Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
IP Medical Oxygen Production SOP
Загружено:
Ram NОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
IP Medical Oxygen Production SOP
Загружено:
Ram NАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Standard Operating Procedure for IP Medical Oxygen
Introduction
Medical oxygen is used in treating patients with reduced tissue oxygen saturation levels and
reduced perfusion to the brain. By supplying oxygen from external source at high concentration,
saturation levels above 90% is maintained.
Industrial production of medical oxygen as per IP 2014 monograph requires oxygen not less than
90 per cent v/v, carbon dioxide not more than 300 ppm v/v, carbon monoxide not more than 5 ppm
v/v and water vapour not more than 67 ppm v/v.
Quality Adherence
manufacturing at our unit is done by air separation and compression process to achieve purities
greater than 99.5 plus/minus 0.2 per cent with pressure of around 145 pounds per square
inch.The analysis for purity is continuously done with the help of assay method which is one of the
methods specified as per Indian Pharmacopeia 2014 before batch sample testing, labelling and
dispatch.
Process
The air from atmosphere is suctioned through the filter which absorbs particulate matter in the air.
The air is then passed through a four stage compressor which is a horizontal tandem type. The
compressor has both inter and after cooler to cool the ambient atmospheric air. The air is then
passed through moisture separator chamber which is part of the compressor assembly. The
medium processed dry ambient air then is passed through a nitran cooler where the outgoing
nitrogen cools the incoming air. The medium pressure dry cooled air then passes through the
vaporisation cooler where moisture is absorbed. It then passes through filter where acetylene
impurities are absorbed, then it enters the chilling unit where the air is further chilled. Further it
passes through molecular sieve column where the carbon dioxide is adsorbed before entering the
column. The air then contains two major gases i.e. Oxygen, Nitrogen and rare gases.
The column has three levels the lower part where partial liquefaction takes place forming liquid rich
in oxygen at minus 183 degree centigrade.
The rising vapours in bottom column consisting mostly of Nitrogen are condensed by liquid oxygen
in the condenser of the rectification column.
The condensed liquid collects in the skirt bath at the bottom of the condenser and is called poor
liquid.
The rich and poor liquids thus formed are passed through an expansion engine where they are
expanded through valves and are taken to appropriate points of the top column.
Nitrogen being more volatile passes out as a gas from the tap of it in a vapour form . Nitrogen and
oxygen pass through heat exchangers 1 & 2 thus cooling the incoming air.
Thus high purity oxygen is formed which is then pumped under pressure into the filling points
where cylinders are connected.
Вам также может понравиться
- Oxygen Plant Process GuideДокумент4 страницыOxygen Plant Process Guidebrad100% (1)
- Oxygen PlantДокумент10 страницOxygen Plantshoaib705Оценок пока нет
- Manufact Liquid OxygenДокумент2 страницыManufact Liquid Oxygenz leeОценок пока нет
- 01 OxygenДокумент2 страницы01 OxygenMani ManiОценок пока нет
- Oxygen Plant ManualДокумент54 страницыOxygen Plant Manualmahaveen89% (18)
- Air Generation & Distribution SystemsДокумент46 страницAir Generation & Distribution SystemsHuzai AzmanОценок пока нет
- An Air Separation Plant Separates Atmospheric Air Into Its Primary ComponentsДокумент4 страницыAn Air Separation Plant Separates Atmospheric Air Into Its Primary ComponentsAbhinav AjmaniОценок пока нет
- Department of Mechatronics and Control Engineering University of Engineering and Technology, LahoreДокумент20 страницDepartment of Mechatronics and Control Engineering University of Engineering and Technology, LahoreEman FatimaОценок пока нет
- Introduction WPS OfficeДокумент4 страницыIntroduction WPS Officealhag alhebirОценок пока нет
- Epa CertificationДокумент124 страницыEpa Certificationplumbguru100% (5)
- Basic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Unit V Refrigeration and Airconditioning Support NotesДокумент9 страницBasic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Unit V Refrigeration and Airconditioning Support NotesA.R. Pradeep Kumar100% (1)
- Process Description Nitric Acid ProductionДокумент2 страницыProcess Description Nitric Acid ProductionLaman AlipashayevaОценок пока нет
- Assignment: Oxygen Sugar Industries M.Noman Raza CHДокумент7 страницAssignment: Oxygen Sugar Industries M.Noman Raza CHGlobal PMC100% (1)
- Cryogenic Air Separation Unit Maintenance TipsДокумент14 страницCryogenic Air Separation Unit Maintenance Tipsokoro matthewОценок пока нет
- Performance (COP) Analysis of A Vapour Compression Refrigeration System Component With Nano CoatingДокумент4 страницыPerformance (COP) Analysis of A Vapour Compression Refrigeration System Component With Nano CoatingantonytechnoОценок пока нет
- Performance Evaluation of Wick Cooled Evaporative CondenserДокумент14 страницPerformance Evaluation of Wick Cooled Evaporative CondenserShobhit GargОценок пока нет
- Nitrogen Production From AirДокумент9 страницNitrogen Production From AirOusseini SidibeОценок пока нет
- Refrigeration Air ConditioningДокумент7 страницRefrigeration Air Conditioningkonduri chaitanyaОценок пока нет
- Oxygen, Nitrogen, Propane Methane CondenseДокумент7 страницOxygen, Nitrogen, Propane Methane Condensekonduri chaitanyaОценок пока нет
- Startup of An Air Separation PlantДокумент3 страницыStartup of An Air Separation Plantcymy0% (1)
- Automotive Air Conditioning and Heating System PDFДокумент19 страницAutomotive Air Conditioning and Heating System PDFCarl AriffОценок пока нет
- Oxygen ProjectДокумент9 страницOxygen ProjectMukesh TamangОценок пока нет
- Oxygen PlantsДокумент7 страницOxygen PlantsAlina SweetОценок пока нет
- Air Composition DryДокумент11 страницAir Composition DryrahulОценок пока нет
- Group 5 Melab3Документ14 страницGroup 5 Melab3Gigi SalesОценок пока нет
- Hvac Lab Report: Name: Ali Raza Roll No: 18-MCE-18 Submitted To: Sir Murawat Abbas Semester 6Документ11 страницHvac Lab Report: Name: Ali Raza Roll No: 18-MCE-18 Submitted To: Sir Murawat Abbas Semester 6AliОценок пока нет
- Pipeline DryingДокумент14 страницPipeline DryingMAHESH CHANDОценок пока нет
- Air DryersДокумент4 страницыAir Dryersmanpreetsodhi08Оценок пока нет
- Heat Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC)Документ46 страницHeat Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC)Sagar GoyalОценок пока нет
- Combined PPT PSA Oxygen PlantДокумент39 страницCombined PPT PSA Oxygen Plantshivani50% (2)
- 1 Chapter Eight INERT GAS PLANT 8.1 DesignДокумент15 страниц1 Chapter Eight INERT GAS PLANT 8.1 DesignsugumarОценок пока нет
- Industrial Visit To Centralized Air Conditioning SystemДокумент9 страницIndustrial Visit To Centralized Air Conditioning SystemsoumikОценок пока нет
- Medical-GasesДокумент3 страницыMedical-GasesRavikumar VejandlaОценок пока нет
- Different Type Air DryerДокумент9 страницDifferent Type Air DryermishtinilОценок пока нет
- 4.4 Principles To Air Conditioning SystemДокумент14 страниц4.4 Principles To Air Conditioning SystemRose EizzaОценок пока нет
- Sterile Products 2023 Part DДокумент63 страницыSterile Products 2023 Part DSHAHIQОценок пока нет
- Air SamplingДокумент47 страницAir SamplingSkariah MathewsОценок пока нет
- ASU - Air Separation UnitДокумент2 страницыASU - Air Separation Unitsajalkk25Оценок пока нет
- My Time at Urea-2 Plant and Key Equipment DetailsДокумент6 страницMy Time at Urea-2 Plant and Key Equipment DetailsUzair AshrafОценок пока нет
- Pressure Swing AdsorptionДокумент10 страницPressure Swing Adsorptionradhika.rdtОценок пока нет
- Report of DehumidificationДокумент5 страницReport of DehumidificationMahmoud MerdanОценок пока нет
- Brief Description of Urea ProcessДокумент7 страницBrief Description of Urea ProcessGaurav Mishra100% (1)
- Instrument AirДокумент6 страницInstrument Airasarobin1989Оценок пока нет
- Refregeration, Psychrometry & Air ConditioningДокумент47 страницRefregeration, Psychrometry & Air ConditioningTamim Islam JoyОценок пока нет
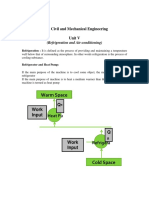
- Warm Space: Basic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Unit VДокумент11 страницWarm Space: Basic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Unit VThulasi RamОценок пока нет
- Nitric Acid Process AbstractДокумент2 страницыNitric Acid Process AbstractEduardo MagallonОценок пока нет
- Hvac Notes With Manual Heat Load CalculationsДокумент129 страницHvac Notes With Manual Heat Load CalculationsUzorОценок пока нет
- Hvac Notes With Heat Load Calculation For 2 ProjectsДокумент256 страницHvac Notes With Heat Load Calculation For 2 ProjectsAjayОценок пока нет
- Scheme To Produce Liquid Nitrogen - From Boschi in ItalyДокумент3 страницыScheme To Produce Liquid Nitrogen - From Boschi in ItalyjohnОценок пока нет
- Argon Recovery UnitsДокумент6 страницArgon Recovery UnitsazizahmonikaОценок пока нет
- Air Refrigerant 2015Документ18 страницAir Refrigerant 2015Aman RedhaОценок пока нет
- Gas Plant ProcessingДокумент36 страницGas Plant Processingvanmurthy100% (1)
- Addis Ababa Institute of Technology: Center of Biomedical EngineeringДокумент6 страницAddis Ababa Institute of Technology: Center of Biomedical EngineeringYabОценок пока нет
- 500 TPD Nitric Acid PlantДокумент18 страниц500 TPD Nitric Acid PlantAndreea Ioana100% (1)
- Nitric AcidДокумент18 страницNitric AcidJaamac DhiilОценок пока нет
- Basic Operation of The SystemДокумент23 страницыBasic Operation of The SystemBARNABAS DOGOОценок пока нет
- Single Effect Evaporator 2Документ22 страницыSingle Effect Evaporator 2Shailesh Lohare100% (1)
- Liqifaction Lesson 6Документ10 страницLiqifaction Lesson 6navlesh kumarОценок пока нет
- Contemporary Anaesthetic Equipments.: An Aid for Healthcare ProfessionalsОт EverandContemporary Anaesthetic Equipments.: An Aid for Healthcare ProfessionalsОценок пока нет
- AMGG-S - 1 - Environmental Safeguard Monitoring - 25.03.2021Документ48 страницAMGG-S - 1 - Environmental Safeguard Monitoring - 25.03.2021Mahidul Islam RatulОценок пока нет
- Chemical Process Safety Toxicology Dose Response Data AnalysisДокумент8 страницChemical Process Safety Toxicology Dose Response Data AnalysisMuhammad Noor WaliОценок пока нет
- Osteo Book Final 2014Документ51 страницаOsteo Book Final 2014hyanandОценок пока нет
- Agri & Food Processing - Biscuit Manufacturing UnitДокумент6 страницAgri & Food Processing - Biscuit Manufacturing Unitvijayind2006Оценок пока нет
- Eng & FLS Standards Rev.1 (Dec. 2018)Документ72 страницыEng & FLS Standards Rev.1 (Dec. 2018)Nalan BAHCEKAPILIОценок пока нет
- Single Inlet Centrifugal FanДокумент43 страницыSingle Inlet Centrifugal Fan4uengineerОценок пока нет
- Cyril Cromier, Frost & SullivanДокумент24 страницыCyril Cromier, Frost & SullivanGaurav SahuОценок пока нет
- Gimnazjum Exam Practice GuideДокумент74 страницыGimnazjum Exam Practice GuideVaserd MoasleОценок пока нет
- Tracking SARDO StudentsДокумент2 страницыTracking SARDO StudentsLean ABОценок пока нет
- Extraction and Isolation of Saponins PDFДокумент2 страницыExtraction and Isolation of Saponins PDFMikeОценок пока нет
- Measles/ Rubella & VPD Surveillance:: Allotment of EPID Number and Outbreak IDДокумент7 страницMeasles/ Rubella & VPD Surveillance:: Allotment of EPID Number and Outbreak IDDevendra Singh TomarОценок пока нет
- Prof Educ 2: Foundation of Special and Inclusive EducationДокумент12 страницProf Educ 2: Foundation of Special and Inclusive EducationNerissa Custosa BastoОценок пока нет
- Stormwater CalculationДокумент66 страницStormwater CalculationDinesh DurairajОценок пока нет
- Polymer MaterialsДокумент31 страницаPolymer MaterialsDaithi Mac DomhnaillОценок пока нет
- EMAAR HOUSING HVAC SYSTEM SPECIFICATIONSДокумент91 страницаEMAAR HOUSING HVAC SYSTEM SPECIFICATIONSBhuvan BajajОценок пока нет
- MIDWIFE1115ra Tugue e PDFДокумент9 страницMIDWIFE1115ra Tugue e PDFPhilBoardResultsОценок пока нет
- Deltair BrochureДокумент4 страницыDeltair BrochureForum PompieriiОценок пока нет
- Review of Literature Review of LiteratureДокумент31 страницаReview of Literature Review of LiteratureeswariОценок пока нет
- Environmental Stewardship - Sustainability Assignment - Ethan GabrielДокумент3 страницыEnvironmental Stewardship - Sustainability Assignment - Ethan GabrielEthan GabrielОценок пока нет
- Strategies and Tactics for Collecting on Overdue AccountsДокумент9 страницStrategies and Tactics for Collecting on Overdue AccountsAkii WingОценок пока нет
- Assignment of PsychologyДокумент28 страницAssignment of PsychologyMuhammad Hamza AshfaqОценок пока нет
- Three Little PigsДокумент9 страницThree Little PigsrОценок пока нет
- NCM 117 Rle NAME: Guerzo, Danniel Dave Y. DATE/TIME: March 9, 2023 Section/Year Level: BSN 3B Group No:10 CIДокумент2 страницыNCM 117 Rle NAME: Guerzo, Danniel Dave Y. DATE/TIME: March 9, 2023 Section/Year Level: BSN 3B Group No:10 CISherlyn Miranda GarcesОценок пока нет
- Weld Procedure Specification (WPS) : Joint Design Welding SequenceДокумент1 страницаWeld Procedure Specification (WPS) : Joint Design Welding SequenceRicardo SoaresОценок пока нет
- Case Digest 16Документ2 страницыCase Digest 16Mavic MoralesОценок пока нет
- HZB-15S Service ManualДокумент20 страницHZB-15S Service ManualJason Cravy100% (1)
- HRLM - Catalogue # Ex Apparatus - AC-Z Series Explosion Proof Plug and ReceptaclesДокумент2 страницыHRLM - Catalogue # Ex Apparatus - AC-Z Series Explosion Proof Plug and Receptaclesa wsОценок пока нет
- The 24-Inch Gauge and The Common Gavel - An Entered Apprentice Mason's Perspective On The Medical ProfessionДокумент4 страницыThe 24-Inch Gauge and The Common Gavel - An Entered Apprentice Mason's Perspective On The Medical ProfessionMarcelo Carlos RibeiroОценок пока нет
- Tata Bluescope Steel Limited, Jamshedpur.: Liquefied Petroleum Gas Material Safety Data SheetДокумент6 страницTata Bluescope Steel Limited, Jamshedpur.: Liquefied Petroleum Gas Material Safety Data Sheetsujit5584Оценок пока нет
- Environmental Pollution and DegradationДокумент2 страницыEnvironmental Pollution and DegradationCharLene MaRieОценок пока нет