Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
We Can Create Dictionary With Following Four Methods
Загружено:
Ghanshyam SharmaОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
We Can Create Dictionary With Following Four Methods
Загружено:
Ghanshyam SharmaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
We can create dictionary with following four methods
# Creating an empty Dictionary
Dict = {}
print("Empty Dictionary: ")
print(Dict)
# Creating a Dictionary
# with Integer Keys
Dict = {1: 'Delhi', 2: 'Ajmer', 3: 'Beawar'}
print("\nDictionary with the use of Integer Keys: ")
print(Dict)
# Creating a Dictionary
# with Mixed keys
Dict = {'Name': 'INFOTECH', 1: [1, 2, 3, 4]}
print("\nDictionary with the use of Mixed Keys: ")
print(Dict)
# Creating a Dictionary
# with dict() method
Dict = dict({1: 'yellow', 2: 'white', 3:'green'})
print("\nDictionary with the use of dict(): ")
print(Dict)
# Creating a Dictionary
# with each item as a Pair
Dict = dict([(1, 'Amit'), (2, 'Sumit')])
print("\nDictionary with each item as a pair: ")
print(Dict)
# Creating a Nested Dictionary
# as shown in the below image
Dict = {1: 'Anita', 2: 'Sunita',
3:{'First Name' : 'Vinita', 'Middle Name' : 'Sumit', 'Last Name' :
'Surana'}}
print(Dict)
Adding Elements to Dictionary
# Creating an empty Dictionary
Dict = {}
print("Empty Dictionary: ")
print(Dict)
# Adding elements one at a time
Dict[0] = ‘INFOTECH’
Dict[2] = ‘COMPUTER’
Dict[3] = ‘EDUCATION’
print("\nDictionary after adding 3 elements: ")
print(Dict)
# Adding set of values
# to a single Key
Dict['Value_set'] = 2, 3, 4
print("\nDictionary after adding 3 elements: ")
print(Dict)
# Updating existing Key's Value
Dict[2] = 'Welcome'
print("\nUpdated key value: ")
print(Dict)
# Adding Nested Key value to Dictionary
Dict[5] = {'Nested' :{'1' : 'Ajmer', '2' : 'Jaipur'}}
print("\nAdding a Nested Key: ")
print(Dict)
Accessing Elements from the Dictionary
# Python program to demonstrate
# accesing a element from a Dictionary
# Creating a Dictionary
Dict = {1: 'Computer', 'name': 'INFOTECH', 3: 'Education'}
# accessing a element using key
print("Acessing a element using key:")
print(Dict['name'])
# accessing a element using key
print("Acessing a element using key:")
print(Dict[1])
# accessing a element using get()
# method
print("Acessing a element using get:")
print(Dict.get(3))
Removing Elements from Dictionary
# Initial Dictionary
Dict = { 5 : 'Welcome', 6 : 'To', 7 : 'INFOTECH',
'A' : {1 : 'Ajmer', 2 : 'Road', 3 : 'Kishangarh'},
'B' : {1 : 'Rajasthan', 2 : 'India'}}
print("Initial Dictionary: ")
print(Dict)
# Deleting a Key value
del Dict[6]
print("\nDeleting a specific key: ")
print(Dict)
# Deleting a Key from
# Nested Dictionary
del Dict['A'][2]
print("\nDeleting a key from Nested Dictionary: ")
print(Dict)
# Deleting a Key
# using pop()
Dict.pop(5)
print("\nPopping specific element: ")
print(Dict)
# Deleting a Key
# using popitem()
Dict.popitem()
print("\nPops first element: ")
print(Dict)
# Deleting entire Dictionary
Dict.clear()
print("\nDeleting Entire Dictionary: ")
print(Dict)
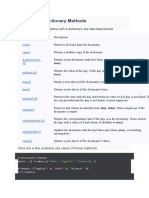
Dictionary Methods
METHODS DESCRIPTION
copy() They copy() method returns a shallow copy of the dictionary.
clear() The clear() method removes all items from the dictionary.
pop() Removes and returns an element from a dictionary having the given key.
popitem() Removes the arbitrary key-value pair from the dictionary and returns it as tuple.
get() It is a conventional method to access a value for a key.
dictionary_name.values() returns a list of all the values available in a given dictionary.
str() Produces a printable string representation of a dictionary.
update() Adds dictionary dict2’s key-values pairs to dict
setdefault() Set dict[key]=default if key is not already in dict
keys() Returns list of dictionary dict’s keys
items() Returns a list of dict’s (key, value) tuple pairs
has_key() Returns true if key in dictionary dict, false otherwise
fromkeys() Create a new dictionary with keys from seq and values set to value.
type() Returns the type of the passed variable.
cmp() Compares elements of both dict.
Q1. WAP to create a phone directory and print phone numbers of all the friends?
An.s.
Pd={“ram”:9829089288,”shyam”:9938934844,”Mohan”:93849899,”Sohan”:93489349}
for name in pd:
print (name,”:”,pd[name])
NOTE : we can print all the keys with pd.keys();
NOTE : we can print all the values with pd.values();
Вам также может понравиться
- Dictionary in PythonДокумент7 страницDictionary in PythonErishaОценок пока нет
- DICTIONARIESДокумент8 страницDICTIONARIEStechno gamesОценок пока нет
- Lecture 5 DictionaryДокумент12 страницLecture 5 Dictionaryfarhanriaz0000Оценок пока нет
- Snowflake NoteДокумент170 страницSnowflake NoteRick VОценок пока нет
- DictionaryДокумент6 страницDictionaryjp samaОценок пока нет
- Dictionary, Its Built-In Functions and MethodsДокумент24 страницыDictionary, Its Built-In Functions and MethodsObulesh AОценок пока нет
- Creating Python DictionaryДокумент6 страницCreating Python DictionarytotabankОценок пока нет
- Dictionary: ExampleДокумент5 страницDictionary: ExampleChandra SenОценок пока нет
- DictionaryДокумент3 страницыDictionaryVamshika KattaОценок пока нет
- FALLSEM2015 16 CP1025 01 Sep 2015 RM02 Dictionary ExamplesДокумент12 страницFALLSEM2015 16 CP1025 01 Sep 2015 RM02 Dictionary ExamplesjasonОценок пока нет
- Dictionary NotesДокумент4 страницыDictionary NotesIlakkiyaa KPОценок пока нет
- Dictionary in PythonДокумент4 страницыDictionary in PythonbipinОценок пока нет
- 14 DictionaryДокумент27 страниц14 DictionaryAdhiraj LahonОценок пока нет
- Dictionaries: PythonДокумент16 страницDictionaries: PythonKsОценок пока нет
- Python DictionaryДокумент3 страницыPython DictionaryHari NandhuОценок пока нет
- ExerciseДокумент3 страницыExerciseShruti LakheОценок пока нет
- Lec-8-Dictionary - Lab-8Документ8 страницLec-8-Dictionary - Lab-8Meghs KeshОценок пока нет
- Advantages of DictionaryДокумент8 страницAdvantages of DictionaryJyotirmay SahuОценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент38 страницUntitledIswarya SreeОценок пока нет
- Basics of PythonДокумент8 страницBasics of PythonsumitОценок пока нет
- Dict (: ,: 22) : "Name" "Tom" "Age"Документ8 страницDict (: ,: 22) : "Name" "Tom" "Age"Rinki SinghОценок пока нет
- Q.1: Python Dictionary Methods: Methods That Are Available With A Dictionary Are Tabulated BelowДокумент6 страницQ.1: Python Dictionary Methods: Methods That Are Available With A Dictionary Are Tabulated BelowkunjuОценок пока нет
- Dictionary in PythonДокумент21 страницаDictionary in PythonRupesh ChaudharyОценок пока нет
- DictionaryДокумент60 страницDictionaryManan kansaraОценок пока нет
- Programming Fundamentals: Tuple and DictionaryДокумент12 страницProgramming Fundamentals: Tuple and DictionarySarah GoharОценок пока нет
- Handouts On DictionaryДокумент7 страницHandouts On DictionaryAnonymous zrAfrkPOJ7Оценок пока нет
- Data Structure (Dictionary)Документ13 страницData Structure (Dictionary)Radha AdhikariОценок пока нет
- Unit Iii List, Tuples, Set and DictionariesДокумент7 страницUnit Iii List, Tuples, Set and DictionariesManaswini MadarapuОценок пока нет
- Dictionary in PythonДокумент9 страницDictionary in PythonNargis AliОценок пока нет
- Python Code ExamplesДокумент30 страницPython Code ExamplesAsaf KatzОценок пока нет
- Dictionaries in PythonДокумент15 страницDictionaries in PythonPritika SachdevaОценок пока нет
- Unit 5Документ27 страницUnit 5Mohamed AliОценок пока нет
- Swe-102 Lab 10!Документ4 страницыSwe-102 Lab 10!Kaif malik100% (1)
- Chapter 9 DictionariesДокумент6 страницChapter 9 Dictionariessanju kumarОценок пока нет
- Python RulesДокумент9 страницPython Rulesshrivastavanuj823Оценок пока нет
- PFC - Workshop 05: Question 1 (2.5 Marks) : Write A Program To Perform These TasksДокумент7 страницPFC - Workshop 05: Question 1 (2.5 Marks) : Write A Program To Perform These TasksDuong Thanh Duy (K17 QN)Оценок пока нет
- Python Lab ManualДокумент13 страницPython Lab ManualSanjay DilipОценок пока нет
- Python Week-3Документ11 страницPython Week-3jaswanreddy1159Оценок пока нет
- Julia Basic CommandsДокумент10 страницJulia Basic CommandsLazarus PittОценок пока нет
- Dictionary in PythonДокумент8 страницDictionary in Pythonvivekbc71Оценок пока нет
- Python Assignment-2 Solutions PDFДокумент91 страницаPython Assignment-2 Solutions PDFRAMYA S HОценок пока нет
- Dictionaries in PythonДокумент17 страницDictionaries in Pythonrishiraj goswamiОценок пока нет
- Problem: Write A Kids Play Program That Prints The Capital of A Country Given The Name of The CountryДокумент28 страницProblem: Write A Kids Play Program That Prints The Capital of A Country Given The Name of The CountryluckyОценок пока нет
- Discrete Structures Lab 1 Python Basics: 1 Python Installation 2 Python TutorialДокумент8 страницDiscrete Structures Lab 1 Python Basics: 1 Python Installation 2 Python Tutorialhuy phanОценок пока нет
- Dictionaries: Hash MapsДокумент12 страницDictionaries: Hash MapskunsangОценок пока нет
- Class 12th Python Lecture 6Документ12 страницClass 12th Python Lecture 6HARSH KUMARОценок пока нет
- Week 8: Structured Types - Lists, Tuples, DictionariesДокумент14 страницWeek 8: Structured Types - Lists, Tuples, DictionariesKemalhan AydınОценок пока нет
- Dictionaries in PythonДокумент23 страницыDictionaries in PythonGyОценок пока нет
- Assignment 2Документ11 страницAssignment 2Kalp ParikhОценок пока нет
- Python Libraries PDFДокумент22 страницыPython Libraries PDFPistol CostinОценок пока нет
- LEC9 Python DictionoryДокумент15 страницLEC9 Python DictionoryKruthika AОценок пока нет
- Dictionary: Dict ('Name': 'Geeks', 1: (1, 2, 3, 4) )Документ14 страницDictionary: Dict ('Name': 'Geeks', 1: (1, 2, 3, 4) )ahmedОценок пока нет
- Python Collections ModuleДокумент19 страницPython Collections Moduleyaar1220Оценок пока нет
- DictionaryДокумент30 страницDictionarymanoharrish3Оценок пока нет
- PythonДокумент2 страницыPythonSWATANTRA SRIVASTAVОценок пока нет
- J.K. Institute of Applied Physics and Technology: Natural Language Processing AssignmentДокумент22 страницыJ.K. Institute of Applied Physics and Technology: Natural Language Processing AssignmentVivek AryaОценок пока нет
- Government College of Engineering and Textile Technology BerhamporeДокумент20 страницGovernment College of Engineering and Textile Technology BerhamporeIndraniОценок пока нет
- NumPy, SciPy and MatPlotLibДокумент18 страницNumPy, SciPy and MatPlotLibVandana DulaniОценок пока нет
- Joining Notes NewДокумент8 страницJoining Notes NewGhanshyam SharmaОценок пока нет
- Mysql Assignment - 2: Where Quality MattersДокумент1 страницаMysql Assignment - 2: Where Quality MattersGhanshyam SharmaОценок пока нет
- Question Bank Class Xi Ip To Be UploadedДокумент19 страницQuestion Bank Class Xi Ip To Be UploadedGhanshyam SharmaОценок пока нет
- Mysql Assignment - 15: Where Quality MattersДокумент1 страницаMysql Assignment - 15: Where Quality MattersGhanshyam SharmaОценок пока нет
- MYSQL Assignments Final PDFДокумент1 страницаMYSQL Assignments Final PDFGhanshyam SharmaОценок пока нет
- Mysql Assignment - 1: Where Quality MattersДокумент1 страницаMysql Assignment - 1: Where Quality MattersGhanshyam SharmaОценок пока нет
- Payment Status: Thank You Your Payment Is SuccessfulДокумент1 страницаPayment Status: Thank You Your Payment Is SuccessfulGhanshyam SharmaОценок пока нет
- Application Development: 14 Years Experience in Websites & Applications DevelopmentДокумент12 страницApplication Development: 14 Years Experience in Websites & Applications DevelopmentGhanshyam SharmaОценок пока нет
- Preeti Arora List QuestionsДокумент8 страницPreeti Arora List QuestionsGhanshyam Sharma100% (1)
- INFOTECH PYTHON Class XIth LIST ChapterДокумент23 страницыINFOTECH PYTHON Class XIth LIST ChapterGhanshyam SharmaОценок пока нет
- 15 1312MH CH09 PDFДокумент17 страниц15 1312MH CH09 PDFAntora HoqueОценок пока нет
- Python Primer: Patrice Koehl Modified by Xin Liu in Apr., 2011Документ33 страницыPython Primer: Patrice Koehl Modified by Xin Liu in Apr., 2011Ghanshyam SharmaОценок пока нет
- Java String Functions': Visit at "JH X.KS'KK Ue%"Документ5 страницJava String Functions': Visit at "JH X.KS'KK Ue%"Ghanshyam SharmaОценок пока нет
- Preeti Arora Dictionary QuestionsДокумент6 страницPreeti Arora Dictionary QuestionsGhanshyam Sharma33% (3)
- © Educational Technology Department, Group Head Office, The City School. 1Документ13 страниц© Educational Technology Department, Group Head Office, The City School. 1Ghanshyam SharmaОценок пока нет
- Xith Ip Mysql PartДокумент13 страницXith Ip Mysql PartGhanshyam SharmaОценок пока нет
- XIth IP PythonДокумент17 страницXIth IP PythonGhanshyam SharmaОценок пока нет
- Xith Ip Mysql PartДокумент13 страницXith Ip Mysql PartGhanshyam SharmaОценок пока нет
- G 083 19 LIC Sales Brochure Jeevan Amar Hindi Proof 12Документ2 страницыG 083 19 LIC Sales Brochure Jeevan Amar Hindi Proof 12Ghanshyam SharmaОценок пока нет
- View / Download Account Statement: Savings Account No.: 50100021996040, CYBERCITYДокумент2 страницыView / Download Account Statement: Savings Account No.: 50100021996040, CYBERCITYGhanshyam SharmaОценок пока нет
- Question Bank Class Xi Ip To Be UploadedДокумент19 страницQuestion Bank Class Xi Ip To Be UploadedGhanshyam SharmaОценок пока нет
- Application Development: 14 Years Experience in Websites & Applications DevelopmentДокумент12 страницApplication Development: 14 Years Experience in Websites & Applications DevelopmentGhanshyam SharmaОценок пока нет
- Web Technology BrochureДокумент11 страницWeb Technology BrochureGhanshyam SharmaОценок пока нет
- Tally Assignment 12Документ90 страницTally Assignment 12Kaushal SharmaОценок пока нет
- PHP Basic String FunctionsДокумент1 страницаPHP Basic String FunctionsGhanshyam SharmaОценок пока нет
- Class Xi Guess Paper Informatics Practices: General Instructions: MM: 70Документ8 страницClass Xi Guess Paper Informatics Practices: General Instructions: MM: 70Ghanshyam SharmaОценок пока нет
- BCA 301 SolutionsДокумент12 страницBCA 301 SolutionsGhanshyam SharmaОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Accounting by T S GrewalДокумент9 страницIntroduction To Accounting by T S GrewalGhanshyam SharmaОценок пока нет
- MBA IT 108 SolutionsДокумент10 страницMBA IT 108 SolutionsGhanshyam SharmaОценок пока нет
- Lecture 6 Convolution Using DFTДокумент38 страницLecture 6 Convolution Using DFTAman SharmaОценок пока нет
- Mutual InformationДокумент8 страницMutual Informationbalasha_937617969Оценок пока нет
- The Design of Approximation Algorithm 2011 PDFДокумент500 страницThe Design of Approximation Algorithm 2011 PDFThanh Thiện Trần ChâuОценок пока нет
- CPPS Unit 3Документ7 страницCPPS Unit 3jsanandkumar22Оценок пока нет
- Radix SortДокумент10 страницRadix SortC-1962 Anwesha BaruaОценок пока нет
- Von Wright, Truth-LogicsДокумент24 страницыVon Wright, Truth-LogicsEzequiel MontiОценок пока нет
- Armiet AOA Lab ManualДокумент47 страницArmiet AOA Lab ManualAmit DubeyОценок пока нет
- Arithmetic Operations On Binary Numbers: Two's Complement AdditionДокумент11 страницArithmetic Operations On Binary Numbers: Two's Complement AdditionAjay RavuriОценок пока нет
- Ece-V-Information Theory & Coding (10ec55) - AssignmentДокумент10 страницEce-V-Information Theory & Coding (10ec55) - AssignmentLavanya Vaishnavi D.A.Оценок пока нет
- Ai Asignmnt 2Документ7 страницAi Asignmnt 2Aayush MehtaОценок пока нет
- Tch13 Searching and SortingДокумент43 страницыTch13 Searching and SortingNora MasoudОценок пока нет
- An Efficient Line AlgorithmДокумент3 страницыAn Efficient Line Algorithmapi-3754855Оценок пока нет
- CE NotesДокумент32 страницыCE Notesece.kavitha mamcetОценок пока нет
- Coloring of Triangle Free Girth Graphs With Minimal K-ColorsДокумент4 страницыColoring of Triangle Free Girth Graphs With Minimal K-Colorsvol2no5Оценок пока нет
- Bitwise Operators in JavaДокумент4 страницыBitwise Operators in JavaPrabir KamilaОценок пока нет
- Delta RuleДокумент3 страницыDelta RulemomavОценок пока нет
- Int404 (Syllabus)Документ1 страницаInt404 (Syllabus)Anish KumarОценок пока нет
- Binary Search TreesДокумент39 страницBinary Search Treesআরব বেদুঈনОценок пока нет
- Question BankДокумент16 страницQuestion BankrishikarthickОценок пока нет
- Cyclic Redundancy CodeДокумент20 страницCyclic Redundancy Codesumit kumarОценок пока нет
- Test Bank For Introduction To Java Programming Comprehensive Version 9 e 9th Edition 0133050572 DownloadДокумент8 страницTest Bank For Introduction To Java Programming Comprehensive Version 9 e 9th Edition 0133050572 DownloadTeresaMoorecsrby100% (42)
- CS F222Документ2 страницыCS F222Naman GoyalОценок пока нет
- Dsi EccДокумент7 страницDsi Ecckumarsanjeev.net9511Оценок пока нет
- Garden PDFДокумент3 страницыGarden PDFadinaiseОценок пока нет
- KKT ScribedДокумент7 страницKKT ScribedRupaj NayakОценок пока нет
- B ATPGДокумент98 страницB ATPGAnindita DashОценок пока нет
- Noise, Information Theory, and EntropyДокумент34 страницыNoise, Information Theory, and EntropyReetika AroraОценок пока нет
- Artificial Neural NetworkДокумент31 страницаArtificial Neural NetworkPavanpreet KaurОценок пока нет
- P, NP and NP-Complete ProblemsДокумент20 страницP, NP and NP-Complete ProblemsAnandha RajanОценок пока нет
- U3 Test Review MPM 2D: True/FalseДокумент4 страницыU3 Test Review MPM 2D: True/FalsessszszszszОценок пока нет