Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
System Organ Function Illness Digestive System Mouth: Crohn's Disease
Загружено:
Fharida Amurao0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
7 просмотров6 страницОригинальное название
SYSTEM.pdf
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
7 просмотров6 страницSystem Organ Function Illness Digestive System Mouth: Crohn's Disease
Загружено:
Fharida AmuraoАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 6
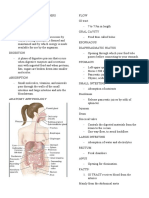
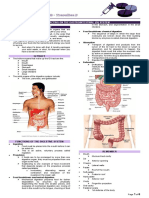
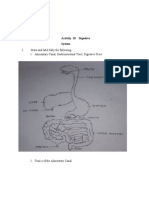
SYSTEM ORGAN FUNCTION ILLNESS
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Mouth breaks the food into
pieces that are
more easily
digested, while
saliva mixes with
food to begin the
process of breaking
it down into a form
your body can
absorb and use
Esophagus delivers food to GERD
your stomach.
Stomach The stomach is a Diarrhea
hollow organ, or
"container," that
holds food while it
is being mixed with
enzymes
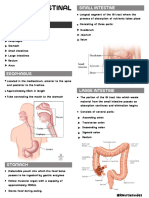
Small intestine Pectic ulcer
Once the nutrients
have been
absorbed and the
leftover-food
residue liquid has
passed through the
small intestine, it
then moves on to
the large intestine,
or colon.
Large intestine
responsible for Crohn's
processing waste disease
so that emptying
the bowels is easy
and convenient
and convenient
Pancreas Pacreatic cancer
The pancreas also
makes insulin,
secreting it directly
into the
bloodstream.
Insulin is the chief
hormone for
metabolizing sugar
Liver Hepatitis A&B
process the
nutrients absorbed
from the small
intestine
Gallbladder The gallbladder Gallstones
stores and
concentrates bile,
and then releases it
into the duodenum
to help absorb and
digest fats.
Rectum Rectal Diseases
acts as a temporary
storage site for
feces
Anus
surrounded by Anal abscess:
sphincter muscles
that are important
in allowing control
of stool.
Lymphatic System
Tymus serves a vital role in hypogammagl
the training and obulinemia
development of T-
lymphocytes or T
cells, an extremely
lymphocytes or T
cells, an extremely
important type of
white blood cell.
Spleen It acts as a filter for Lupus
blood as part of the
immune system
Tonsils Tonsillitis
trap germs
(bacteria and
viruses) which you
may breathe in.
Bone marrow Cancer of the Blood
produce blood cells
Endocrine system
Hypothalamus This part of the Hypothalamic
brain is important in disease
regulation of
satiety, metabolism,
and body
temperature
Pituitary Gland produces hormones
that control many sarcoidosis
functions of other
endocrine glands
Thyroid Gland produces thyroid Goiter
hormones that
regulate the body's
metabolism
Parathyroid Gland regulating calcium
levels in the blood hyperparathyr
and bone oidism
metabolism
Andrenal Gland
help the body cope Addison's disease
with physical and
emotional stress by
Addison's disease
with physical and
emotional stress by
increasing the heart
rate and blood
pressure.
Pineal Body It secretes a Sexual dysfunction
hormone called
melatonin, which
may help regulate
the wake-sleep
cycle of the body.
Reproductive main source of sex
Glands hormones abnormal hormone
production
INTERGUMENTARY
SYSTEM
Epidermis rests upon and bullous congenital
protects the deeper ichthyosiform
and thicker dermis erythroderma
layer of the skin (BCIE)
Dermis dense irregular
connective tissue Eczema
along with nervous
tissue, blood, and
blood vessels
Hypodermis serves as the
flexible connection thinning of the
between the skin hypodermis
and the underlying
muscles and bones
as well as a fat
storage area
Hair Baldness
helps to protect the
body from UV
radiation by
preventing sunlight
radiation by
preventing sunlight
from striking the
skin
Nails reinforce and
protect the end of onychomycosi
the digits and are s
used for scraping
and manipulating
small objects
Sudoriferous glands they produce a
thick, oily liquid that Hidradenitis
is consumed by suppurativa
bacteria living on
the skin
Sebaceous glands Acne
acts to waterproof
and increase the
elasticity of the skin
Skeleton System
Bones They support the Osteoporosis
body structurally,
protect our vital
organs, and allow
us to move
Ligaments
connect bone TMJ Disorder
to bone
Tendons connect skeletal
muscle to bones. tendinopathies
Cartilage Connect bones
together Relapsing
polychondritis
Вам также может понравиться
- Digeestive System Structures and FunctionsДокумент3 страницыDigeestive System Structures and FunctionsyeshenbehariОценок пока нет
- Digestive System Lecture NotesdocxДокумент11 страницDigestive System Lecture NotesdocxAdaОценок пока нет
- The Digestive System BrochureДокумент2 страницыThe Digestive System BrochureWasna Osama Al SaifОценок пока нет
- Digestive SystemДокумент10 страницDigestive SystemJohn Roi PeñafloridaОценок пока нет
- Bal Bharati Public School, Pitampura, Delhi - 110034 Subject: Biology Class X: Chapter: Life Processes Topic-Life Processes (Heterotrophic Nutrition)Документ5 страницBal Bharati Public School, Pitampura, Delhi - 110034 Subject: Biology Class X: Chapter: Life Processes Topic-Life Processes (Heterotrophic Nutrition)SUHANEERIYAОценок пока нет
- Unit 3. Digestive SystemДокумент46 страницUnit 3. Digestive SystemNURIA VAZQUEZОценок пока нет
- The Digestive System AaaaДокумент21 страницаThe Digestive System AaaaRirin A SaputriОценок пока нет
- Lecture 1 Digestive SystemДокумент17 страницLecture 1 Digestive Systembabaaijaz01Оценок пока нет
- Gastro NotesДокумент11 страницGastro NotesMonica JubaneОценок пока нет
- Enrique Santos Week 3 HW - Digestive System - Parts and Their FunctionsДокумент1 страницаEnrique Santos Week 3 HW - Digestive System - Parts and Their Functionsenrsa11Оценок пока нет
- Human Digestive SystemДокумент5 страницHuman Digestive SystemPau BurceОценок пока нет
- How Your Digestive System WorksДокумент11 страницHow Your Digestive System WorksVALERIA ALEJANDRA CHINCHON OLIVERAОценок пока нет
- Digestive System: by DR Vipan GoyalДокумент18 страницDigestive System: by DR Vipan GoyalAmit ChoudharyОценок пока нет
- NCM 116 Prelims ReviewerДокумент28 страницNCM 116 Prelims ReviewerMary Cruz100% (2)
- Biokimia 2 Sistem PencernaanДокумент18 страницBiokimia 2 Sistem PencernaanAnugrah NugraОценок пока нет
- Topic 2.1 - Human Digestive SystemДокумент31 страницаTopic 2.1 - Human Digestive Systembienfrancis.reyes.jhsОценок пока нет
- Topic 6. Digestive SystemДокумент27 страницTopic 6. Digestive SystemNicolas EstradaОценок пока нет
- 11 Animal PhysiologyДокумент10 страниц11 Animal Physiologyaj.kd.jmОценок пока нет
- Gastro highlightCHAPTER1Документ12 страницGastro highlightCHAPTER1Lovely CruzxОценок пока нет
- Gastro 4Документ537 страницGastro 4Andrei ManeaОценок пока нет
- Gonzales - CHECK IN ACTIVITY DIGESTIVE SYSTEMДокумент1 страницаGonzales - CHECK IN ACTIVITY DIGESTIVE SYSTEMGonzales Neil AlexanderОценок пока нет
- Handout NRG201Документ13 страницHandout NRG201Kyle DoloritosОценок пока нет
- Digestive System SlideДокумент69 страницDigestive System SlideRobert obispoОценок пока нет
- Module 4 Digestive SystemДокумент9 страницModule 4 Digestive SystemupadhiОценок пока нет
- 3 - Nutrition (I) - The Digestive SystemДокумент36 страниц3 - Nutrition (I) - The Digestive SystemValery GvОценок пока нет
- Digestive System ContinuationДокумент38 страницDigestive System ContinuationLocal ClownОценок пока нет
- Digestive System AdlynaДокумент2 страницыDigestive System AdlynaSN2-0622 NURUL ADLYNA BINTI LOKMANОценок пока нет
- 5 Handouts - Ust MBR 2022 - Gi Physiology - Dr. SangalangДокумент23 страницы5 Handouts - Ust MBR 2022 - Gi Physiology - Dr. SangalangRhon Andrew RañesesОценок пока нет
- Triptico Digestive SystemДокумент2 страницыTriptico Digestive SystemKamil HenriquezОценок пока нет
- Digestive System and Nutritional StatusДокумент4 страницыDigestive System and Nutritional StatusarsyzahraОценок пока нет
- The Digestive SystemДокумент45 страницThe Digestive SystemgwormtalaveraОценок пока нет
- Slide 1: Assessing The AbdomenДокумент18 страницSlide 1: Assessing The AbdomenKristil ChavezОценок пока нет
- C - Other SystemsДокумент29 страницC - Other SystemsVũ Xuân MinhОценок пока нет
- NCM 105 Lec 2Документ2 страницыNCM 105 Lec 2Rizaga, Carlos BenedictОценок пока нет
- Digestive and Endocrine System: 5141 CN 111 - Anatomy and PhysiologyДокумент4 страницыDigestive and Endocrine System: 5141 CN 111 - Anatomy and PhysiologyAlthea Joyce OngОценок пока нет
- Midterm MedsurgДокумент54 страницыMidterm MedsurgKylle AlimosaОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology: Cardiovascular SystermДокумент67 страницAnatomy and Physiology: Cardiovascular SystermFrancesca TejadaОценок пока нет
- MS GiДокумент35 страницMS GiFrances GabbuatОценок пока нет
- Chapter 06Документ47 страницChapter 06gayathmipereraОценок пока нет
- Module 6Документ26 страницModule 6xtnreyesОценок пока нет
- JHS Digestive SystemДокумент35 страницJHS Digestive SystemGojo KaisenОценок пока нет
- Digestive SystemДокумент36 страницDigestive SystemNyasha RumhezaОценок пока нет
- Q4 Science8Документ60 страницQ4 Science8AILEEN LUZON100% (1)
- Drugs Acting On The Gastrointestinal (Gi) System Digestive SystemДокумент6 страницDrugs Acting On The Gastrointestinal (Gi) System Digestive SystemAdiel CalsaОценок пока нет
- The Digestive SystemДокумент10 страницThe Digestive Systemofurumchinyere9Оценок пока нет
- Activity-10-Digestive-System - PERALTAДокумент12 страницActivity-10-Digestive-System - PERALTACogie PeraltaОценок пока нет
- Systems of The Body (5C, D, E)Документ24 страницыSystems of The Body (5C, D, E)reneeОценок пока нет
- Digestive SystemДокумент14 страницDigestive SystemValeria ZárateОценок пока нет
- 3.1 - The Digestive SystemДокумент21 страница3.1 - The Digestive SystemJavierОценок пока нет
- Digestive SystemДокумент7 страницDigestive Systemkirsten merielleОценок пока нет
- Can Hold 4l of Food (Maximum)Документ4 страницыCan Hold 4l of Food (Maximum)Sofronio OmboyОценок пока нет
- Digestive SystemДокумент4 страницыDigestive Systemmallorca albertОценок пока нет
- VisibleBody Digestive SystemДокумент13 страницVisibleBody Digestive SystemcascaveletteОценок пока нет
- Science: Quarter 4 - Module 1 The Human Digestive SystemДокумент43 страницыScience: Quarter 4 - Module 1 The Human Digestive SystemGenesis SarengoОценок пока нет
- Digestive SystemДокумент4 страницыDigestive SystemHannahnel Anasco QuidatoОценок пока нет
- Objectives: Prepared By: Grace Manalo (Teacher)Документ22 страницыObjectives: Prepared By: Grace Manalo (Teacher)Grace GaraldeОценок пока нет
- General Zoology LabДокумент3 страницыGeneral Zoology Labgerlyn duranОценок пока нет
- Systems and Their ControlДокумент38 страницSystems and Their ControlsurainiОценок пока нет
- Gastrointestinal System Disorders - MedSurg NursingДокумент56 страницGastrointestinal System Disorders - MedSurg NursingJermaine S. TeodoroОценок пока нет
- Anatomy ReviewДокумент9 страницAnatomy ReviewAndreaQuinteroОценок пока нет
- IvacaftorДокумент25 страницIvacaftorSmart PharmacistОценок пока нет
- Lecture 20: ApoptosisДокумент56 страницLecture 20: ApoptosisTran Nhat ThangОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan For Impaired Comfort NCPДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan For Impaired Comfort NCPderic82% (11)
- Lymphatic SystemДокумент29 страницLymphatic SystemlecturioОценок пока нет
- The Perceived Self Ecological and Interpersonal Sources of Self Knowledge Emory Symposia in Cognition PDFДокумент331 страницаThe Perceived Self Ecological and Interpersonal Sources of Self Knowledge Emory Symposia in Cognition PDFtsiky100% (1)
- BIO 1133 Exercise 7 (Skeletal System of The Frog)Документ7 страницBIO 1133 Exercise 7 (Skeletal System of The Frog)Tonet LapeОценок пока нет
- Mercy Job Description CVICU PolicyДокумент5 страницMercy Job Description CVICU PolicyJessica Kiszka100% (1)
- Analzying Sensory Somatic Responces - System Reinforcemnt Worksheet1Документ2 страницыAnalzying Sensory Somatic Responces - System Reinforcemnt Worksheet1Creative DestinyОценок пока нет
- Cytoplasmic Membrane SystemДокумент58 страницCytoplasmic Membrane Systemsjbiotech0% (1)
- Radiotherapy Inlung Cancer PDFДокумент539 страницRadiotherapy Inlung Cancer PDFStefania CarboneОценок пока нет
- Big Picture On The Cell PosterДокумент1 страницаBig Picture On The Cell PosterWellcome Trust100% (1)
- Biology Paper 1 HLДокумент14 страницBiology Paper 1 HLLéo Signorini NovaesОценок пока нет
- მიტოქონდრიის ფუნქცია და კიბოДокумент1 страницаმიტოქონდრიის ფუნქცია და კიბოEMD GROUPОценок пока нет
- Sclera AnatomyДокумент21 страницаSclera AnatomyMiriam Mwangi100% (1)
- Detoxification Kriya PDFДокумент2 страницыDetoxification Kriya PDFClaudia MoyaОценок пока нет
- Uva-Dare (Digital Academic Repository) : Etiology, Diagnosis and Treatment of Non-Allergic RhinitisДокумент411 страницUva-Dare (Digital Academic Repository) : Etiology, Diagnosis and Treatment of Non-Allergic RhinitiswircexdjОценок пока нет
- Ice TherapyДокумент5 страницIce TherapyDiane CastillonОценок пока нет
- Charge AssociationДокумент2 страницыCharge AssociationBlueash BehОценок пока нет
- Biology G10 Unit PlanДокумент70 страницBiology G10 Unit PlanHoney Fe RestauroОценок пока нет
- Plasma ExpandersДокумент4 страницыPlasma ExpandersNix EnarioОценок пока нет
- OPIANA CHRISTIAN JOSEPH - PulmonaryDisorderДокумент9 страницOPIANA CHRISTIAN JOSEPH - PulmonaryDisorderChristian Joseph OpianaОценок пока нет
- Acute Complication of DM: Clinical Manifestation Laboratory Procedures Therapeutic Plan Possible Problem AssociatedДокумент12 страницAcute Complication of DM: Clinical Manifestation Laboratory Procedures Therapeutic Plan Possible Problem AssociatedironОценок пока нет
- Animal Behavior & Stimulus EnergyДокумент17 страницAnimal Behavior & Stimulus Energylevonbachdasarian100% (1)
- Toxicity of Shea OilДокумент6 страницToxicity of Shea OilDawson ChungОценок пока нет
- ReZero Kara Hajimeru Isekai Seikatsu - V03 (Yen Press) (Kobo - Kitzoku) - (51FC8430)Документ325 страницReZero Kara Hajimeru Isekai Seikatsu - V03 (Yen Press) (Kobo - Kitzoku) - (51FC8430)Mohammad Tanveer Hassan SarkerОценок пока нет
- AH Biology QP 2014Документ30 страницAH Biology QP 2014Agreni TeacherОценок пока нет
- Radha KrishnaДокумент32 страницыRadha KrishnaShii'winNdaTwiniddsОценок пока нет
- 2 Biological Level of Analysis: Short AnswersДокумент12 страниц2 Biological Level of Analysis: Short AnswersCheezy HeadОценок пока нет
- 911Документ1 страница911Cj Nicole SuriagaОценок пока нет