Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Stage II of Labor
Загружено:
JharaИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Stage II of Labor
Загружено:
JharaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
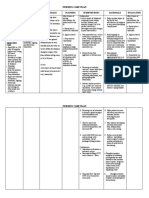
TOPIC: STAGE II OF LABOR Pain/Discomfort
May moan/groan during
Definition: contractions.
the stage of expulsion Amnesia between contractions
begins with full cervical dilation (10 cm) and may be noted.
ends with the birth of the newborn. Reports of burning/stretching
maternal efforts to bear down occur sensation of the perineum.
involuntarily during contractions that are 1.5–2 Legs may tremble during
min apart, lasting 60–90 sec. pushing efforts.
the average rate of fetal descent is 1 cm/hour Uterine contractions strong,
for nulliparas, 2 cm or more per hour for occurring 1.5–2 min apart and
multiparas. lasting 60–90 sec.
May fight contractions,
Two Phases especially if she did not
1. Propulsive phase: participate in childbirth
From full dilatation until presenting part preparation classes.
has descended to the pelvic floor Respiratory
2. Expulsive phase: Respiratory rate increases.
Ends with the delivery of the fetus Safety
Diaphoresis often present
Fetal bradycardia appearing as
NURSING CARE PLAN early decelerations on electric
I. Assessment monitor during contractions
Activity/Rest (head compression) or variables
Reports of fatigue (cord compression)
May report inability to self- Sexuality
initiate pushing/relaxation Cervix fully dilated (10 cm) and
techniques 100% effaced.
Lethargic Increased vaginal bloody show.
Dark circles under eyes Rectal/perineal bulging with
Circulation fetal descent.
BP may rise 5–10 mm Hg in Membranes may rupture at this
between contractions. point if still intact.
Ego Integrity Increased expulsion of amniotic
Emotional responses may range fluid during contractions.
from feelings of fear/irritation Crowning occurs; caput is
to relief/joy. visible just before birth in
May feel a loss of control or the vertex presentation.
reverse as she is now actively
involved in bearing down.
II. Nursing Diagnosis
Elimination Pain (acute)
Involuntary urge to
defecate/push with i. May Be Related To:
contractions, combining Mechanical pressure of
intraabdominal pressure with presenting part, tissue
uterine pressure. dilation/stretching, nerve
May have fecal discharge while compression, muscle hypoxia,
bearing down. intensified contractile pattern
Bladder distension may be ii. Possibly Evidenced By:
present, with urine expressed
during pushing efforts.
Verbalizations, distraction Assess bladder fullness. Catheterize
behavior (e.g., restlessness), between contractions if distension is
facial mask of pain, narrowed noted and client is unable to void.
focus, autonomic responses
V. Evaluation
III. Planning Patient verbalized reduction of pain.
Facilitate normal progression of labor
and fetal descent.
Promote maternal and fetal well-being.
Support client’s/couple’s wishes
regarding delivery experience,
maintaining safety as a priority.
IV. Interventions
Identify degree of discomfort and its
sources.
Provide comfort measures, such as
mouth care; Promotes psychological
and physical comfort, perineal
care/massage; clean, dry linen and
allowing client to focus on labor, and
may reduce underpads; cool
environment (68°F–72°F [20°C–22.1°C]),
the need for analgesia or anesthesia.
cool, moist cloths to face and neck; or
hot compresses to perineum, abdomen,
or back, as desired.
Monitor and record uterine activity with
each contraction.
Provide information and support
related to progress of labor.
Encourage client/couple to manage
efforts to bear down with spontaneous,
pushing during contractions. Stress
importance of using abdominal muscles
and relaxing pelvic floor.
Observe for perineal and rectal bulging,
opening of vaginal introitus, and
changes in fetal station.
Assist client in assuming optimal
position for bearing down; (e.g.,
squatting or lateral recumbent, semi-
Fowler’s position (elevated 30–60
degrees).
Encourage client to relax all muscles
and rest between contractions.
Monitor maternal BP and pulse, and
FHR. Observe unusual adverse reactions
to medication, such as antigen-antibody
reactions, respiratory paralysis, or
spinal blockage.
Вам также может понравиться
- Hernia, (Different Types) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОт EverandHernia, (Different Types) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Polyvagal Toolbox: 50 Polyvagal Exercises for Safety and ConnectionОт EverandPolyvagal Toolbox: 50 Polyvagal Exercises for Safety and ConnectionОценок пока нет
- Intrapartum 11: The Stages of LaborДокумент9 страницIntrapartum 11: The Stages of LaborJane MartinОценок пока нет
- Labor Stage II (Expulsion)Документ15 страницLabor Stage II (Expulsion)nursereview100% (7)
- OB2 - Problems With The PowerДокумент10 страницOB2 - Problems With The PowerYanaОценок пока нет
- Common Causes of Dysfunctional Labor:: DystociaДокумент8 страницCommon Causes of Dysfunctional Labor:: DystociaAngelo ArabejoОценок пока нет
- DystociaДокумент1 страницаDystociaAngielyn P. VicenteОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care PlansДокумент4 страницыNursing Care PlansRITIK KUMARОценок пока нет
- Second Stage of LaborДокумент25 страницSecond Stage of LaborAna67% (6)
- Problem With The PowersДокумент9 страницProblem With The PowersNicole Claire LegaspiОценок пока нет
- Stages of Labor Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Interventions: Navarro, Ruth Laureen P. BSN 2 StemДокумент1 страницаStages of Labor Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Interventions: Navarro, Ruth Laureen P. BSN 2 StemRaphael Lorenz NavarroОценок пока нет
- NCP: Labor Stage 2 (Expulsion)Документ15 страницNCP: Labor Stage 2 (Expulsion)Javie100% (1)
- The Client at 4 Hours To 2 Days PostpartumДокумент23 страницыThe Client at 4 Hours To 2 Days Postpartumnursereview100% (6)
- Dysfunctional Labor DystociaДокумент8 страницDysfunctional Labor Dystocianursereview100% (4)
- Dysfunctional Labor DystociaДокумент8 страницDysfunctional Labor Dystociamardsz100% (2)
- Assesment and Monitoring During 2nd Stage of LabourДокумент11 страницAssesment and Monitoring During 2nd Stage of LabourPragati BholeОценок пока нет
- ANALAB - Reproductive SystemДокумент5 страницANALAB - Reproductive SystemIvy cencie AgawinОценок пока нет
- NCP Severe Labor PainДокумент3 страницыNCP Severe Labor PainPaolo EspinosaОценок пока нет
- NCM 109 Module 2mДокумент29 страницNCM 109 Module 2mKyle ChuaОценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент3 страницыUntitledMON RUSSEL FRIASОценок пока нет
- Labor and Delivery FinalДокумент8 страницLabor and Delivery FinalMarie Ashley CasiaОценок пока нет
- INTRAPARTUMДокумент174 страницыINTRAPARTUMRUSTOM JAKEОценок пока нет
- MCN Lect Module 2.5 Complications of Labor and Birth 1 and 2Документ7 страницMCN Lect Module 2.5 Complications of Labor and Birth 1 and 2AmethystОценок пока нет
- 02 Newborn Concept TRANSESДокумент7 страниц02 Newborn Concept TRANSES2022102004Оценок пока нет
- First Stage Second Stage Third Stage I. The Powers: A. Physiology of LaborДокумент4 страницыFirst Stage Second Stage Third Stage I. The Powers: A. Physiology of LaborfinellajanОценок пока нет
- NCM 107 Skills Lab NCPДокумент1 страницаNCM 107 Skills Lab NCPMoises Clerick BalloguingОценок пока нет
- Leifer Chapter 08 Study Guide Answer KeyДокумент5 страницLeifer Chapter 08 Study Guide Answer KeyTyler Finkle81% (21)
- Stages of LaborДокумент4 страницыStages of LaborAizy BastionОценок пока нет
- Research MethodsДокумент6 страницResearch MethodsDesmond Grasie ZumankyereОценок пока нет
- 5 DystociaДокумент9 страниц5 DystociaKarylle Joy WacguisanОценок пока нет
- DystociaДокумент5 страницDystociaMondee PSОценок пока нет
- Amponin, Elisa Jillian E. - Intrapartum Labor and Delivery Activity SheetДокумент7 страницAmponin, Elisa Jillian E. - Intrapartum Labor and Delivery Activity SheetJillian AmponinОценок пока нет
- PATHO OB DystociaДокумент14 страницPATHO OB Dystociasailor MoonОценок пока нет
- NCP Acute PainДокумент2 страницыNCP Acute PainMillicent Faye G. Gelit50% (2)
- CMCALEC Lesson9MДокумент14 страницCMCALEC Lesson9Mluisgregory113Оценок пока нет
- Complications of Labor and Birth 11Документ12 страницComplications of Labor and Birth 11Gian AnchetaОценок пока нет
- MCN Normal LaborДокумент37 страницMCN Normal LaborJharaОценок пока нет
- OB 1.01 DystociaДокумент9 страницOB 1.01 DystociaRaquel Reyes100% (1)
- NCP AppendicitisДокумент4 страницыNCP AppendicitisAisha LakibulОценок пока нет
- I. Dystocia: A. CausesДокумент9 страницI. Dystocia: A. CausesDianne GalangОценок пока нет
- Stage of DilatationДокумент9 страницStage of DilatationanonymousОценок пока нет
- Intrartum/Intrapartal Period: Phenomena and Process of Labor and Delivery I. Onset of LaborДокумент14 страницIntrartum/Intrapartal Period: Phenomena and Process of Labor and Delivery I. Onset of Laborclaireaongchua1275Оценок пока нет
- Face PresentationДокумент4 страницыFace PresentationRose Ann HajironОценок пока нет
- Abnormal Labor + InfertilityДокумент12 страницAbnormal Labor + InfertilityKristine VanzuelaОценок пока нет
- Abnormal Labor and Infertility 2016 PDFДокумент12 страницAbnormal Labor and Infertility 2016 PDFLarissa TacalanОценок пока нет
- Case Discussion: Mayan, Mercurio, Murillo BSN 2-AДокумент11 страницCase Discussion: Mayan, Mercurio, Murillo BSN 2-ADhen MarcОценок пока нет
- Finals Reviewer 102517Документ20 страницFinals Reviewer 102517Kyla R. PinedaОценок пока нет
- Rationale LeopoldsДокумент6 страницRationale LeopoldsJulianne Kyla MercadoОценок пока нет
- Signs of LaborДокумент5 страницSigns of Labormarianne_07Оценок пока нет
- NCP: Labor Stage 1 Active PhaseДокумент10 страницNCP: Labor Stage 1 Active PhaseJavie100% (3)
- Stages of LBRДокумент3 страницыStages of LBRpjformoso99Оценок пока нет
- Intrapartum Complications: Kristen AzusanoДокумент3 страницыIntrapartum Complications: Kristen AzusanokirbsОценок пока нет
- Intrapartum 111: 1. Examine The Woman For Emergency SignsДокумент7 страницIntrapartum 111: 1. Examine The Woman For Emergency SignsJane MartinОценок пока нет
- Regaining Bladder Control: For Incontinence on Exertion or Following Pelvic SurgeryОт EverandRegaining Bladder Control: For Incontinence on Exertion or Following Pelvic SurgeryОценок пока нет
- First Aid & Emergency Companions: First Aid & Emergencies at SeaОт EverandFirst Aid & Emergency Companions: First Aid & Emergencies at SeaОценок пока нет
- Vagus Nerve: Beginner’s Guide: How to Activate the Natural Healing Power of Your Body with Exercises to Overcome Anxiety, Depression, Trauma, Inflammation, Brain Fog, and Improve Your Life.От EverandVagus Nerve: Beginner’s Guide: How to Activate the Natural Healing Power of Your Body with Exercises to Overcome Anxiety, Depression, Trauma, Inflammation, Brain Fog, and Improve Your Life.Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (24)
- The Psychology of Hysteria - A Selection of Classic Articles on the Analysis and Symptoms of HysteriaОт EverandThe Psychology of Hysteria - A Selection of Classic Articles on the Analysis and Symptoms of HysteriaОценок пока нет
- Antifungal Medication and TherapyДокумент2 страницыAntifungal Medication and TherapyJharaОценок пока нет
- CH34 Child Health AssessmentДокумент6 страницCH34 Child Health AssessmentJharaОценок пока нет
- CH43 Child With Infectious DisorderДокумент1 страницаCH43 Child With Infectious DisorderJharaОценок пока нет
- Healthcare InformaticsДокумент7 страницHealthcare InformaticsJhara100% (1)
- Complication of PregnancyДокумент44 страницыComplication of PregnancyJharaОценок пока нет
- Progress Report TemplateДокумент1 страницаProgress Report TemplateJharaОценок пока нет
- MCN Normal LaborДокумент37 страницMCN Normal LaborJharaОценок пока нет
- Respiratory Disorders in ChildrenДокумент77 страницRespiratory Disorders in ChildrenJharaОценок пока нет
- Neonatal Resuscitation ProgramДокумент40 страницNeonatal Resuscitation ProgramJharaОценок пока нет
- Tracheostomy CareДокумент44 страницыTracheostomy CareJharaОценок пока нет
- Pedia Case PresДокумент44 страницыPedia Case PresJharaОценок пока нет
- Obstetrics Nursing Questions Answer KeyДокумент13 страницObstetrics Nursing Questions Answer Keyicy431100% (2)
- LetrozoleДокумент3 страницыLetrozoleSalima A. PundamdagОценок пока нет
- Homeopathy For Plants Questions and AnswersДокумент21 страницаHomeopathy For Plants Questions and Answershayasaka100% (1)
- Endometrial Polyps: MR Imaging Features: Acta Med. Okayama, Vol., No., PPДокумент11 страницEndometrial Polyps: MR Imaging Features: Acta Med. Okayama, Vol., No., PPapache_sp2208465Оценок пока нет
- Puberty: Normal, Early, and Late DevelopmentДокумент2 страницыPuberty: Normal, Early, and Late Developmentnisa_neyshaaljufri0% (1)
- 40 Reasons You Should Quit Watching Porn TodayДокумент12 страниц40 Reasons You Should Quit Watching Porn TodayThavam RatnaОценок пока нет
- Lintah Tapa UrutДокумент1 страницаLintah Tapa Urutzaidie76Оценок пока нет
- Pengaruh Pemberian Jus Jambu Biji Terhadap Kadar HB Pada Ibu Hamil Trimester Iii Di Polindes Krebet Kecamatan Bululawang Kabupaten MalangДокумент8 страницPengaruh Pemberian Jus Jambu Biji Terhadap Kadar HB Pada Ibu Hamil Trimester Iii Di Polindes Krebet Kecamatan Bululawang Kabupaten MalangRosita Komala DewiОценок пока нет
- Bicornuate Uterus With Associated Bilateral Tubal Blockage and Fibroid TumorsДокумент3 страницыBicornuate Uterus With Associated Bilateral Tubal Blockage and Fibroid TumorsPutu AndreОценок пока нет
- 2019 Book TheGeographiesOfDigitalSexualiДокумент290 страниц2019 Book TheGeographiesOfDigitalSexualiQian HuiОценок пока нет
- Organization of Maternity ServicesДокумент39 страницOrganization of Maternity ServicesAnivasa KabirОценок пока нет
- vARICOCELE3 PDFДокумент3 страницыvARICOCELE3 PDFSylvia AnggraeniОценок пока нет
- 6 PubertasДокумент70 страниц6 PubertasBudi KhangОценок пока нет
- New Microsoft Office PowerPoint PresentationДокумент33 страницыNew Microsoft Office PowerPoint PresentationVasuda Devi MalepatiОценок пока нет
- Intro To MycologyДокумент8 страницIntro To Mycologycamille chuaОценок пока нет
- Gross Anatomy of Uterus: D R. Vibhash Kumar Vaidya Department of AnatomyДокумент25 страницGross Anatomy of Uterus: D R. Vibhash Kumar Vaidya Department of AnatomyAhsan TariqОценок пока нет
- A Guide To Semen Analysis: Information For PatientsДокумент8 страницA Guide To Semen Analysis: Information For PatientsgalvigarciaОценок пока нет
- Advantages of ContraceptivesДокумент4 страницыAdvantages of ContraceptivesArgel Linard Francisco MabagaОценок пока нет
- Printable - Thesis On Bishop ScoreДокумент103 страницыPrintable - Thesis On Bishop Scoreanuaurv100% (3)
- Autogynephilia: A Paraphilic Model of Gender Identity Disorder Anne A. LawrenceДокумент10 страницAutogynephilia: A Paraphilic Model of Gender Identity Disorder Anne A. Lawrencejasper_gregoryОценок пока нет
- Annotated BibliographyДокумент11 страницAnnotated BibliographykjbjkОценок пока нет
- Physical Assessment: The Breast and AxillaeДокумент13 страницPhysical Assessment: The Breast and Axillaemalyn1218Оценок пока нет
- Artificial InseminationДокумент29 страницArtificial InseminationMayuri VohraОценок пока нет
- Zoology II PDFДокумент6 страницZoology II PDFKasuriZaffarОценок пока нет
- Legal Personality of Unborn - A Jurisprudential AnalysisДокумент27 страницLegal Personality of Unborn - A Jurisprudential AnalysisManu J PlamootilОценок пока нет
- INFERTILITY - Bioengineering Strategies of TreatmentДокумент31 страницаINFERTILITY - Bioengineering Strategies of TreatmentAnsar K M HimbranОценок пока нет
- F5 T1 Biology P2 2010-2011Документ14 страницF5 T1 Biology P2 2010-2011asjawolverineОценок пока нет
- 4 2 38.1Документ6 страниц4 2 38.1Alonso Barrios TrillerasОценок пока нет
- Benefits and Risks of SterilizationДокумент29 страницBenefits and Risks of Sterilizationvado_727Оценок пока нет
- Invertebrate Endocrine SystemsДокумент8 страницInvertebrate Endocrine Systemsyudi poponОценок пока нет