Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Parts of Speech: ST ND RD
Загружено:
Nasimah CapalОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Parts of Speech: ST ND RD
Загружено:
Nasimah CapalАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
PARTS OF SPEECH
Parts of speech is used to describe the mechanism of the language, in other words, the grammar which is defined as the art of speaking and writing the
language correctly according to the rules in general.
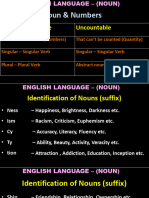
NOUN – name of person, animal, place, events, things, or ideas.
Example: lawyer, teacher, province, table, New Year, freedom
Kinds of Nouns
1. Proper Nouns – are specific and written in capital letter. 4. Mass Nouns – cannot be counted.
2. Common Nouns – are general. 5. Concrete Nouns – exist in the physical world.
3. Collective Nouns – name groups. 6. Abstract Nouns – refer to ideas and feelings.
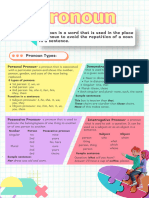
PRONOUNS – is a substitute for nouns.
Kinds of Pronouns
1. Demonstrative Pronouns (this, these, that, those)
2. Indefinite Pronouns
*Singular: any, anybody, anyone, nobody, no one, anything, each, everyone, one, someone, somebody, every, either, neither, everything
*Plural: all, some, few, both, several, many, none
3. Interrogative Pronouns (who, which, what, whom, whose, whoever, whomever)
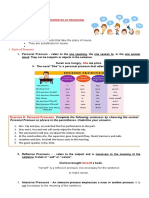
4. Personal Pronouns
NOMINATIVE CASE OBJECTIVE CASE POSSESSIVE CASE
SINGULAR
1ST person I Me My, mine
2nd person You You Your, yours *First person – refers to the speaker.
3rd person He, she, it Him, her, it His, her, hers *Second person – refers to the person spoken to.
PLURAL *Third person – refers to the person/s spoken about.
1ST person We Us Our, ours
2nd person You You Your, yours
3rd person they them Their, theirs
VERB – expresses action or state of being.
Kinds of Verbs
1. Regular Verb – form their past tense by addition of d or ed to the base form.
2. Irregular Verb – form their past tense and past participle in several ways.
3. Linking Verbs – are used to link or join the subject with a word in the predicate which relates to the subject. The be form of the verb (am, is, are,
was, were) is the most commonly used linking verb. Others are the verbs of the senses: become, seem, look, smell, appear, feel, taste, sound, remain.
ADJECTIVES – are words that describe, limit or modify nouns and pronouns. Adjectives answer the questions “Which one?”, “What kind?”, and “How many?”.
Kinds of Adjective
1. Indefinite Adjective – some, many, much, several, few, a few, a great deal of little, a little
2. Numerals – one, two, three, etc. cardinal numbers
3. Descriptive Adjectives – new, tall, blue, charming, etc.
4. Proper Adjectives – Filipino flag, English language, Persian carpet, etc.
5. Nouns that modify nouns
6. Phrases and clauses that modify nouns
7. A clause modifying a noun is usually introduced by a relative pronoun – that, which, whom, whose, where
ADVERB – an adverb modifies a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. Adverbs answer the questions “How?”, “Where?”, “When?”, “How often?”, and “To what
degree?”.
Kinds of Adverb
1. Adverb of manner (how) 4. Adverb of frequency (how often)
2. Adverb of time (when) 5. Adverb of negation or affirmation
3. Adverb of place (where)
CONJUNCTIONS – connect words or groups of words.
PREPOSITIONS – shows the relation between a word and a noun or pronoun that follows. It indicates:
a. Place and position – at, in, across, above, below, between, behind, beyond
b. Direction and motion – in, towards, out, about, around, through, by, down, over
c. Time – at, before, after, during, since, until
INTERJECTION – expresses emotion, acts as a signal, or adds a conversational touch. It usually ends with an exclamation point.
Вам также может понравиться
- The Birds and Bees of Words: A Guide to the Most Common Errors in Usage, Spelling, and GrammarОт EverandThe Birds and Bees of Words: A Guide to the Most Common Errors in Usage, Spelling, and GrammarРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Parts of Speech: By: Tiyas Saputri, S.S., M.PDДокумент42 страницыParts of Speech: By: Tiyas Saputri, S.S., M.PDFirda JinanОценок пока нет
- Parts of Speech: By: Tiyas Saputri, S.S., M.PDДокумент41 страницаParts of Speech: By: Tiyas Saputri, S.S., M.PDDenna Refnaldi SatryaОценок пока нет
- English: 1. Concrete Noun - Noun That CanДокумент4 страницыEnglish: 1. Concrete Noun - Noun That CanIrish VillanuevaОценок пока нет
- Gen Ed Eng-LessonДокумент11 страницGen Ed Eng-LessonEciram Yusi MacabantiОценок пока нет
- Parts of The SpeechДокумент7 страницParts of The SpeechJessica MereyОценок пока нет
- Yellow Booklet - Revised 2013 PDFДокумент42 страницыYellow Booklet - Revised 2013 PDFBabak EbrahimiОценок пока нет
- English BookДокумент100 страницEnglish BookchaostheoristОценок пока нет
- English CET Review NotesДокумент1 страницаEnglish CET Review NotesIzelwyn DaguioОценок пока нет
- Pronouns Lesson PlanДокумент2 страницыPronouns Lesson PlanAshford Thom100% (1)
- G - 11 GRAMMAR (Complete)Документ10 страницG - 11 GRAMMAR (Complete)abdullahharoonabbasi13Оценок пока нет
- Day 3 - General EducationДокумент33 страницыDay 3 - General EducationJessamen TinoОценок пока нет
- Teaching and Assessment of Grammar Midterm CoverageДокумент4 страницыTeaching and Assessment of Grammar Midterm CoverageRoselyn AlbisoОценок пока нет
- Grammar G - 9 - 12Документ18 страницGrammar G - 9 - 12DreadОценок пока нет
- Grammar Elfrida BakaraДокумент34 страницыGrammar Elfrida BakaraLesbra SandyОценок пока нет
- Hers, It, Its, They, Them, Their, Theirs.: Table of Personal PronounsДокумент5 страницHers, It, Its, They, Them, Their, Theirs.: Table of Personal PronounsWolfo ChicoОценок пока нет
- ELE123 Structure of English LessonsДокумент110 страницELE123 Structure of English LessonsRain Raven Barlizo LabanzaОценок пока нет
- Eight Parts of SpeechДокумент24 страницыEight Parts of SpeechDara (Vine)Оценок пока нет
- Module 1Документ14 страницModule 1Estrella RetiroОценок пока нет
- Grammar Erisa Newati SihombingДокумент38 страницGrammar Erisa Newati SihombingLesbra SandyОценок пока нет
- Module 1 - Understanding The Nature of Technical Writing: Basic Grammar Elements NounsДокумент7 страницModule 1 - Understanding The Nature of Technical Writing: Basic Grammar Elements NounsDarryl PagalanОценок пока нет
- GEN - ED.ENG-FOR CS - HandoutДокумент6 страницGEN - ED.ENG-FOR CS - HandoutJochelle Mae SucuanoОценок пока нет
- Eng Plus - Parts of SpeechДокумент25 страницEng Plus - Parts of SpeechJia DagandanОценок пока нет
- English Formal Grammar (Part of Speech)Документ24 страницыEnglish Formal Grammar (Part of Speech)Hasna Wafia MumtaziaОценок пока нет
- CursuriДокумент6 страницCursuriBlendea EmiliaОценок пока нет
- 1 3 5 6.mastering Advanced English LanguageДокумент21 страница1 3 5 6.mastering Advanced English LanguageAnnapia Giuffrida67% (3)
- English Language: Semester 2Документ63 страницыEnglish Language: Semester 2lelanieОценок пока нет
- Makalah Semantics (Language in Use)Документ11 страницMakalah Semantics (Language in Use)SariiiОценок пока нет
- Pronouns 1Документ2 страницыPronouns 1SMbunnyleeОценок пока нет
- English Assignment 1Документ9 страницEnglish Assignment 1ha khanОценок пока нет
- BY Honey Beth D. Atis, Edd, Ht-IДокумент40 страницBY Honey Beth D. Atis, Edd, Ht-IGreta SuОценок пока нет
- Pronouns - Basic NotesДокумент4 страницыPronouns - Basic NotesFrancis Guerrero TimbalОценок пока нет
- Grammatical-Categories 2.5Документ12 страницGrammatical-Categories 2.5arl somarОценок пока нет
- Pronouns and Verb Latest New 1647056114519Документ102 страницыPronouns and Verb Latest New 1647056114519vivek singhОценок пока нет
- Grammar Complete NotesДокумент34 страницыGrammar Complete Notesfarhad.mr37100% (1)
- 2 Facing Challenges: "SMOOTH Sea Does Not Make A SKILFULL Sailor"Документ27 страниц2 Facing Challenges: "SMOOTH Sea Does Not Make A SKILFULL Sailor"Nadeesha LankadhikaraОценок пока нет
- LecturesДокумент7 страницLecturesNimrod CabreraОценок пока нет
- LECTURESДокумент7 страницLECTURESNimrod CabreraОценок пока нет
- PronounДокумент25 страницPronounJolina VelascoОценок пока нет
- Elements of GrammarДокумент4 страницыElements of GrammarDorothy Biag VallenteОценок пока нет
- English GrammarДокумент17 страницEnglish GrammarsaleemОценок пока нет
- Types of Pronoun: TheyДокумент3 страницыTypes of Pronoun: TheyMr. AK RajОценок пока нет
- Week 1 - HandoutДокумент49 страницWeek 1 - Handoutvima tista putrianaОценок пока нет
- Generic Things.: SentencesДокумент8 страницGeneric Things.: SentencesJossan Ramones AgustinОценок пока нет
- CEBallДокумент70 страницCEBallCZYSTYОценок пока нет
- CEBGAДокумент28 страницCEBGACZYSTYОценок пока нет
- English Proficiency ReviewerДокумент4 страницыEnglish Proficiency ReviewerlenОценок пока нет
- Tugas PronounsДокумент4 страницыTugas PronounsputuОценок пока нет
- CS English Review Oct 2015 Pronouns PDFДокумент25 страницCS English Review Oct 2015 Pronouns PDFMark Anthony CasupangОценок пока нет
- Complementary Help in English (Advance & Intermediates)Документ32 страницыComplementary Help in English (Advance & Intermediates)halconfenixОценок пока нет
- KOMUNIKASYON SHORT FILE by YasiДокумент7 страницKOMUNIKASYON SHORT FILE by Yasibtihs.grantianpadillaОценок пока нет
- Syntax As Parts of Speech by Christine Joy B. OroДокумент39 страницSyntax As Parts of Speech by Christine Joy B. OroAnamie Dela Cruz ParoОценок пока нет
- University of Technology - English - Language - First - Year - 2018 - 2019Документ47 страницUniversity of Technology - English - Language - First - Year - 2018 - 2019Sajad HayderОценок пока нет
- Handout 2 - Pronouns (Kinds and Properties)Документ5 страницHandout 2 - Pronouns (Kinds and Properties)Sangie CenetaОценок пока нет
- Grammar Friska SipayungДокумент36 страницGrammar Friska SipayungLesbra SandyОценок пока нет
- MAJOR 1 3rd HandoutДокумент4 страницыMAJOR 1 3rd HandoutSteffany FrnndzОценок пока нет
- TSL 1024 Language Description: Sem. 2/ 2016 Week 2Документ29 страницTSL 1024 Language Description: Sem. 2/ 2016 Week 2Miziana Suhana Binti Saboo IPGKPIОценок пока нет
- SEMANTICSДокумент21 страницаSEMANTICSQuỳnh ThưОценок пока нет
- Parts of Speech-1Документ7 страницParts of Speech-1Chithra ShreeОценок пока нет
- Parts of Speech 2Документ14 страницParts of Speech 2cagasanjelian112001Оценок пока нет
- A Filipina Writer's StoryДокумент5 страницA Filipina Writer's StoryNasimah CapalОценок пока нет
- Practice Exercise Practice ExerciseДокумент2 страницыPractice Exercise Practice ExerciseNasimah CapalОценок пока нет
- Determiners: Types of Determiners 1. Articles (The Hat, A Hat, An Opera)Документ5 страницDeterminers: Types of Determiners 1. Articles (The Hat, A Hat, An Opera)Nasimah CapalОценок пока нет
- Determiners: Types of Determiners 1. Articles (The Hat, A Hat, An Opera)Документ5 страницDeterminers: Types of Determiners 1. Articles (The Hat, A Hat, An Opera)Nasimah CapalОценок пока нет
- The Rules For Book 1 With An Explanation in The English LanguageДокумент40 страницThe Rules For Book 1 With An Explanation in The English Languageapi-19708996Оценок пока нет
- Building of Database For English-Azerbaijani Machine Translation Expert SystemДокумент7 страницBuilding of Database For English-Azerbaijani Machine Translation Expert SystemAI Coordinator - CSC JournalsОценок пока нет
- Content Words and Structure WordsДокумент4 страницыContent Words and Structure WordsdeepkrishnanОценок пока нет
- Gen Ed Guide English-GrammarДокумент12 страницGen Ed Guide English-GrammarShane AlfonsoОценок пока нет
- /εɪ/ /bi/ /εf/ /waɪ/ /ɔ/ /kyu//// /ar/: Supplementary Pronunciation Lessons (Unit 1)Документ13 страниц/εɪ/ /bi/ /εf/ /waɪ/ /ɔ/ /kyu//// /ar/: Supplementary Pronunciation Lessons (Unit 1)Saulo UrzagasteОценок пока нет
- Instant Immersion Spanish: Audio Course GuideДокумент56 страницInstant Immersion Spanish: Audio Course GuideNina SerovaОценок пока нет
- Methods in Criminological Research Part 1Документ8 страницMethods in Criminological Research Part 1Sirenthorne ChaiyaraОценок пока нет
- Grammar For KidДокумент96 страницGrammar For KidMajidKhanKakerОценок пока нет
- Pronouns (Table)Документ40 страницPronouns (Table)Iana CruzОценок пока нет
- Nahwa (Unknown) (Z-Library)Документ66 страницNahwa (Unknown) (Z-Library)Ahmad AliОценок пока нет
- Report Minor Project Ucs1173Документ8 страницReport Minor Project Ucs1173Nurul IffahОценок пока нет
- Articles Use ExДокумент3 страницыArticles Use ExEmmanuel CancheОценок пока нет
- Want Present TenseДокумент4 страницыWant Present Tensekarenpegueros92Оценок пока нет
- Vee Q1 W7 Dll-English 5Документ6 страницVee Q1 W7 Dll-English 5Venus BorromeoОценок пока нет
- Curs Sintxa Limbi Moderne AplicateДокумент18 страницCurs Sintxa Limbi Moderne AplicateLorena CostanОценок пока нет
- Noun & Numbers: Countable UncountableДокумент109 страницNoun & Numbers: Countable UncountableManish KumarОценок пока нет
- English 4 q2 w4 Day 1-5Документ90 страницEnglish 4 q2 w4 Day 1-5Jessica QuiniaОценок пока нет
- Thatcher - Arabic Grammar of The Written LanguageДокумент486 страницThatcher - Arabic Grammar of The Written LanguageTaliba Roumaniya100% (2)
- Word Classes or Parts of Speech For TamilДокумент30 страницWord Classes or Parts of Speech For TamilKumar RamasamyОценок пока нет
- Al-Jallad. 2019. Safaitic The Semitic La PDFДокумент25 страницAl-Jallad. 2019. Safaitic The Semitic La PDFFadlОценок пока нет
- University of Ghana Language Centre: Academic Writing ManualДокумент94 страницыUniversity of Ghana Language Centre: Academic Writing ManualHALEEM SUNGUMO ABDULAIОценок пока нет
- Paper Noun and PronounДокумент13 страницPaper Noun and PronounNyaa100% (1)
- Buku Lab Semester Genap ItenasДокумент41 страницаBuku Lab Semester Genap ItenasUtia MuflihaОценок пока нет
- Ответы к теорвопросамДокумент28 страницОтветы к теорвопросамValeriya BudalovskayaОценок пока нет
- Exam Academic WritingДокумент24 страницыExam Academic Writingpigeon 8Оценок пока нет
- Pashto Course AzamiДокумент73 страницыPashto Course Azamizait ullah100% (1)
- Lesson 14 - Verb Object PronounsДокумент14 страницLesson 14 - Verb Object PronounsJamar Armenta GonzalezОценок пока нет
- Countable and Uncountable NounsДокумент6 страницCountable and Uncountable NounsJoahaОценок пока нет
- Cot 1 July 23 2019Документ2 страницыCot 1 July 23 2019DL Cerna LeizlОценок пока нет
- SAT Writing Notes CollegeboardДокумент43 страницыSAT Writing Notes CollegeboardEric JoОценок пока нет