Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Aortic Exam
Загружено:
Reda So0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
14 просмотров3 страницыn
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документn
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
14 просмотров3 страницыAortic Exam
Загружено:
Reda Son
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 3
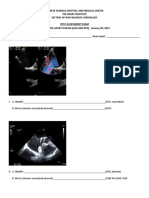
The Heart Institute
Caridology Fellows Valve Exam
1. The principal causes of valvular AS except:
a. Congenital bicuspid valve with superimposed calcification
b. Calcification of a normal trileaflet valve
c. Rheumatic disease
d. Unicuspid valves
2. Key features of the PE in patients with AS
a. Palpaation of the carotid upstroke revealing slow rising, late peaking, low amplitude
carotid pulse
b. Pulsus parvus et tardus is not specific for severe AS
c. Normal carotid pulse excludes severe AS
d. Splitting of S1
3. Normal aortic valve area in adult
a. 1-2 cm2
b. 2-3cm2
c. 3-4cm2
d. 4-6cm2
4. True of the annual hemodynamic progression of AS
a. Decrease in the AVA of 0.3cm2/yr
b. Increase in aortic jet velocity of 0.4m/sec/yr
c. Increase in mean gradient of 7mmHg/yr
d. Serum BNP can be used in the risk stratification of symptomatic patients
5. Chronic pressure overload in AS results in
a. CLVH with increased wall thickness and chamber size
b. Afterload normalization maintaining LV contractile function
c. Decreased myocardial cell mass and increased interstitial fibrosis resulting to systolic
dysfunction
d. LV pressure pulse exhibits a rounded summit and doppler velocity curve of
progressively later peak
6. Severe obstruction to LV outflow is characterized by all except
a. Aortic jet velocity of >4m/sec
b. Mean systolic gradient of at least 60mmHg in the presence of normal cardiac output
c. An EROA of <0.6cm2/sq meter BSA or 25% of the normal aortic orifice
d. An EROA of <1cm2
7. True in the management of AS
a. All patients should be cautioned against vigorous athletic sports and physical
activities
b. Echocardiography should be conducted every 1-2 years for severe AS
c. AVR is recommended for adults with symptomatic AS even with mild symptoms
d. TAVI benefits those with STS score of >15
8. Predictor of clinical outcome of AR except
a. LV size
b. Systolic function
c. Quantitative measures of AR
d. Age
9. Criteria for acute AR except
a. Vena contracta >06cm
b. RF >50% or more than
c. ERO >0.3cm2 or more than
d. RV > 50ml/beat or more
10. True of hemodynamics in AR
a. Immediately after valve replacement: decrease both ESV and EDV, Ef initially
increases then decreases
b. Acute AR: Total stroke volume increases, Forward SV increased
c. Chronic decompensated AR: increased in ESV, decreased in total and Forward SV,
decrease EF
d. Chronic compensated AR: increased EDV, increase in total and forward SV, ELVH
11. Management of AR except
a. Mild to moderate AR who are asymptomatic requires no therapy but needs echo
twice annually
b. RAS blocker provides vasodilatation and reduce interstitial fibrosis and remodeling
c. CMR is helpful in all patients with AR
d. Nifedipine, ACEI and BB are anti hypertensives of choice
12. Indications for surgical repair In AVR
a. Asymptomatic chronic severe AR with EF >50%, LVESD of <50mm
b. Asymptomatic chronic severe AR with EF <50%
c. Asymptomatic chronic severe AR with EF >50%, LVEDD > 65MM with high surgical
risk
d. Asymptomatic chronic severe AR with EF >50%,LVEDD <50mm, <65mm
13. Acute AR except
a. Caused commonly by IE, aortic dissection and trauma
b. Characterized by tachycardia and increase diastolic pressures
c. Forward SV is higher
d. Can cause profound hypotension and sudden CV collapse
Matching type
14. Symptomatic severe high gradient AS
15. Symptomatic severe low gradient AS with reduced LVEF
16. Symptomatic severe low gradient AS with paradoxical low flow severe AS
17. Asymptomatic severe S with LV dysfunction
18. Asymptomatic severe AS
a. AV max >= 4m/sec; AVA <1cm2, LV diastolic dysfunction, normal LVEF
b. AV max >= 4m/sec; AVA <1cm2, LV diastolic dysfunction, LVEF <50%
c. AV max >= 4m/sec; AVA <1cm2, LV diastolic dysfunction, LVEF <50%, heart failure,
angina and syncope
d. AV max >= 4m/sec; AVA <1cm2, LV diastolic dysfunction, pulmonary HTN with
dyspnea, angina and syncope
e. AV max >= 4m/sec; AVA <1cm2, small LV chamber with low stroke volume and
restrictive filling, LVEF >50%
19. Austin flint murmur
20. Pinkish purplish cheek
21. Sharp carotid upstroke
22. Delayed carotid upstroke
a. AR
b. AS
c. MS
d. MR
Вам также может понравиться
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- CHAPTER 27 - Heart Failure With A Preserved Ejection FractionДокумент15 страницCHAPTER 27 - Heart Failure With A Preserved Ejection FractionReda SoОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Name: - Year LevelДокумент6 страницName: - Year LevelReda SoОценок пока нет
- Chinese General Hospital and Medical Center Department of Medical Education and Research Research Ethics Review Board (Rerb)Документ11 страницChinese General Hospital and Medical Center Department of Medical Education and Research Research Ethics Review Board (Rerb)Reda SoОценок пока нет
- Private Ward Admission Census 1Документ6 страницPrivate Ward Admission Census 1Reda SoОценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Chapter 32 - Genetic Cardiac ArrythmiasДокумент7 страницChapter 32 - Genetic Cardiac ArrythmiasReda SoОценок пока нет
- Risk Factors in Developing Diabetic Foot Ulcers Among Patients in DM Foot Clinic at East Avenue Medical Center From January 2013 To January 2015Документ7 страницRisk Factors in Developing Diabetic Foot Ulcers Among Patients in DM Foot Clinic at East Avenue Medical Center From January 2013 To January 2015Reda SoОценок пока нет
- EXAM-MITRAL VALVE DISEASE - Reda SoДокумент5 страницEXAM-MITRAL VALVE DISEASE - Reda SoReda SoОценок пока нет
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- CHAPTER 11: The History and Physical Examination: An Evidence Based ApproachДокумент5 страницCHAPTER 11: The History and Physical Examination: An Evidence Based ApproachReda SoОценок пока нет
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Tilt Table Testing: Name Age/Sex APДокумент1 страницаTilt Table Testing: Name Age/Sex APReda SoОценок пока нет
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Ward Reflection PaperДокумент1 страницаWard Reflection PaperReda SoОценок пока нет
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Answer Key-Mitral ValveДокумент6 страницAnswer Key-Mitral ValveReda SoОценок пока нет
- Rapid Response Team and Cardiac Arrest/Resuscitation TeamДокумент11 страницRapid Response Team and Cardiac Arrest/Resuscitation TeamReda SoОценок пока нет
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- December 12Документ12 страницDecember 12Reda SoОценок пока нет
- 2011 PadДокумент19 страниц2011 PadReda SoОценок пока нет
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- Coronary Blood Flow & Myocardial Ischemia Cardiology Fellows Exam July 23, 2018Документ3 страницыCoronary Blood Flow & Myocardial Ischemia Cardiology Fellows Exam July 23, 2018Reda SoОценок пока нет
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- Trials SummaryДокумент12 страницTrials SummaryReda SoОценок пока нет
- Vascular Conference: JUNE 2018 - MARCH 2019Документ2 страницыVascular Conference: JUNE 2018 - MARCH 2019Reda SoОценок пока нет
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Daily Activities 2019Документ1 страницаDaily Activities 2019Reda SoОценок пока нет
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Team BLDG LetterДокумент1 страницаTeam BLDG LetterReda SoОценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- ECHO CensusДокумент9 страницECHO CensusReda SoОценок пока нет
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Tilt Table Testing: Name Age/Sex APДокумент1 страницаTilt Table Testing: Name Age/Sex APReda SoОценок пока нет
- Case Protocol 3Документ5 страницCase Protocol 3Reda SoОценок пока нет
- Compu Ted Tomogra Phy: (M90Us - LiДокумент1 страницаCompu Ted Tomogra Phy: (M90Us - LiReda SoОценок пока нет
- IungДокумент8 страницIungReda SoОценок пока нет
- Mckee 2012Документ10 страницMckee 2012Reda SoОценок пока нет
- Sept 3 2017Документ7 страницSept 3 2017Reda SoОценок пока нет
- Research ProtocolДокумент13 страницResearch ProtocolReda SoОценок пока нет
- 7 Overview of LipidДокумент85 страниц7 Overview of LipidReda SoОценок пока нет
- HUAWEI P8 Lite - Software Upgrade GuidelineДокумент8 страницHUAWEI P8 Lite - Software Upgrade GuidelineSedin HasanbasicОценок пока нет
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Channels of CommunicationДокумент3 страницыChannels of CommunicationIrin ChhinchaniОценок пока нет
- Coerver Sample Session Age 10 Age 12Документ5 страницCoerver Sample Session Age 10 Age 12Moreno LuponiОценок пока нет
- Pesticides 2015 - Full BookДокумент297 страницPesticides 2015 - Full BookTushar Savaliya100% (1)
- RPS Manajemen Keuangan IIДокумент2 страницыRPS Manajemen Keuangan IIaulia endiniОценок пока нет
- Did Angels Have WingsДокумент14 страницDid Angels Have WingsArnaldo Esteves HofileñaОценок пока нет
- Design and Experimental Performance Assessment of An Outer Rotor PM Assisted SynRM For The Electric Bike PropulsionДокумент11 страницDesign and Experimental Performance Assessment of An Outer Rotor PM Assisted SynRM For The Electric Bike PropulsionTejas PanchalОценок пока нет
- Anglicisms in TranslationДокумент63 страницыAnglicisms in TranslationZhuka GumbaridzeОценок пока нет
- Alankit Assignments LTD.: Project Report ONДокумент84 страницыAlankit Assignments LTD.: Project Report ONmannuОценок пока нет
- A Mercy Guided StudyДокумент23 страницыA Mercy Guided StudyAnas HudsonОценок пока нет
- Waldorf Curriculum ChartДокумент1 страницаWaldorf Curriculum Chartplanetalingua2020100% (1)
- Isolated Foundation PDFДокумент6 страницIsolated Foundation PDFsoroware100% (1)
- Knowledge, Attitude and Practice of Non-Allied Health Sciences Students of Southwestern University Phinma During The Covid-19 PandemicДокумент81 страницаKnowledge, Attitude and Practice of Non-Allied Health Sciences Students of Southwestern University Phinma During The Covid-19 Pandemicgeorgemayhew1030Оценок пока нет
- Skylab Our First Space StationДокумент184 страницыSkylab Our First Space StationBob AndrepontОценок пока нет
- Sikarep® Microcrete-4: Product Data SheetДокумент2 страницыSikarep® Microcrete-4: Product Data Sheetsidharthsud28Оценок пока нет
- ReportДокумент8 страницReportTrust Asia Cargo in OfficeОценок пока нет
- Filipino Chicken Cordon BleuДокумент7 страницFilipino Chicken Cordon BleuHazel Castro Valentin-VillamorОценок пока нет
- ESS Revision Session 2 - Topics 5-8 & P1 - 2Документ54 страницыESS Revision Session 2 - Topics 5-8 & P1 - 2jinLОценок пока нет
- Indiabix PDFДокумент273 страницыIndiabix PDFMehedi Hasan ShuvoОценок пока нет
- Statement 876xxxx299 19052022 113832Документ2 страницыStatement 876xxxx299 19052022 113832vndurgararao angatiОценок пока нет
- Bakery Management SynopsisДокумент13 страницBakery Management SynopsisSHiVaM KRОценок пока нет
- Effect of Innovative Leadership On Teacher's Job Satisfaction Mediated of A Supportive EnvironmentДокумент10 страницEffect of Innovative Leadership On Teacher's Job Satisfaction Mediated of A Supportive EnvironmentAPJAET JournalОценок пока нет
- أثر البحث والتطوير على النمو الاقتصادي - دراسة قياسية لحالة الجزائر (1990 -2014)Документ17 страницأثر البحث والتطوير على النمو الاقتصادي - دراسة قياسية لحالة الجزائر (1990 -2014)Star FleurОценок пока нет
- Curriculum Vitae For Modern MutumwaДокумент4 страницыCurriculum Vitae For Modern MutumwaKudakwashe QuQu MaxineОценок пока нет
- 7 CAAT-AIR-GM03 Guidance-Material-for-Foreign-Approved-Maintenance-Organization - I3R0 - 30oct2019 PDFДокумент59 страниц7 CAAT-AIR-GM03 Guidance-Material-for-Foreign-Approved-Maintenance-Organization - I3R0 - 30oct2019 PDFJindarat KasemsooksakulОценок пока нет
- Air Microbiology 2018 - IswДокумент26 страницAir Microbiology 2018 - IswOktalia Suci AnggraeniОценок пока нет
- Thick Teak PVT LTD Aoa and MoaДокумент17 страницThick Teak PVT LTD Aoa and MoaVj EnthiranОценок пока нет
- Emergency Rescue DrillДокумент13 страницEmergency Rescue DrillbalasubramaniamОценок пока нет
- Compare Visual Studio 2013 EditionsДокумент3 страницыCompare Visual Studio 2013 EditionsankurbhatiaОценок пока нет
- Music 10: 1 Quarterly Assessment (Mapeh 10 Written Work)Документ4 страницыMusic 10: 1 Quarterly Assessment (Mapeh 10 Written Work)Kate Mary50% (2)
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)От EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Рейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (1)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityОт EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (30)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsОт EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsОценок пока нет
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionОт EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (404)