Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Biomolecules
Загружено:
quellyОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Biomolecules
Загружено:
quellyАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
1. Biomolecules are molecules that occur naturally in living organisms.
Biomolecules include
macromolecules like proteins, carbohydrates, lipids and nucleic acids. It also includes small
molecules like primary and secondary metabolites and natural products. Biomolecules consists
mainly of carbon and hydrogen with nitrogen, oxygen, sulphur, and phosphorus. Biomolecules
are very large molecules of many atoms, that are covalently bound together
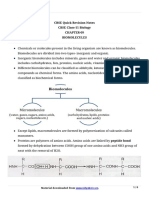
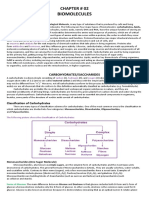
2. Carbohydrates are good source of energy. Carbohydrates (polysaccharides) are long chains of
sugars. Monosaccharides are simple sugars that are composed of 3-7 carbon atoms. They have
a free aldehyde or ketone group, which acts as reducing agents and are known as reducing
sugars. Disaccharides are made of two monosaccharides. The bonds shared between two
monosaccharides is the glycosidic bonds. Monosaccharides and disaccharides are sweet,
crystalline and water soluble substances.Polysaccharides are polymers of monosaccharides.
They are unsweet, and complex carbohydrates.They are insoluble in water and are not in
crystalline form. Example: glucose, fructose, sucrose, maltose, starch, cellulose etc.
Lipids are composed of long hydrocarbon chains. Lipid molecules hold a large amount of energy
and are energy storage molecules. Lipids are generally esters of fatty acids and are building
blocks of biological membranes. Most of the lipids have a polar head and non-polar tail. Fatty
acids can be unsaturated and saturated fatty acids. Example of lipids: oils, fats, phospholipids,
glycolipids,
Proteins are heteropolymers of stings of amino acids. Amino acids are joined together by the
peptide bond which is formed in between the carboxyl group and amino group of successive
amino acids. Proteins are formed from 20 different amino acids, depending on the number of
amino acids and the sequence of amino acids.
Nucleic acids are organic compounds with heterocyclic rings. Nucleic acids are made of polymer
of nucleotides. Nucleotides consists of nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate
group. A nucleoside is made of nitrogenous base attached to a pentose sugar. The nitrogenous
bases are adenine, guanine, thyamine, cytosine and uracil. Polymerized nucleotides form DNA
and RNA which are genetic material.
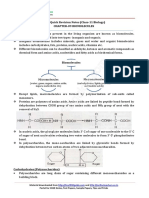
3. oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction is a type of chemical reaction that involves a transfer of
electrons between two species. An oxidation-reduction reaction is any chemical reaction in which
the oxidation number of a molecule, atom, or ion changes by gaining or losing an electron. Redox
reactions are common and vital to some of the basic functions of life,
including photosynthesis, respiration, combustion, and corrosion or rusting.
4. Extremely high or low pH values generally result in complete loss of activity for most enzymes.
pH is also a factor in the stability of enzymes. As with activity, for each enzyme there is also a
region of pH optimal stability.
5. Like most chemical reactions, the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction increases as the
temperature is raised. A ten degree Centigrade rise in temperature will increase the activity of
most enzymes by 50 to 100%. Variations in reaction temperature as small as 1 or 2 degrees may
introduce changes of 10 to 20% in the results. In the case of enzymatic reactions, this is
complicated by the fact that many enzymes are adversely affected by high temperatures. As
shown in Figure 13, the reaction rate increases with temperature to a maximum level, then
abruptly declines with further increase of temperature. Because most animal enzymes rapidly
become denatured at temperatures above 40°C, most enzyme determinations are carried out
somewhat below that temperature.
6. Increasing Substrate Concentration increases the rate of reaction. This is because more
substrate molecules will be colliding with enzyme molecules, so more product will be
formed.
Вам также может понравиться
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsОт EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- Class 11 Biomol-WPS OfficeДокумент3 страницыClass 11 Biomol-WPS Officegapandey58Оценок пока нет
- 87314094-83be-428d-9d4d-a459e43691a9Документ21 страница87314094-83be-428d-9d4d-a459e43691a9SAMPATH SPОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5: Inorganic Compound Inorganic Compound: Acid Base BalanceДокумент12 страницChapter 5: Inorganic Compound Inorganic Compound: Acid Base BalanceSeth SiegfriedОценок пока нет
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes CBSE Class-11 Biology Chapter-09 BiomoleculesДокумент8 страницCBSE Quick Revision Notes CBSE Class-11 Biology Chapter-09 BiomoleculesabhiОценок пока нет
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes CBSE Class-11 Biology Chapter-09 BiomoleculesДокумент8 страницCBSE Quick Revision Notes CBSE Class-11 Biology Chapter-09 BiomoleculesHARSH PahwaОценок пока нет
- Class 11 Biology NotesДокумент147 страницClass 11 Biology NotesreilyshawnОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry NotesДокумент21 страницаBiochemistry NotestariqabuothmanОценок пока нет
- Biology For The IB Diploma Chapter 2 SummaryДокумент8 страницBiology For The IB Diploma Chapter 2 SummaryJulian WolfgangОценок пока нет
- Module 7 General Biology 1Документ10 страницModule 7 General Biology 1kimberlyfritzzunigaОценок пока нет
- Chemical Reactions Part II: Week 7: Organic ChemistryДокумент24 страницыChemical Reactions Part II: Week 7: Organic Chemistrymia kris quiatchonОценок пока нет
- 11 Biology Notes ch09 Biomolecules PDFДокумент5 страниц11 Biology Notes ch09 Biomolecules PDFprashanth100% (1)
- 11 Biology Notes BiomoleculesДокумент5 страниц11 Biology Notes Biomoleculesprashanth100% (1)
- Module 4-Biomolecules: Chemical Composition of Living FormsДокумент6 страницModule 4-Biomolecules: Chemical Composition of Living Formsmpstme placementОценок пока нет
- Ilovepdf Merged PDFДокумент12 страницIlovepdf Merged PDFharshОценок пока нет
- Drug MetabolismДокумент43 страницыDrug MetabolismKelly PatrickОценок пока нет
- List of Headings: CarbohydratesДокумент5 страницList of Headings: Carbohydratessneh1509Оценок пока нет
- BIOCHEMISTRY II PPT'S.PPTX Carbohydrate MetabolismДокумент184 страницыBIOCHEMISTRY II PPT'S.PPTX Carbohydrate MetabolismVandini LohanaОценок пока нет
- Bio Transforming EnzymesДокумент13 страницBio Transforming EnzymesRadowan AhmadОценок пока нет
- Lesson-6 General Biology 2Документ46 страницLesson-6 General Biology 2Mhaica GalagataОценок пока нет
- Chemical Composition of The CellДокумент37 страницChemical Composition of The CellCik DilaОценок пока нет
- Amino AcidsДокумент7 страницAmino Acidsrida khanОценок пока нет
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes CBSE Class-11 Biology Chapter-09 BiomoleculesДокумент8 страницCBSE Quick Revision Notes CBSE Class-11 Biology Chapter-09 BiomoleculesShilpaОценок пока нет
- Chemistry FileДокумент17 страницChemistry FilePrakhar33% (3)
- UntitledДокумент84 страницыUntitledTài Nguyễn XuânОценок пока нет
- Identify and Describe Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins As Food Substances State The Chemical and Physical Properties of Different Food SubstancesДокумент18 страницIdentify and Describe Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins As Food Substances State The Chemical and Physical Properties of Different Food SubstancesLunactic ThanosОценок пока нет
- Biology Study Paper: #6 The Chemistry of Living OrganismsДокумент4 страницыBiology Study Paper: #6 The Chemistry of Living OrganismsAkili ArmaniОценок пока нет
- Carbohydrates Definition: What Is Monomer?Документ11 страницCarbohydrates Definition: What Is Monomer?Rica NorcioОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 - Biological MoleculesДокумент28 страницChapter 4 - Biological MoleculesshammmssОценок пока нет
- Atoms and MoleculesДокумент5 страницAtoms and MoleculesRelaisa CimafrancaОценок пока нет
- Bio Molecules GuideДокумент8 страницBio Molecules GuideRahul SinghОценок пока нет
- The Chemical Level of OrganizationДокумент50 страницThe Chemical Level of OrganizationAizat FarhanОценок пока нет
- Organic Compounds: CarbohydratesДокумент11 страницOrganic Compounds: CarbohydratesDhimas MahardhikaОценок пока нет
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-09 BiomoleculesДокумент5 страницCBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) Chapter-09 BiomoleculesSIDHARTH SBОценок пока нет
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 Biomolecules Revision Notes1Документ42 страницыCBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 Biomolecules Revision Notes1skumarkushwaha504Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 3: The Molecules of LifeДокумент8 страницChapter 3: The Molecules of LifeCourtney FazioОценок пока нет
- Biological MoleculesДокумент6 страницBiological MoleculessanaullahОценок пока нет
- Chemistry of Life NotesДокумент8 страницChemistry of Life Noteskolejose88Оценок пока нет
- Chapter Six, GeneticsДокумент10 страницChapter Six, GeneticsHashim GhazoОценок пока нет
- Xenobiotics MetabolismДокумент47 страницXenobiotics Metabolismademabdella38Оценок пока нет
- Walang MakakaseethisДокумент3 страницыWalang MakakaseethisAlissa YangОценок пока нет
- Parikh Sneh 100478966 List of HeadingsДокумент5 страницParikh Sneh 100478966 List of Headingssneh1509Оценок пока нет
- 25 of These Elements Are Essential To Life. ComposingДокумент4 страницы25 of These Elements Are Essential To Life. ComposingMarianne Charisse TubigОценок пока нет
- Chemistry of Living Things: © Lisa MichalekДокумент18 страницChemistry of Living Things: © Lisa MichalekmooninkedОценок пока нет
- BiomoleculesДокумент11 страницBiomoleculesAdul basit mughalОценок пока нет
- BiomoleculesДокумент58 страницBiomoleculesLili MagossОценок пока нет
- Metabolism of XenobioticsДокумент54 страницыMetabolism of XenobioticsAurellia ShafitriОценок пока нет
- Types of BiomoleculesДокумент7 страницTypes of BiomoleculesAnalyza PatocОценок пока нет
- Chemistry of Living ThingsДокумент47 страницChemistry of Living Thingsapi-2174392830% (1)
- Intro Macromolecule LectureДокумент34 страницыIntro Macromolecule Lectureapi-300252239Оценок пока нет
- Lab 2 - Identifying MacromoleculesДокумент9 страницLab 2 - Identifying MacromoleculesG TeenaОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry: Chemistry of Life!Документ40 страницBiochemistry: Chemistry of Life!Akhil DonapatiОценок пока нет
- BiomoleculesДокумент11 страницBiomoleculesHarrish SandeevОценок пока нет
- CarbohydrateДокумент45 страницCarbohydratescropion_78Оценок пока нет
- Mrs. Tarawally - 045400Документ11 страницMrs. Tarawally - 045400koromamoses235Оценок пока нет
- BIOMOLECULES NOTE 11aaДокумент9 страницBIOMOLECULES NOTE 11aaGyaniОценок пока нет
- BiomoleculesДокумент7 страницBiomoleculesvjaОценок пока нет
- Proteins and Amino AcidsДокумент24 страницыProteins and Amino Acidsqwerty masterОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 The Basis of BiochemistryДокумент34 страницыUnit 1 The Basis of Biochemistryarun231187Оценок пока нет
- Protoplasm Chemical CompositionДокумент4 страницыProtoplasm Chemical CompositionNorberto R. BautistaОценок пока нет
- J.vibspec.2013.02.001 Ftir Batio3Документ6 страницJ.vibspec.2013.02.001 Ftir Batio3Seni Ramadhanti SОценок пока нет
- S355J2G3Документ3 страницыS355J2G3rjueiОценок пока нет
- Selective Reduction of Organic Compounds With Al-Acetoxy-And Al-TrifluoroacetoxydiisobutylalaneДокумент9 страницSelective Reduction of Organic Compounds With Al-Acetoxy-And Al-TrifluoroacetoxydiisobutylalanelauraОценок пока нет
- Grade11 Physical Science - Module 3Документ5 страницGrade11 Physical Science - Module 3Erickson SongcalОценок пока нет
- Idoc - Pub - Astm A570 Steel Grade 50 PDFДокумент1 страницаIdoc - Pub - Astm A570 Steel Grade 50 PDFFrancisco Javier Torres AlvaradoОценок пока нет
- C123 W4 F2F E CarbohydratesДокумент5 страницC123 W4 F2F E Carbohydratesarmanuel1390antОценок пока нет
- Lesson 3Документ107 страницLesson 3Christian CuevasОценок пока нет
- BiochemistryДокумент20 страницBiochemistryRitesh SinghОценок пока нет
- Section A: CLASS X (2020-21) Science (Code 086) Sample Paper-1Документ8 страницSection A: CLASS X (2020-21) Science (Code 086) Sample Paper-1Anime FeelsОценок пока нет
- Astm b912 - 00 Passivation of Stainless Steels Using Electropolishing PDFДокумент4 страницыAstm b912 - 00 Passivation of Stainless Steels Using Electropolishing PDFcaballerolangОценок пока нет
- Applying Principles of Conservation of Mass To Chemical ReactionДокумент28 страницApplying Principles of Conservation of Mass To Chemical ReactionNovie Jane Hontiveros100% (1)
- NC Block NaamsДокумент46 страницNC Block NaamseldibujanteОценок пока нет
- Heat Treatment of SteelsДокумент162 страницыHeat Treatment of SteelsINSTECH ConsultingОценок пока нет
- PJST15 - 2 - 240effects of Freezing Point Depression On Molecular Weight Determination of Hydrocarbon Mixtures.Документ5 страницPJST15 - 2 - 240effects of Freezing Point Depression On Molecular Weight Determination of Hydrocarbon Mixtures.OguamahIfeanyiОценок пока нет
- Unit 3 - Chemistry - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inДокумент16 страницUnit 3 - Chemistry - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inN S PatidarОценок пока нет
- Hozelock KillaSpray Plus Manual PDFДокумент32 страницыHozelock KillaSpray Plus Manual PDFbernoullisОценок пока нет
- Clariant Coating Light Stabilizers Jan 2017 PDFДокумент53 страницыClariant Coating Light Stabilizers Jan 2017 PDFTamer BidakОценок пока нет
- 1 s2.0 S1674987123000919 MainДокумент21 страница1 s2.0 S1674987123000919 MainMatteo MainoОценок пока нет
- Poly SugaGlycinateДокумент2 страницыPoly SugaGlycinatemndmattОценок пока нет
- Downloads-Apds-Flexiwet NF Mist ApdsДокумент2 страницыDownloads-Apds-Flexiwet NF Mist ApdsZaffran Al QozzaОценок пока нет
- Detection of Sulfur Compounds in Natural Gas According To ASTM D5504 With An Agilent Dual Plasma Sulfur Chemiluminescence DetectorДокумент6 страницDetection of Sulfur Compounds in Natural Gas According To ASTM D5504 With An Agilent Dual Plasma Sulfur Chemiluminescence DetectorrezaroohollahiОценок пока нет
- Co2 Utilization Developments in Conversion ProcessesДокумент44 страницыCo2 Utilization Developments in Conversion ProcessesRungrawin Ngamkhum100% (1)
- Parlon - PyroData 5Документ3 страницыParlon - PyroData 5ricoОценок пока нет
- Materials and Design: Da Li, Ligang Liu, Yunkun Zhang, Chunlei Ye, Xuejun Ren, Yulin Yang, Qingxiang YangДокумент6 страницMaterials and Design: Da Li, Ligang Liu, Yunkun Zhang, Chunlei Ye, Xuejun Ren, Yulin Yang, Qingxiang YangjoeljОценок пока нет
- Irrigation in EndodonticsДокумент142 страницыIrrigation in EndodonticsArmanThaman100% (2)
- Analysis of ToothpasteДокумент3 страницыAnalysis of ToothpastepaceabcОценок пока нет
- Nucleotide and Nucleic Acids Slide 1Документ43 страницыNucleotide and Nucleic Acids Slide 1Cindy OctavianiОценок пока нет
- Catalogo Kappler 2016Документ32 страницыCatalogo Kappler 2016Ronal Champi MamaniОценок пока нет
- Chemistry 2 Year Ch-08 & 10 Marks.50 Timing: 1:30 HourДокумент2 страницыChemistry 2 Year Ch-08 & 10 Marks.50 Timing: 1:30 HourMusaddiq AzizОценок пока нет
- Hygiene Product CatalogueДокумент7 страницHygiene Product Catalogueolabi abdullahОценок пока нет