Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Geotechnical Engineering 2 (Foundation Engineering) Lecturer: Engr. Mmrtating
Загружено:
Jose Leo Icaro Talion0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
9 просмотров1 страницаThis document outlines the course content for a Geotechnical Engineering 2 course focused on foundation engineering. The course covers topics such as compressibility and shear strength of soils, triaxial tests, soil bearing capacity, settlement analysis, lateral earth pressure, slope stability, retaining walls, sheet pile walls, braced cuts, and pile foundations. Key concepts covered include Rankine's and Coulomb's theories of lateral earth pressure, factors of safety for slope stability, types of retaining walls and piles, and methods for estimating pile capacity and settlement. Design of reinforced concrete footings is also addressed, including isolated, combined, trapezoidal, and strap footings.
Исходное описание:
Geotechnical Engineering
Оригинальное название
Course Outline
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThis document outlines the course content for a Geotechnical Engineering 2 course focused on foundation engineering. The course covers topics such as compressibility and shear strength of soils, triaxial tests, soil bearing capacity, settlement analysis, lateral earth pressure, slope stability, retaining walls, sheet pile walls, braced cuts, and pile foundations. Key concepts covered include Rankine's and Coulomb's theories of lateral earth pressure, factors of safety for slope stability, types of retaining walls and piles, and methods for estimating pile capacity and settlement. Design of reinforced concrete footings is also addressed, including isolated, combined, trapezoidal, and strap footings.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
9 просмотров1 страницаGeotechnical Engineering 2 (Foundation Engineering) Lecturer: Engr. Mmrtating
Загружено:
Jose Leo Icaro TalionThis document outlines the course content for a Geotechnical Engineering 2 course focused on foundation engineering. The course covers topics such as compressibility and shear strength of soils, triaxial tests, soil bearing capacity, settlement analysis, lateral earth pressure, slope stability, retaining walls, sheet pile walls, braced cuts, and pile foundations. Key concepts covered include Rankine's and Coulomb's theories of lateral earth pressure, factors of safety for slope stability, types of retaining walls and piles, and methods for estimating pile capacity and settlement. Design of reinforced concrete footings is also addressed, including isolated, combined, trapezoidal, and strap footings.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 1
GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING 2(Foundation Engineering)
Lecturer: Engr. MMRTating
COURSE TITLE: GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING 2 • Rectangular isolated footing.
(Foundation Engineering) • Footing on piles.
COURSE CODE: CE -17/CE -17D • Rectangular combined footing.
TIME/DAYS : 1:00 - 2:30/2:30 – 4:O0/MTh • Trapezoidal footing.
ROOM : SML • Strap footing.
CHAPTER 6 : LATERAL EARTH PRESSURE
COURSE DESCRIPTION: ➢ At – rest Lateral Earth pressure
The introductory part of this course deals with the ➢ Rankine’s Theory of Active and Passive Earth
some fundamentals of geotechnical engineering that Pressure
includes compressibility of soil, shear strength of soils, ➢ Coulumb’s Theory of Active and Passive Earth
triaxial tests of soils, settlement, lateral earth pressure, Pressure
soil bearing capacity, slope stability, and earth retaining
➢ Lateral earth pressure – Curved Failure Surface
structures.
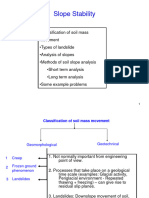
CHAPTER 7 : SLOPE STABILITY
The second part of this course deals with the design
of reinforced concrete footings such as wall footing, ➢ Factor of Safety
square isolated footing (subject to axial load, and to ➢ Stability of infinite slopes
axial load and bending moment), rectangular footing ➢ Stability of finite slopes
(isolated and combined), trapezoid footing, footing on CHAPTER 8 : RETAINING WALLS
piles, and strap footing. ➢ Gravity and Cantilever walls
• Proportioning Retaining walls
COURSE OUTLINE: • Stability of Retaining walls
CHAPTER 1 : COMPRESSIBILITY OF SOILS (Overturning, sliding and bearing
➢ Immediate Settlement capacity failure)
➢ Settlement due to primary consolidation of soil CHAPTER 9 : SHEET PILE WALLS
(for normally consolidated soil and ➢ Cantilever Sheet pile wall
overconsolidated clays), ➢ Anchored sheet pile walls
➢ Compression Index (Cc) and Swell index (Cs) CHAPTER 10 : BRACED CUTS
➢ Secondary Consolidation settlement ➢ Pressure envelope for braced cut design
CHAPTER 2 : SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOILS ➢ Pressure envelope for cuts in layered soil
➢ Mohr Coulomb Failure Criterion ➢ Design of various components of braced cut.
➢ Inclination of the failure plane caused by shear CHAPTER 11 : PILE FOUNDATIONS
➢ Direct shear test (normally consolidated and ➢ Types of piles and its structural characteristics
overconsolidated clays). ➢ Estimating pile capacity Qp and Qs
CHAPTER 3 : TRIAXIAL TESTS OF SOIL ➢ Elastic settlement of piles
➢ Consolidated-Drained triaxial test. ➢ Negative skin friction
➢ Consolidated-Undrained Triaxial Test ➢ Pile Group
➢ Unconsolidated – Undrained Triaxial Test
➢ Unconfined Compression Test REFERENCES:
➢ Stress Path
CHAPTER 4 : SOIL BEARING CAPACITY AND SETTLEMENT 1. PRINCIPLES OF FOUNDATION ENGINEERING
ANALYSIS BRAJA DAS
➢ Terzaghi’s Bearing Capacity, Factor of Safety 2. PRINCIPLES OF GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING
➢ Modification due to effect of Water Table BRAJA DAS
➢ General Bearing Capacity Equation (Meyerof’s 3. FOUNDATION ANALYSIS AND DESIGN
bearing capacity factors) JOSEPH E. BOWLES
➢ Vertical Stress Increase due to foundation load
• Point Load, Line load, uniformly
loaded circular and rectangular area
CHAPTER 5: FOUNDATION STRUCTURES
(SHALLOW FOUNDATIONS)
➢ DESIGN OF REINFORCED CONCRETE FOOTING:
• Wall footing.
• Square isolated footing subjected to axial
load, and axial load and bending moment.
Вам также может понравиться
- Structural Concrete: The Commonwealth and International Library: Structures and Solid Body Mechanics DivisionОт EverandStructural Concrete: The Commonwealth and International Library: Structures and Solid Body Mechanics DivisionОценок пока нет
- Basic Theory of Structures: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionОт EverandBasic Theory of Structures: The Commonwealth and International Library: Mechanical Engineering DivisionРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (4)
- Geotechnical Engineering-Ii: BSC Civil Engineering - 5 SemesterДокумент33 страницыGeotechnical Engineering-Ii: BSC Civil Engineering - 5 SemesterInam UllahОценок пока нет
- Shoring Design Criteria - Anchored Soldier Pile and Lagging - HJY - Oct 2015Документ114 страницShoring Design Criteria - Anchored Soldier Pile and Lagging - HJY - Oct 2015KHOA TRANОценок пока нет
- 4610 sl4Документ73 страницы4610 sl4Rodrigo de León100% (1)
- HATTI Mengajar - 19082021Документ47 страницHATTI Mengajar - 19082021Hilmy anugrah indra karya pola teknikОценок пока нет
- Study of Failure of Pile Foundation Due To Earthquake & Its Remedial MeasuresДокумент6 страницStudy of Failure of Pile Foundation Due To Earthquake & Its Remedial MeasuresSaurabhmani ChaturvediОценок пока нет
- ECS478 CHAPTER 6-Retaining WallДокумент56 страницECS478 CHAPTER 6-Retaining Wallmuhammad nuruddin che ab malik100% (1)
- Amit Kumar CE18M021 Guided by Prof P AlagusundaramoorthyДокумент14 страницAmit Kumar CE18M021 Guided by Prof P AlagusundaramoorthyAmit KumarОценок пока нет
- Lecture 1 Lateral Earth PressureДокумент17 страницLecture 1 Lateral Earth PressureAbel MekbibОценок пока нет
- Analysis of Retaining Wall On Sap 2000Документ34 страницыAnalysis of Retaining Wall On Sap 2000Swamy ManiОценок пока нет
- Seismic Design of Retaining WallsДокумент23 страницыSeismic Design of Retaining WallsRutvik ShethОценок пока нет
- Bearing Capacity Analysis For Earthquakes: Dr. G. Kalyan KumarДокумент65 страницBearing Capacity Analysis For Earthquakes: Dr. G. Kalyan KumarSai Asrith PylaОценок пока нет
- Pile & Pier Foundation Analysis & DesignДокумент73 страницыPile & Pier Foundation Analysis & DesignOentoeng KartonoОценок пока нет
- Well Foundation-Dr. S. G. ShahДокумент48 страницWell Foundation-Dr. S. G. ShahSG ShahОценок пока нет
- Module 01Документ21 страницаModule 01Niña Criselle PasiaОценок пока нет
- C0 IntroductionДокумент27 страницC0 IntroductionSara LaiОценок пока нет
- Analysis of Retaining Wall On Sap 2000Документ34 страницыAnalysis of Retaining Wall On Sap 2000qwerty qwerty75% (4)
- Strata Control Coal SyllabusДокумент9 страницStrata Control Coal Syllabusgopotso NgaloОценок пока нет
- Supported Excavations: Sheet Pile Retaining Walls and Bracing Frame Retaining WallsДокумент65 страницSupported Excavations: Sheet Pile Retaining Walls and Bracing Frame Retaining WallsZaid AlsarayrehОценок пока нет
- Presentation For PT Building and DesignДокумент28 страницPresentation For PT Building and DesignAmarjeet ChauhanОценок пока нет
- Stresses and Strains: LE/CIVL 3110 Soil MechanicsДокумент25 страницStresses and Strains: LE/CIVL 3110 Soil MechanicsSteven KhanОценок пока нет
- CVLE 432 Foundation Engineering: Course Syllabus - Spring 2015-2016Документ2 страницыCVLE 432 Foundation Engineering: Course Syllabus - Spring 2015-2016Marc Edwin VergaraОценок пока нет
- Lateral Earth Pressures For Seismic Design of Cantilever Retaining WallsДокумент8 страницLateral Earth Pressures For Seismic Design of Cantilever Retaining Wallsredpol100% (2)
- 8.CE 483 Retaining Walls CH 17 3rd 1444 - 2Документ95 страниц8.CE 483 Retaining Walls CH 17 3rd 1444 - 2Saad MohammedОценок пока нет
- Fancisco Crisafull Seminar PDFДокумент21 страницаFancisco Crisafull Seminar PDFarvindОценок пока нет
- C1 IntroductionANDShear StrengthДокумент38 страницC1 IntroductionANDShear StrengthabeybОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3a) Retaining WallsДокумент18 страницChapter 3a) Retaining WallslawrenceОценок пока нет
- 1soil Slope - All - Slides - 2023-24Документ50 страниц1soil Slope - All - Slides - 2023-24sidhparanikunj91Оценок пока нет
- 26.9 PH I Slope StabilityДокумент34 страницы26.9 PH I Slope Stabilitydharkaranij217Оценок пока нет
- Chapter2 FoundationДокумент80 страницChapter2 FoundationSusi MulyaniОценок пока нет
- Sheet Pile Retaining Walls: Methods and Materials in Building ConstructionsДокумент23 страницыSheet Pile Retaining Walls: Methods and Materials in Building ConstructionsHarshini YogaОценок пока нет
- EG-223 6-Shear Strength of Soils v2 EdSNДокумент34 страницыEG-223 6-Shear Strength of Soils v2 EdSNehscribdphdОценок пока нет
- Chapt 5 Shear Strength in Soil Upload PDFДокумент38 страницChapt 5 Shear Strength in Soil Upload PDFabdirahmanОценок пока нет
- Tsavdaridis 2015Документ1 328 страницTsavdaridis 2015MIRZAОценок пока нет
- ChapterE7 PresentationДокумент41 страницаChapterE7 Presentation万少震Оценок пока нет
- Notes For Retaining Wall DesignДокумент95 страницNotes For Retaining Wall Designalwil144548100% (3)
- Bearing CapacityДокумент54 страницыBearing CapacityMasood AhmedОценок пока нет
- 5.3 Dynamic Earth Pressure Methods: Mononobe-Okabe MethodДокумент2 страницы5.3 Dynamic Earth Pressure Methods: Mononobe-Okabe MethodJesús Rodríguez RodríguezОценок пока нет
- Lateral Earth Pressure PDFДокумент80 страницLateral Earth Pressure PDFRadifan Halif100% (1)
- Thesis 1948 Z72sДокумент26 страницThesis 1948 Z72sselda durmazОценок пока нет
- Lecture of Transportation EngineeringДокумент27 страницLecture of Transportation EngineeringhassanОценок пока нет
- 18 - SUZUKI Et Al (2018) Issues For The Reduction Stiff GroundДокумент8 страниц18 - SUZUKI Et Al (2018) Issues For The Reduction Stiff GroundHarsha TejaОценок пока нет
- Earth Pressure & Retaining Walls-3Документ31 страницаEarth Pressure & Retaining Walls-3naman.h.cogniОценок пока нет
- Cellular RaftДокумент6 страницCellular Raftaminjoles100% (1)
- MK 11863Документ97 страницMK 11863Chitti Sanath KarriОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Deep Foundations - Part1Документ16 страницIntroduction To Deep Foundations - Part1ناهض عهد عبد المحسن ناهضОценок пока нет
- Jiang Segmental LinerДокумент68 страницJiang Segmental LinerrodolfoОценок пока нет
- 9 - Steel Strutting Systems For Braced ExcavationДокумент29 страниц9 - Steel Strutting Systems For Braced Excavationlim kang haiОценок пока нет
- 11.stability Methods - Vivek KapadiaДокумент63 страницы11.stability Methods - Vivek KapadiaRakesh7770Оценок пока нет
- Oluseyi Presentation SoilmechanicsДокумент186 страницOluseyi Presentation SoilmechanicsOluseyi AbegundeОценок пока нет
- Lecture - 2-1 - COEM 6012 - Geotechnics in ConstructionДокумент20 страницLecture - 2-1 - COEM 6012 - Geotechnics in ConstructionAJR365Оценок пока нет
- Day 3-4 Impt Considerations in Design of Struct Perf FoundationДокумент26 страницDay 3-4 Impt Considerations in Design of Struct Perf FoundationMIHDI PALAPUZ100% (1)
- Design of Retaining WallДокумент15 страницDesign of Retaining WallAmirah Syahirah MashorОценок пока нет
- Fault and Joint Development: In Brittle and Semi-Brittle RockОт EverandFault and Joint Development: In Brittle and Semi-Brittle RockОценок пока нет
- Fault and Joint Development in Brittle and Semi-Brittle Rock: The Commonwealth and International Library: Geology DivisionОт EverandFault and Joint Development in Brittle and Semi-Brittle Rock: The Commonwealth and International Library: Geology DivisionОценок пока нет
- Hydrostatically Loaded Structures: The Structural Mechanics, Analysis and Design of Powered SubmersiblesОт EverandHydrostatically Loaded Structures: The Structural Mechanics, Analysis and Design of Powered SubmersiblesОценок пока нет
- Analysis and Design of Structural Sandwich Panels: The Commonwealth and International Library: Structures and Solid Body Mechanics DivisionОт EverandAnalysis and Design of Structural Sandwich Panels: The Commonwealth and International Library: Structures and Solid Body Mechanics DivisionРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Physical Education: AssignmentДокумент7 страницPhysical Education: AssignmentJose Leo Icaro TalionОценок пока нет
- Workbook/ LAB Workbook/ Lab Manual: Computer Aided Design and Drafting I Computer Aided Design and Drafting I (CADD-I)Документ5 страницWorkbook/ LAB Workbook/ Lab Manual: Computer Aided Design and Drafting I Computer Aided Design and Drafting I (CADD-I)Jose Leo Icaro TalionОценок пока нет
- Science Technology and Society: Catanduanes State University Virac CatanduanesДокумент2 страницыScience Technology and Society: Catanduanes State University Virac CatanduanesJose Leo Icaro TalionОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 - Traffic FlowДокумент46 страницChapter 7 - Traffic FlowJose Leo Icaro TalionОценок пока нет
- Youth Profiling Catanduanes 2018Документ10 страницYouth Profiling Catanduanes 2018Jose Leo Icaro TalionОценок пока нет
- Timber Design - 3 Civil Engineering Licensure Examination ReviewДокумент2 страницыTimber Design - 3 Civil Engineering Licensure Examination ReviewJose Leo Icaro TalionОценок пока нет
- Timber Design - 1 Civil Engineering Licensure Examination ReviewДокумент1 страницаTimber Design - 1 Civil Engineering Licensure Examination ReviewJose Leo Icaro TalionОценок пока нет
- Timber Design - 2 Civil Engineering Licensure Examination ReviewДокумент1 страницаTimber Design - 2 Civil Engineering Licensure Examination ReviewJose Leo Icaro TalionОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 - Traffic FlowДокумент46 страницChapter 7 - Traffic FlowJose Leo Icaro TalionОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ2 страницыChapter 2Jose Leo Icaro TalionОценок пока нет
- Acad Manual 3Документ8 страницAcad Manual 3Jose Leo Icaro TalionОценок пока нет
- 5 SKMT Certificate of AppearanceДокумент1 страница5 SKMT Certificate of AppearanceJose Leo Icaro Talion50% (2)
- Attendance Sheet: Sangguniang Kabataan Mandatory TrainingДокумент1 страницаAttendance Sheet: Sangguniang Kabataan Mandatory TrainingJose Leo Icaro TalionОценок пока нет
- Acad Manual 1Документ24 страницыAcad Manual 1Jose Leo Icaro TalionОценок пока нет
- 3 - SKMT - Pre-Activity Evaluation Questionnaire TemplateДокумент1 страница3 - SKMT - Pre-Activity Evaluation Questionnaire TemplateJose Leo Icaro Talion100% (1)
- Building Contruction - Chapter3Документ13 страницBuilding Contruction - Chapter3Marwa HassounОценок пока нет
- Design of Steel and Timber Structure Beg 361 CiДокумент20 страницDesign of Steel and Timber Structure Beg 361 CiMilan KarkiОценок пока нет
- SPD and Others For STDДокумент34 страницыSPD and Others For STDTewodros TadesseОценок пока нет
- E18189 Full Set - BATCHED PDFДокумент13 страницE18189 Full Set - BATCHED PDFchristineОценок пока нет
- Chapter 18 - Foundations and Retaining WallsДокумент32 страницыChapter 18 - Foundations and Retaining WallsShyamОценок пока нет
- Design CWRДокумент45 страницDesign CWRMaitrayee AdityaОценок пока нет
- Cabana StructuralДокумент1 страницаCabana StructuralAlsean Soriano DetubioОценок пока нет
- Tensar International Corporation: Laying The Groundwork For TomorrowДокумент28 страницTensar International Corporation: Laying The Groundwork For TomorrowCrimsonPoshОценок пока нет
- Foundation Engineering (PDF) File PDFДокумент44 страницыFoundation Engineering (PDF) File PDFRebwar Ata M.Aldeen100% (1)
- Pile Design PDFДокумент14 страницPile Design PDFhiren_22286Оценок пока нет
- Caissons1 191008083542Документ97 страницCaissons1 191008083542Linda Di FrancoОценок пока нет
- Question of BTMДокумент8 страницQuestion of BTMSameer PatelОценок пока нет
- Final Thesis Foundation ReportДокумент64 страницыFinal Thesis Foundation ReportDuong TranОценок пока нет
- Pile FoundationДокумент38 страницPile FoundationChowdhury PriodeepОценок пока нет
- (Annexure - I) Lump Sum Tender Market Rate Analysis As Per Table 'H' of Contract ManualДокумент75 страниц(Annexure - I) Lump Sum Tender Market Rate Analysis As Per Table 'H' of Contract ManualPankaj BansalОценок пока нет
- Literature ReviewДокумент29 страницLiterature ReviewAzmil Fishol67% (3)
- Transmission Line Planning, Coordination & MonitoringДокумент3 страницыTransmission Line Planning, Coordination & MonitoringSanjay RoutОценок пока нет
- Chapter 8 - Building Types S1/S1A: Steel Moment Frames: 8.1 Description of The Model Building TypeДокумент295 страницChapter 8 - Building Types S1/S1A: Steel Moment Frames: 8.1 Description of The Model Building Typefasih_baqai4252Оценок пока нет
- Vodic Za Dozvole - UsaidДокумент218 страницVodic Za Dozvole - UsaidAca IlijevОценок пока нет
- Bridge Const 19FEB2019Документ302 страницыBridge Const 19FEB2019Brian Paul100% (3)
- 2 FE - Foundation TypesДокумент15 страниц2 FE - Foundation TypesYang ZhengОценок пока нет
- Green House (Final) Est & MT For 4 Part Bills 1.60-Cumbum - With FinaДокумент181 страницаGreen House (Final) Est & MT For 4 Part Bills 1.60-Cumbum - With FinarkpragadeeshОценок пока нет
- 1 Project Description: Hospital - DBRДокумент19 страниц1 Project Description: Hospital - DBRkiran raghukiranОценок пока нет
- Etabs & Safe and ProkonДокумент22 страницыEtabs & Safe and Prokonammarsteel68Оценок пока нет
- Pump House BuildingДокумент18 страницPump House BuildingYash SinghОценок пока нет
- Construction of Residential ApartmentsДокумент60 страницConstruction of Residential ApartmentsAdeelBaigОценок пока нет
- Deep FoundationsДокумент75 страницDeep FoundationsMuhd SyahidОценок пока нет
- Foundation DesignДокумент84 страницыFoundation DesignIngeniero Estructural100% (2)
- Structural Scheme For IStructE Exam - Scheme 1 Beam SlabДокумент7 страницStructural Scheme For IStructE Exam - Scheme 1 Beam SlabKwan Chun LauОценок пока нет
- Technical Report For A Structural Design ProjectДокумент95 страницTechnical Report For A Structural Design ProjectHayman AhmedОценок пока нет