Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Fuel and Combustion
Загружено:
Bhadz BositoИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Fuel and Combustion
Загружено:
Bhadz BositoАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
19/07/2017
FUELS and COMBUSTION 2. Liquid fuels
- a mixture of numerous
Fuel
hydrocarbons and are obtained from
-any material that can be burned to release thermal
crude oil by distillation.
energy.
-in all fuels the two basic combustible elements are
carbon and hydrogen.
Classification of Fuel 3. Gaseous Fuels
1. Solid Fuels -As natural gas, oil derivatives (LPG),
- Are coal, chiefly anthracite and coke. acetylene, manufacture gas (from coal
-Coal contains varying amounts of oxygen, hydrogen, or oil residue) and biogas (from manure
nitrogen, sulfur, moisture, and ash. or sewage).
Analysis of Coal Basis of Reporting Analysis
1. Proximate Analysis - The Bureau of Mines reports coal in the following
- Determines the percentage of moisture, volatile matter, manner:
fixed carbon, and ash.
- In some cases the percentage of sulfur is also obtained. 1. As Received or As Fired
2. Dry or Moisture Free
3. Moisture and Ash Free or Combustible
2. Ultimate Analysis
4. Moisture, Ash, and Sulfur Free
- ultimate analysis divides all the remaining part of the coal into
the elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, sulfur, and nitrogen in
percentages by weight.
- The ash content of the coal is independent of the type of analysis
and is therefore the same for both.
19/07/2017
Sample Problem
1. Convert the proximate analysis of Cherokee County, Kansas coal given in
Table 5-1 to (a.) dry and (b.) to moisture and ash free. Composition of Fuels
-in all fuels the two combustible elements are carbon and
Proximate analysis of coal: (as fired) hydrogen, encountered either separately or in combinations
Moisture = 5.09% called hydrocarbons.
Volatile Matter = 34.47% - The general formula for all hydrocarbons is CnHm.
Fixed Carbon = 52.48%
Ash = 7.96%
2. Convert the ultimate analysis of Cherokee County, Kansas coal given in Table
5-1 to (a.) dry (b.) to moisture and ash free (c.) to moisture, ash, and sulfur free
bases.
Ultimate analysis of coal:
Carbon = 71.81% Sulfur = 3.34% Moisture = 5.09%
Hydrogen = 4.67% Nitrogen = 1.20%
Oxygen = 5.62% Ash = 8.27%
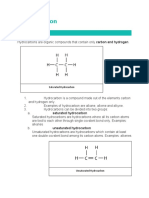
2. Alkenes or Olefins (CnH2n)
Types of Hydrocarbons -Chainlike hydrocarbons with double bonds
1. Alkanes or Paraffin (CnH2n+2)
- Chainlike hydrocarbons with purely single bonds
3. Alkines or Acetylenes (CnH2n-2)
-Chainlike hydrocarbons with one triple bond
Note: Hydrocarbons with chainlike structures are
Aliphatic hydrocarbon compounds
19/07/2017
4. Cyclo-alkanes or Naphthenes (CnH2n)
-hydrocarbons with circular structures and purely single bonds
Note: Hydrocarbons with open
chain structures are Alicyclic
hydrocarbon compounds
5. Aromatics
- hydrocarbons with circular structures and double bonds
Combustion
6. Alcohol
-is a chemical reaction in which certain elements of the fuel
-Alcohol are similar to paraffins with one of the hydrogen
combine with oxygen causing an increase n temperature of
atoms replaced with hydroxyl radical OH.
the gases.
Reactants Products
Fuel + Oxidizer Products
19/07/2017
Balancing Chemical Equations 1. Methane (CH ) is burned with stoichiometric amount of
4
-Chemical equations are balanced on the basis of the air during a combustion process. Assuming complete
conservation of mass principle, which states that the total mass combustion, determine the air–fuel and fuel–air ratios.
of each element is conserved during a chemical reaction.
2. Propane fuel (C H ) is burned in the presence of air.
3 8
Assuming that the combustion is theoretical—that is,
1 only nitrogen (N2), water vapor (H2O), and carbon
O2 + H2 → H2O dioxide (CO2) are present in the products—determine
2
(a) the mass fraction of carbon dioxide and (b) the mole
and mass fractions of the water vapor in the products.
3. Octane (C H ) is burned with dry air. The volumetric analysis
8 18
of the products on a dry basis is 9.21 percent CO , 0.61 2
percent CO, 7.06 percent O , and 83.12 percent N . Determine
2 2
(a) the air-fuel ratio and (b) the percentage of theoretical air
used.
4. A coal from Illinois which has an ultimate analysis (by mass)
as 67.40 percent C, 5.31 percent H , 15.11 percent O , 1.44
2 2
percent N , 2.36 percent S, and 8.38 percent ash (non-
2
combustibles) is burned with 40 percent excess air. Calculate
the mass of air required per unit mass of coal burned and the
apparent molecular weight of the product gas neglecting the ash
constituent.
Вам также может понравиться
- Combustion of FuelsДокумент6 страницCombustion of FuelsRobby Royce Casida100% (1)
- Alkanes Lecture Notes PDFДокумент23 страницыAlkanes Lecture Notes PDFPrivate AccountОценок пока нет
- FrukДокумент33 страницыFrukdaney67299Оценок пока нет
- Worksheet IGCSE Match Key Words and Definition For Revision 4Документ2 страницыWorksheet IGCSE Match Key Words and Definition For Revision 4oscarbec0% (1)
- HydrocarbonsДокумент7 страницHydrocarbonsMariella MarianoОценок пока нет
- Four Classes of HydrocarbonsДокумент4 страницыFour Classes of HydrocarbonsFaller, Fiona Luie C.Оценок пока нет
- Fuel Combustion RkrajputДокумент34 страницыFuel Combustion Rkrajputsunita.storage01Оценок пока нет
- 6 184623437Документ24 страницы6 184623437Dr.Srinivasa Rao K.V.NОценок пока нет
- Hydrocarbons - Types, Classification, Properties, Preparation, UsesДокумент1 страницаHydrocarbons - Types, Classification, Properties, Preparation, Usesjaindhruv850Оценок пока нет
- 5 - B Main Constituents of PetrДокумент25 страниц5 - B Main Constituents of PetrBogdanAlin100% (1)
- Fuels and Combustion ClassificationДокумент35 страницFuels and Combustion ClassificationAlbert Bancolita100% (1)
- Q2 - Hydrocarbons and Functional GroupsДокумент54 страницыQ2 - Hydrocarbons and Functional GroupsTosee istosee100% (1)
- Chapter2 CarboncompoundДокумент76 страницChapter2 CarboncompoundWENJINGОценок пока нет
- Organic ChemДокумент15 страницOrganic ChemasjfkdОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ15 страницChapter 2vinОценок пока нет
- Organic Chemistry: Fuels and Crude Oil Hydrocarbons Alcohols Organic AcidsДокумент48 страницOrganic Chemistry: Fuels and Crude Oil Hydrocarbons Alcohols Organic AcidsGideon CavidaОценок пока нет
- G9 - Ch8 - Alkanes-1Документ17 страницG9 - Ch8 - Alkanes-1hamza arroubОценок пока нет
- 6.1 Types of Fuels - 4 MarksДокумент17 страниц6.1 Types of Fuels - 4 Marksaditya yadavОценок пока нет
- ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - Tr. BДокумент47 страницORGANIC CHEMISTRY - Tr. BChishala IsaacОценок пока нет
- 3 Chapter Three Hydrocarbons and ClassificationsДокумент48 страниц3 Chapter Three Hydrocarbons and ClassificationsMohamed AbdelaalОценок пока нет
- Cha 6 and 7Документ37 страницCha 6 and 7beila.amu.22Оценок пока нет
- 10.chemzone - Organic CompoundsДокумент16 страниц10.chemzone - Organic Compoundssincerely reverieОценок пока нет
- General Chemistry: 1 Semester - Petroleum Engineering Koya University 2021 - 2022 Hawar J. Sadiq HawezyДокумент41 страницаGeneral Chemistry: 1 Semester - Petroleum Engineering Koya University 2021 - 2022 Hawar J. Sadiq HawezyZana NajatОценок пока нет
- Organic Compounds IntroductionДокумент40 страницOrganic Compounds IntroductionShanice LangamanОценок пока нет
- IGCSE (v.15) Organic ChemistryДокумент36 страницIGCSE (v.15) Organic ChemistryBruce CourtinОценок пока нет
- Hydrocarbons, Alcohols, Phenols - Written Report - SolidumДокумент13 страницHydrocarbons, Alcohols, Phenols - Written Report - SolidumAva Mae SolidumОценок пока нет
- Organic: ChemistryДокумент16 страницOrganic: ChemistryroythomascОценок пока нет
- HYDROCARBONS Module3Документ22 страницыHYDROCARBONS Module3Mugara Waitega PeterОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Form-Four (Chapters Summery of Questions With Answers)Документ13 страницChemistry Form-Four (Chapters Summery of Questions With Answers)Mohamed Abuukar AbdukadirОценок пока нет
- Organic Compounds and Functional GroupsДокумент38 страницOrganic Compounds and Functional GroupsEunice AnogОценок пока нет
- Ogranic Chemistry (FULL NOTES) - 1Документ11 страницOgranic Chemistry (FULL NOTES) - 1Ali NyallОценок пока нет
- 1 Organic Compounds HydrocarbonsДокумент29 страниц1 Organic Compounds HydrocarbonsatОценок пока нет
- Che Calc 2 Unit 1 PDFДокумент31 страницаChe Calc 2 Unit 1 PDFJerico Hercules MutiaОценок пока нет
- Carbon Compounds: Homologous Series, Alkanes and AlkenesДокумент22 страницыCarbon Compounds: Homologous Series, Alkanes and Alkenesdr lailaОценок пока нет
- IC Engine FuelДокумент116 страницIC Engine FueluchihaenomiОценок пока нет
- UNIT 13 Hydrocarbons For More Visit HTTP://WWW - Ncert.nic - In/textbooks/testing/index - HTMДокумент33 страницыUNIT 13 Hydrocarbons For More Visit HTTP://WWW - Ncert.nic - In/textbooks/testing/index - HTMArun Kumar100% (1)
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryДокумент13 страницIntroduction To Organic ChemistryDahyun KimОценок пока нет
- Intro To Organic Chemistry 2Документ16 страницIntro To Organic Chemistry 2Sunshine Gura RomoОценок пока нет
- Lecture 6 - CombustionДокумент18 страницLecture 6 - CombustionPride PuleОценок пока нет
- 1 Intro AlkanesДокумент8 страниц1 Intro Alkanesc21-0403-639Оценок пока нет
- Kech206 PDFДокумент33 страницыKech206 PDFNeeraj Kumar Neeraj KumarОценок пока нет
- INTRODUCTION_TO_ORGANIC_CHEMISTRYДокумент2 страницыINTRODUCTION_TO_ORGANIC_CHEMISTRYmwashingweleyolanta7Оценок пока нет
- Hydrocarbon Types and PropertiesДокумент5 страницHydrocarbon Types and PropertiesMaxwell RipinОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ32 страницыChapter 2alicia sambaiОценок пока нет
- Carbon CompoundДокумент48 страницCarbon CompoundIlakiya Sharvinee KumarОценок пока нет
- Carbon CompoundsДокумент5 страницCarbon Compoundsmonteboncomshop01Оценок пока нет
- Hydrocarbons: Structures, Naming, and Isomers/TITLEДокумент33 страницыHydrocarbons: Structures, Naming, and Isomers/TITLEGomtesh GandhiОценок пока нет
- Organic Chemistry 2Документ3 страницыOrganic Chemistry 266rdsmh2mwОценок пока нет
- Science 9 4th QTRДокумент3 страницыScience 9 4th QTRClyde Owain Rocafort VidalОценок пока нет
- Non-Aromatic vs Aromatic HydrocarbonsДокумент15 страницNon-Aromatic vs Aromatic Hydrocarbonssisi slayОценок пока нет
- AlkenesДокумент4 страницыAlkenestsdwfps68nОценок пока нет
- Reviewer Chem Finals Print1Документ13 страницReviewer Chem Finals Print1rhymeОценок пока нет
- The Role of Gas Chromatography in Compositional Analyses in The Petroleum Industry PDFДокумент16 страницThe Role of Gas Chromatography in Compositional Analyses in The Petroleum Industry PDFPiyush SinhaОценок пока нет
- Organic Chemistry PDFДокумент40 страницOrganic Chemistry PDFMax SinghОценок пока нет
- Chapter 12 Saturated HydrocarbonsДокумент17 страницChapter 12 Saturated HydrocarbonsChristian Guimmayen ArizoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Carbon CompoundДокумент38 страницChapter 2 Carbon CompoundHING LEE NA MoeОценок пока нет
- Annual Reports in Organic Synthesis — 1971От EverandAnnual Reports in Organic Synthesis — 1971John McMurryОценок пока нет
- Annual Reports in Organic Synthesis — 1970От EverandAnnual Reports in Organic Synthesis — 1970John McMurryОценок пока нет
- Annual Reports in Organic Synthesis — 1987От EverandAnnual Reports in Organic Synthesis — 1987Eric F. V. ScrivenОценок пока нет
- Annual Reports in Organic Synthesis-1973От EverandAnnual Reports in Organic Synthesis-1973R. Bryan MillerОценок пока нет
- Novena Prayer to St Jude for HelpДокумент2 страницыNovena Prayer to St Jude for HelpBhadz BositoОценок пока нет
- Tables RefДокумент75 страницTables RefBhadz BositoОценок пока нет
- Heat Treatment DFNTДокумент1 страницаHeat Treatment DFNTEnkie PaladanОценок пока нет
- And CBNДокумент1 страницаAnd CBNBhadz BositoОценок пока нет
- LAB Find Out The Bottle ContentsДокумент4 страницыLAB Find Out The Bottle ContentschanОценок пока нет
- Word Equation PracticeДокумент20 страницWord Equation PracticePrimoОценок пока нет
- Sulfide: DR 900 Analytical ProcedureДокумент4 страницыSulfide: DR 900 Analytical Procedurewulalan wulanОценок пока нет
- Chemistry: Pearson Edexcel International Advanced LevelДокумент32 страницыChemistry: Pearson Edexcel International Advanced LevelRose RamisaОценок пока нет
- CRU Group - Global Sulphur Market OutlookДокумент22 страницыCRU Group - Global Sulphur Market OutlookHvalbye Capital MarketsОценок пока нет
- DynamicДокумент34 страницыDynamicCentral HydraulicsОценок пока нет
- Chemical Engineering Calculations Problem SetДокумент4 страницыChemical Engineering Calculations Problem SetLizvel Keith TorresОценок пока нет
- 415 Chapter 1 - Final PDFДокумент25 страниц415 Chapter 1 - Final PDFFelipe FonsecaОценок пока нет
- Science Bowl Organic Chemistry NotesДокумент44 страницыScience Bowl Organic Chemistry Notestaosat11Оценок пока нет
- 14) Coordination Chemistry PDFДокумент28 страниц14) Coordination Chemistry PDFBj Larracas100% (6)
- Serpentinite: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaДокумент19 страницSerpentinite: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopedialeniucvasileОценок пока нет
- Subject Knowledge Tests: Pre-16 ChemistryДокумент10 страницSubject Knowledge Tests: Pre-16 ChemistryPolEak ZincMelodicОценок пока нет
- Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers (CBSE)Документ25 страницAlcohols, Phenols and Ethers (CBSE)Vishu Bansal100% (1)
- Recipes For SoapsДокумент396 страницRecipes For SoapsYannis Pentsios100% (1)
- Aldehydes Ketones, Carboxylic AcidsДокумент11 страницAldehydes Ketones, Carboxylic AcidsAssishОценок пока нет
- Titration Calculations ConcentrationsДокумент1 страницаTitration Calculations ConcentrationsRaymond ScottОценок пока нет
- Waterproof: Seccosolv® Dried Solvents Seccosept® Closure SystemДокумент6 страницWaterproof: Seccosolv® Dried Solvents Seccosept® Closure Systemdaniela ratuleaОценок пока нет
- Ascotran H 14 (Anti Flash Rust)Документ1 страницаAscotran H 14 (Anti Flash Rust)Yến HoàngОценок пока нет
- IA Planning DocumentДокумент3 страницыIA Planning DocumentGeorgie HancockОценок пока нет
- Chemical Bonding (Quick Recap)Документ9 страницChemical Bonding (Quick Recap)Anant JainОценок пока нет
- Eumann 2012Документ10 страницEumann 2012Kike PadillaОценок пока нет
- Zmoq : Narjmwu H$Mos H$Mo Cîma NWPÑVH$M Ho$ - Wi N Ð Na Adí' (Bio & Amob ZДокумент19 страницZmoq : Narjmwu H$Mos H$Mo Cîma NWPÑVH$M Ho$ - Wi N Ð Na Adí' (Bio & Amob ZRavneet KaurОценок пока нет
- Qualitative Analysis of Cations PDFДокумент28 страницQualitative Analysis of Cations PDFJerneth Nyka FloresОценок пока нет
- Cement Hydration Inhibition With SucroseДокумент8 страницCement Hydration Inhibition With SucroseJaq Plin PlinОценок пока нет
- Autumn 2 Y8 Pathway XДокумент47 страницAutumn 2 Y8 Pathway XH ChowdreyОценок пока нет
- 7829 PDFДокумент13 страниц7829 PDFDiogomussumОценок пока нет
- 2013 Capline Crude Oil Assay ReportДокумент4 страницы2013 Capline Crude Oil Assay Reportkwing175Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 10 S Block Elements NCERT Class 11 SolutionsДокумент20 страницChapter 10 S Block Elements NCERT Class 11 SolutionsZagreus OfficialОценок пока нет
- Metathesis ReactionsДокумент11 страницMetathesis Reactionsfranciscrick69Оценок пока нет
- Chap03 CarbonylsДокумент10 страницChap03 CarbonylsAPLCTNОценок пока нет