Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Higher Cortical Functions Multimodal Association Areas
Загружено:
wifol0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
30 просмотров1 страницаphysiology
Оригинальное название
Higher Functions
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документphysiology
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
30 просмотров1 страницаHigher Cortical Functions Multimodal Association Areas
Загружено:
wifolphysiology
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 1
HIGHER CORTICAL FUNCTIONS
MULTIMODAL ASSOCIATION AREAS
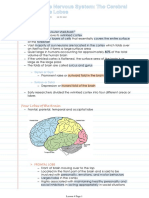
Parieto-Occipitotemporal Association Area Prefrontal Association Area Limbic Association Area Area for recognition of faces
- largest multimodal association area - association with the motor cortex to plan - behavior, emotion and motivation
- interpret meaning for signals complex patterns and sequences of motor - emotional drives
Functional sub-areas: movements - motivational drives for learning
1. Spatial coordinates (visual, auditory, body - motor planning: signals basal ganglia -
surroundings) (caudate nucleus) motor cortex carries
2. Language comprehension out specific plan of action/movement
Wernicke’s area - elaboration of thought
– higher intellectual function - process motor and non-motor information
– language comprehension and intelligence - stores “working memories” (short term) or
– connected to Broca’s area by arcuate planning memories
fasciculus Broca’s area
3. Initial processing of visual language (reading) - word formation
Angular gyrus - where plans and motor patterns for expressing
- makes meaning out of visually perceived individual words or short phrases
words - when a person learns a new language, are in
4. Area of naming objects brain where new language is stored is slightly
- names are learned mainly through auditory input removed from storage from the storage area
for the first language
- If both languages learned simultaneously =>
stored in the same area of brain
lesions/damage: lesions or damage: Prosopagnosia
Wernicke’s aphasia Motor disorders - inability to recognize faces
- loss of function of language comprehension - damage between prefrontal and basal - abnormal behavior, fluctuating emotions, loss of - damage to medial undersides of occipital
- damaged areas: supramarginal and angular ganglia motivation lobes and medioventral surface of temporal
gyrus and superior temporal gyrus Broca’s aphasia lobes
Dyslexia - lesions in pars opercularis and pars
- damage to angular gyrus triangularis
- - impaired articulation of speech
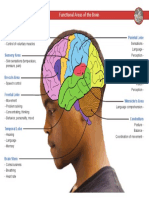
Locations:
posterior occipital cortex – visual sensory information posterior lateral prefrontal cortex and premotor area – occipital portion- visual cortex
anterior parietal cortex – somatosensory information Broca’s area temporal portion – limbic system
anterolateral region of occipital lobe- reading
lateral portions od anterior occipital lobe and posterior
temporal lobe – naming objects (auditory)
Вам также может понравиться
- Motor Cortex: (Intellectual Functions of The Brain, Learning and Memory)Документ3 страницыMotor Cortex: (Intellectual Functions of The Brain, Learning and Memory)22 - Fernandez, Lyza Mae D.Оценок пока нет
- Higher Cortical FunctionДокумент4 страницыHigher Cortical FunctionSiti Fairuz NadyaОценок пока нет
- Cerebral CortexДокумент11 страницCerebral CortexGaby SanchezОценок пока нет
- Cerebral Cortex Intellectual Functions of The Brain Learning and MemoryДокумент66 страницCerebral Cortex Intellectual Functions of The Brain Learning and MemoryAlexe VillagomezОценок пока нет
- Physiology of SpeechДокумент14 страницPhysiology of Speechvz2pj6n9m4Оценок пока нет
- Neuro Notes #3: Surface Anatomy of The Brain 60 Points: Landmark OR Structure Location Function (S) PathologyДокумент12 страницNeuro Notes #3: Surface Anatomy of The Brain 60 Points: Landmark OR Structure Location Function (S) PathologyTalia GarciaОценок пока нет
- Are Fundamental Processes That Can Not Be Classified As: - Sensory - MotorДокумент84 страницыAre Fundamental Processes That Can Not Be Classified As: - Sensory - Motornapoleon tesfayeОценок пока нет
- 2.1 Tutorial Task 10& 11Документ8 страниц2.1 Tutorial Task 10& 11ENOCH NAPARI ABRAMANОценок пока нет
- Week 5 CerebrumДокумент38 страницWeek 5 Cerebrumsuen sarahОценок пока нет
- FX BrainДокумент1 страницаFX BrainAnonymous r8QGPePLqCОценок пока нет
- AnII Curs FC IntelectДокумент27 страницAnII Curs FC IntelectNicole.IОценок пока нет
- Cortical FunctionДокумент75 страницCortical FunctionFiizhda BaqarizkyОценок пока нет
- Brain Lobes & FunctionsДокумент15 страницBrain Lobes & FunctionsAlyssa PangОценок пока нет
- Bio621 MindmapДокумент3 страницыBio621 MindmapMizahОценок пока нет
- Language and The BrainДокумент17 страницLanguage and The Brainrgerodias02Оценок пока нет
- A Guide To Brain AnatomyДокумент7 страницA Guide To Brain AnatomyPuppa AlexandraОценок пока нет
- Aphasia, Memory Loss, and Other Focal Cerebral Disorders: From: Dr. Camomot Modified by Dr. Canete For SWU 2016Документ48 страницAphasia, Memory Loss, and Other Focal Cerebral Disorders: From: Dr. Camomot Modified by Dr. Canete For SWU 2016Nogra CarlОценок пока нет
- R3 Basic Mental ProcessesДокумент3 страницыR3 Basic Mental ProcessesScribdTranslationsОценок пока нет
- Module 3.2 The Cerebral CortexДокумент3 страницыModule 3.2 The Cerebral CortexChriscelle Ann PimentelОценок пока нет
- The Nervous System (Notes)Документ3 страницыThe Nervous System (Notes)Trisha LaidenОценок пока нет
- Physiology Nervous System - Lecture 3 - NinoДокумент51 страницаPhysiology Nervous System - Lecture 3 - NinoSania KhanОценок пока нет
- NEUROSCIENCE 10 SPEECH 2019 WebДокумент22 страницыNEUROSCIENCE 10 SPEECH 2019 Webouma.idrissi11Оценок пока нет
- Traumatic Brain InjuryДокумент15 страницTraumatic Brain InjuryAbbey Janine Mandapat Passi100% (3)
- Nervous SystemДокумент4 страницыNervous SystemEllanny GloriaОценок пока нет
- Human BrainДокумент33 страницыHuman BrainSadiq Abdo92Оценок пока нет
- Aula T2 - Neuropsychology - Sensory - VisualДокумент25 страницAula T2 - Neuropsychology - Sensory - VisualBeatriz SantosОценок пока нет
- PSYC 21 2022 Brain Structures - Short Edited - ForebrainДокумент3 страницыPSYC 21 2022 Brain Structures - Short Edited - ForebrainsdahjdhasjkdhaskdОценок пока нет
- VisibleBody Brain Ebook May2021Документ38 страницVisibleBody Brain Ebook May2021Sandra RubianoОценок пока нет
- CEREBRUM Functional Areas 2022Документ7 страницCEREBRUM Functional Areas 2022GURNOOR DHILLONОценок пока нет
- A1. Functional Areas of Cerebral CortexДокумент3 страницыA1. Functional Areas of Cerebral Cortexspindr07Оценок пока нет
- Speec H: DR Jyoti Prasad DeoriДокумент32 страницыSpeec H: DR Jyoti Prasad DeoriDorin PathakОценок пока нет
- Functional Cortical Areas of BrainДокумент10 страницFunctional Cortical Areas of BrainAdeel MasoodОценок пока нет
- Writeup Physio Doc Agor 1Документ15 страницWriteup Physio Doc Agor 1Luis PadillaОценок пока нет
- Frontal and Temporal Lobe PresentationДокумент30 страницFrontal and Temporal Lobe PresentationVann RhymeОценок пока нет
- Cortical Function: Dr. Paulus Anam Ong SP.S Dr. Yustiani Dikot SP.S (K) Bagian I.P. Saraf RSHS FKUPДокумент78 страницCortical Function: Dr. Paulus Anam Ong SP.S Dr. Yustiani Dikot SP.S (K) Bagian I.P. Saraf RSHS FKUPMuhammad Hamid MuktashimОценок пока нет
- Xquh 87 Ji 6 T 0 NJWP 5 X 4 MT 467 y 56 Onvs 5 Dhupi 7 G 2 T 0 BP 4 FuДокумент3 страницыXquh 87 Ji 6 T 0 NJWP 5 X 4 MT 467 y 56 Onvs 5 Dhupi 7 G 2 T 0 BP 4 FuНурила ҚапарОценок пока нет
- Language, Mind and BrainДокумент7 страницLanguage, Mind and BrainSaket SonarОценок пока нет
- 07.5 AQA Psych Course Companion Localisation and Lateralisation.206804846Документ13 страниц07.5 AQA Psych Course Companion Localisation and Lateralisation.206804846khushi.avatharaОценок пока нет
- Neuro PDFДокумент8 страницNeuro PDFHira SheikhОценок пока нет
- Cerebral Cortex: Gyrus or Gyri Sulcus or SulciДокумент7 страницCerebral Cortex: Gyrus or Gyri Sulcus or SulciPaolo GozonОценок пока нет
- Neurolingusitics: Brain & Languages Language & Brain Development The Modular MindДокумент1 страницаNeurolingusitics: Brain & Languages Language & Brain Development The Modular MindhamizahОценок пока нет
- Beyparids Midterm-Read ReviewerДокумент8 страницBeyparids Midterm-Read ReviewerBea ParidoОценок пока нет
- Sixth LectureДокумент2 страницыSixth Lecturegeorge bensonОценок пока нет
- Functional Areas of BrainДокумент1 страницаFunctional Areas of Brainsattya.nОценок пока нет
- SpeechДокумент8 страницSpeechyosramr636Оценок пока нет
- Corteza Cerebral y ÁreasДокумент1 страницаCorteza Cerebral y ÁreasLUCIANA MARIELA ACU�A CANNATAОценок пока нет
- Neuro 1Документ11 страницNeuro 1Soundararajan RajagopalanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5Документ41 страницаChapter 5Reneilwe MoshidiОценок пока нет
- PT Neuro Intro NotesДокумент13 страницPT Neuro Intro NotesSusan K100% (1)
- 2020 - 10 - 29 - Εγκεφαλικά Ημισφαίρια και Αγγειακά Σύνδρομα - ΜήτσιαςДокумент67 страниц2020 - 10 - 29 - Εγκεφαλικά Ημισφαίρια και Αγγειακά Σύνδρομα - ΜήτσιαςΖέτα ΤσίρκαОценок пока нет
- l15 CerebrumДокумент31 страницаl15 CerebrumDr. Pinki RaiОценок пока нет
- Brodmann Areas TableДокумент2 страницыBrodmann Areas TableMimi Olaguer Vaporoso50% (2)
- Cerebral Lobes: Department of Neurosurgery Dr. Soetomo General Hospital - Airlangga UniversityДокумент46 страницCerebral Lobes: Department of Neurosurgery Dr. Soetomo General Hospital - Airlangga UniversityMogiMediawanОценок пока нет
- Cortex Cerebri (NeoCortex)Документ43 страницыCortex Cerebri (NeoCortex)saidahrahmatОценок пока нет
- CNS NotesДокумент197 страницCNS Notespranjal shahОценок пока нет
- Neurological ConditionsДокумент43 страницыNeurological Conditionszm2h8hpsq8Оценок пока нет
- Neural Basis 5Документ24 страницыNeural Basis 5zainabbu2023Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 6Документ4 страницыChapter 6Neus Sangrós VidalОценок пока нет
- HNNS42 - Higher Cortical Function: OrientationДокумент5 страницHNNS42 - Higher Cortical Function: Orientationbryan chanОценок пока нет
- Nervous Sysytem SeminarДокумент34 страницыNervous Sysytem SeminarShalini ChanduОценок пока нет
- Internal Capsule of BrainДокумент10 страницInternal Capsule of BrainTAL WALKERSОценок пока нет
- Powerpoint LextureДокумент20 страницPowerpoint Lextureapi-449532718Оценок пока нет
- Unit 5 Cognitive PsychologyДокумент3 страницыUnit 5 Cognitive Psychologyhellastupid1Оценок пока нет
- How To Improve MemoryДокумент138 страницHow To Improve MemorySrimathi Amala Pushpika95% (22)
- School of Foreign Languages: Introduction To Academic EnglishДокумент42 страницыSchool of Foreign Languages: Introduction To Academic EnglishnecosharpОценок пока нет
- Braverman Personality Type AssessmentДокумент24 страницыBraverman Personality Type AssessmentDaniela Stoica100% (2)
- Braintumor 160822132617Документ39 страницBraintumor 160822132617krishnasreeОценок пока нет
- Neuroanatomy QbankДокумент27 страницNeuroanatomy Qbankbbbanyi67% (3)
- Your BodyДокумент19 страницYour Bodybbe43196% (25)
- Gateway To The Human MindДокумент51 страницаGateway To The Human Minddza_hippie100% (12)
- Cia RDP96 00788R001700210016 5Документ29 страницCia RDP96 00788R001700210016 5Juan Manuel MH100% (6)
- Introduction To NeuroanatomyДокумент21 страницаIntroduction To Neuroanatomybelete abyuОценок пока нет
- Roger Walsh M.D., Ph.D. (Auth.) - Towards An Ecology of Brain-Springer Netherlands (1981) PDFДокумент194 страницыRoger Walsh M.D., Ph.D. (Auth.) - Towards An Ecology of Brain-Springer Netherlands (1981) PDFLeo RuilovaОценок пока нет
- Diasquisis L PDFДокумент5 страницDiasquisis L PDFValentina Sanhueza Gatica100% (1)
- Brain Bee R1 P2Документ9 страницBrain Bee R1 P2sarahsyedazakiОценок пока нет
- XI Term 1 QPДокумент7 страницXI Term 1 QPstwilfred primaryОценок пока нет
- ASD Brain AUG222014 PDFДокумент2 страницыASD Brain AUG222014 PDFcitra suhalimОценок пока нет
- Ati Teas 7 Biology ReviewДокумент51 страницаAti Teas 7 Biology ReviewSAMUEL WAMОценок пока нет
- Two GUARANTEED Ways To ProfoundlyДокумент12 страницTwo GUARANTEED Ways To Profoundlycolderas jethОценок пока нет
- 21CS54 Module 1Документ35 страниц21CS54 Module 1Saad Sk100% (2)
- The Thalamus Is A Scanner: All Information Comes Into The Thalamus Before Being Distributed To Other Parts of The BrainДокумент54 страницыThe Thalamus Is A Scanner: All Information Comes Into The Thalamus Before Being Distributed To Other Parts of The BrainBaguma MichaelОценок пока нет
- Faci 1Документ3 страницыFaci 1John Philip ParasОценок пока нет
- Paternina-Die Et Al-2024-Nature NeuroscienceДокумент18 страницPaternina-Die Et Al-2024-Nature NeuroscienceRamón Díaz-AlersiОценок пока нет
- Comprehensive Guide To The New Brain-Based Teaching (W.W. Norton) A BookДокумент13 страницComprehensive Guide To The New Brain-Based Teaching (W.W. Norton) A BookBASTIAN FELIPE GOMEZ SALASОценок пока нет
- Meditation - Kamlesh Patel in HFN Magazine-Issue 2-2015 PDFДокумент1 страницаMeditation - Kamlesh Patel in HFN Magazine-Issue 2-2015 PDFanon_630497556Оценок пока нет
- Genes and BehaviourДокумент11 страницGenes and BehaviourRutuja BhoyarОценок пока нет
- Malandain Leo Pharmacotherapy of Sexual AddictionДокумент8 страницMalandain Leo Pharmacotherapy of Sexual AddictionSergio De PanfilisОценок пока нет
- DAR - Dreams Analysis and Resolution by Col Sudip MukerjeeДокумент12 страницDAR - Dreams Analysis and Resolution by Col Sudip MukerjeeSudip Mukerjee100% (1)
- Brain ReprogrammingДокумент50 страницBrain Reprogramminghohgch100% (4)