страницFor More Study Material & Test Papers: Manoj Chauhan Sir (Iit-Delhi) Ex. Sr. Faculty (Bansal Classes)jaspreet singhОценок пока нет
- For More Study Material & Test Papers: Manoj Chauhan Sir (Iit-Delhi) Ex. Sr. Faculty (Bansal Classes)Документ5 страницFor More Study Material & Test Papers: Manoj Chauhan Sir (Iit-Delhi) Ex. Sr. Faculty (Bansal Classes)jaspreet singhОценок пока нет
- Chapter Five GraphicsДокумент37 страницChapter Five GraphicswalelegneОценок пока нет
- ZolakДокумент4 страницыZolakDavid MitchelleОценок пока нет
- MATH 4A - 51091 Summer 2020 Exam IДокумент2 страницыMATH 4A - 51091 Summer 2020 Exam Iron nsОценок пока нет
- F3 Ch11 SuppWSДокумент16 страницF3 Ch11 SuppWSJustin ChanОценок пока нет
- 2345unit11geometrynotes TransformationalgeometryДокумент24 страницы2345unit11geometrynotes Transformationalgeometryapi-326933003Оценок пока нет
- CAD & A Second Series QPДокумент1 страницаCAD & A Second Series QPimnithinОценок пока нет
- 3673 Tut 05Документ1 страница3673 Tut 05Kuroko BasukeNОценок пока нет
- Straight Line GB Sir ModuleДокумент15 страницStraight Line GB Sir ModuleSaptarshiОценок пока нет
- Cs 6212 ManualДокумент96 страницCs 6212 ManualVishnu KumarОценок пока нет
- 1532748281262Документ31 страница1532748281262FranciscoОценок пока нет
- 58 62SmartRoboticArmДокумент5 страниц58 62SmartRoboticArmLakshmi PriyaОценок пока нет
- AДокумент18 страницAPrince Oscar Jr. SabbalucaОценок пока нет
- Performance Analysis of Dual Core, Core 2 Duo and Core I3 Intel ProcessorДокумент7 страницPerformance Analysis of Dual Core, Core 2 Duo and Core I3 Intel ProcessorPRAFULKUMAR PARMARОценок пока нет
- Master User Guide: Premier 412/816/832Документ24 страницыMaster User Guide: Premier 412/816/832وسام نصر يوسفОценок пока нет
- Catalog Altivar Process ATV600 Variable Speed DrivesДокумент133 страницыCatalog Altivar Process ATV600 Variable Speed Drivesrabia akramОценок пока нет
- Vrealize Automation TransitionДокумент93 страницыVrealize Automation TransitionBao Vy LeОценок пока нет
- A Benchmark of Dual Constellations GNSS Solutions For Vehicle Localization in Container TerminalsДокумент7 страницA Benchmark of Dual Constellations GNSS Solutions For Vehicle Localization in Container TerminalsjfrasconОценок пока нет
- When Data Visualization Works - and When It Doesn'tДокумент8 страницWhen Data Visualization Works - and When It Doesn'tronald johannОценок пока нет
- TestДокумент12 страницTestdineshkmr88Оценок пока нет
- 2019 - 2 - Advertisement No 3-2019 (Various Posts)Документ9 страниц2019 - 2 - Advertisement No 3-2019 (Various Posts)Shubham GautamОценок пока нет
- SDM No. 238, S. 2019Документ8 страницSDM No. 238, S. 2019Shiela E. EladОценок пока нет
- Grade 10 Computer Appications Project PDFДокумент45 страницGrade 10 Computer Appications Project PDFkarthikeya kakarlapudi100% (1)
- Mabl Worksheet Starting and Scaling Functional Automated TestingДокумент23 страницыMabl Worksheet Starting and Scaling Functional Automated TestingktbalajiОценок пока нет
- Hướng Dẫn Web Design and DevelopmentДокумент4 страницыHướng Dẫn Web Design and DevelopmentCONFESSIONS ADMINОценок пока нет
- 43-TV-25-30 Manuel MinirendДокумент444 страницы43-TV-25-30 Manuel MinirendFamc CmafОценок пока нет
- Huawei OMC IManager M2000 Engineering Parameters IntroductionДокумент11 страницHuawei OMC IManager M2000 Engineering Parameters IntroductionaricomenОценок пока нет
- CA Tut14 ANSДокумент2 страницыCA Tut14 ANSTamizharasan P SОценок пока нет
- 108-1 SL ManualДокумент19 страниц108-1 SL ManualphongredОценок пока нет
- Cyber PornographyДокумент15 страницCyber PornographyNivesh DixitОценок пока нет
- User Manual EPC48601800-F3 Outdoor Power SystemДокумент53 страницыUser Manual EPC48601800-F3 Outdoor Power SystemThịnh NguyễnОценок пока нет
- Let's Learn About SpreadsheetsДокумент48 страницLet's Learn About SpreadsheetsHiltanasОценок пока нет
- HMMERДокумент5 страницHMMERemma698Оценок пока нет