Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Speed Vs Velocity
Загружено:
saintEmОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Speed Vs Velocity
Загружено:
saintEmАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Speed and Velocity
Learning objectives:
The learners will be able to
Understand the concept of speed and velocity
Calculate speed and velocity of moving objects using appropriate units.
Skills
Observation, recording, numerical ability, graphical representation, analyzing, inferring
and drawing conclusions based on evidence.
Materials:
Ball/marble
Stopwatch
Meterstick
Various other materials from around the room
Pre-requisite knowledge & skills
Knowledge of measuring time and distance (length)
Knowledge of fundamental units: Time second(s); Length – meter (m).
Difference between rest and motion.
Motion is relative to time and point of reference.
Different types of motion – slow and fast; uniform and non-uniform.
Objects travel in different directions and different speeds.
ENGAGE
The teacher places a car (or any object) on a table and asks students the following questions:
Is this car moving?
What is the state of car?
The class shall be divided into groups and each group will be given a ball, a car, charts and
markers. Students are asked to follow the instructions and answer the questions.
Instructions Questions
Does the position of the ball change with
respect to the position of the car?
Place the ball and car on a table
Does the car remain in the same position
with respect to the position of the ball?
What is the state of ball with respect to the car?
Now move the ball
What is the state of car with respect to the ball?
The groups will present their findings to the entire class.
Some real life situations can be given to students to draw their attention to this concept.
Q. Are we in rest or in motion while sitting in the class?
Q. Would we appear to be in rest or in motion to someone who observes us from the moon?
The motion of an object is its relative change in position with time. It is measured with respect to
a point of reference by an observer.
EXPLORE
Objective: Calculating speed using appropriate unit.
Activity: Draw a straight line on the ground with chalk powder. Ask a student to roll the
ball gently in a straight line perpendicular to the line drawn. Note the time when the ball touches
the line and when it comes to rest using a stopwatch. The distance between the two points
(point at which the ball crosses the line and the point where it comes to rest) is measured using
a ruler or a measuring tape. All these observations are recorded in the table below. The speed
of the ball in each case is calculated.
Table-1- To calculate the speed of a moving ball.
Distance moved by the Ave. Speed=
ball (m) Time taken (s) Distance/time taken (m/s)
Speed is the distance travelled by a moving body in one unit of time.
Вам также может понравиться
- Part 1: Motion Card GameДокумент12 страницPart 1: Motion Card GameNunag Mary AnnОценок пока нет
- Revised Bartels Lessonplan1 Cs WeeblyДокумент6 страницRevised Bartels Lessonplan1 Cs Weeblyapi-253521718Оценок пока нет
- Jadhav Sir - Class VI Chapter 10 - Motion and Measurement of DistancesДокумент7 страницJadhav Sir - Class VI Chapter 10 - Motion and Measurement of DistancesJoshua Hicks100% (1)
- TechnologyДокумент4 страницыTechnologyapi-297909206Оценок пока нет
- ScienceSLM G7 Q3 M2 Describing-MotionДокумент26 страницScienceSLM G7 Q3 M2 Describing-MotionXemelle SuelloОценок пока нет
- Seminar Lesson PlanДокумент18 страницSeminar Lesson PlanNo one KnowsОценок пока нет
- Developmental Lesson Plan: Common Core/PA Standard(s)Документ5 страницDevelopmental Lesson Plan: Common Core/PA Standard(s)api-542321775Оценок пока нет
- Energy in Motion: Forms, Transfers & ManifestationsДокумент103 страницыEnergy in Motion: Forms, Transfers & ManifestationsMarc XandersОценок пока нет
- Isi Makalah 3Документ25 страницIsi Makalah 3Mely TriastutiОценок пока нет
- Science Lesson 2 - Road RaceДокумент12 страницScience Lesson 2 - Road Raceapi-302768850Оценок пока нет
- Physics w5-6Документ4 страницыPhysics w5-6John JohnnyОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plans ScienceДокумент18 страницLesson Plans Scienceapi-302425735Оценок пока нет
- Connected Lesson PortfolioДокумент17 страницConnected Lesson Portfolioapi-250609869Оценок пока нет
- Cms Lesson Plan 3Документ2 страницыCms Lesson Plan 3api-272317161Оценок пока нет
- 3rd Quarter Las in Science 5Документ4 страницы3rd Quarter Las in Science 5Michael Edward De VillaОценок пока нет
- Flag Football Lesson Plan 1 FinalДокумент4 страницыFlag Football Lesson Plan 1 Finalapi-284127004Оценок пока нет
- Grade 7 Energy Guide Part 2Документ14 страницGrade 7 Energy Guide Part 2Lary BagsОценок пока нет
- J Hager Lesson Plan Locomotor and Object Control StationsДокумент4 страницыJ Hager Lesson Plan Locomotor and Object Control Stationsapi-256469641Оценок пока нет
- Autorecovery Save of FalessondanceДокумент4 страницыAutorecovery Save of Falessondanceapi-207257841Оценок пока нет
- Day 1Документ2 страницыDay 1Cyjie tanlawanОценок пока нет
- A Detailed Lesson PlanДокумент13 страницA Detailed Lesson PlanJamaicca Taboy92% (13)
- Pep 4 GymnasticsДокумент6 страницPep 4 GymnasticsPaul ChristyОценок пока нет
- 6401 Winslow p4Документ64 страницы6401 Winslow p4api-336277944Оценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan Day 2Документ4 страницыLesson Plan Day 2api-240922421Оценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan 4-6 MotionДокумент45 страницLesson Plan 4-6 MotionJ'Jane S'SiripornОценок пока нет
- Directed Reading LessonДокумент14 страницDirected Reading LessonSean SelbaОценок пока нет
- Grade 5 Q3 Week 1Документ9 страницGrade 5 Q3 Week 1joan marie PeliasОценок пока нет
- Projectile Motion Lesson PlanДокумент6 страницProjectile Motion Lesson PlanJeanRachoPaynandosОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan #1Документ4 страницыLesson Plan #1Shot TimeОценок пока нет
- One Dimensional Kinematics - Chapter OutlineДокумент55 страницOne Dimensional Kinematics - Chapter OutlineAnonymous GTCOMvОценок пока нет
- Towson University: Physical Education Lesson Plan Department of KinesiologyДокумент4 страницыTowson University: Physical Education Lesson Plan Department of KinesiologyTaylor VeraОценок пока нет
- Science IntermediateДокумент6 страницScience Intermediateaileen coleteОценок пока нет
- Teacher: Miss Cooper Grade: 10-11 Content Area: Honors Physics 1. Content and StandardsДокумент4 страницыTeacher: Miss Cooper Grade: 10-11 Content Area: Honors Physics 1. Content and Standardsapi-590983365Оценок пока нет
- Activity Sheet 3rd QTRДокумент6 страницActivity Sheet 3rd QTRMarian Anion-GauranoОценок пока нет
- Motion: Speed and Velocity: Resource ID#: 51000 Primary Type: Lesson PlanДокумент9 страницMotion: Speed and Velocity: Resource ID#: 51000 Primary Type: Lesson PlanJuloura PastorОценок пока нет
- Science7 q3 Mod2 Week3 Motion-As-A-Visual-RepresentationДокумент24 страницыScience7 q3 Mod2 Week3 Motion-As-A-Visual-RepresentationJaken Mack100% (3)
- Edug 899 - Grade 2 Forces and Motion Unit - CompletedДокумент37 страницEdug 899 - Grade 2 Forces and Motion Unit - Completedapi-241358660Оценок пока нет
- Lesson Plans Science UnitДокумент18 страницLesson Plans Science Unitapi-252157943Оценок пока нет
- Write Down The Effect It Has OnДокумент4 страницыWrite Down The Effect It Has OnWave NewОценок пока нет
- Physics ClassroomДокумент76 страницPhysics ClassroomSkefadiutoОценок пока нет
- Write Down The Effect It Has OnДокумент4 страницыWrite Down The Effect It Has OnMadhumika ThammaliОценок пока нет
- Lesson3withreflection WordДокумент5 страницLesson3withreflection Wordapi-241359020Оценок пока нет
- Physics LearningДокумент107 страницPhysics LearningcutejhomzОценок пока нет
- Kinematics LectureДокумент60 страницKinematics LectureHart GensoliОценок пока нет
- SHLT Sci 7 Q3 WK 1 OkДокумент7 страницSHLT Sci 7 Q3 WK 1 Oknoera angel montemayorОценок пока нет
- Chapter 8 MotionДокумент16 страницChapter 8 MotionSagarika MishraОценок пока нет
- Q3 Science 5 Module 1Документ19 страницQ3 Science 5 Module 1Cecilia Guevarra Dumlao100% (3)
- Motion Distance and DisplacementДокумент6 страницMotion Distance and DisplacementMaika Julian100% (1)
- Lesson 3 - UnitДокумент6 страницLesson 3 - Unitapi-242431906Оценок пока нет
- Science 9Документ22 страницыScience 9marife gupaalОценок пока нет
- Understanding Motion and Energy TransfersДокумент54 страницыUnderstanding Motion and Energy TransfersValkyrie delos Santos0% (2)
- Dribbling With Feet Unit Plan-1Документ5 страницDribbling With Feet Unit Plan-1api-284670729Оценок пока нет
- Science 4 Unit B Lesson 3Документ5 страницScience 4 Unit B Lesson 3api-380164800Оценок пока нет
- Small Group Presentation Pictures 1Документ16 страницSmall Group Presentation Pictures 1api-242929269Оценок пока нет
- GeometryДокумент4 страницыGeometryapi-252715380Оценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan Force and Motion 2Документ5 страницLesson Plan Force and Motion 2api-307403882Оценок пока нет
- Q3-Q4 Teachers Guide v1.0 PDFДокумент103 страницыQ3-Q4 Teachers Guide v1.0 PDFTitat Placedes Taniog100% (1)
- Student Teaching - Observation 4 Lesson PlanДокумент3 страницыStudent Teaching - Observation 4 Lesson Planapi-251469426Оценок пока нет
- Time Clocks: MaterialsДокумент5 страницTime Clocks: MaterialssaintEmОценок пока нет
- DLL M8 C1Документ10 страницDLL M8 C1saintEmОценок пока нет
- DLL M8 C1Документ10 страницDLL M8 C1saintEmОценок пока нет
- DLL M8 C25Документ4 страницыDLL M8 C25saintEmОценок пока нет
- DLL M8 53Документ4 страницыDLL M8 53saintEmОценок пока нет
- Create A Timeline of EarthДокумент2 страницыCreate A Timeline of EarthsaintEmОценок пока нет
- Quiz 2 History of EarthДокумент14 страницQuiz 2 History of EarthsaintEmОценок пока нет
- DLL M8 C3Документ6 страницDLL M8 C3saintEmОценок пока нет
- GeologicalTimeline PDFДокумент2 страницыGeologicalTimeline PDFMel ClancyОценок пока нет
- Typhoon Barez Caminong BlaseДокумент20 страницTyphoon Barez Caminong BlasesaintEmОценок пока нет
- Philippines Earthquake Hazard MapДокумент4 страницыPhilippines Earthquake Hazard MapsaintEmОценок пока нет
- Electricity: Flows in Only One Direction Through A WireДокумент3 страницыElectricity: Flows in Only One Direction Through A WiresaintEmОценок пока нет
- Carbon Compounds: Standard/ Class/ Grade - 10 SSC, CBSE - 8 ICSEДокумент53 страницыCarbon Compounds: Standard/ Class/ Grade - 10 SSC, CBSE - 8 ICSEsaintEmОценок пока нет
- Partsofthemicroscopeandtheirfunctions 130824115451 Phpapp02Документ20 страницPartsofthemicroscopeandtheirfunctions 130824115451 Phpapp02saintEmОценок пока нет
- Earthquakesfaults 170823093223Документ43 страницыEarthquakesfaults 170823093223saintEmОценок пока нет
- Invention of The Microscope.: The First Known Lens: 721-705BCДокумент11 страницInvention of The Microscope.: The First Known Lens: 721-705BCsaintEmОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Microscopes History Parts1606Документ28 страницIntroduction To Microscopes History Parts1606saintEmОценок пока нет
- Activity 3 Draw MeДокумент1 страницаActivity 3 Draw MesaintEmОценок пока нет
- First Quarter Examination in Science IvДокумент5 страницFirst Quarter Examination in Science IvsaintEmОценок пока нет
- OhmsLaw PSДокумент2 страницыOhmsLaw PSsaintEmОценок пока нет
- PlickersCards 2upДокумент20 страницPlickersCards 2upabrahman423Оценок пока нет
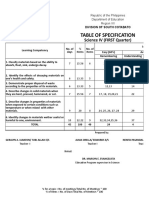
- Table of Specification: Science IV (FIRST Quarter)Документ2 страницыTable of Specification: Science IV (FIRST Quarter)saintEmОценок пока нет
- Activity 4A & 4B The Electrical Connections!Документ2 страницыActivity 4A & 4B The Electrical Connections!saintEmОценок пока нет
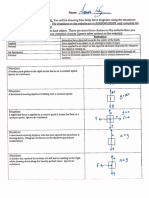
- Measure current and voltage using an ammeter and voltmeterДокумент1 страницаMeasure current and voltage using an ammeter and voltmetersaintEmОценок пока нет
- Electric Circuit Attachment 1: The LoopДокумент4 страницыElectric Circuit Attachment 1: The LoopsaintEmОценок пока нет
- Electric Circuit Attachment 1: The ShortcutДокумент5 страницElectric Circuit Attachment 1: The ShortcutsaintEmОценок пока нет
- Velocity Acceleration Lab PDFДокумент6 страницVelocity Acceleration Lab PDFUltramixОценок пока нет
- Circular Motion Lab RelationshipsДокумент3 страницыCircular Motion Lab RelationshipssaintEmОценок пока нет
- Free-Body Force Diagrams AnswersДокумент2 страницыFree-Body Force Diagrams AnswerssaintEmОценок пока нет
- Even The Rat Was White PDFДокумент2 страницыEven The Rat Was White PDFAshley0% (23)
- Se QBДокумент6 страницSe QBpriyajv14Оценок пока нет
- Organizational EffectivenessДокумент29 страницOrganizational Effectivenessabhishek ibsar100% (2)
- The Evolution of Winnicotts ThinkingДокумент369 страницThe Evolution of Winnicotts ThinkingJuan Pedro GareseОценок пока нет
- A Guide To Writing SubmissionsДокумент10 страницA Guide To Writing SubmissionsELIJAH M. OMBEOОценок пока нет
- Safety Management and Risk Modelling in AviationДокумент254 страницыSafety Management and Risk Modelling in AviationSp AndaОценок пока нет
- Self Management Strategies of Patients On Long Term DialysisДокумент57 страницSelf Management Strategies of Patients On Long Term DialysisHarby Ongbay Abellanosa100% (1)
- Understanding Social Enterprise - Theory and PracticeДокумент8 страницUnderstanding Social Enterprise - Theory and PracticeRory Ridley Duff100% (5)
- Hon. Mayor Silvestre T. Lumarda of Inopacan, Leyte, PhilippinesДокумент18 страницHon. Mayor Silvestre T. Lumarda of Inopacan, Leyte, PhilippinesPerla Pelicano Corpez100% (1)
- Prayer - PDF - TitusДокумент11 страницPrayer - PDF - TitusthepillquillОценок пока нет
- M.Tech Mechanical (Design) Semester I Scheme of Examination & Detailed SyllabusДокумент11 страницM.Tech Mechanical (Design) Semester I Scheme of Examination & Detailed SyllabuskbhattacОценок пока нет
- Should You Believe in The Trinity ?Документ8 страницShould You Believe in The Trinity ?api-26605500100% (1)
- LW Starseed TransmissionsДокумент11 страницLW Starseed Transmissionskoochimetal75% (4)
- Boling - Literary Analysis of Judges 13Документ9 страницBoling - Literary Analysis of Judges 13Michael Boling100% (1)
- Osamu Dazai and The Beauty of His LiteratureДокумент5 страницOsamu Dazai and The Beauty of His LiteratureRohan BasuОценок пока нет
- The Orthodox Tradition on Divorced and Remarried Faithful: What Can the Catholic Church LearnДокумент21 страницаThe Orthodox Tradition on Divorced and Remarried Faithful: What Can the Catholic Church LearnB.N.-RaresОценок пока нет
- Jurisprudence Ass. 5th SemДокумент21 страницаJurisprudence Ass. 5th SemanasОценок пока нет
- Ancient Civilization Brochure RubricДокумент1 страницаAncient Civilization Brochure Rubricapi-359761811Оценок пока нет
- Implementasi Pembelajaran Berbasis Hots Dalam Meningkatkan Kemampuan Analisis Mata Kuliah Pembelajaran Ips Di Sekolah DasarДокумент9 страницImplementasi Pembelajaran Berbasis Hots Dalam Meningkatkan Kemampuan Analisis Mata Kuliah Pembelajaran Ips Di Sekolah DasarMuhajir HajirОценок пока нет
- SwitchwordДокумент17 страницSwitchwordnaya17817100% (2)
- KSU Biostatistics Course OverviewДокумент157 страницKSU Biostatistics Course OverviewAdel Dib Al-jubeh100% (4)
- Afterlife of Billy Fingers ExcerptДокумент12 страницAfterlife of Billy Fingers ExcerptYady Rosario100% (3)
- Basic English Skills STT04209Документ18 страницBasic English Skills STT04209JudithОценок пока нет
- Pearsall (1991) Harmonic Progressions and Prolongation in Post Tonal MusicДокумент12 страницPearsall (1991) Harmonic Progressions and Prolongation in Post Tonal MusicLógica UsbОценок пока нет
- Kab Scout AdvancementДокумент16 страницKab Scout AdvancementJONNA BERNARDINOОценок пока нет
- Practice Is The Criterion of Truth - FumingДокумент11 страницPractice Is The Criterion of Truth - FumingAbel SoutoОценок пока нет
- Bodo Winter's ANOVA TutorialДокумент18 страницBodo Winter's ANOVA TutorialMohammad Haris MinaiОценок пока нет
- (Bernard Stiegler) Technics and Time, 1 The FaultДокумент313 страниц(Bernard Stiegler) Technics and Time, 1 The FaultFedi GloОценок пока нет
- Bailey Et Al. 2016. Using A Narrative Approach To Understand Place AttachmentsДокумент12 страницBailey Et Al. 2016. Using A Narrative Approach To Understand Place AttachmentsNatalia MolinaОценок пока нет
- Halal Diakui JAKIMДокумент28 страницHalal Diakui JAKIMwangnadaОценок пока нет
- Mental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorОт EverandMental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsОт EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingОт EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (21)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormОт EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- Making and Tinkering With STEM: Solving Design Challenges With Young ChildrenОт EverandMaking and Tinkering With STEM: Solving Design Challenges With Young ChildrenОценок пока нет
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.От EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Calculus Made Easy: Being a Very-Simplest Introduction to Those Beautiful Methods of Reckoning Which are Generally Called by the Terrifying Names of the Differential Calculus and the Integral CalculusОт EverandCalculus Made Easy: Being a Very-Simplest Introduction to Those Beautiful Methods of Reckoning Which are Generally Called by the Terrifying Names of the Differential Calculus and the Integral CalculusРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeОт EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (2)
- Strategies for Problem Solving: Equip Kids to Solve Math Problems With ConfidenceОт EverandStrategies for Problem Solving: Equip Kids to Solve Math Problems With ConfidenceОценок пока нет
- Mental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)От EverandMental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)Оценок пока нет
- Psychology Behind Mathematics - The Comprehensive GuideОт EverandPsychology Behind Mathematics - The Comprehensive GuideОценок пока нет
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsОт EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (8)
- Math Magic: How To Master Everyday Math ProblemsОт EverandMath Magic: How To Master Everyday Math ProblemsРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (15)
- Limitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersОт EverandLimitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (6)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormОт EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (20)
- How Math Explains the World: A Guide to the Power of Numbers, from Car Repair to Modern PhysicsОт EverandHow Math Explains the World: A Guide to the Power of Numbers, from Car Repair to Modern PhysicsРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (9)