Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
CENG 198 Problem Set 1 Part1 Questions
Загружено:
Bryan Christian MendozaАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CENG 198 Problem Set 1 Part1 Questions
Загружено:
Bryan Christian MendozaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CENG198 – CE Competency Appraisal III at A and 290mm from the center on the opposite side
Problem Set – Engineering Mechanics from A. There are three supports, A, B, and C that are
Static of Rigid Bodies equally spaced. Determine the following: (a) reaction
Dynamics of Rigid Bodies at A; (b) reaction at B; (c) reaction at C.
11. The 80 + (n+10) kN block is suspended from the
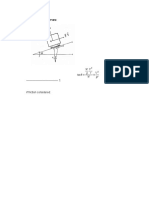
1. Refer to Figure CECA3.SRB.001. Determine the horizontal ring using three springs each having an
following: (a) magnitude of the horizontal component unstretched length of 1.50 m and stiffness of 50+n/10
of the resultant of the force system; (b) magnitude of kN/m. Refer to Figure CECA3.SRB.009. Determine the
the resultant force; (c) angle that the equilibrant following: (a) angle that each spring makes with the
makes with the horizontal axis. vertical for equilibrium; (b) vertical distance “h” from
Note: Add “n”, last 2-digit of student no., to the 86.60 N the right to the point A for equilibrium; (c) tensile force
force. in each spring for equilibrium.
2. The resultant of the concurrent force system shown in 12. The shear-leg derrick sown in Figure CECA3.SRB.010
Figure CECA3.SRB.002 has a magnitude of 300 + n kN supports a vertical load of 2 000+5n N applied at A.
acting vertically upward along the y-axis. Determine Points B, C, and D are in the same horizontal plane and
the following: (a) value of θ, for the resultant force to A, O and D are in the x-y plane. Determine the
act as described; (b) the value of force F1 for the following: (a) force in member AB; (b) force in
resultant to act as described; (c) If F1 = 600 + n kN and member AC; (c) force in member AD.
θ = 60 + n/10 °, find the resultant of the concurrent 13. If member AB is subjected to a compressive force of
system. 600+2n N. Refer to Figure CECA3.SRB.011. Determine
3. A weight of W is suspended from a fine wire AB and a the following: (a) force in member AD; (b) force in
very flexible wire BCD which passes over a frictionless member AC; (c) vertical force P.
pulley at C. The end of the wire BCD is attached to a 10 14. A 150+n kg. man stands on the middle rung of a 50+n
+ n kN weight, and the wires makes an angle shown in kg ladder as shown in Figure CECA3.SRB.012.
Figure CECA3.SRB.003 with the vertical. Determine the Assuming the floor and wall are perfectly smooth and
following: (a) tension in wire AB; (b) weight W; (c) that slipping is prevented a string DE. Determine the
vertical reaction at C. following: (a) reaction at B; (b) reaction at A; (c)
4. A bottom AB is supported in a horizontal position by a tension in string DE.
hinge at A and a cable which runs from C over a small 15. From Figure CECA3.SRB.013, the two identical spheres
pulley at D as shown in Figure CECA3.SRB.004. If the having equal weights of 367+n N is placed on top of the
cable pulls the boom AB into a position at which it is three identical spheres arranged as shown. Determine
inclined at 20+n/10° above the horizontal, the loads the following: (a) reaction at A; (b) reaction at B; (c)
remains in a vertical position and neglecting the size of reaction at C.
pulley at D. Determine the following (a) tension in the 16. The three-hinged arc supports the load F1 =
cable; (b) horizontal component of the reaction at A; 8+((n+10)/10) kN and F2 = 5+((n+20)/10).
(c) vertical component of the reaction at B. Assuming h = 2m. Refer to Figure CECA3.SRB.014
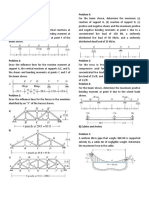
5. A crane cable is supporting a 100+n kN load as shown 17. A catenary cable shown in Figure CECA3.SRB.015 has a
in CECA3.SRB.005. Determine the following: (a) weight of 200+n kN/m. It has a tension of 250 + n kN
tension in cable CD; (b) tension in cable CE; (c) force F. at its lowest point of the cable. Determine the
6. A boom AB supports a load of 5 600+2n N supported following: (a) sag of the cable; (b) tension at B; (c) total
by cable BC at point B. The boom has a length of 9 m length of the cable.
and has a weight of 2 900+1.5n with its centroid at G, 18. The idealized model for a suspension bridge is shown
3.6 m. from B. Boom AB makes an angle of 30° with the in Figure CECA3.SRB.016. The trusses are pin
horizontal. Refer to Figure CECA3.SRB.006. Determine connected at D, on hinged support at C and on roller
the following: (a) force in cable BC; (b) reaction at the support at E. The parabolic cable is supported on
hinge at A; (c) reaction of the boom at B. towers at AC and at BE. Determine the following: (a)
7. The frame shown in Figure CECA3.SRB.007 is tension in the cable at mid-length; (b) vertical reaction
subjected to a triangular load of which varies from zero
at the pin at D; (c) vertical force at the tower AC; (d)
at the top to 29+3n kN/m at the bottom section at A.
max. force in the cable.
Neglecting the weight of all members. Determine the
following: (a) reaction at A; (b) reaction at B; (c) 19. The given blocks have weights of Wa = 10+n/10 kN,
reaction at C. Wb = 30+n/10 kN and Wc = 50+n/10 kN, respectively.
8. A cylindrical drum having a weight of 250 + 3n kN is Coefficient of static friction at the surfaces of contact
supported by an inclined wall making an angle of 60° are shown in Figure CECA3.SRB.017. Determine the
with the horizontal and a vertical bar AB. The bar is pin following: (a) smallest horizontal force P needed to
connected to the wall at point A and connected to a move block A; (b) tension of the cable supporting block
flexible cable at point B. Neglect the weight of the bar C; (c) normal force between blocks A and B.
and assume all surfaces are smooth. Refer to Figure 20. The coefficient of static friction for all contact surfaces
CECA3.SRB.008. Determine the following: (a) reaction is 0.20. The weight of block A is 200+(10+2n) kN and
at the point of contact at C; (b) tension in the flexible that of B is 100+(20+n) kN. Determine the following:
cable at point B; (c) reaction at point A. (a) force P to cause impending motion of block B to the
9. Six steel cables are supporting a circular heavy
left; (b) force P to cause impending motion of block B
moulding of diameter 2.9 m from an overhead point. If
the moulding weighs 2.9 + n/10 kN/m and the to the right; (c) if a force P = 50 kN is applied to the
attachment point 1.8+n/92 above it. left: a. will it move the block A up? b. will hold it in
10. The circular table 1029 mm in diameter supports a equilibrium? c. is it too small to prevent A from coming
load of 92+10n N located on a diameter through the down? d. is it too small to prevent B from moving out?
support at A located on a diameter through the support
Вам также может понравиться
- Structural Theory Refresher SetДокумент6 страницStructural Theory Refresher SetLa BeamОценок пока нет
- Theory Part 02 PDF FormatДокумент9 страницTheory Part 02 PDF Formatlonyx27100% (1)
- Question BankДокумент9 страницQuestion Bankpragash100% (1)
- Experiment 3 Air Compressor PDFДокумент9 страницExperiment 3 Air Compressor PDFah qian100% (1)
- Manik - ME 072052 Ruet: Chapter 11, Solution 1Документ211 страницManik - ME 072052 Ruet: Chapter 11, Solution 1Selino CruzОценок пока нет
- AccelerationДокумент24 страницыAccelerationZa Natividad MarzanОценок пока нет
- Geometry and Physics by Atiyah, Dijkgraaf, HitchinДокумент15 страницGeometry and Physics by Atiyah, Dijkgraaf, HitchinTensegrity Wiki100% (2)
- GRABSUM School Inc. Name: Grade Level and Section: 12 - STEMДокумент6 страницGRABSUM School Inc. Name: Grade Level and Section: 12 - STEMWendell CapiliОценок пока нет
- LECTURE - FoundationsДокумент6 страницLECTURE - FoundationsFazelah YakubОценок пока нет
- Cent Pumps PresentationДокумент75 страницCent Pumps PresentationSushma Medikonda100% (1)
- Rigid Body DynamicsДокумент123 страницыRigid Body DynamicsyakvinОценок пока нет
- Assignment Questions For All UnitsДокумент10 страницAssignment Questions For All UnitsPiyush BhandariОценок пока нет
- Problem Set in DynamicsДокумент6 страницProblem Set in DynamicsEugene Embalzado Jr.Оценок пока нет
- Civil Iii Year 2017-2018Документ109 страницCivil Iii Year 2017-2018Frank JohnОценок пока нет
- CE Board Nov 2022 Engineering Mechanics Set 1Документ3 страницыCE Board Nov 2022 Engineering Mechanics Set 1Meverlyn RoqueroОценок пока нет
- Hydraulics 3Документ2 страницыHydraulics 3IZОценок пока нет
- November 2023 - PSAD 1Документ2 страницыNovember 2023 - PSAD 1Viele Antonette NaranjoОценок пока нет
- Activity 4 (Data Sheet) - Alban, Ronel D.Документ1 страницаActivity 4 (Data Sheet) - Alban, Ronel D.Ronel AlbanОценок пока нет
- Activity 4 - Projectile and Air Resistance (Activity Guide) - Alban, Ronel D.Документ4 страницыActivity 4 - Projectile and Air Resistance (Activity Guide) - Alban, Ronel D.Ronel AlbanОценок пока нет
- CE RefДокумент3 страницыCE Refcat buenafeОценок пока нет
- Activity 3 (Lab Report) - Alban, Ronel D.Документ3 страницыActivity 3 (Lab Report) - Alban, Ronel D.Ronel AlbanОценок пока нет
- Local Media3116916508017834053 2Документ7 страницLocal Media3116916508017834053 2Ben BenbenОценок пока нет
- Banking of Highway Curves:: W G V R W V GRДокумент10 страницBanking of Highway Curves:: W G V R W V GRRetro GamerОценок пока нет
- Republic of The Philippines: Set - AДокумент3 страницыRepublic of The Philippines: Set - AJeana Rick GallanoОценок пока нет
- Engineering Economy: Choose The Letter of The Best Answer in Each Questions - Avoid ERASURESДокумент131 страницаEngineering Economy: Choose The Letter of The Best Answer in Each Questions - Avoid ERASURESStephanie ParkОценок пока нет
- Activity 2 (Activity Guide)Документ3 страницыActivity 2 (Activity Guide)Ronel AlbanОценок пока нет
- Practice Problems - Strema Part 1Документ4 страницыPractice Problems - Strema Part 1Meverlyn RoqueroОценок пока нет
- Earthquake Engineering LectureДокумент12 страницEarthquake Engineering LectureMeverlyn RoqueroОценок пока нет
- Dynamics of Rigid BodiesДокумент7 страницDynamics of Rigid BodiesRichelle Valerie BastroОценок пока нет
- Ce60 Theory of StructuresДокумент2 страницыCe60 Theory of StructuresKhryzzia Maye FelicildaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 Equilibrium of A Rigid BodyДокумент12 страницChapter 4 Equilibrium of A Rigid BodyWilliam JugalbotОценок пока нет
- GEOTECH 1 Module 8Документ12 страницGEOTECH 1 Module 8Earl averzosaОценок пока нет
- CE 200 GuideДокумент76 страницCE 200 GuideHeliomaykPacheco100% (1)
- Plate No. 1Документ7 страницPlate No. 1haeeyОценок пока нет
- CE3Документ20 страницCE3Memo LyОценок пока нет
- 03 Intro. Tension MemberДокумент10 страниц03 Intro. Tension MemberRi MarkuОценок пока нет
- Republic of The Philippines: Battery - 2Документ7 страницRepublic of The Philippines: Battery - 2Aileen AntipoloОценок пока нет
- Villarama Christian Michael AS1Документ11 страницVillarama Christian Michael AS1ThortheGreayОценок пока нет
- AsdfasdfasdfabДокумент4 страницыAsdfasdfasdfabFleight VandollinОценок пока нет
- Correl 2 - MathДокумент10 страницCorrel 2 - MathKevin Luis Markus PinedaОценок пока нет
- MSTE Module 6Документ2 страницыMSTE Module 6jovar jumao-asОценок пока нет
- Ce Integration: Exercise No. 2Документ3 страницыCe Integration: Exercise No. 2RonaldОценок пока нет
- University of MindanaoДокумент9 страницUniversity of MindanaoAim HighОценок пока нет
- Republic of The Philippines: Battery - 1Документ7 страницRepublic of The Philippines: Battery - 1Michael James ll BanawisОценок пока нет
- Quiz No 1Документ2 страницыQuiz No 1Tris ZackОценок пока нет
- Sample Reviewer GEOДокумент10 страницSample Reviewer GEOOwen Radaza PiranteОценок пока нет
- Refresh Module 25 (M19) - Engineering Economy 2Документ2 страницыRefresh Module 25 (M19) - Engineering Economy 2Fely Joy RelatoresОценок пока нет
- E303 Transverse WaveДокумент6 страницE303 Transverse WaveApril SaccuanОценок пока нет
- Strength of Materials: de La Salle University - DasmariñasДокумент5 страницStrength of Materials: de La Salle University - DasmariñasChynna Camille FortesОценок пока нет
- CE11 CE MATH 113A Mathematics in Modern World Trigonometry and Analytic GeometryДокумент2 страницыCE11 CE MATH 113A Mathematics in Modern World Trigonometry and Analytic GeometryJoshua John JulioОценок пока нет
- Activity 4 - Projectile and Air Resistance (Activity Guide)Документ3 страницыActivity 4 - Projectile and Air Resistance (Activity Guide)Ronel AlbanОценок пока нет
- Activity # 5: Solve The Following Problems. Show Clean and Complete Solutions For Each NumberДокумент3 страницыActivity # 5: Solve The Following Problems. Show Clean and Complete Solutions For Each NumberEurydiceОценок пока нет
- MS TowerДокумент2 страницыMS TowerSamuelОценок пока нет
- Reinforced Concrete - Shear StrengthДокумент7 страницReinforced Concrete - Shear StrengthDenice CastroОценок пока нет
- Besavilla Notes - Set 3 - 14 March 2022Документ1 страницаBesavilla Notes - Set 3 - 14 March 2022Abubakar SalikОценок пока нет
- PROBLEM SET in Hydraulics-1Документ4 страницыPROBLEM SET in Hydraulics-1Earl averzosaОценок пока нет
- CE Board May 2021 - Engineering Mechanics - Set 1Документ3 страницыCE Board May 2021 - Engineering Mechanics - Set 1paul macasaetОценок пока нет
- Ce Correl Solid GeometryДокумент3 страницыCe Correl Solid GeometryGlenn Frey LayugОценок пока нет
- Tutorials 2016Документ54 страницыTutorials 2016Mankush Jain100% (1)
- Evaluation Exam 4 April 2023Документ5 страницEvaluation Exam 4 April 2023Rena Mae BalmesОценок пока нет
- Republic of The Philippines: Battery - 2Документ8 страницRepublic of The Philippines: Battery - 2Ariel LunaОценок пока нет
- Review Module 23 Geotechnical Engineering 4 Part 1Документ2 страницыReview Module 23 Geotechnical Engineering 4 Part 1Mark Daren Patrona RamonОценок пока нет
- Basic Mathematics LectureДокумент8 страницBasic Mathematics LectureMeverlyn RoqueroОценок пока нет
- Umay DesignДокумент55 страницUmay DesignMhel CenidozaОценок пока нет
- Module 3 and 5 PDFДокумент55 страницModule 3 and 5 PDFSaptadip SahaОценок пока нет
- C1609-Flex Test For GFRCДокумент9 страницC1609-Flex Test For GFRCBrinder DhanoaОценок пока нет
- CENG198 CE Competency Appraisal IllДокумент4 страницыCENG198 CE Competency Appraisal IllJeric DinglasanОценок пока нет
- Experiment 4Документ7 страницExperiment 4Sunil FranklinОценок пока нет
- A Mini-Baja Active Suspension Modelling Using ADAMS/CAR®Документ6 страницA Mini-Baja Active Suspension Modelling Using ADAMS/CAR®Higor SufiattiОценок пока нет
- Physics Art IntegrationДокумент10 страницPhysics Art IntegrationpranjaliОценок пока нет
- CyclocopterДокумент13 страницCyclocopterAJINKYAОценок пока нет
- How Fast and Which Way?: Friday 13 October MR PatelДокумент20 страницHow Fast and Which Way?: Friday 13 October MR PatelBenjamin WatsonОценок пока нет
- Permeability Measurement - Set 1Документ6 страницPermeability Measurement - Set 1ahm531Оценок пока нет
- Sun Orifice Pressure Drop ChartsДокумент1 страницаSun Orifice Pressure Drop ChartsViji SvrОценок пока нет
- Assgn 3Документ2 страницыAssgn 3Zhiguang LiОценок пока нет
- Laboratory Shear Strength of Soils-Townsend 1981Документ720 страницLaboratory Shear Strength of Soils-Townsend 1981wabiyeomunguyeОценок пока нет
- 97 2.0f AboutДокумент12 страниц97 2.0f AboutAndrea GibsonОценок пока нет
- Lecture 3 Short Columns Small Eccentricity-Analysis-1Документ57 страницLecture 3 Short Columns Small Eccentricity-Analysis-1Syed Agha Shah AliОценок пока нет
- Ib Phys DC ESQ B 231118 135653Документ25 страницIb Phys DC ESQ B 231118 135653sammeaan khanОценок пока нет
- Stress Concentration For Transverse Circular Hole in A Round BarДокумент5 страницStress Concentration For Transverse Circular Hole in A Round BarAlem LoajnerОценок пока нет
- Paper 2Документ12 страницPaper 2Aisha ShaikhОценок пока нет
- Reinforced Concrete Beams Ultimate Strength Design: Architecture 324 Structures IIДокумент24 страницыReinforced Concrete Beams Ultimate Strength Design: Architecture 324 Structures IIanonymousupldr666Оценок пока нет
- Syllabus For Admission TestДокумент2 страницыSyllabus For Admission TestSyed Moinul HoqueОценок пока нет
- Module ListДокумент24 страницыModule ListMohammed AlnasharОценок пока нет
- Topik 6b - ExerciseДокумент4 страницыTopik 6b - ExerciseMd KhairulОценок пока нет
- The Van't Hoff Equation: Chemistry 360 Spring 2012 Dr. Jean M. StandardДокумент3 страницыThe Van't Hoff Equation: Chemistry 360 Spring 2012 Dr. Jean M. StandardAndam PluffОценок пока нет
- EjercicosДокумент8 страницEjercicosdavidОценок пока нет
- Atoms and NucleiДокумент12 страницAtoms and NucleiBablu ChaudharyОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 Lab ManualДокумент3 страницыUnit 1 Lab ManualNeidy100% (1)
- Design and Analysis of Two Stage Reduction Gearbox For All Terrain VehiclesДокумент6 страницDesign and Analysis of Two Stage Reduction Gearbox For All Terrain VehiclesKunal KoreОценок пока нет