Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Clustering With Conga
Загружено:
Sathiya Narayanan.gИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Clustering With Conga
Загружено:
Sathiya Narayanan.gАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
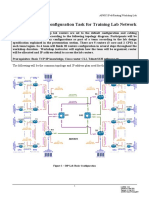
Managing RHEL Cluster with Conga
TRAINING HANDOUT
REDHAT CLUSTER
VERSION 5
Author: <BCT-Managed services >
Creation Date: Oct 10, 2011
Last Updated: October 10, 2011
Version: 1.1
Approvals:
<Name> Alagappan Vairavan
Document Control 1
1. Conga and its features 3
2. Implementing Clustering with conga 3
2.1 Patching conga Error: Reference source not found
2.2 Starting conga components 4
3. Providing login for luci server 6
4. Creating a Cluster
7
4.1 Snap-view of inputting for new cluster 8
4.2 Cluster config tab snap-view 9
5. Cluster shared ip 10
5.1 Assigning shared ip for cluster 10
5.2 Configuring an ip address resources 11
5.3 Testing shared ip accessiblity 13
6. Service Relocation 13
7. Apache HTTPD Server as Cluster Service 16
Name-Type - 14 September 2011 Page No. - 1 -
7.1 Basic httpd server configuration
16
7.2 Cluster Service Configuration
17
1. Conga and its features
Conga is an integrated set of software
components that provides centralized configuration
and Management of Red Hat clusters and storage.
Conga provides the following major features:
• One Web interface for managing cluster and
storage
• Automated Deployment of Cluster Data and
Supporting Packages
• Easy Integration with Existing Clusters
• No Need to Re-Authenticate
• Integration of Cluster Status and Logs
• Fine-Grained Control over User Permissions
2. Implementing clustering with conga
The implementation of clustering with
conga requires the
Primary component namely luci and ricci where,
Luci:
Name-Type - 14 September 2011 Page No. - 2 -
Luci is a server that runs on one computer
and communicates with multiple clusters and
computers via ricci.
Ricci:
ricci is an agent that runs on each computer
(either a cluster member or a standalone computer)
managed by Conga.
2.1 Patching Conga
The primary component of conga can be patched
as the following
a) #rpm –ivh luci-0.12.2-12.el5.i386.rpm
(Here the luci component will be installed)
b) #rpm –ivh ricci-0.12.2-12.el5.i386.rpm
(Here the ricci component will be
installed, should be patched for the each nodes
involving in the cluster)
The lists of rpm needed for Conga component are
luci-0.12.2-12.el5.i386.rpm
lvm2-cluster-2.02.56-7.el5.i386.rpm
modcluster-0.12.1-2.el5.i386.rpm
oddjob-devel-0.27-9.el5.i386.rpm
oddjob-libs-0.27-9.el5.i386.rpm
openais-0.80.6-28.el5.i386.rpm
perl-Net-Telnet-3.03-5.noarch.rpm
perl-XML-LibXML-1.58-6.i386.rpm
perl-XML-LibXML-Common-0.13-
8.2.2.i386.rpm
perl-XML-NamespaceSupport-1.09-
1.2.1.noarch.rpm
perl-XML-SAX-0.12-6_3.0.el5.noarch.rpm
pexpect-2.3-3.el5.noarch.rpm
python-imaging-1.1.5-5.el5.i386.rpm
python-pycurl-7.15.5.1-8.el5.i386.rpm
rgmanager-2.0.52-6.el5.i386.rpm
Name-Type - 14 September 2011 Page No. - 3 -
ricci-0.12.2-12.el5.i386.rpm
system-config-cluster-1.0.57-3.noarch.rpm
tix-8.4.0-11.fc6.i386.rpm
cman-2.0.115-68.el5.i386.rpm
tkinter-2.4.3-27.el5.i386.rpm
2.2 Starting the conga component services
The luci and ricci service can be started by the
following commands
#service ricci start
After input of the above command the ricci service
will be started successfully.
The start of the ricci service results in the
generation of the SSL certificate and service can be
checked out by the command
#ps –ef |grep ricci
#luci_admin init
To initialize the luci server, we use the luci_admin
init command, which results in the prompting for
the luci server admin’s password setting.
The passwd we provide with luci_admin init
command is used for accessing the luci server.
Name-Type - 14 September 2011 Page No. - 4 -
#service luci restart
The start of the luci service results in the generation
of the SSL certificate and to provide the access url
for the luci as https://192.168.1.251: 8084
The start of the luci service results in the
generation of the SSL certificate and service can be
checked out by the command
#ps –ef |grep luci
3. Providing Login for luci server
Name-Type - 14 September 2011 Page No. - 5 -
By the url https://192.168.1.251:8084, we are
able to locate in the login screen for the luci server,
which prompts for the username and the password..
Login screen snap view:
i. By default administrator is the one who can
access the luci server with login name admin
and the passwd assigned using the
luci_admin init command which can be
notified from the above snap view.
ii. Here admin is the login name inputted and
respective password too.
iii. Then the login in button is clicked to
authenticate into the luci server.
Name-Type - 14 September 2011 Page No. - 6 -
4. Creating a cluster
Conga automatically installs software
into the cluster nodes and starts the cluster. Create
a cluster as follows:
1. As administrator of luci, select the cluster tab.
2. Click Create a New Cluster.
3. At the Cluster Name text box, enter a cluster
name. The cluster name cannot exceed 15
characters. Add the node name and password for
each cluster node. Enter the node name for each
node in the Node Hostname column; enter the
root password for each node in the in the Root
Password column. Check the Enable Shared
Storage Support checkbox if clustered storage is
required.
4. Click Submit. Clicking Submit causes the
following actions:
a. Cluster software packages to be downloaded
onto each cluster node.
b. Cluster software to be installed onto each
cluster node.
c. Cluster configuration file to be created and
propagated to each node in the cluster.
d. Starting the cluster. A progress page shows
the progress of those actions for each node in the
cluster. When the process of creating a new cluster
is complete, a page is displayed providing a
configuration interface for the newly created cluster.
Name-Type - 14 September 2011 Page No. - 7 -
4.1 Snap-View of Inputting for new cluster
In the above snap view,
i. srini is the name chosen for cluster name
ii. In the node hostname column the ip
address of the cluster node have been
inputted where 192.168.1.251 is the first
cluster node ip and the 192.168.1.238 is the
second cluster node ip
iii. According to cluster node their root
password are provided in respectively
columns.
iv. Then choose the option for cluster packages
that to be installed way i.e. by manually or by
machine, any of the one option is mandatory
Name-Type - 14 September 2011 Page No. - 8 -
remaining check boxes are as per the admin
requisites.
Selecting the download packages
option is for machine automatically
downloading the packages.
The use locally installed packages
option for manual installation of the
cluster packages. Here we chosen
manual installation option so the
necessary rpm are to be installed
manually as follows
#rpm –ivh rgmanager-2.0.52-
6.el5.i386.rpm
Where,
rgmanager manages and provides
failover capabilities for collections of
resources called services, resource
groups, or resource trees in a
cluster.
#rpm –ivh clumanager-1.2.9-
1.i386.rpm
Where,
Red Hat Cluster Manager(clumanager)
provides high availability of critical
server applications in the event of
planned or unplanned system
downtime.
Click Submit. Clicking Submit causes
the clustering of the nodes, after the
successful cluster task we will be landed
in the cluster config tab of the newly
created cluster as shown in the
4.2 Cluster Config tab snap-view.
4.2 Cluster Config tab snap-view
Name-Type - 14 September 2011 Page No. - 9 -
In the above snap view, the config tab of the cluster
is shown. From that we can notify the 4 different
tabs are available
i. General tab:
The general tab issues the general properties
for the cluster like cluster name, configuration
version( the how much the cluster Config file is
edited), show advanced cluster properties(the
timeout for networking connectivity values are
assigned over here ).
ii. Fence tab:
Here the fence device we required for the
fencing and the corresponding ip address of the
fence device are inputted.
iii. Multicast tab:
The multicast address for the cluster is provided
in this tab
iv. Quorum partition tab:
The values for quorum disk are inputted here.
5. Cluster Shared ip
Name-Type - 14 September 2011 Page No. - 10 -
The shared ip for the cluster in the sense
providing a ip for accessing the cluster independent
of the ip of cluster nodes.
For example:
Consider that in the cluster we have two
nodes and there ip’s as 192.168.141,
192.168.1.164. Here we create a shared ip for the
cluster as 192.168.1.135, so that by using this
shared ip 192.168.1.135 we can access the both
cluster independent of cluster node ip's.
5.1 Assigning a Shared Ip for the Cluster
For assigning the shared ip, add the service as
follows
As an administrator of luci Select the cluster tab
and choose the cluster for which the shared ip to be
assigned, here the cluster with the name myclust
1) At the menu for cluster myclust (below
the clusters menu), click Services. This
causes the display of menu items for service
configuration: Add a
Service and Configure a Service
Name-Type - 14 September 2011 Page No. - 11 -
2) Click Add a Service. Clicking Add a
Service causes the Add a Service page to
be displayed
3) For Name, enter clust_sharedip
4) Leave the checkbox labeled automatically
start this service checked, which is the
default setting. When the checkbox is
checked, the service is started automatically
when a cluster is started and running.
5) Leave the Run Exclusive checkbox
unchecked. The Run Exclusive checkbox
sets a policy wherein the service only runs
on nodes that have no other services
running on them.
6) For Failover Domain, leave the drop-down
box default value of none. In this
configuration, all of the nodes in the cluster
may be used for failover.
7) For Recovery Policy, the drop-down box
displays select a recovery policy. Click
the drop-down box and select relocate.
8) Add the Ip Address Resource to this
resource, as described in the 5.2
configuring an ip address resource
sections.
9) After you have added the NFS resources to
the service, click Submit. The system
prompts you to verify that you want to
create this service. Clicking OK causes a
progress page to be displayed followed by
the display of Services page for the cluster.
5.2. Configuring an ip address resource
The following procedure adds the IP Address
resource 192.168.1.135 to cluster myclust.
1. At the Add a Resource page for
cluster myclust, click the drop-down box
Name-Type - 14 September 2011 Page No. - 12 -
under Select a Resource Type and select IP
Address
2. For IP Address, enter 192.168.1.135.
3. Leave the Monitor Link checkbox selected to
enable link status monitoring of the IP
address resource.
4. Click Submit. Clicking Submit displays a
verification page. Verifying that you want to
add this resource displays a progress page
followed by the display of Resources page,
which displays the resources that have been
configured for the cluster.
a) Service processing view
Once we click the submit button the cluster service
will be processed as in the above snap shot.
b) Cluster service page view
Name-Type - 14 September 2011 Page No. - 13 -
The above snap view is the page we will be landed
after successful creation of cluster service
5.3 Testing the shared ip accessibility
Now the shared ip is ready, let we test the
accessibility for the cluster.
1) Use any of source terminal emulator
application like putty, xterm etc...Here we
use putty.
Name-Type - 14 September 2011 Page No. - 14 -
2) Run the putty application, input our shared ip
in that hostname or ip address column and
select the connection type as SSH.
3) Then Click open, by pressing the open button
the connection to the 192.168.1.135 will be
established.
4) The terminal will prompt for login name and
a password. After the authentication is
success we will be placed in the cluster node
5) To make sure that we landed in cluster node,
use the ifconfig command .the output of the
ifconfig command will result in the ip address
any of the cluster nodes
6. Service Relocation
When the system crashes or rebooted,
the service running in the system are
to be served to the client with minimal
downtime.
To attain this we need to select the
relocation policies from the
dropdown list box in add a service
page.
Let we consider the scenario that the cluster node
running a service suddenly crashed , so by this
time the service running in the system need to be
relocated with the minimal downtime .
Name-Type - 14 September 2011 Page No. - 15 -
i. Checking the status of the cluster using the
clustat command
Outputs the no. of nodes presented in the
cluster and cluster service running in the
respective machines.
ii. When the system crashed , the particular
systems service will be stopped for a
instance i.e. the service state started will
be changed to stopping which can be
observed from the below snap shot.
Here the cluster node 192.168.1.115 is
crashed or leaving from system so the
service running in this system is moved to
stopping state.
iii. After the stopping state of the service it
will be move to stopped state, this
stopped state remains for a while till
another node takes the responsibility i.e.
the relocation of the service occurs, which
can be observed from the below snap
shot.
Name-Type - 14 September 2011 Page No. - 16 -
When the crashing of the system or
cluster node leaving the cluster is
confirmed, the service in the stopping
state is pushed out to the stopped state.
iv. When the relocation done the service
stopped in the crashed machine will be
relocated to the some other node in
cluster and pushed to the started state.
So the service will be available for clients.
Here the cluster node 192.168.1.107 takes the
responsbility of the crashed machine or the
machine not available in the cluster. The service
myip running in the 192.168.1.115 node is
relocated to the cluster node 192.168.1.107
and state of the service is pushed to running
state.
7. Apache HTTPD server as Cluster
Service:
The httpd server must be installed and
configured on all members in the assigned
Name-Type - 14 September 2011 Page No. - 17 -
failover domain, if used, or in the cluster. The
basic server configuration must be the same on
all members on which it runs for the service to
fail over correctly.
Checking for httpd package installed or not:-
#rpm –qa |grep httpd
7.1 Basic httpd server configuration:
The following steps provides the basic httpd
server configuration,
#cd /var/www/html
#mkdir –m 777 www.clustertesting.com
#cd /www.clustertesting.com
#vi index.html
(The index.html is the file used as the welcome
page for “www.clustertesting.com”)
#cd /etc/httpd/conf
#vi httpd.conf
(In this file edit following lines as
shown in the snap shot)
Then comment all of the lines presented in the
file” /etc/httpd/conf.d/welcome.conf “
Name-Type - 14 September 2011 Page No. - 18 -
Once the basic configuration is done, now
we can proceed with the httpd cluster
service configuration.
7.2 Cluster Service configuration:-
For cluster service configuration, we need to configure
the resources and then added to the service configuration
of Apache Httpd Server.
1) Select the Resource tab and click New. The Resource
properties dialog box with drop-down box is displayed.
a) From the drop-down list select Script option.
b) Give the Resource a name (for example, httpd-
script).
c) Specify /etc/rc.d/init.d/httpd in the User
Script field.
d) Click OK.
Name-Type - 14 September 2011 Page No. - 19 -
2) Select the Resource tab and click New. The Resource
properties dialog box with drop-down list box is
displayed from that select Ip address.
a) Then IP Address Resource Configuration properties
dialog box is displayed.
b) In the IP Address field, specify an IP address, which
the cluster infrastructure binds to the network
interface on the cluster system that runs the httpd
service (for example, 192.168.139.132).
c) Ensure that monitor link check box is checked out
d) Click Submit.
3) Select the Services tab and click New. The Service
properties dialog box is displayed.
a. Give the service a name (for example, httpd_service).
b. Check out the Automatically start this service check box
c. Choose httpd-domain from the Failover Domain
list.
Name-Type - 14 September 2011 Page No. - 20 -
d. Then choose Recovery policy as relocate form the
drop list
e. Click Add a resource to this service button and select
the resources which we have created in the above
two steps
f. Click OK.
g. Then select the httpd service and start it.
h. Navigate to the web server and check out for the
www.clustering.com as we configured
-END-
Name-Type - 14 September 2011 Page No. - 21 -
Вам также может понравиться
- Red Hat Cluster Configuration and Management: Available ResourcesДокумент55 страницRed Hat Cluster Configuration and Management: Available ResourcesParuchuri Renukadevi YerneniОценок пока нет
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkОт EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkОценок пока нет
- Web Hosting Using ISPConfigДокумент41 страницаWeb Hosting Using ISPConfigDejan NОценок пока нет
- Lab 1: ISE Familiarization and Certificate UsageДокумент15 страницLab 1: ISE Familiarization and Certificate UsageJosel ArevaloОценок пока нет
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 Administration: Real World Skills for Red Hat AdministratorsОт EverandRed Hat Enterprise Linux 6 Administration: Real World Skills for Red Hat AdministratorsОценок пока нет
- An Introduction To Kubernetes: ComponentsДокумент6 страницAn Introduction To Kubernetes: Componentsbharath_mv7-1Оценок пока нет
- Unicentre - Uniform Server User GuideДокумент97 страницUnicentre - Uniform Server User GuideggmaheshpОценок пока нет
- Set Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNОт EverandSet Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Assignment 6Документ9 страницAssignment 6api-540237180Оценок пока нет
- Nagios and Cluster On CentOSДокумент5 страницNagios and Cluster On CentOSunix500Оценок пока нет
- NF RegistrationДокумент18 страницNF Registrationmanepalli vamsiОценок пока нет
- Squid Proxy Server Configuration in Rhel 6 Step by StepДокумент4 страницыSquid Proxy Server Configuration in Rhel 6 Step by StepJithuMarrapuОценок пока нет
- k8s PrimerДокумент40 страницk8s Primersunil kalvaОценок пока нет
- Installation/Configuration Documentation of NagiosДокумент13 страницInstallation/Configuration Documentation of NagiosSyed Merazul Haque ShihabОценок пока нет
- Cheatsheet Port Forwarding and TunnelingДокумент52 страницыCheatsheet Port Forwarding and TunnelingRicky SvenchevОценок пока нет
- Port Forwarding and TunnellingДокумент54 страницыPort Forwarding and TunnellingtesthostrkОценок пока нет
- Technical Assessment For Deployment Support Engineer - Hery MunanzarДокумент6 страницTechnical Assessment For Deployment Support Engineer - Hery MunanzarMuhammad HafizОценок пока нет
- Installing and Configuring Suricata On Centos 7Документ28 страницInstalling and Configuring Suricata On Centos 7AlexanVOОценок пока нет
- AWW OnPremise Install ManualДокумент15 страницAWW OnPremise Install ManualCueindiazОценок пока нет
- Proxy Server: Amaba, Marcus Albert M. August 12, 2018 CPE51FC1 Engr. ArielДокумент14 страницProxy Server: Amaba, Marcus Albert M. August 12, 2018 CPE51FC1 Engr. ArielMarcus AmabaОценок пока нет
- Web Server & Application Lab Setup PDFДокумент70 страницWeb Server & Application Lab Setup PDFSachin BairagiОценок пока нет
- Comparing Rancher Orchestration Engine OptionsДокумент16 страницComparing Rancher Orchestration Engine OptionspalimariumОценок пока нет
- Transparent HTTPS Filtering Proxy On CentOSДокумент24 страницыTransparent HTTPS Filtering Proxy On CentOSmjtyОценок пока нет
- LABACI 1011 Python LockedДокумент23 страницыLABACI 1011 Python LockedMuhammad Shahzad100% (1)
- Modul 2 - Linux Island PDFДокумент9 страницModul 2 - Linux Island PDFKevin TimotiusОценок пока нет
- Current Situation: Dave J. Franco Devops Blanclink, IncДокумент13 страницCurrent Situation: Dave J. Franco Devops Blanclink, IncJean Carlos VicuñaОценок пока нет
- Cluster On RHL5 PDFДокумент22 страницыCluster On RHL5 PDFNoman Islam RiadОценок пока нет
- Consul Devops HandbookДокумент64 страницыConsul Devops HandbookkunalsingОценок пока нет
- IBM Two Node RHEL ClisterДокумент17 страницIBM Two Node RHEL ClisterShahulОценок пока нет
- S.D.N Implementation Using Mininet PDFДокумент7 страницS.D.N Implementation Using Mininet PDFguimanolОценок пока нет
- CCNA Security 1.0: Instructor Packet Tracer ManualДокумент53 страницыCCNA Security 1.0: Instructor Packet Tracer ManualJuanJose CMОценок пока нет
- CentOS7 Server HardeningДокумент23 страницыCentOS7 Server Hardeningmayurmorepatil96Оценок пока нет
- Integrating Zabbix and PA Subinterfaces Via APIДокумент16 страницIntegrating Zabbix and PA Subinterfaces Via APIlawОценок пока нет
- Mastering Go Network Automation: Automating Networks, Container Orchestration, Kubernetes with Puppet, Vegeta and Apache JMeterОт EverandMastering Go Network Automation: Automating Networks, Container Orchestration, Kubernetes with Puppet, Vegeta and Apache JMeterОценок пока нет
- Kubernetes For World PDFДокумент9 страницKubernetes For World PDFcumar2014Оценок пока нет
- How To Install and Use Kubernetes On Ubuntu 20.04 - CloudSigmaДокумент15 страницHow To Install and Use Kubernetes On Ubuntu 20.04 - CloudSigmaAymenОценок пока нет
- M - Controller Self Signed CertificateДокумент8 страницM - Controller Self Signed Certificateshola ogundipeОценок пока нет
- CCNASv2 SKillsAssessment-B Student Training Using ASA5506-XДокумент9 страницCCNASv2 SKillsAssessment-B Student Training Using ASA5506-XTai In Choi0% (1)
- Conjur CLI Setup - CyberArk DocsДокумент3 страницыConjur CLI Setup - CyberArk Docseduardoestrada1231013Оценок пока нет
- Publicar en LinuxДокумент8 страницPublicar en LinuxnatojОценок пока нет
- LKSN TKJ 2019 Modul DДокумент11 страницLKSN TKJ 2019 Modul DMøhâmmƎd Ålqî FahrƎziОценок пока нет
- Lksn2019 Itnetwork Modul D ActualДокумент11 страницLksn2019 Itnetwork Modul D Actualarizal putraОценок пока нет
- Docker SwarmДокумент9 страницDocker SwarmAnkit RathoreОценок пока нет
- 1-Module 01 Basic & InterfaceДокумент35 страниц1-Module 01 Basic & InterfacevajragantaОценок пока нет
- Configure High Availability Cluster in Centos 7 (Step by Step Guide)Документ9 страницConfigure High Availability Cluster in Centos 7 (Step by Step Guide)HamzaKhanОценок пока нет
- ELK SetupДокумент16 страницELK Setupdell xpsОценок пока нет
- SCA Scan Vulnerabilities On Nutanix IlosДокумент24 страницыSCA Scan Vulnerabilities On Nutanix IlosToonkraft SchefferОценок пока нет
- Install and Configure Freeipa Server On Centos 8 / Rhel 8Документ10 страницInstall and Configure Freeipa Server On Centos 8 / Rhel 8Pappu KumarОценок пока нет
- ProjectДокумент13 страницProjectakhil krishnanОценок пока нет
- TutorialsДокумент175 страницTutorialsmanshul.ahuja9841Оценок пока нет
- DCA - SecurityДокумент12 страницDCA - SecurityMuntashir IslamОценок пока нет
- DCA - Section 6 SecurityДокумент12 страницDCA - Section 6 SecurityValiS1234Оценок пока нет
- Cisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3От EverandCisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3Оценок пока нет
- Micro Framework Readthedocs Io en LatestДокумент279 страницMicro Framework Readthedocs Io en LatestJenal AbidinОценок пока нет
- Intelligent Wan Public Key Infrastructure Deployment Guide: Cisco Validated DesignДокумент25 страницIntelligent Wan Public Key Infrastructure Deployment Guide: Cisco Validated Designsrinivas gavaraОценок пока нет
- Which Security Implementation Will Provide Control Plane Protection For A Network DeviceДокумент34 страницыWhich Security Implementation Will Provide Control Plane Protection For A Network DeviceCallyNnaemekaOkekeОценок пока нет
- Practical: 5Документ19 страницPractical: 520DCS138 MEET VAGAHNIОценок пока нет
- Zabbix Manual v1.6Документ314 страницZabbix Manual v1.6alexander.rozhkov100% (2)
- Computer ProgrammingДокумент30 страницComputer ProgrammingJeavs VargasОценок пока нет
- Manual 2002024 Charger For Cylindrical Cells Nicd Nimh Nizn Voltcraft Charge Manager cm2024 Aaa Aa C D 9v pp3Документ13 страницManual 2002024 Charger For Cylindrical Cells Nicd Nimh Nizn Voltcraft Charge Manager cm2024 Aaa Aa C D 9v pp3GonzalezОценок пока нет
- Feedback: Your Answer Is Correct. The Correct Answer Is: The Strings FileДокумент9 страницFeedback: Your Answer Is Correct. The Correct Answer Is: The Strings Fileeiram etteirrahОценок пока нет
- Kenwood Kdc-203s 209sДокумент19 страницKenwood Kdc-203s 209skriegsterОценок пока нет
- HP Bladesystem C-Class Architecture: Technology Brief, 2Nd EditionДокумент28 страницHP Bladesystem C-Class Architecture: Technology Brief, 2Nd EditionNone NoneОценок пока нет
- MVC Sample IndtroductionДокумент3 страницыMVC Sample Indtroductionrajeshb1392Оценок пока нет
- Profibus Encoder ConnectionДокумент74 страницыProfibus Encoder ConnectionRoberto CedilloОценок пока нет
- Tiers PDFДокумент13 страницTiers PDFAditya BalodiОценок пока нет
- Www.tutorialspoint.comДокумент16 страницWww.tutorialspoint.comGyanendra SinghОценок пока нет
- David Both, Cyndi Bulka - Linux For Small Business Owners - Using Free and Open Source Software To Power Your Dreams-Apress (2022)Документ391 страницаDavid Both, Cyndi Bulka - Linux For Small Business Owners - Using Free and Open Source Software To Power Your Dreams-Apress (2022)trading bitgetОценок пока нет
- More ImportantДокумент30 страницMore ImportantJanaki BaskaranОценок пока нет
- Imagerunner Advance v3.8 System SM en 3.0Документ215 страницImagerunner Advance v3.8 System SM en 3.0Майор ДеяновОценок пока нет
- Matrikon - OPC Tunneller User Manual PDFДокумент79 страницMatrikon - OPC Tunneller User Manual PDFAshish GowandeОценок пока нет
- Formateo de DUW para Carga de DiscosДокумент3 страницыFormateo de DUW para Carga de DiscosTHE jerexd777Оценок пока нет
- Lab9 MT127Документ16 страницLab9 MT127Jordan laucoОценок пока нет
- Mipi D-PHY Specification v2-5 PDFДокумент234 страницыMipi D-PHY Specification v2-5 PDFson nguyen100% (1)
- 02:network Routers and Routing ProtocolsДокумент48 страниц02:network Routers and Routing ProtocolsJohnBenardОценок пока нет
- Learn More About The ASUS G750JX-IB71: ModelДокумент2 страницыLearn More About The ASUS G750JX-IB71: ModelMihai ZamfirОценок пока нет
- Azure Deployment Offer FAQ - FY15 (Internal Only)Документ51 страницаAzure Deployment Offer FAQ - FY15 (Internal Only)SergeyОценок пока нет
- sx60-100 - Operating Manual PDFДокумент112 страницsx60-100 - Operating Manual PDFmirceaОценок пока нет
- Plugins Check - in Maintenance Mode-2022!01!16-Jam18.57Документ13 страницPlugins Check - in Maintenance Mode-2022!01!16-Jam18.57peterОценок пока нет
- Von Neumann ArchitectureДокумент13 страницVon Neumann ArchitectureRavi Anand100% (1)
- ZTE EMS Client Installation Guide PDFДокумент11 страницZTE EMS Client Installation Guide PDFSohaib AbdullahОценок пока нет
- PT 10 SierraДокумент1 страницаPT 10 SierraFernando Se-Ord Jr.100% (1)
- JVM Out of Memory in PlkanningДокумент7 страницJVM Out of Memory in PlkanningBiswanath NandaОценок пока нет
- Progscilab SoДокумент76 страницProgscilab Sostephen562001Оценок пока нет
- BigData - Sem 4 - Elective 1 - Module 2 - PPTДокумент29 страницBigData - Sem 4 - Elective 1 - Module 2 - PPThitaarnavОценок пока нет
- Infamous 2 PC Game Torrent Free Download PDFДокумент4 страницыInfamous 2 PC Game Torrent Free Download PDFAshleyОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1: Introduction: Jurusan Teknik Informatika UNTAG Surabaya 1Документ39 страницChapter 1: Introduction: Jurusan Teknik Informatika UNTAG Surabaya 1dayat_ridersОценок пока нет