Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
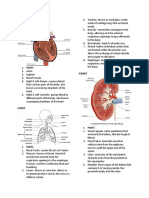
Blood Vessel and Lymphatic Lab Output
Загружено:
Dayledaniel SorvetoИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Blood Vessel and Lymphatic Lab Output
Загружено:
Dayledaniel SorvetoАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
4374_Ch15_187-204 10/14/14 1:43 PM Page 187
chapter 15
VASCULAR SYSTEM
The vascular system consists of an elaborate network of vessels designed to deliver oxygen and nutrients to the
body’s cells, remove waste products, and carry hormones from one part of the body to another. Varying in size
and structure according to their purpose, many of these vessels have names that are important to remember. Use
this chapter to learn the names of the various vessels and also to review their structure and function.
Drawing Conclusions: Vessel Structure
The walls of arteries and veins consist of three layers. Color and label each of these layers in the following figure.
Then, in the corresponding space below the figure, identify the type of tissue making up each layer as well as the
mechanism allowing the vessel to change diameter (if applicable).
1.
2.
3.
Chapter 15 Vascular System 187
4374_Ch15_187-204 10/14/14 1:43 PM Page 188
Make a Connection: Arteries
The body contains three types of arteries. Unscramble the following words to discover the names of these types.
Then draw lines to link each artery to its characteristics.
1. DUCTCOGINN a. These are the body’s largest arteries.
b. Also called muscular arteries, these arteries have
names.
2. TIDBITSRUING
c. These are the smallest arteries.
d. These are also called resistance vessels.
3. EARLIESTOR
e. Also called elastic arteries, these arteries have
names.
f. These vessels are too numerous to be named.
g. Examples include the aorta, common carotid, and
subclavian arteries.
h. Examples include the brachial, femoral, and renal
arteries.
i. These are connected to capillaries by short
connecting vessels called metarterioles.
j. These arteries expand as blood surges into them
and recoil when ventricles relax.
k. These arteries carry blood to specific organs and
areas of the body.
Just the Highlights: Veins
Highlight in orange the sentences that pertain to large veins, the sentences that pertain to medium-sized veins in
blue, and the sentences that pertain to venules in pink.
1. Contain one-way valves
2. Include the vena cavae, pulmonary veins, and internal jugular veins
3. Have a tunica media that is poorly developed, resulting in very thin vessel walls
4. Include the radial and ulnar veins of the forearm and the saphenous veins in the legs
5. Collect blood from the capillaries
6. Formed by the convergence of medium-sized veins
7. Formed by the convergence of venules on their route toward the heart
8. Are porous and can exchange fluid with surrounding tissue
188 Chapter 15 Vascular System
4374_Ch15_187-204 10/14/14 1:43 PM Page 189
Puzzle It Out: Vascular Terms
Test your knowledge of vascular terms by completing the following crossword puzzle.
ACROSS DOWN
2. Results from the pressure of blood against a 1. The circulatory system that begins at the right
weakened area in the wall of an artery ventricle and involves the circulation of blood
6. Veins are sometimes called ______________ through the lungs
vessels because of their capacity for storing blood. 3. Vessels that carry blood away from the heart
9. Results when fluid filters out of the capillaries 4. Unique capillary found in liver and bone marrow
faster than it’s reabsorbed and accumulates in the that allows for passage of large substances, such as
tissues proteins
10. The most important mechanism of capillary 5. Where nutrients, wastes, and hormones are
exchange transferred between the blood and tissues
11. The circulatory system that begins at the left 7. Capillaries are called the ____________________
ventricle and involves the circulation of blood vessels of the circulatory system.
through the body 8. Vessels that return blood to the heart
Chapter 15 Vascular System 189
4374_Ch15_187-204 10/14/14 1:43 PM Page 190
Illuminate the Truth: Capillaries
Highlight the word or phrase that makes each of the following statements true.
1. Capillaries (are)(are not) evenly distributed throughout the body.
2. The majority of the capillaries in skeletal muscles are (constantly filled with blood)(shut down during periods
of rest).
3. Capillaries (take up)(release) wastes, such as carbon dioxide and ammonia.
4. Water (flows into)(moves into and out of) capillaries.
5. In diffusion, substances move from areas of (greater)(lesser) to (greater)(lesser) concentration.
6. The concentration of oxygen within capillaries is (greater than)(less than) the concentration of oxygen in the
surrounding tissue fluid; therefore, oxygen diffuses (into)(out of) the capillaries.
7. (Osmosis) (Filtration) occurs close to the arterial side of the capillary bed, while (colloid osmotic
pressure)(diffusion) operates toward the venous side.
8. Of all the fluid filtered at the arterial end of the capillary bed, about (85%)(15%) is reabsorbed at the venous end.
190 Chapter 15 Vascular System
4374_Ch16_205-220 10/22/14 10:27 AM Page 205
chapter 16
LYMPHATIC & IMMUNE
SYSTEMS
The lymphatic and immune systems work together to protect the body against disease. The immune system consists
primarily of a population of cells that defend the body against invasion by viruses, bacteria, and other disease-causing
agents. These cells inhabit the lymphatic system: a network of organs and vessels that extend throughout the body.
Make a Connection: Lymphatic Organs
Patches of specialized tissue containing lymphocytes exist throughout the body. Lymphatic organs, however, are well
defined. Unscramble the words on the left to discover the names of the lymphatic organs. Then draw lines to link
each organ to its description or function. (Hint: Some organs have more than one correct answer.)
1. MYTHUS a. Consists of masses of lymphoid tissue that form a
protective circle at the back of the throat
b. Analyzed to determine whether cancer has
2. MYPHL SNEDO
metastasized
c. The body’s largest lymphatic organ
3. LISTSNO
d. Large in children, this organ shrinks to a fraction
of its former size by adulthood.
4. PLESNE e. Besides cleansing lymph, also serve as sites for final
maturation of some types of lymphocytes and
monocytes
f. Provides a location for B and T lymphocytes to
mature
g. Prone to injury, rupture of this organ could result
in a fatal hemorrhage
h. Removes 99% of the impurities in lymph before it
returns the fluid to the bloodstream
Chapter 16 Lymphatic & Immune Systems 205
4374_Ch16_205-220 10/22/14 10:27 AM Page 206
List for Learning: Functions of Lymph
Lymphatic vessels are filled with lymph: a clear, colorless fluid that originates in the tissues as the fluid left behind
following capillary exchange. Using the spaces provided, list the three functions of lymph.
1.
2.
3.
Drawing Conclusions: Lymphatic Vessels
Although lymphatic vessels are similar to veins, they have some key differences. Review your knowledge of lymphatic
vessels by first filling in the blanks with the correct word or words. Then follow the instructions after each sentence
to color the figure as described.
1. Lymphatic vessels originate in as microscopic, blind-ended
sacs within a bed of .
(Color the lymphatic vessel shown in the figure green.)
2. flows into lymphatic vessels through gaps between cells. ,
, and flow in with the fluid.
(Insert arrows in the figure to illustrate how fluid enters the vessel.)
3. Valves prevent backflow, ensuring that lymph moves from tissues and
the heart.
(Color the valves in the figure dark blue; insert arrows to show the direction of flow.)
4. anchor the lymphatic vessels to surrounding cells, which helps to
keep the vessels from collapsing.
(Color these structures in the figure purple.)
206 Chapter 16 Lymphatic & Immune Systems
4374_Ch16_205-220 10/22/14 10:27 AM Page 207
Conceptualize in Color: Overview of the Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system consists of lymphatic vessels, lymph, lymphatic tissue, and lymphatic organs. Identify the
structures of the lymphatic system by coloring them as suggested or choose your own colors.
● Spleen: Red
● Red bone marrow: Pink
● Cervical lymph nodes: Green
● Axillary lymph nodes: Purple
● Inguinal lymph nodes: Orange
● Tonsils: Brown
● Thymus gland: Tan
● Trace the lymphatic vessels in blue
● Shade the area drained by the right lymphatic duct
yellow
● Shade the area drained by the thoracic duct light
purple
Chapter 16 Lymphatic & Immune Systems 207
4374_Ch16_205-220 10/22/14 10:27 AM Page 208
Conceptualize in Color: Lymph Node
As lymph flows through lymphatic vessels, it passes through multiple lymph nodes. Identify the structures of the
lymph node using the colors suggested or choose your own colors.
● Fibrous capsule: Tan ● Cortical nodules: Purple ● Efferent vessel: Orange
● Trabeculae: Green ● Germinal centers: Pink ● Insert arrows showing direction
of lymph flow
● Sinuses: Light blue ● Afferent vessels: Brown
Artery and
vein
List for Learning: Functions of the Spleen
The spleen is the body’s largest lymphatic organ. Using the spaces provided, list four functions of this major
lymphatic organ.
1.
2.
3.
4.
208 Chapter 16 Lymphatic & Immune Systems
4374_Ch16_205-220 10/22/14 10:27 AM Page 209
Drawing Conclusions: The Spleen
Build your knowledge about the spleen by filling in the blanks in the sentences with the correct word or words.
Then color the splenic structures using the colors suggested or choose your own colors.
1. The spleen lies in the upper quadrant of the abdomen.
2. The spleen is structurally similar to the .
3. Lymphocytes and macrophages in the pulp screen the passing blood for foreign
antigens.
4. Macrophages in the remove and digest worn-out blood cells.
5. The spleen stores 20% to 30% of the body’s .
6. The spleen produces in the fetus.
Color the following structures:
● Spleen: Brown ● Red pulp: Pink ● Veins: Blue
● Venous sinuses: Purple ● Capsule: Tan ● Splenic artery: Red
● White pulp: Yellow ● Artery: Red ● Splenic vein: Blue
Chapter 16 Lymphatic & Immune Systems 209
4374_Ch16_205-220 10/22/14 10:27 AM Page 210
Puzzle It Out: The Lymphatic System
Complete the crossword puzzle to review some key facts about the lymphatic system.
ACROSS DOWN
1. Red bone marrow and the thymus are known as 1. Lymph has a lower
lymphatic organs content than does plasma.
because they provide a location for B and 2. Term for pharyngeal tonsils
T lymphocytes to mature. 3. Lymph nodes through which most breast cancers
5. An acute inflammation of the tonsils metastasize
7. The tonsils most likely to become infected 4. Tonsils concentrated in patches on either side of
8. Location of lymph nodes that monitor lymph the tongue
coming from the head and neck 6. Swelling that results when the lymphatic vessel is
obstructed
210 Chapter 16 Lymphatic & Immune Systems
4374_Ch17_221-238 10/23/14 11:57 AM Page 226
Fill in the Gaps: Alveoli
Fill in the blanks to correctly complete the following sentences. Choose from the words listed in the Word Bank.
(Hint: Not all the words will be used.)
BLOOD CAPILLARIES LIQUID MEMBRANE MUCUS SURFACTANT VEINS
1. The alveoli are wrapped in a fine mesh of .
2. Gas exchange occurs through the respiratory .
3. For gas to enter or leave a cell, it must be dissolved in .
4. is a substance that helps reduce surface tension inside the alveolus to keep it from collapsing.
Drawing Conclusions: The Lungs
Fissures divide the lungs into lobes. In the following figure, draw lines to show the locations of the fissures. Write
the name of each fissure by the appropriate line. Then write the name of each lobe within the appropriate space
inside the lungs.
226 Chapter 17 Respiratory System
4374_Ch17_221-238 10/23/14 11:57 AM Page 227
Drawing Conclusions: Pleura
In the following illustration, color the structures as suggested. Then, in the spaces provided, state the two purposes of
pleural fluid.
● Visceral pleura: Green
● Parietal pleura: Orange
● Pleural space: Light blue
Trachea Vertebra
Bronchi Posterior Esophagus
Aorta
Right lung Left lung
Heart
Ribs
Anterior Sternum
Pleural fluid serves two purposes:
1.
2.
Chapter 17 Respiratory System 227
Вам также может понравиться
- Cardiovascular System - Elearning NotesДокумент3 страницыCardiovascular System - Elearning NotesfallenОценок пока нет
- Blood Vessels, AnatomyДокумент20 страницBlood Vessels, AnatomyAbu BakarОценок пока нет
- IHA-Chap. 5-Circulatory SystemДокумент18 страницIHA-Chap. 5-Circulatory SystemVarsha SОценок пока нет
- Pp17. Bloodvessels and Valves Structure and FunctionsДокумент10 страницPp17. Bloodvessels and Valves Structure and Functionsdakalothathani029Оценок пока нет
- Note On F3 SC C2 TransportationДокумент4 страницыNote On F3 SC C2 Transportationgan tong hock a.k.a ganosОценок пока нет
- Blood VesselsДокумент7 страницBlood VesselsJireh AcabalОценок пока нет
- Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels and Circulation: Student Learning OutcomesДокумент10 страницCardiovascular System: Blood Vessels and Circulation: Student Learning Outcomeslily1liang-1Оценок пока нет
- 2nd Day OF Exams in 1st QTR 2016Документ9 страниц2nd Day OF Exams in 1st QTR 2016John RoasaОценок пока нет
- Cardiorespiratory QuestionsДокумент12 страницCardiorespiratory QuestionsKim Oliveri ReedОценок пока нет
- Activities Unit 2. Systems of The Nutrition FunctionДокумент6 страницActivities Unit 2. Systems of The Nutrition FunctionIdayra M. Neira CastilloОценок пока нет
- Need For Circulatory SystemsДокумент13 страницNeed For Circulatory SystemsKevin LlorenteОценок пока нет
- Transport in Animals-Topic 9Документ14 страницTransport in Animals-Topic 9sukiiОценок пока нет
- Solution Manual For High Acuity Nursing 7th Edition WagnerДокумент25 страницSolution Manual For High Acuity Nursing 7th Edition WagnerJamesThomasngec100% (31)
- Lab Module Activity - Blood and Blood VesselsДокумент19 страницLab Module Activity - Blood and Blood VesselsJecel LazarraОценок пока нет
- Lesson AssignmentДокумент26 страницLesson AssignmentFatima AzziffОценок пока нет
- Define Arteries, Veins and Capillaries. Explain The Differences Between ThemДокумент5 страницDefine Arteries, Veins and Capillaries. Explain The Differences Between Themzeenat gaziОценок пока нет
- Exercise No. 10 Circulatory System (Blood Vessels and Heart)Документ3 страницыExercise No. 10 Circulatory System (Blood Vessels and Heart)Rio Geline EdralinОценок пока нет
- Cardiovascular System Lecture - NotesДокумент23 страницыCardiovascular System Lecture - NotesParker KapembwaОценок пока нет
- Blood Cells and Blood Vessels WorksheetДокумент5 страницBlood Cells and Blood Vessels WorksheetCedrick MedinaОценок пока нет
- Worksheet 1Документ12 страницWorksheet 1Jessabelle RamosОценок пока нет
- Circulatory and Respiratory ReviewДокумент5 страницCirculatory and Respiratory ReviewNur ShaОценок пока нет
- Module 11 Blood VesselsДокумент9 страницModule 11 Blood VesselsMisha WilliamsОценок пока нет
- Weeks 12-16 Learning ObjectivesДокумент14 страницWeeks 12-16 Learning ObjectivesAmber DavisОценок пока нет
- What Makes Blood Flow pdf1Документ3 страницыWhat Makes Blood Flow pdf1blackruiner2008Оценок пока нет
- Circulatory and Respiratory ReviewДокумент5 страницCirculatory and Respiratory ReviewTristan PereyОценок пока нет
- The Cardiovascular SystemДокумент5 страницThe Cardiovascular Systemjuly3ciaОценок пока нет
- Assignment-Ch 11-Ans SheetДокумент6 страницAssignment-Ch 11-Ans Sheetrachna sharmaОценок пока нет
- Types of Circulatory SystemsДокумент8 страницTypes of Circulatory SystemsJanis Micaela EsmasОценок пока нет
- In Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements in Biological ScienceДокумент11 страницIn Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements in Biological ScienceGodfrey Loth Sales Alcansare Jr.Оценок пока нет
- MTF Solar 2: Jabatan Pelajaran PerakДокумент13 страницMTF Solar 2: Jabatan Pelajaran PerakizazuanОценок пока нет
- 11S HSB Notes The Circulatory SystemДокумент4 страницы11S HSB Notes The Circulatory SystemTenika RodriguezОценок пока нет
- G9 - Lesson 1 Cardiovascular SystemДокумент7 страницG9 - Lesson 1 Cardiovascular SystemKhrean Kae SantiagoОценок пока нет
- The Heart and The Immunity BsoaДокумент26 страницThe Heart and The Immunity BsoaJaniegh LJan CerxyseОценок пока нет
- Grade Level Standards: Governor Andres Pascual CollegeДокумент7 страницGrade Level Standards: Governor Andres Pascual CollegeIm BusyОценок пока нет
- General Format Genre AnalysisДокумент3 страницыGeneral Format Genre AnalysisSajid Islam MindogОценок пока нет
- 37 1Документ3 страницы37 1MoneymakerОценок пока нет
- 6.2 The Blood System IB PDFДокумент69 страниц6.2 The Blood System IB PDFEva OrtizОценок пока нет
- Biology C - Lesson 1 - Circulatory SystemДокумент46 страницBiology C - Lesson 1 - Circulatory SystemMuhammad Azrie0% (1)
- Circulation Notes I To VIДокумент8 страницCirculation Notes I To VIStacey KwiatkowskiОценок пока нет
- Cardiovascular XiДокумент27 страницCardiovascular XiKhairunnisa KhairunnisaОценок пока нет
- Blood VesselsДокумент60 страницBlood VesselsJerick Sevilla SearesОценок пока нет
- SCIENCE 9 Q1-WK 1-2.b FOR STUDENTДокумент16 страницSCIENCE 9 Q1-WK 1-2.b FOR STUDENTErra PeñafloridaОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan No 2Документ7 страницLesson Plan No 2hafeez ahmedОценок пока нет
- Blood Vessels NotesДокумент5 страницBlood Vessels NotesJan Vincent GoОценок пока нет
- Life Processes - Transportation QB 2019-20 PDFДокумент5 страницLife Processes - Transportation QB 2019-20 PDFRatheesh HrishikeshОценок пока нет
- Transport in AnimalsДокумент6 страницTransport in Animalsmakah2711Оценок пока нет
- +1 Bio Zoo em Vol 2Документ38 страниц+1 Bio Zoo em Vol 2Ameena BegumОценок пока нет
- Circulatory System PDFДокумент1 страницаCirculatory System PDFLauraОценок пока нет
- Urinary SystemДокумент6 страницUrinary SystemKirsten CruzadoОценок пока нет
- Activity 7 OrgansДокумент9 страницActivity 7 OrgansKEILAH ENCILAYОценок пока нет
- A. MODUL PDP 8Документ29 страницA. MODUL PDP 8Suraya Eiman ZafiraОценок пока нет
- Circulation: Chapter OutlineДокумент7 страницCirculation: Chapter OutlineKaye Selene Raphaelle SyОценок пока нет
- RRD 6 Circulatory and Peripheral Vascular Disorders SP 18Документ21 страницаRRD 6 Circulatory and Peripheral Vascular Disorders SP 18bmzlatteОценок пока нет
- Chapter 8 - Circulation and ImmunityДокумент94 страницыChapter 8 - Circulation and Immunitychloe06muller.mОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9 - Transport of Substances in Humans: Learning ObjectivesДокумент18 страницChapter 9 - Transport of Substances in Humans: Learning Objectivesthanks btОценок пока нет
- Document 9Документ2 страницыDocument 9RYCO ALVAREZОценок пока нет
- Vessel FlowOutlineДокумент5 страницVessel FlowOutlineDeva ChiruОценок пока нет
- Circulatory System: A Tutorial Study GuideОт EverandCirculatory System: A Tutorial Study GuideРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)
- Anatomy and Physiology Lecture DiscussionДокумент27 страницAnatomy and Physiology Lecture DiscussionDayledaniel SorvetoОценок пока нет
- PMLS LAB EXERCISE IN Venipuncture ProceduresДокумент3 страницыPMLS LAB EXERCISE IN Venipuncture ProceduresDayledaniel SorvetoОценок пока нет
- Anaerobe of Clinical ImportanceДокумент43 страницыAnaerobe of Clinical ImportanceDayledaniel SorvetoОценок пока нет
- Real-Time PCR Automations of Quant Studio 5 and MA6000 PlusДокумент15 страницReal-Time PCR Automations of Quant Studio 5 and MA6000 PlusDayledaniel SorvetoОценок пока нет
- Case Study Analysis (1,2,3,4) ENDOCRINOLOGYДокумент3 страницыCase Study Analysis (1,2,3,4) ENDOCRINOLOGYDayledaniel Sorveto100% (1)
- Chapter 33: Protein SynthesisДокумент64 страницыChapter 33: Protein SynthesisDayledaniel SorvetoОценок пока нет
- Proteins: Prepared By: Dayle Daniel G. Sorveto, RMT, MSMTДокумент64 страницыProteins: Prepared By: Dayle Daniel G. Sorveto, RMT, MSMTDayledaniel SorvetoОценок пока нет
- Connective Tissue ComparisonДокумент1 страницаConnective Tissue ComparisonDayledaniel SorvetoОценок пока нет
- ANAPHY Disease PathologyДокумент19 страницANAPHY Disease PathologyDayledaniel SorvetoОценок пока нет
- Non Hodgkin's Lymphoma: Rakesh BiswasДокумент16 страницNon Hodgkin's Lymphoma: Rakesh BiswasDayledaniel SorvetoОценок пока нет
- Week 1 Pmls2Документ45 страницWeek 1 Pmls2Dayledaniel SorvetoОценок пока нет
- Endocrine SystemДокумент11 страницEndocrine SystemDayledaniel SorvetoОценок пока нет
- Lab Output For Blood (Human Anatomy and Physiology)Документ8 страницLab Output For Blood (Human Anatomy and Physiology)Dayledaniel Sorveto0% (1)
- Skin Model ProjectДокумент2 страницыSkin Model ProjectDayledaniel SorvetoОценок пока нет
- Analysis of Urine and Other Body Fluids (WLP Draft)Документ1 страницаAnalysis of Urine and Other Body Fluids (WLP Draft)Dayledaniel SorvetoОценок пока нет
- Week 2 Cellular LevelДокумент6 страницWeek 2 Cellular LevelDayledaniel SorvetoОценок пока нет
- Week 2 Cellular LevelДокумент7 страницWeek 2 Cellular LevelDayledaniel Sorveto100% (1)
- Principles of Anatomy and Physiology: 14th EditionДокумент47 страницPrinciples of Anatomy and Physiology: 14th EditionDayledaniel SorvetoОценок пока нет
- Week 4 Tissue Levels of OrganizatioДокумент49 страницWeek 4 Tissue Levels of OrganizatioDayledaniel SorvetoОценок пока нет
- Schedule Class of Seminar 1Документ1 страницаSchedule Class of Seminar 1Dayledaniel SorvetoОценок пока нет
- AUB The MicroscopeДокумент1 страницаAUB The MicroscopeDayledaniel SorvetoОценок пока нет
- Week 6 Skeletal SystemДокумент25 страницWeek 6 Skeletal SystemDayledaniel SorvetoОценок пока нет
- GCE Biology Marking Scheme (January 2007)Документ21 страницаGCE Biology Marking Scheme (January 2007)potterhead1DОценок пока нет
- MCQДокумент20 страницMCQanuj sharma100% (2)
- Chapter - 002-Medical TДокумент22 страницыChapter - 002-Medical TPrecilou CutandaОценок пока нет
- Pain PhysiologyДокумент40 страницPain PhysiologyAnmol Jain100% (1)
- Pathology List PDFДокумент22 страницыPathology List PDFsafaiisafaОценок пока нет
- 7396 26182 1 PBДокумент17 страниц7396 26182 1 PBdavideОценок пока нет
- Blg1501 May June 2011 - Memorandum-1Документ4 страницыBlg1501 May June 2011 - Memorandum-1Janine Toffar100% (1)
- Nyas12203Becoming Conscious The Science of MindfulnessДокумент18 страницNyas12203Becoming Conscious The Science of MindfulnesscgrossОценок пока нет
- Probiota 18Документ27 страницProbiota 18BambangОценок пока нет
- Addictive DisordersДокумент117 страницAddictive DisordersGlory MimiОценок пока нет
- Nutrition 1Документ5 страницNutrition 1Christine PunsalanОценок пока нет
- Owen A O'Connor, Stephen M Ansell, John F Seymo 230518 053705Документ514 страницOwen A O'Connor, Stephen M Ansell, John F Seymo 230518 053705Juan RivasОценок пока нет
- Zomedica Patent 11486878Документ14 страницZomedica Patent 11486878Charles GrossОценок пока нет
- Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine 6th EdДокумент9 страницFitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine 6th Ednadia salsabilaОценок пока нет
- Gastrointestinal System: Git Brief Introduction: Dr. S. M. A. WaseemДокумент20 страницGastrointestinal System: Git Brief Introduction: Dr. S. M. A. WaseemHoping HeartsОценок пока нет
- Body Cavities PPT & Anatomical SystemДокумент10 страницBody Cavities PPT & Anatomical Systemnandhini raguОценок пока нет
- General Feedback For MICR2011 RationalesДокумент2 страницыGeneral Feedback For MICR2011 Rationalesshahriar khanОценок пока нет
- Hematology Ii Lectures Introduction To HemostasisДокумент28 страницHematology Ii Lectures Introduction To HemostasisJoshua Trinidad100% (1)
- Ari Whitten The Ultimate Guide To Red Light TherapyДокумент41 страницаAri Whitten The Ultimate Guide To Red Light TherapyJulianne Bsc94% (35)
- Sturge Weber Syndrome Case Report StudyДокумент11 страницSturge Weber Syndrome Case Report StudyOphtalmology100% (3)
- Congenital and Hereditary Diseases Introduction-1Документ21 страницаCongenital and Hereditary Diseases Introduction-1Melvin OnyanchaОценок пока нет
- Laboratory Handbook PDFДокумент184 страницыLaboratory Handbook PDFReymi Then50% (2)
- CO2 Liquefied Gas MSDSДокумент9 страницCO2 Liquefied Gas MSDSsalcabes100% (1)
- ProteusДокумент20 страницProteusMonishaОценок пока нет
- Dog Contract - No BreedingДокумент2 страницыDog Contract - No Breedingapi-271337917Оценок пока нет
- Laboratory Diagnosis of CMV Infection: A ReviewДокумент6 страницLaboratory Diagnosis of CMV Infection: A ReviewAchmad ArrizalОценок пока нет
- Similarities and DifferencesДокумент8 страницSimilarities and DifferencesEduard IvanovОценок пока нет
- Gestalt Transference PDFДокумент7 страницGestalt Transference PDFAdriana Bogdanovska Toskic100% (2)
- (Methods in Enzymology 529) Jon Lorsch (Eds.) - Laboratory Methods in Enzymology - DNA-Academic Press (2013)Документ379 страниц(Methods in Enzymology 529) Jon Lorsch (Eds.) - Laboratory Methods in Enzymology - DNA-Academic Press (2013)Gabriela QueirozОценок пока нет
- NEET GT-5 SolutionsДокумент12 страницNEET GT-5 Solutionsabcxyz7799Оценок пока нет