Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Post Traumatic Stress Disorder
Загружено:
ML EstavilloАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Post Traumatic Stress Disorder
Загружено:
ML EstavilloАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
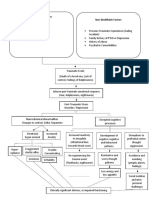
Posttraumatic Stress Disorder
• Symptoms develop after exposure to a traumatic event
• Exposure to actual of threatened death, serious injury or sexual violence in one (or more) of the
following:
• Direct experience traumatic event
• Witnessing, in person, the event occurring to others
• Learning that the event occurred to close family member of friend
• Experiencing repeated or extreme exposure to aversive details of the event.
• One or more Intrusion symptoms associated with the event, after it occurred:
• Recurrent, involuntary and intrusive distressing memories of event
• Recurrent distressing dreams related to the event
• Dissociated reactions (e.g. Flashbacks) as if event were recurring
• Intense or prolonged psychological distress at exposure to internal or external cues
symbolic or resembling the event
• Marked physiological reactions to cues related to event .
• Persistent avoidance of stimuli associated with the event
• Distressing memories, thoughts or feelings
• External reminders
• Negative alterations in cognitions and mood associated with event (two or more)
• Inability to remember important aspects of event
• Persistent and exaggerated negative beliefs or expectations about self, others or the
world
• Persistent, distorted cognitions about cause or consequences of event
• Persistent negative emotional state
• Markedly diminished interest or participation in significant activities
• Feelings of detachment or estrangement from others
• Persistent inability to experience positive emotions
• Marked alterations in arousal and reactivity associated with event (two or more):
• Irritable behavior and angry outbursts
• Reckless or self- destructive behavior
• Hypervigilance
• Exaggerated startle response
• Problems with concentration
• Sleep disturbance
Duration: more than 1 month
Causes significant distress or impairment
PTSD for Children (6 years old –below)
• Similar to PTSD for beyond 6 years except for exposure and developmental expressions
of symptoms
• Fear of being separated from parents
• Losing previously- acquired skills
• Sleep problems and nightmares without recognizable content
• Somber, compulsive play in which themes or aspects of the trauma are repeated
• New phobias and anxieties that seem unrelated to the trauma
• Acting out the trauma through play, stories or drawings
• Aches and pain with no apparent cause
• Irritability and aggression
Risk Factors
• Pretraumatic Factors
• Temperament (childhood emotional problems, prior mental disorders)
• Environment (low SES, low education, lower intelligence, prior trauma, childhood
adversity, cultural characteristics related to coping)
• Gender (female)
• Peritraumatic Factors
• Severity
• Personal injury
• Interpersonal violence
• Posttraumatic Factors
• Temperament (negative appraisals, inappropriate coping, acute stress disorder)
• Environment (adverse life events, other traumatic losses, social support)
Etiology
• Psychological
• Related Symptoms prior to trauma
• Inadequate coping strategies
• Temperament
• Biological
• Reactivity and dampening reactivity: Amygdala; Hippocampus; Prefontal Cortex
• Biochemical: Cortisol
Reference: (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Disorders, Fifth Edition , 2016)
Вам также может понравиться
- Posttraumatic Stress DisorderДокумент12 страницPosttraumatic Stress DisorderML EstavilloОценок пока нет
- Trauma and Stress Related Disorder For PGY 1Документ28 страницTrauma and Stress Related Disorder For PGY 1AbelОценок пока нет
- Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)Документ28 страницPosttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)Karl Angelo MontanoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 Anxiety Trauma and Stressor Related and Obsessive Compulsive and Related DisorderДокумент43 страницыChapter 5 Anxiety Trauma and Stressor Related and Obsessive Compulsive and Related DisorderGabriel Jeremy OrtegaОценок пока нет
- Trauma - and Stressor-Related DisordersДокумент34 страницыTrauma - and Stressor-Related DisordersjenОценок пока нет
- Biopsychosocial ModelДокумент12 страницBiopsychosocial Modelkatg121387Оценок пока нет
- Slides CHPT 5 - Trauma and Stress DisordersДокумент45 страницSlides CHPT 5 - Trauma and Stress DisordersSofiaОценок пока нет
- 7-Anxiety DisordersДокумент26 страниц7-Anxiety DisordersZ26Оценок пока нет
- Tutorial 9 Trauma Stressor Related and Dissociative DisorderДокумент77 страницTutorial 9 Trauma Stressor Related and Dissociative DisorderGan Ming JerОценок пока нет
- Surg LT Oo For WNCNMДокумент29 страницSurg LT Oo For WNCNMSola SokeyeОценок пока нет
- MR21npE3Eem xg4p7cmXwA - Module 9 Lecture 1Документ16 страницMR21npE3Eem xg4p7cmXwA - Module 9 Lecture 1Edward RamirezОценок пока нет
- DSM-5: Assessment and Treatment of PTSDДокумент63 страницыDSM-5: Assessment and Treatment of PTSDŁukasz Ostrowski100% (1)
- Acute Stress DisorderДокумент14 страницAcute Stress DisorderDevika VijayanОценок пока нет
- Dissociative DisordersДокумент13 страницDissociative DisordersMwangi LizОценок пока нет
- Anxiety and Anxiety DisordersДокумент2 страницыAnxiety and Anxiety DisordersJohn Haider Colorado GamolОценок пока нет
- Schizophrenia Spectrum and Other Psychotic DisordersДокумент31 страницаSchizophrenia Spectrum and Other Psychotic DisordersNoelle Grace Ulep BaromanОценок пока нет
- Trauma & Stress Related Disorders Review Lecture 05.15Документ6 страницTrauma & Stress Related Disorders Review Lecture 05.15Mane SharОценок пока нет
- Anxiety DisordersДокумент30 страницAnxiety DisordersAbelОценок пока нет
- Mood Disorders - DepressionДокумент58 страницMood Disorders - Depressionmaha abdallahОценок пока нет
- Psychiatric EmergencyДокумент26 страницPsychiatric EmergencyHoi Chung LamОценок пока нет
- Personality Disorder English 2011 EditДокумент31 страницаPersonality Disorder English 2011 EditNyoman Dianita CandradewiОценок пока нет
- SSRD Presentation RevisedДокумент22 страницыSSRD Presentation RevisedCalvoniaОценок пока нет
- Schizophrenia Spectrum and Other Psychotic DisordersДокумент51 страницаSchizophrenia Spectrum and Other Psychotic DisordersHaley Vest MustaficОценок пока нет
- Anxiety DisordersДокумент40 страницAnxiety Disordersamal abdulrahmanОценок пока нет
- HERO-Ethiopia Module 3Документ31 страницаHERO-Ethiopia Module 3RahelAdmasuОценок пока нет
- Glossary Handout For MSLBD PresentationДокумент2 страницыGlossary Handout For MSLBD PresentationMohammad Ashraf UddinОценок пока нет
- Trauma-And Stressor - Related DisordersДокумент24 страницыTrauma-And Stressor - Related DisordersNoelle Grace Ulep BaromanОценок пока нет
- Anxiety DisorderДокумент35 страницAnxiety Disorderrajesh duttaОценок пока нет
- Anxiety & Anxiety Disorders ClassДокумент27 страницAnxiety & Anxiety Disorders Classbrianmuthomi851Оценок пока нет
- Unit 10 - Psychological DisordersДокумент28 страницUnit 10 - Psychological Disordersajghjerkday21Оценок пока нет
- PTSD and Autoimmune DiseasesДокумент24 страницыPTSD and Autoimmune DiseasesEnida XhaferiОценок пока нет
- Symptoms and Signs in Psychiatry: Dr. Wendel AbelДокумент44 страницыSymptoms and Signs in Psychiatry: Dr. Wendel AbelJamie Anthony GordonОценок пока нет
- Anxietydisorder LectureДокумент37 страницAnxietydisorder Lecturetazam94Оценок пока нет
- Post Traumatic Stress DisorderДокумент25 страницPost Traumatic Stress Disordereduard.vlaston100% (2)
- Anxietydisorder LectureДокумент37 страницAnxietydisorder LecturesundariОценок пока нет
- Trauma Focused PTSDДокумент20 страницTrauma Focused PTSDapi-548625849Оценок пока нет
- Anxiety Disorders: Diagnostic Criteria and Common SymptomologiesДокумент15 страницAnxiety Disorders: Diagnostic Criteria and Common SymptomologiesMuhammad BilalОценок пока нет
- Impact of Disaster On Mental HealthДокумент29 страницImpact of Disaster On Mental HealthsehaОценок пока нет
- Post-Traumatic Stress DisorderДокумент18 страницPost-Traumatic Stress DisorderMoritz SolivenОценок пока нет
- Abnormal Psychology: Dr. Rabia Mushtaq Assistant Professor, Iqra UniversityДокумент20 страницAbnormal Psychology: Dr. Rabia Mushtaq Assistant Professor, Iqra UniversityKumachiОценок пока нет
- Anxiety DisordersДокумент70 страницAnxiety DisordersNishantYadav100% (1)
- Anxiety Disorders 2Документ30 страницAnxiety Disorders 2João Marco Rodrigues SantanaОценок пока нет
- Stress-Related Anxiety DisordersДокумент13 страницStress-Related Anxiety DisordersPatrick Ross Serquiña DulayОценок пока нет
- Mental Health Disease and DisordersДокумент28 страницMental Health Disease and DisordersCharleson OtubuОценок пока нет
- Introduction To PTSD and Trauma: William Harryman, MSC, NCC, MSДокумент34 страницыIntroduction To PTSD and Trauma: William Harryman, MSC, NCC, MSWilliam Harryman100% (1)
- Cspu 512 - Trauma-Informed In-ServiceДокумент30 страницCspu 512 - Trauma-Informed In-Serviceapi-542152634Оценок пока нет
- Psychology ProjectДокумент14 страницPsychology ProjectLogan RiversОценок пока нет
- Anxiety DisordersДокумент62 страницыAnxiety DisordersJOHN PAUL KEVIN ESTAОценок пока нет
- Human Behavior 12 2016Документ15 страницHuman Behavior 12 2016aalijahabbasОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9Документ11 страницChapter 9nayaddouaihyОценок пока нет
- Schizophrenia: by Byawele Jairus WangusaДокумент30 страницSchizophrenia: by Byawele Jairus WangusaAYO NELSONОценок пока нет
- Classifying Abnormal BehaviorДокумент4 страницыClassifying Abnormal BehaviorLyanna MormontОценок пока нет
- Risk Factors 2009Документ2 страницыRisk Factors 2009katie-swanson-6936Оценок пока нет
- Concept and Nosological Status of Pathological Grief ReactionДокумент60 страницConcept and Nosological Status of Pathological Grief ReactionJonty ArputhemОценок пока нет
- Anxiety and Psychosexual Disorders in ChildДокумент60 страницAnxiety and Psychosexual Disorders in ChildAnnalesa BarkerОценок пока нет
- Introduction To PsychosisДокумент31 страницаIntroduction To Psychosisمحمد القرنيОценок пока нет
- Modifiable Factors Non-Modifiable FactorsДокумент8 страницModifiable Factors Non-Modifiable Factorskim cortezОценок пока нет
- HERO-Ethiopia Module 2Документ24 страницыHERO-Ethiopia Module 2RahelAdmasuОценок пока нет
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Workbook: Practical Help and Information for PTSDОт EverandPost-Traumatic Stress Disorder Workbook: Practical Help and Information for PTSDРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (6)
- Overcoming PTSD: The workbook designed to help you understand and overcome post-traumatic stress disorderОт EverandOvercoming PTSD: The workbook designed to help you understand and overcome post-traumatic stress disorderОценок пока нет
- Sleep and Pain ConstiousnesДокумент35 страницSleep and Pain Constiousnestwity 1Оценок пока нет
- Stretching TherapyДокумент95 страницStretching TherapySpineCare Physiotherapy100% (2)
- First Steps in REBT - Windy DrydenДокумент44 страницыFirst Steps in REBT - Windy DrydenStefan Alexandru100% (4)
- Cervical Exercise: The Backbone of Spine TreatmentДокумент9 страницCervical Exercise: The Backbone of Spine TreatmentCorina SovieticaОценок пока нет
- Signs, Symptoms, Help For Drug Problems and Substance AbuseДокумент14 страницSigns, Symptoms, Help For Drug Problems and Substance AbuseditaokkyОценок пока нет
- Biopharmaceutics Supplemental NotesДокумент19 страницBiopharmaceutics Supplemental NotesChristine Joy De Ocampo0% (1)
- Updated at ResumeДокумент3 страницыUpdated at Resumeapi-356396463Оценок пока нет
- Spine Care Technologies Inc. To Attend Arab Health2020 in Dubai, UAEДокумент2 страницыSpine Care Technologies Inc. To Attend Arab Health2020 in Dubai, UAEPR.comОценок пока нет
- Medhu Spa MenuДокумент24 страницыMedhu Spa Menumiki832Оценок пока нет
- Balance of Five Elements (Wood, Fire, WaterДокумент26 страницBalance of Five Elements (Wood, Fire, WaterCharls John Ercillo100% (3)
- Tobias Anxiety Research in Educational PsychologyДокумент10 страницTobias Anxiety Research in Educational PsychologyMagdalena100% (1)
- Nasogastric Tube InsertionДокумент17 страницNasogastric Tube InsertionMichael Jude MedallaОценок пока нет
- Ift PDFДокумент10 страницIft PDFJulyhathul KuraishiОценок пока нет
- 4.penyembuhan LukaДокумент52 страницы4.penyembuhan LukaazisaaidrОценок пока нет
- Buccal Mucosa Cancer Final PDF 9.6.14 PDFДокумент36 страницBuccal Mucosa Cancer Final PDF 9.6.14 PDFTaufiqurrahman Abdul DjabbarОценок пока нет
- Lsuhsc Nursing Licensed Personnel Inpatient RN Pharmacology Exam InstructionsДокумент10 страницLsuhsc Nursing Licensed Personnel Inpatient RN Pharmacology Exam Instructionskellly100% (1)
- Liver Function Tests (LFTS) : Git Block 1 Lecture Dr. Usman GhaniДокумент26 страницLiver Function Tests (LFTS) : Git Block 1 Lecture Dr. Usman Ghaniraanja2100% (1)
- QuizДокумент8 страницQuizJohara Mae De RamaОценок пока нет
- Requirement IN Psychiatric Nursing: Gencris M. Giray Bsn-3AДокумент5 страницRequirement IN Psychiatric Nursing: Gencris M. Giray Bsn-3AGencris Medrano Giray RN100% (2)
- Jim Humble Update 120519Документ6 страницJim Humble Update 120519kitty katОценок пока нет
- A Review On LozengesДокумент9 страницA Review On LozengesShakrie AbdullahОценок пока нет
- HypoglicemiaДокумент4 страницыHypoglicemiayeniОценок пока нет
- TANTUM VERDE Benzydamin PDFДокумент32 страницыTANTUM VERDE Benzydamin PDFAri KurniasariОценок пока нет
- Cri 188 FinalsДокумент12 страницCri 188 FinalsKaren Angel AbaoОценок пока нет
- 50 State Survey - Scope - 07.2015Документ85 страниц50 State Survey - Scope - 07.2015Anonymous kdBDppigEОценок пока нет
- She PlusДокумент2 страницыShe PlusHarjinder SinghОценок пока нет
- 4 Square Step TestДокумент6 страниц4 Square Step TestAntónio EstevesОценок пока нет
- Endodontic ErrorsДокумент50 страницEndodontic Errorsasop06Оценок пока нет
- 160 Nursing Bullets - Medical Surgical NursingДокумент7 страниц160 Nursing Bullets - Medical Surgical Nursingdecsag06Оценок пока нет
- Corticosteroid Injection For de Quervain's Tenosynovitis (Review)Документ19 страницCorticosteroid Injection For de Quervain's Tenosynovitis (Review)intan rosliОценок пока нет