Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
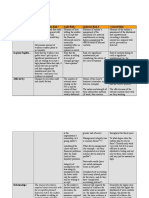
Audit Control Matrix
Загружено:
Planco RosanaАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Audit Control Matrix
Загружено:
Planco RosanaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
PROCESS 5.2.
1: PROCESS ACOUNTS PAYABLE RISK AND CONTROL MATRIX (RCM)
PROCESS 5.2.1: PROCESS ACOUNTS PAYABLE RISK AND CONTROL MATRIX (RCM)
NO. RISK
1 A user may edit, modify or delete a matched invoice.
2 A user may edit, modify or delete a matched invoice.
3 A user may edit, modify or delete a matched invoice.
Adjustments may be approved that are not acceptable to management; this could affect operating
4
results adversely and result in dissatisfied vendors and/or unrecorded liabilities.
Adjustments may be approved that are not acceptable to management; this could affect operating
5
results adversely and result in dissatisfied vendors and/or unrecorded liabilities.
Adjustments may be approved that are not acceptable to management; this could affect operating
6
results adversely and result in dissatisfied vendors and/or unrecorded liabilities.
Adjustments may be approved that are not acceptable to management; this could affect operating
7
results adversely and result in dissatisfied vendors and/or unrecorded liabilities.
Adjustments may be approved that are not acceptable to management; this could affect operating
8
results adversely and result in dissatisfied vendors and/or unrecorded liabilities.
Adjustments may be approved that are not acceptable to management; this could affect operating
9
results adversely and result in dissatisfied vendors and/or unrecorded liabilities.
Adjustments may be approved that are not acceptable to management; this could affect operating
10
results adversely and result in dissatisfied vendors and/or unrecorded liabilities.
Adjustments may be approved that are not acceptable to management; this could affect operating
11
results adversely and result in dissatisfied vendors and/or unrecorded liabilities.
12 An adequate audit trail may not be available.
13 An incorrect purchase order is sent to a vendor.
14 An incorrect purchase order is sent to a vendor.
15 An incorrect purchase order is sent to a vendor.
16 An incorrect purchase order is sent to a vendor.
17 An incorrect purchase order is sent to a vendor.
18 An incorrect purchase order is sent to a vendor.
19 An open, unresolved invoice may not be posted by the closing deadline.
20 An open, unresolved invoice may not be posted by the closing deadline.
21 An open, unresolved invoice may not be posted by the closing deadline.
22 An open, unresolved invoice may not be posted by the closing deadline.
23 An open, unresolved invoice may not be posted by the closing deadline.
24 An open, unresolved invoice may not be posted by the closing deadline.
Source: www.knowledgeleader.com Page 1
PROCESS 5.2.1: PROCESS ACOUNTS PAYABLE RISK AND CONTROL MATRIX (RCM)
PROCESS 5.2.1: PROCESS ACOUNTS PAYABLE RISK AND CONTROL MATRIX (RCM)
NO. RISK
Appropriate matching between invoices, receiving documents and purchase orders may not be
25
performed.
Appropriate matching between invoices, receiving documents and purchase orders may not be
26
performed.
Appropriate matching between invoices, receiving documents and purchase orders may not be
27
performed.
Cash may be disbursed and short pays may be resolved for goods and services never received
28
(or in advance of receipt).
Cash may be disbursed and short pays may be resolved for goods and services never received
29
(or in advance of receipt).
Cash may be disbursed and short pays may be resolved for goods and services never received
30
(or in advance of receipt).
Cash may be disbursed and short pays may be resolved for goods and services never received
31
(or in advance of receipt).
Cash may be disbursed and short pays may be resolved for goods and services never received
32
(or in advance of receipt).
33 Checks are paid in the wrong amount or to the wrong vendor.
34 Data inconsistency may exist between accounts payable and the general ledger.
35 Data inconsistency may exist between accounts payable and the general ledger.
36 Data inconsistency may exist between accounts payable and the general ledger.
37 Data inconsistency may exist between accounts payable and the general ledger.
38 Data inconsistency may exist between accounts payable and the general ledger.
39 Data inconsistency may exist between accounts payable and the general ledger.
40 Data inconsistency may exist between accounts payable and the general ledger.
Source: www.knowledgeleader.com Page 2
PROCESS 5.2.1: PROCESS ACOUNTS PAYABLE RISK AND CONTROL MATRIX (RCM)
PROCESS 5.2.1: PROCESS ACOUNTS PAYABLE RISK AND CONTROL MATRIX (RCM)
NO. RISK
41 Data inconsistency may exist between accounts payable and the general ledger.
42 Data inconsistency may exist between accounts payable and the general ledger.
43 Detail activity may be incorrectly posted in the subsidiary ledger.
44 Detail activity may be incorrectly posted in the subsidiary ledger.
45 Detail activity may be incorrectly posted in the subsidiary ledger.
46 Detail activity may be incorrectly posted in the subsidiary ledger.
47 Discrepancies exist between amounts on supplier invoice and supporting documents.
48 Discrepancies exist between amounts on supplier invoice and supporting documents.
49 Discrepancies exist between amounts on supplier invoice and supporting documents.
50 Discrepancies exist between amounts on supplier invoice and supporting documents.
51 Duplicate invoices are received and processed, leading to duplicate payments.
52 Duplicate invoices are received and processed, leading to duplicate payments.
53 Duties are not adequately segregated.
54 Duties are not adequately segregated.
55 Duties are not adequately segregated.
56 Duties are not adequately segregated.
Employees do not complete a purchase request or an expense reimbursement is not approved by
57
the department manager.
Employees do not complete a purchase request or an expense reimbursement is not approved by
58
the department manager.
Employees do not complete a purchase request or an expense reimbursement is not approved by
59
the department manager.
Goods are received for unauthorized or invalid purchase orders and are not appropriately
60
recorded in the system.
Goods are received for unauthorized or invalid purchase orders and are not appropriately
61
recorded in the system.
Goods are received for unauthorized or invalid purchase orders and are not appropriately
62
recorded in the system.
Goods are received for unauthorized or invalid purchase orders and are not appropriately
63
recorded in the system.
Goods are received for unauthorized or invalid purchase orders and are not appropriately
64
recorded in the system.
Source: www.knowledgeleader.com Page 3
PROCESS 5.2.1: PROCESS ACOUNTS PAYABLE RISK AND CONTROL MATRIX (RCM)
PROCESS 5.2.1: PROCESS ACOUNTS PAYABLE RISK AND CONTROL MATRIX (RCM)
NO. RISK
65 Invoice does not match the receiver documents.
66 Invoices are not properly authorized, complete, accurate and timely.
67 Invoices are not properly authorized, complete, accurate and timely.
68 Invoices are not properly authorized, complete, accurate and timely.
69 Invoices are not properly authorized, complete, accurate and timely.
70 Invoices are not properly authorized, complete, accurate and timely.
71 Invoices are not properly authorized, complete, accurate and timely.
72 Invoices are not properly authorized, complete, accurate and timely.
73 Invoices are not properly authorized, complete, accurate and timely.
74 Invoices are not properly authorized, complete, accurate and timely.
75 Invoices are not properly authorized, complete, accurate and timely.
76 Invoices are not properly authorized, complete, accurate and timely.
77 Invoices are not properly authorized, complete, accurate and timely.
78 Invoices are not properly authorized, complete, accurate and timely.
79 Invoices are not properly authorized, complete, accurate and timely.
80 Invoices are not properly authorized, complete, accurate and timely.
81 Invoices are not properly authorized, complete, accurate and timely.
82 Invoices are not properly authorized, complete, accurate and timely.
Source: www.knowledgeleader.com Page 4
PROCESS 5.2.1: PROCESS ACOUNTS PAYABLE RISK AND CONTROL MATRIX (RCM)
PROCESS 5.2.1: PROCESS ACOUNTS PAYABLE RISK AND CONTROL MATRIX (RCM)
NO. RISK
83 Invoices are not properly authorized, complete, accurate and timely.
84 Invoices are not properly authorized, complete, accurate and timely.
Invoices for goods/services are paid in advance of the due date without regard to the time value
85
of money.
Invoices for goods/services are paid in advance of the due date without regard to the time value
86
of money.
Invoices for goods/services are paid in advance of the due date without regard to the time value
87
of money.
Invoices may be received but never reported or reported inaccurately; this could result in a
88
misstatement of unrecorded liabilities.
Invoices may be received but never reported or reported inaccurately; this could result in a
89
misstatement of unrecorded liabilities.
Invoices may be received but never reported or reported inaccurately; this could result in a
90
misstatement of unrecorded liabilities.
91 Misappropriations or fraudulent payments may be made.
92 Misappropriations or fraudulent payments may be made.
93 Misappropriations or fraudulent payments may be made.
94 Misappropriations or fraudulent payments may be made.
95 Misappropriations or fraudulent payments may be made.
96 Misappropriations or fraudulent payments may be made.
97 Misappropriations or fraudulent payments may be made.
98 Misappropriations or fraudulent payments may be made.
99 Misappropriations or fraudulent payments may be made.
100 Misappropriations or fraudulent payments may be made.
101 Misappropriations or fraudulent payments may be made.
102 Misappropriations or fraudulent payments may be made.
103 Misappropriations or fraudulent payments may be made.
Source: www.knowledgeleader.com Page 5
PROCESS 5.2.1: PROCESS ACOUNTS PAYABLE RISK AND CONTROL MATRIX (RCM)
PROCESS 5.2.1: PROCESS ACOUNTS PAYABLE RISK AND CONTROL MATRIX (RCM)
NO. RISK
104 Misappropriations or fraudulent payments may be made.
105 Misappropriations or fraudulent payments may be made.
106 Misappropriations or fraudulent payments may be made.
107 Misappropriations or fraudulent payments may be made.
108 Misappropriations or fraudulent payments may be made.
109 Misappropriations or fraudulent payments may be made.
110 Misappropriations or fraudulent payments may be made.
111 Misappropriations or fraudulent payments may be made.
112 Misappropriations or fraudulent payments may be made.
Payable and related accounts may be misstated because of incorrect adjustments or incorrect
113
reclassifications of distributed amounts.
Payable and related accounts may be misstated because of incorrect adjustments or incorrect
114
reclassifications of distributed amounts.
Payable and related accounts may be misstated because of incorrect adjustments or incorrect
115
reclassifications of distributed amounts.
116 Payment discounts are not maximized.
117 Payment discounts are not maximized.
118 Payment discounts are not maximized.
119 Payment may be disbursed for goods and services not received.
120 Payment may be made to the wrong person or a fraudulent/non-existent company.
121 Payment may be made to the wrong person or a fraudulent/non-existent company.
122 Payment may be made to the wrong person or a fraudulent/non-existent company.
123 Payment may be made to the wrong person or a fraudulent/non-existent company.
124 Payment may be made to the wrong person or a fraudulent/non-existent company.
125 Payments may not be made timely, resulting in lost discounts and late charges.
126 Policies and procedures do not exist to support the accounts payable function.
127 Policies and procedures do not exist to support the accounts payable function.
Source: www.knowledgeleader.com Page 6
PROCESS 5.2.1: PROCESS ACOUNTS PAYABLE RISK AND CONTROL MATRIX (RCM)
PROCESS 5.2.1: PROCESS ACOUNTS PAYABLE RISK AND CONTROL MATRIX (RCM)
NO. RISK
128 Policies and procedures do not exist to support the accounts payable function.
129 Policies and procedures do not exist to support the accounts payable function.
130 Policies and procedures do not exist to support the accounts payable function.
131 Policies and procedures do not exist to support the accounts payable function.
132 Policies and procedures do not exist to support the accounts payable function.
Purchase order price differs from invoice price, resulting in price discrepancies that are resolved in
133
favor of the supplier.
134 Purchase orders, receivers and invoices are improperly processed, leading to variances.
135 Purchase orders, receivers and invoices are improperly processed, leading to variances.
136 Quantities received differ from quantities billed on the invoice.
137 Quantities received differ from quantities billed on the invoice.
138 Quantities received differ from quantities billed on the invoice.
139 Quantities received differ from quantities billed on the invoice.
140 Special terms are not taken into account.
141 Special terms are not taken into account.
142 Special terms are not taken into account.
143 Suppliers are paid an inaccurate amount due to improper tracking of account balances.
144 Suppliers are paid an inaccurate amount due to improper tracking of account balances.
Tax data (state and local tax [SALT], etc.) associated with an invoice is not accurate and
145
complete.
146 There are discrepancies in vendor/supplier management.
147 There are discrepancies in vendor/supplier management.
Source: www.knowledgeleader.com Page 7
PROCESS 5.2.1: PROCESS ACOUNTS PAYABLE RISK AND CONTROL MATRIX (RCM)
PROCESS 5.2.1: PROCESS ACOUNTS PAYABLE RISK AND CONTROL MATRIX (RCM)
NO. RISK
148 There are discrepancies in vendor/supplier management.
149 There are discrepancies in vendor/supplier management.
150 There are discrepancies in vendor/supplier management.
151 There are discrepancies in vendor/supplier management.
152 There are discrepancies in vendor/supplier management.
153 There are discrepancies in vendor/supplier management.
154 There are discrepancies in vendor/supplier management.
155 There are discrepancies in vendor/supplier management.
156 There are discrepancies in vendor/supplier management.
157 There are discrepancies in vendor/supplier management.
158 There are discrepancies in vendor/supplier management.
159 There are discrepancies in vendor/supplier management.
160 There are discrepancies in vendor/supplier management.
161 There are misappropriations or fraudulent payments.
162 There are misappropriations or fraudulent payments.
163 There are misappropriations or fraudulent payments.
164 There are misappropriations or fraudulent payments.
165 There are misappropriations or fraudulent payments.
166 There are misappropriations or fraudulent payments.
167 There are misappropriations or fraudulent payments.
168 There are misappropriations or fraudulent payments.
169 There are misappropriations or fraudulent payments.
170 There are misappropriations or fraudulent payments.
171 There is a discrepancy between the amounts on the supplier invoice and supporting documents.
Source: www.knowledgeleader.com Page 8
PROCESS 5.2.1: PROCESS ACOUNTS PAYABLE RISK AND CONTROL MATRIX (RCM)
PROCESS 5.2.1: PROCESS ACOUNTS PAYABLE RISK AND CONTROL MATRIX (RCM)
NO. RISK
172 There is a discrepancy between the amounts on the supplier invoice and supporting documents.
173 There is a discrepancy between the amounts on the supplier invoice and supporting documents.
174 There is a discrepancy between the amounts on the supplier invoice and supporting documents.
175 There is a discrepancy between the amounts on the supplier invoice and supporting documents.
176 There is inadequate safeguarding of accounts payable documents.
177 There is inadequate safeguarding of accounts payable documents.
178 There is inadequate safeguarding of accounts payable documents.
179 There is inadequate safeguarding of accounts payable documents.
180 There is inadequate safeguarding of accounts payable documents.
181 There is inadequate safeguarding of accounts payable documents.
182 There is inadequate safeguarding of accounts payable documents.
183 Unauthorized checks are issued.
184 Unauthorized checks are issued.
185 Unauthorized checks are issued.
186 Unauthorized checks are issued.
Unauthorized, fictitious or improper commitments or expenses may be incurred without
187
management's knowledge or approval.
Unauthorized, fictitious or improper commitments or expenses may be incurred without
188
management's knowledge or approval.
Unauthorized, fictitious or improper commitments or expenses may be incurred without
189
management's knowledge or approval.
Source: www.knowledgeleader.com Page 9
PROCESS 5.2.1: PROCESS ACOUNTS PAYABLE RISK AND CONTROL MATRIX (RCM)
CONTROL DESCRIPTION
The software/system logs user entry activity, including time stamp and entry activity.
Rights are restricted within the accounts payable user structure to limit powerful commands (batch approvals, add/del/mod/invoice, etc.).
Workflow notifications are used to report any modifications to existing suppliers' key fields, remittance info, etc.
The company has established tolerances for commodity purchases as appropriate. Receipts in excess of the tolerances may be returned
to the vendor.
Critical forms (e.g., check requests, adjustment forms and checks) are prenumbered and controlled. The system generates the next check
number, which must match the check number in the routing code at the bottom of the check.
Only managers can review, approve and code professional services and capital invoices for payment.
Trends in amounts and types of adjustments are periodically analyzed.
User access is designed and configured to support the segregation of duties between procurement, receiving, invoice processing, payment
processing and the vendor master.
Regular reporting, investigation and follow-up on backlog of unprocessed vendor invoices, receiving reports or rejected data occurs.
A currency threshold is established for checks requiring two signatures (either two manual signatures or one manual signature and one
computer-generated signature).
The disbursement process is automated to generate checks based on invoice payment due date and post the appropriate accounting
entries.
All invoice batches are entered with a standard naming convention.
Purchase orders are reviewed for accuracy and approved by an officer before they are submitted by the purchasing manager (PM).
The system/software requires that all fields are completed to initiate a purchase order.
Generation of purchase orders is restricted to appropriate personnel.
Changes to purchase orders are reviewed and approved by management prior to mailing to the supplier/vendor.
The staff member who initiates the initial purchase order is responsible for comparing rates and other important information to vendor
contracts.
The accounting manager reviews the PO Request Form, checks the account coding and signs off on the PO Request Form.
The software/system tracks all open invoice issues and is reviewed by the accounts payable supervisor at the end of each month to ensure
open items are cleared.
Invoices which are held from payment due to system or processing errors are required to be resolved within a certain number of days.
Workflow notifications are used to report any modifications to existing suppliers' key fields, remittance info, etc.
Error messages by the system indicate greater than acceptable tolerance levels, etc.
Invoices without purchase orders are routed to the appropriate cost center manager for resolution.
Payments are posted prior to being released for payment.
Source: www.knowledgeleader.com Page 10
PROCESS 5.2.1: PROCESS ACOUNTS PAYABLE RISK AND CONTROL MATRIX (RCM)
CONTROL DESCRIPTION
A limited number of suppliers are authorized for automatic release of payment. Tolerance levels are established for these vendors.
The system/software provides for matching of purchase orders, receipts and invoices for central supply. Payment can not be processed on
unmatched documents.
Units of measure conversion tables are used to ensure proper matching of purchase orders and invoices, as many vendors use a different
unit of measure for the same product. Additionally, the purchasing department reviews purchase orders to ensure that the appropriate unit
of measure is used.
When matching the receiver and invoice in the system, the accounts payable clerk must enter a valid purchase order number.
An accounts payable staff member compares the invoice to the open purchase order and receipt of goods or services.
Invoice approval is received at the department level. The central supply warehouse manager validates all receipts entered into the
system/software at the central supply warehouse.
The duplicate payments option prevents the generation or editing of a duplicate payment number by displaying an error when a preexisting
invoice number is entered for the same vendor during voucher creation.
The company has established tolerances for commodity purchases as appropriate. Receipts in excess of the tolerances may be returned
to the vendor.
Critical forms (e.g., check requests, adjustment forms and checks) are prenumbered and controlled. The system generates the next check
number, which must match the check number in the routing code at the bottom of the check.
Printed checks are submitted with the invoice/purchase order to the controller and another officer for comparison and approval. They
cannot be mailed without the signature of the concerned officers.
Accounts payable personnel periodically reconcile payments to the general ledger.
The corporate controller reviews the accounts payable reconciliations monthly.
A monthly reconciliation of the accounts payable subledger and the general ledger balance is prepared by the concerned personnel. All
variances over a certain amount are explained and all non-standard journal entries are reviewed by the concerned personnel.
Any adjustments to accounts payable are reviewed by the controller and posted to the general ledger.
Shipments are checked against packing slips, which are signed by receiving parties and then compared to the invoices and purchase
orders.
The project manager, using a chart of accounts, adds the general ledger account code to every invoice when it is paid. Before the check
can be printed, this the general ledger code must be entered, automatically updating the general ledger. the general ledger code appearing
on the invoice is then reviewed by the concerned signing officers before the check is signed.
An individual who does not process, authorize or disburse accounts payable is assigned to reconcile the accounts payable bank account
each month.
Source: www.knowledgeleader.com Page 11
PROCESS 5.2.1: PROCESS ACOUNTS PAYABLE RISK AND CONTROL MATRIX (RCM)
CONTROL DESCRIPTION
The accounts payable subsidiary ledger is reconciled with the general ledger.
The accounts payable manager reconciles the accounts payable suspense account regularly.
The general ledger accounts are posted through the system/software cross-validation rules.
Documented cut-off and period-end closing procedures are adhered to.
The general ledger accounts are posted through the system/software cross-validation rules.
Source documentation (checks, vouchers, etc.) is perforated, voided or otherwise cancelled to prevent reuse.
Exception reporting and investigation of processed invoices that vary from purchase orders or other criteria by more than pre-established
limits exist.
Checks are automatically prepared by computer based on the scheduled payment date entered when the voucher is processed.
HOLDs (Account, Funds, Invoice, Matching, Variance) are utilized for non-matching invoices.
Suppliers of goods/services are instructed to forward invoices directly to accounts payable.
The system closes a purchase order once goods and services are received.
The software/system functionality does not permit duplicate invoice numbers; unique transaction IDs are generated.
Limited personnel have the authority to change vendor master information, supplier terms, variances etc.
Roles are segregated in the system/software where individuals responsible for modifying supplier information can not process payments
and invoices.
A range of disbursement numbers is entered into the system before the checks are printed. After printing the checks, the purchasing
manager checks the last disbursement number of the input range with the last check printed.
A purchase authorization list is maintained that specifies the type of expenditures and limits in which individuals have authority to commit
the company. These authorization criteria may be maintained manually and/or within system applications.
Employee expense reimbursements are approved by the employee’s manager.
The approver reviews the PO Request Form against the department’s approved budget for the year to be sure that the purchase is within
the current year's spending budget.
Purchase requests are approved with a signature in accordance with the PO Approval Matrix. The initiator is responsible for obtaining the
appropriate approval for the purchase request.
For all purchased goods, the invoice(s) received are routed to the initiator of the purchase for review and approval for payment processing.
The initiator of the purchase monitors the contract for compliance, performance and costs.
Access to create a return order is restricted to authorized personnel.
Once goods arrive, appropriate personnel complete a receiving report and scan the items into the stock system timely and accurately.
The accounts payable specialist matches the invoice to the purchase order and transcribes the account code, department code and
product number onto the invoice.
Where applicable, the system performs a match between the purchase order and scanned goods received prior to release of the inventory
to post in the general ledger.
Source: www.knowledgeleader.com Page 12
PROCESS 5.2.1: PROCESS ACOUNTS PAYABLE RISK AND CONTROL MATRIX (RCM)
CONTROL DESCRIPTION
Periodically, a report is prepared and the exceptions are analyzed and investigated by the accounts payable supervisor and reported to the
accounts payable manager.
The appropriate authorizations are documented and maintained online for review by the accounts payable clerks. In addition, copies of
authorizing signatures are maintained and available to the clerks in the event a signature is in question.
Upon completion of invoice entry, a clerk compares the input batch detail to the actual invoices to identify key errors.
For voucher processing, the voucher amount is entered on both the voucher and general ledger screens. If one of these amounts is
entered incorrectly, an error occurs. A contingency audit is performed on a regular basis to identify over/under payments. The
system/software performs a check for duplicate invoice numbers.
Subsidiaries review and approve invoices before sending to accounts payable for payment, thus acknowledging receipt of goods or
services.
Only original invoices are accepted by the accounts payable group for processing of payment. Faxed/emailed copies are not processed,
unless specifically approved by the accounts payable supervisor.
Once an invoice has been approved and cleared in the system/software, access to make changes to the related invoice (without the need
for a new check) is only granted by IT.
Department managers are responsible for the review and accuracy of all purchase requisitions that are released from their areas. They are
responsible for ensuring that requisitions are accurate and complete.
Invoices without a purchase order that are not approved via an automated workflow must be approved by appropriate management prior to
payment.
Invoices are paid after three-way match or approval of invoice.
Invoices are approved by appropriate personnel in accordance with the Authority Limit Table for proper functioning.
The concerned/appropriate personnel of each business unit periodically reviews and updates the Authority Limit Table.
Invoice approval is received at the department level. Authorized personnel within the department review the invoices and sign them,
indicating that they are valid and approved for payment. Upon receipt, invoices are date/time stamped for tracking purposes.
The accounts payable clerks review the invoices, noting that appropriate approval was obtained and that proper coding was assigned prior
to entry into the system. The system/software requires the appropriate manager (as defined by the "Approved By" list) to change the batch
of goods status from pending to approved in order for the batch to post.
Special attention will be made on the decimal point entry procedures. The system/software has been configured to display a warning
message reminding users to input the decimal point.
All checks over a certain amount as directed by the company are copied and routed to accounts payable to match with the applicable
voucher.
The invoices are coded and password protected to ensure protection of the invoices.
Invoices are checked for mathematical accuracy.
Processing procedures provide for input verification of critical voucher fields (e.g., vendor, invoice amount, account coding, quantities, part
number, etc.) through manual batch controls, edit exception reports and/or online system edits.
Source: www.knowledgeleader.com Page 13
PROCESS 5.2.1: PROCESS ACOUNTS PAYABLE RISK AND CONTROL MATRIX (RCM)
CONTROL DESCRIPTION
Invoices and new supplier requests are required to be processed by the accounts payable group within a specific number of hours of
receipt of the invoice/requests at the corporate location.
Invoices are only entered for vendors that exist on the approved suppliers list (ASL) in the system/software.
Checks are released for payment based on the due date within the software/system.
Payments within accounts payable designated as blocked are not able to be processed.
Payments within accounts payable designated as blocked are not able to be processed.
The accounts payable specialist stamps the invoice with the date that it was received once received.
The accounts payable specialist sends out a reminder before month-end close to all employees reminding them to submit all expense
reports or advise on the estimated amounts to accrue for unprocessed travel and expenses. The accounts payable specialist creates a
journal entry for all unprocessed invoices and the accounting manager reviews this journal entry for the open invoice accrual account.
Receiving enters all receipts only against an open purchase order in the system. The purchase order receiver processing options have
been configured to receive by purchase order.
The accounts payable supervisor reviews the Proposal for Payment Report weekly for unusual items.
Access to Auto Signature is restricted.
The bank is provided with a listing of all issued checks and amounts to compare to all checks received at the bank. The bank only pays the
checks on the listing and matches the amounts.
The company communicates its policy to vendors informing them that it only pays for goods received. Discrepancies between quantity
shipped vs. billed are short paid.
All checks go through a quality review after being cut and before being distributed to ensure that the amount is correct and supplier
information is accurate and complete.
Only the accounts payable coordinator/the accounts payable concerned personnel can process manual/reprinted checks.
The manager of accounting operations reviews all checks over a certain amount.
Debit balances in the accounts payable subsidiary ledger are promptly investigated and, if necessary, refunds are obtained from vendors.
Disbursements are drawn on a zero balance account.
Voided checks are stamped "VOID" to prevent reuse and filed for subsequent inspection.
A pay system is used to electronically inform the bank of all checks issued in order to prevent payment on forged checks or stolen check
stock. Access to the positive pay system is limited to the appropriate individuals who have been authorized by management.
Only managers can review, approve and code professional services and capital invoices for payment.
Purchase cost files are maintained and current. The company has a policy to only pay the purchase order price regardless of the price on
the invoice.
Source: www.knowledgeleader.com Page 14
PROCESS 5.2.1: PROCESS ACOUNTS PAYABLE RISK AND CONTROL MATRIX (RCM)
CONTROL DESCRIPTION
Non-budgeted items exceeding a certain limit set by the company are approved by the CFO.
The corporate controller reviews the Proposal for Payment Report and supporting documentations, including invoice and approval.
Accounts payable personnel review all checks with supporting documentations.
Accounts payable personnel review all aging reports monthly for credit balances or long outstanding items and resolve any issues.
Requests for manual/quick checks are signed/approved by supervisors.
Vendor names, prices and quantities from invoices are matched to receiving documents and purchase orders by an individual independent
of the purchasing and receiving functions. Discrepancies are resolved prior to processing.
Finance management reviews all check registers for appropriateness.
Non-budgeted items exceeding a certain limit set by the company are approved by the CFO.
For capital expenditures, the PO Request Form is reviewed, approved and signed by the department director and the department VP.
Documented cut-off and period-end closing procedures are adhered to.
User access is designed and configured to support the segregation of duties between procurement, receiving, invoice processing, payment
processing and the vendor master.
Payables are not offset against receivables unless first approved by management.
The treasury/cash manager coordinates with accounts payable as necessary for discounts.
Special discounts can be specified on an individual invoice basis.
The software/system automatically takes discounts as defined in the supplier master file for each individual invoice processed.
The disbursement process is automated to generate checks based on invoice payment due date and post the appropriate accounting
entries.
The company utilizes a vendor certification program and inspects incoming receipts in accordance with its plan.
Critical forms (e.g., check requests, adjustment forms and checks) are prenumbered and controlled. The system generates the next check
number, which must match the check number in the routing code at the bottom of the check.
Managers must review, approve and code professional services and capital invoices for payment.
Cost center managers are responsible for review of monthly costs.
The software/system systematically generates the journal entry upon completion of the payables check run.
The open voucher summary report within the system/software identifies open voucher amounts, due dates and required pay amounts by
vendor/to vendors. The system/software also provides a voucher aging report that gives management the ability to monitor the aging of
entered vouchers. Payment due dates are calculated based on the invoice date and the terms of the invoice. Upon performing the check
run process, payments are made for all vouchers due. Accounts payable management personnel monitor the system/software’s accounts
payable reports on a regular basis.
A formal policies and procedures document exists to guide the accounts payable process.
Policies and procedures are established to define approval limits and authorization requirements.
Source: www.knowledgeleader.com Page 15
PROCESS 5.2.1: PROCESS ACOUNTS PAYABLE RISK AND CONTROL MATRIX (RCM)
CONTROL DESCRIPTION
The company has a cash management policy which is clearly communicated to the accounts payable function. Such a policy is reflected in
the accounts payable system configuration.
Formal procedures exist that ensure that expenditures are approved before committing funds in accordance with management directives.
All contractual agreements are subject to corporate and/or legal review in accordance with local or corporate directives or guidance.
Procedures provide for review of purchase orders to ensure completeness of critical information necessary to execute purchases and
subsequent receipt and payment (e.g., vendor, prices, quantities, terms of payment, part numbers, descriptions, etc.).
Procedures provide for processing of original vendor invoices only. Payments are not processed from faxed copies of invoices or vendor
statements.
HOLDs (Account, Funds, Invoice, Matching, Variance) are utilized for non-matching invoices.
The concerned personnel prepare weekly, monthly and quarterly trend analyses on the volume and percentage of variances to monitor
processing integrity for continuous improvement.
Purchasing agents review an open purchase order listing on a regular basis.
The company has established tolerances for commodity purchases as appropriate. Receipts in excess of the tolerances may be returned
to the vendor.
Payment stubs detailing invoice payments, discounts taken and short pay are provided with the checks.
HOLDs (Account, Funds, Invoice, Matching, Variance) are utilized for non-matching invoices.
A tolerable limit above the purchase order per-unit cost is accepted to minimize minor cost variances (e.g., tax calculations). These items
are reviewed by management for appropriateness.
The treasury/cash management manager coordinates with accounts payable as necessary for discounts.
Special discounts can be specified on an individual invoice basis.
The software/system automatically takes discounts as defined in the supplier master file for each individual invoice processed.
A system link is set up for contra accounts to track payables and receivables associated with the same supplier.
Debit memos are logged in the software/system and associated with the appropriate supplier, allowing the software/system to show only
the net amount due to that supplier.
Tax data is captured at point of entry.
The system/software automatically assigns a unique vendor number based on the configuration of next numbers. It does not allow a
duplicate number to be assigned.
A designated accounts payable clerk reviews vendor transmittal requests and supporting documentation (e.g., business cards, invoices,
etc.) to determine the validity of the vendor. A designated clerk is authorized to create the vendor master record following the review for
validity. Following the creation of the vendor record, a vendor change report is generated and compared to the original transmittal by
another lead accounts payable clerk to ensure data accuracy. The vendor change report and original transmittal are maintained for periodic
review by a supervisor.
Source: www.knowledgeleader.com Page 16
PROCESS 5.2.1: PROCESS ACOUNTS PAYABLE RISK AND CONTROL MATRIX (RCM)
CONTROL DESCRIPTION
A vendor transmittal request is submitted by an authorized party to change the status of the vendor to HOLD. The authorized accounts
payable clerk facilitates the change in the system and notes the reason for the hold. The general accounting manager monitors and
approves vendor hold transactions.
The system/software requires a payment to be issued against a valid vendor/supplier within the system.
The company utilizes a vendor performance program which monitors product quantity, delivery performance, order quality and order fill
rates.
Accounts payable access to vendor master files is restricted to select data fields (address, phone, terms, etc.).
Federal tax ID numbers are required for all suppliers.
Duplicate federal tax ID numbers/vendors or supplier ID numbers are investigated by the accounts payable clerk.
When a new supplier is entered, the system/software performs a check against the existing supplier master to confirm that the new request
does not match a supplier already in the system. It will present an on-screen alert message if a duplicate is found.
The vendor listing is maintained in a vendor master file to ensure all vendors are valid vendors.
If the vendor is not included in the company’s vendor master file, then the accounts payable specialist fills out a New Vendor Form and
sends the New Vendor Form together with the invoice package to the accounting manager for review and approval.
The vendor master file is reviewed on an annual basis by the accounting manager to ensure only valid vendors are in active status.
All supplier information in the vendor master file is appropriately captured as per the laws/regulations, circulars, etc. of a specific region
(example: 1099 series reporting).
Suppliers are established within the software's system upon finalization of procurement procedures.
Standardized supplier setup forms with all required data fields are used.
The company has controls to account for all checks.
User access is designed and configured to support the segregation of duties between procurement, receiving, invoice processing, payment
processing and the vendor master.
A currency threshold is established for checks requiring two signatures (either two manual signatures or one manual signature and one
computer-generated signature).
The proper coding of invoices and automatic accounting instructions (AAIs) have been set up to automatically recognize the appropriate
accounts that are required for a specific batch transaction.
Checks are automatically prepared by computer based on the scheduled payment date entered when the voucher is processed.
All blank checks are kept in a locked drawer where only the accounting manager, assistant controller and controller have access.
Vouchers of physical invoices are matched with the check register.
All supplier payments (except petty cash disbursements) are processed through the software/system.
Source documentation (checks, vouchers, etc.) is perforated, voided or otherwise cancelled to prevent reuse.
The disbursement process is automated to generate checks based on invoice payment due date and post the appropriate accounting
entries.
The company has established tolerances for commodity purchases, as appropriate receipts in excess of the tolerances may be returned to
the vendor.
Source: www.knowledgeleader.com Page 17
PROCESS 5.2.1: PROCESS ACOUNTS PAYABLE RISK AND CONTROL MATRIX (RCM)
CONTROL DESCRIPTION
Critical forms (e.g., check requests, adjustment forms and checks) are prenumbered and controlled. The system generates the next check
number, which must match the check number in the routing code at the bottom of the check.
Trends in amounts and types of adjustments are periodically analyzed.
Purchase cost files are maintained and current. The company has a policy to only pay the purchase order price, regardless of the price on
the invoice.
Regular reporting, investigation, and follow-up on backlog of unprocessed vendor invoices, receiving reports, or rejected data is conducted.
All accounts payable-related documents are kept in a secure facility in the purchase manager's office.
All invoices received are maintained by the accounts payable group indefinitely (a certain number of years onsite followed by maintenance
in an offsite facility).
All vendor/supplier request forms are maintained after they have been entered into the system/software. Electronic versions are maintained
in the online facility and printed versions are maintained onsite by the corporate accounts payable group.
Receipt of a good or service is logged on the associated purchase order in the software/system, which is referenced at the time of payment
approval.
Management performs a review of accruals at month end and a checklist is signed off by the reviewer.
Corporate accountants email all applicable departments requesting support for all accruals or credits to be booked for the current month.
Accounts payable clerks regularly send out notifications to all accountants informing them of any invoices over $X that have not been
processed in accounts payable.
If there are any errors on the check, the check is voided and a new check is printed after the accounting manager’s, controller's, or
assistant controller's review and approval.
All blank checks are kept in a locked drawer where only the accounting manager, assistant controller and controller have access.
Electronic signatures/authorization stamps are appropriately secured.
Source documentation (checks, vouchers, etc.) is perforated, voided or otherwise cancelled to prevent reuse.
Purchase commitments are made on the basis of authorized requisitions from user departments, established contracts, established
inventory reorder points or work order material requirements.
The system automatically sorts invoices by their payment due date to ensure proper issuance by the accounts payable department.
Actual expenditures are compared to budget regularly; management reviews and approves significant variances.
Source: www.knowledgeleader.com Page 18
Вам также может понравиться
- Fraud Risk MДокумент11 страницFraud Risk MEka Septariana PuspaОценок пока нет
- Risk & Controls ToolkitДокумент15 страницRisk & Controls Toolkitvivekan_kumar90% (10)
- Sox GC Ac SpreadsheetcompressedДокумент92 страницыSox GC Ac SpreadsheetcompressedSaugat BoseОценок пока нет
- Control Testing Vs Substantive by CPA MADHAV BHANDARIДокумент59 страницControl Testing Vs Substantive by CPA MADHAV BHANDARIMacmilan Trevor JamuОценок пока нет
- The Audit Risk ModelДокумент3 страницыThe Audit Risk ModelShane LimОценок пока нет
- 2015 SOx Guidance FINAL PDFДокумент35 страниц2015 SOx Guidance FINAL PDFMiruna RaduОценок пока нет
- Entity Control Risk MatrixДокумент5 страницEntity Control Risk Matrixdonmarquez100% (1)
- 2023 Annual Plan Risk ManagementДокумент60 страниц2023 Annual Plan Risk ManagementCatherineОценок пока нет
- Segregation of Duties ReviewДокумент4 страницыSegregation of Duties ReviewManishОценок пока нет
- Audit Risk Assessment Best PracticeДокумент10 страницAudit Risk Assessment Best PracticeEmily MauricioОценок пока нет
- Working Papers - Top Tips PDFДокумент3 страницыWorking Papers - Top Tips PDFYus Ceballos100% (1)
- Internal Controls 101Документ25 страницInternal Controls 101Arcee Orcullo100% (1)
- Risk Rating The Audit UniverseДокумент10 страницRisk Rating The Audit UniverseTahir IqbalОценок пока нет
- Auditing Theory and Practice NotesДокумент187 страницAuditing Theory and Practice NotesMoyo Clifford100% (1)
- Developing A Risk Based Internal Audit PlanДокумент43 страницыDeveloping A Risk Based Internal Audit PlanOSAMA ABUSKAR100% (1)
- Internal Financial Controls WIRC 24062017Документ141 страницаInternal Financial Controls WIRC 24062017Ayush KishanОценок пока нет
- Understanding Internal Financial ControlsДокумент27 страницUnderstanding Internal Financial ControlsCODOMAIN100% (4)
- Control Risk MatrixДокумент7 страницControl Risk Matrixmuhammad andri lowe100% (1)
- I General: Internal Audit ChecklistДокумент33 страницыI General: Internal Audit ChecklistHimanshu GaurОценок пока нет
- Controls in Ordering & PurchasingДокумент32 страницыControls in Ordering & PurchasingGrazel CalubОценок пока нет
- Impact and Likelihood ScalesДокумент3 страницыImpact and Likelihood ScalesRhea SimoneОценок пока нет
- Anti-Money Laundering and Combating The Financing of TerrorismДокумент124 страницыAnti-Money Laundering and Combating The Financing of TerrorismLaurette M. BackerОценок пока нет
- Risk Control MatrixДокумент18 страницRisk Control MatrixRemi AboОценок пока нет
- PURCHASE-TO-PAYMENT PROCESS ASSESSMENT REVIEWДокумент36 страницPURCHASE-TO-PAYMENT PROCESS ASSESSMENT REVIEWviswaja100% (1)
- ITGC Guidance 2Документ15 страницITGC Guidance 2wggonzaga0% (1)
- Risk Control Matrix Template: Name ObjectiveДокумент3 страницыRisk Control Matrix Template: Name ObjectiveKyaw HtutОценок пока нет
- Entity-Level Risk Assessment WorksheetsДокумент26 страницEntity-Level Risk Assessment WorksheetsChinh Lê ĐìnhОценок пока нет
- Internal Control ConceptsДокумент14 страницInternal Control Conceptsmaleenda100% (1)
- 155289907A-133 Compliance Internal Control ToolДокумент43 страницы155289907A-133 Compliance Internal Control ToolrajsalgyanОценок пока нет
- ISA Audit Guide 2010-01Документ243 страницыISA Audit Guide 2010-01Victor JacintoОценок пока нет
- Record-to-Report Risk Control MatrixДокумент30 страницRecord-to-Report Risk Control MatrixAswath SОценок пока нет
- IT audit checklist reviews controlsДокумент11 страницIT audit checklist reviews controlsមនុស្សដែលខកចិត្ត ជាងគេលើលោក100% (1)
- Information Technology General Controls LeafletДокумент2 страницыInformation Technology General Controls LeafletgamallofОценок пока нет
- Fund TransfersДокумент32 страницыFund TransfersvangieОценок пока нет
- SOX Activity FlowchartДокумент3 страницыSOX Activity Flowchartnarasi64100% (1)
- Internal Audit Training SyllabusДокумент2 страницыInternal Audit Training SyllabusIndra Permana SuhermanОценок пока нет
- Rbi A ManualДокумент344 страницыRbi A ManualAlexandru VasileОценок пока нет
- IIIB RICE Digital Audit ProgramsFromAuditNetДокумент100 страницIIIB RICE Digital Audit ProgramsFromAuditNetspicychaitu0% (1)
- At.01 Fundamentals of Assurance and Non Assurance EngagementsДокумент3 страницыAt.01 Fundamentals of Assurance and Non Assurance EngagementsAngelica Sanchez de VeraОценок пока нет
- IT Risk and Control FrameworkДокумент25 страницIT Risk and Control FrameworkAdityaNugrahaОценок пока нет
- Risk ControlДокумент7 страницRisk ControlDinesh AravindhОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4: Revenue CycleДокумент12 страницChapter 4: Revenue CycleCyrene CruzОценок пока нет
- CPF Annual Report 2020Документ22 страницыCPF Annual Report 2020AlioОценок пока нет
- Segregation of Duties Framework OverviewДокумент2 страницыSegregation of Duties Framework OverviewChinh Lê ĐìnhОценок пока нет
- SOX OverviewДокумент29 страницSOX Overviewnarasi64100% (2)
- Draft RCM - ExpensesДокумент9 страницDraft RCM - ExpensesAbhishek Agrawal100% (1)
- 2018 Internal Audit CharterДокумент4 страницы2018 Internal Audit CharterAlezNg100% (1)
- Purchasing Payables ControlДокумент9 страницPurchasing Payables ControljenjenheartsdanОценок пока нет
- Handbook - On - Professional - Opportunities in Internal AuditДокумент278 страницHandbook - On - Professional - Opportunities in Internal Auditahmed raoufОценок пока нет
- True & FalseДокумент13 страницTrue & FalseYasir Ali Gillani100% (2)
- Steam AppidДокумент38 страницSteam AppidMikey Chua67% (3)
- Internal Controls Guidance - Audit and Compliance ServicesДокумент15 страницInternal Controls Guidance - Audit and Compliance Servicestunlinoo.067433Оценок пока нет
- Risk Register FormatДокумент24 страницыRisk Register FormatShyam_Nair_9667Оценок пока нет
- It Audit Risk MatrixДокумент16 страницIt Audit Risk MatrixChinh Lê ĐìnhОценок пока нет
- Taxation Risk Control MatrixДокумент2 страницыTaxation Risk Control MatrixMitchell ShermanОценок пока нет
- Audit Universe and Risk Assessment ToolДокумент10 страницAudit Universe and Risk Assessment ToolAsis KoiralaОценок пока нет
- Uwex Internal Controls Plan 20102Документ89 страницUwex Internal Controls Plan 20102Deasy Nursyafira SariОценок пока нет
- Test of Controls For Some Major ActivitiesДокумент22 страницыTest of Controls For Some Major ActivitiesMohsin RazaОценок пока нет
- Business Risk Assessment - ERM ProcessДокумент26 страницBusiness Risk Assessment - ERM ProcesscarwadevilisbackОценок пока нет
- Financial Controls Closing ProcessДокумент16 страницFinancial Controls Closing Processvikrant durejaОценок пока нет
- E7 - TreasuryRCM TemplateДокумент30 страницE7 - TreasuryRCM Templatenazriya nasarОценок пока нет
- Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX) Project Approach MemoДокумент8 страницSarbanes-Oxley (SOX) Project Approach MemoManna MahadiОценок пока нет
- Interim IT SOX 2018 Preliminary FindingДокумент2 страницыInterim IT SOX 2018 Preliminary FindingT. LyОценок пока нет
- RiskMgt PolicyДокумент10 страницRiskMgt PolicyNeoОценок пока нет
- Information and Communication Audit Work ProgramДокумент4 страницыInformation and Communication Audit Work ProgramLawrence MaretlwaОценок пока нет
- Prevention of SpoilageДокумент1 страницаPrevention of SpoilagePlanco RosanaОценок пока нет
- Inventory Observation MemoДокумент5 страницInventory Observation MemoPlanco RosanaОценок пока нет
- Inventory Observation MemoДокумент5 страницInventory Observation MemoPlanco RosanaОценок пока нет
- Atsilab Form Meeting NoticeДокумент1 страницаAtsilab Form Meeting NoticeAneez AbdulJaleelОценок пока нет
- Inventory Control SpoilageДокумент63 страницыInventory Control SpoilagePlanco RosanaОценок пока нет
- Atsilab Form Meeting NoticeДокумент1 страницаAtsilab Form Meeting NoticeAneez AbdulJaleelОценок пока нет
- GuidelinesДокумент1 страницаGuidelinesPlanco RosanaОценок пока нет
- GuidelinesДокумент1 страницаGuidelinesPlanco RosanaОценок пока нет
- DistributionДокумент2 страницыDistributionPlanco RosanaОценок пока нет
- Sales and Receipts CycleДокумент52 страницыSales and Receipts Cyclejossiah13Оценок пока нет
- GuidelinesДокумент1 страницаGuidelinesPlanco RosanaОценок пока нет
- Audiying TheoryДокумент2 страницыAudiying TheoryPlanco RosanaОценок пока нет
- Audit Report Cash SalesДокумент30 страницAudit Report Cash SalesPlanco RosanaОценок пока нет
- Auditing Theory Key Concepts ExplainedДокумент12 страницAuditing Theory Key Concepts ExplainedKevin Ryan EscobarОценок пока нет
- Finacle Command - TM For Transaction Maintainance Part - I - Finacle Commands - Finacle Wiki, Finacle Tutorial & Finacle Training For BankersДокумент4 страницыFinacle Command - TM For Transaction Maintainance Part - I - Finacle Commands - Finacle Wiki, Finacle Tutorial & Finacle Training For BankersShubham PathakОценок пока нет
- Ankit Gautam ResumeДокумент3 страницыAnkit Gautam ResumeK.d. GargОценок пока нет
- Internal Halal Auditing Documents and MaДокумент20 страницInternal Halal Auditing Documents and Maquality wyzeОценок пока нет
- PTB Annual Report 2020Документ74 страницыPTB Annual Report 2020lurjnoaОценок пока нет
- Exact Globe UserGuide On FinancialsДокумент188 страницExact Globe UserGuide On Financialsaluaman100% (9)
- Illustrative Problem Worksheet AДокумент6 страницIllustrative Problem Worksheet AJoy SantosОценок пока нет
- Auditing-Unit 3-VouchingДокумент12 страницAuditing-Unit 3-VouchingAnitha RОценок пока нет
- CEO CFO COO Vice President in Canada Resume Kenneth TanДокумент3 страницыCEO CFO COO Vice President in Canada Resume Kenneth TanKennethTan2Оценок пока нет
- Red Book & Internal Auditing: Presented By: Maxene M. Bardwell, CPA, CIA, CFE, CISA, CIGA, CITP, CrmaДокумент78 страницRed Book & Internal Auditing: Presented By: Maxene M. Bardwell, CPA, CIA, CFE, CISA, CIGA, CITP, CrmaАндрей МиксоновОценок пока нет
- Advanced M AДокумент276 страницAdvanced M ADark PrincessОценок пока нет
- Sofi XP - Daftar IsiДокумент4 страницыSofi XP - Daftar IsiRobin GohОценок пока нет
- Accounting Changes in The Public Sector in EstoniaДокумент10 страницAccounting Changes in The Public Sector in EstoniaMohammad AlfianОценок пока нет
- Tax Deductions GuideДокумент14 страницTax Deductions GuideJEPZ LEDUNAОценок пока нет
- Intacc 1Документ17 страницIntacc 1Xyza Faye RegaladoОценок пока нет
- Presentation of COGS COST PratikshaДокумент16 страницPresentation of COGS COST PratikshasonalliОценок пока нет
- NSDL IAR New FormatДокумент20 страницNSDL IAR New FormatMansoor Ahmed Siddiqui0% (1)
- Fuje 1990Документ5 страницFuje 1990ibrahimОценок пока нет
- Portfolio Management Association of Canada: Reference Guide To Policies and Procedures For Portfolio ManagersДокумент20 страницPortfolio Management Association of Canada: Reference Guide To Policies and Procedures For Portfolio ManagersShaibyaОценок пока нет
- Corrective Action Report (Car) : Safety & Quality DirectorateДокумент26 страницCorrective Action Report (Car) : Safety & Quality DirectorateNAI HmamiОценок пока нет
- Steven Lim & Associates ProfileДокумент6 страницSteven Lim & Associates ProfileReika KuaОценок пока нет
- Assessment - FNSACC606Документ25 страницAssessment - FNSACC606tunhaОценок пока нет
- RSHBBA207171022215134Документ25 страницRSHBBA207171022215134Suraj MishraОценок пока нет
- Ca Inter NotesДокумент5 страницCa Inter NotesAjay RajputОценок пока нет