Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Be A General Overview of Time Constructions and Us Classroom Posters Grammar Guides 108867
Загружено:
AndreeaMatei0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
13 просмотров1 страницаBe a General Overview of Time Constructions and Us Classroom Posters Grammar Guides 108867
Оригинальное название
Be a General Overview of Time Constructions and Us Classroom Posters Grammar Guides 108867
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документBe a General Overview of Time Constructions and Us Classroom Posters Grammar Guides 108867
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
13 просмотров1 страницаBe A General Overview of Time Constructions and Us Classroom Posters Grammar Guides 108867
Загружено:
AndreeaMateiBe a General Overview of Time Constructions and Us Classroom Posters Grammar Guides 108867
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 1
THE FORMATION OF TENSES OF THE VERB ‘TO BE’
A general (although not complete) overview
The verb ‘to be’ is used as an ordinary verb and as an auxiliary verb.
As an ordinary verb ‘be’ is used to express the state of things and people, it describes and gives
information about a person or thing:
o Look at the state the dog is in! It’s covered in mud.
o How old are you? I’m 27 years old and my brother is 24.
o John is hungry. Are you hungry too?
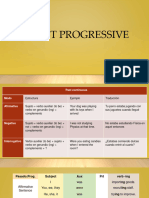
As an auxiliary verb ‘be’ is used together with the present participle (-ing form) of active verbs
to form the continuous (sometimes called the progressive) active form.
o What are you doing? I’m washing the dishes.
o Mum, John isn’t doing his homework. He’s watching a film on his iPad.
‘Be’ is used in all passive forms together with the past particle of the main verb. The passive
form is one of the few verb constructions in which ‘being’ is used.
o They grow coffee beans in Brazil. - Coffee beans are grown in Brazil.
o Did John win the race? - Was the race won by John?
o They are building a hotel here. - A hotel is being built here.
Because of its many irregularities and uses students tend to believe that the more they study English the more difficult
the use of this verb will become. The following table wants to assure them that this is not true. In fact, the present
tense, which is usually the first verb tense they encounter is the most irregular construction and from then on things get
easier.
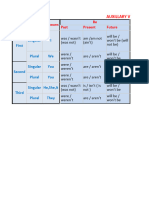
Verb tense pronouns Form of ‘be’ - Affirmative
Simple present (ordinary) I am
he/she/it is
you (sing.)/we, you, they are
Simple past I, he/she/it was
we, you, they were
“Future” simple I, you, he/she/it/we, you, they will + be *
Present Continuous I am + watching
(auxiliary) he/she/it is + working
we, you, they are + playing
Past Continuous I, he/she/it was + going
we, you, they were + going
Future continuous I, you, he/she/it, we, you, they will + be + going *
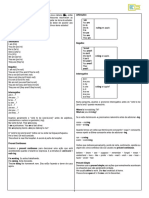
Present Perfect Simple I, you, we, you, they have been
he/she/it has been
Past Perfect Simple I, you, he/she/it, we, you, they had been *
Future Perfect Simple I, you, he/she/it, we, you, they will + have been *
Present Perfect Continuous I, you, we, you, they have been + watching
he/she/it has been + working
Past Perfect Continuous I, you, he/she/it, we, you, they had been + playing *
Future Perfect Continuous I, you, he/she/it, we, you, they will + have been + playing *
*The basic (infinite) form is used for all subjects and pronouns.
The exceptions are only in the 1st (I) and 3rd person (he/she/it) in the present tense, and in the 1st and 3rd person singular
in the past tense. Only in the construction of Present Perfect tenses the 3rd person singular (he/she/it) uses ‘has’ instead
of ‘have’.
Nota: the verb ‘to be’, verbs used as auxiliaries, together with all modal verbs follow the same pattern when forming
questions and negative sentences.
Are you English? - Is he hungry? - Were you in Milan, yesterday? - Will you be having a party next
week?
You aren’t English - She isn’t hungry - They hadn’t been to London - We haven’t been paying attention.
Вам также может понравиться
- Verb BE BritishCouncilДокумент4 страницыVerb BE BritishCouncilFAVargasAОценок пока нет
- Past Perfect Simple or Past SimpleДокумент2 страницыPast Perfect Simple or Past SimplelucaОценок пока нет
- Apuntes Inglés BasicoДокумент8 страницApuntes Inglés BasicoAriadna PinheiroОценок пока нет
- Auxillary VerbsДокумент10 страницAuxillary VerbsSunny soniОценок пока нет
- Công thức bị động của các thìДокумент2 страницыCông thức bị động của các thìPhạm Bích Vân 18150399Оценок пока нет
- Oral Communication Written Communication: Listening SpeakingДокумент21 страницаOral Communication Written Communication: Listening SpeakingSantiagoОценок пока нет
- Basic Tenses With Be: + PositiveДокумент6 страницBasic Tenses With Be: + Positiveomkar digamabar sononeОценок пока нет
- Tenses PDFДокумент14 страницTenses PDFMalaaika SaleemОценок пока нет
- Basic Tenses With BEДокумент5 страницBasic Tenses With BEFarahОценок пока нет
- 12 English TensesДокумент27 страниц12 English Tensesernesto_ayocОценок пока нет
- Passive Voice AssignmentДокумент3 страницыPassive Voice AssignmentIsaac Vázquez YáñezОценок пока нет
- Conjugare Verbe AuxiliareДокумент8 страницConjugare Verbe AuxiliareBalanean Tatiana100% (1)
- Grammaire AnglaiseДокумент48 страницGrammaire AnglaiseMbemba Doumbouya100% (2)
- Tenses - Pronouns OverviewДокумент19 страницTenses - Pronouns Overviewashey jrОценок пока нет
- Scoba TensesДокумент1 страницаScoba TensesNemrac NemracОценок пока нет
- Aff. Neg. Int.: Present SimpleДокумент2 страницыAff. Neg. Int.: Present SimpleRoberto IngraitiОценок пока нет
- Personal PronounsДокумент17 страницPersonal PronounsLexMengasОценок пока нет
- EnglishДокумент38 страницEnglishamalОценок пока нет
- Conjugação Do Verbo To Be em Inglês - Conjugador de Verbos Bab - LaДокумент1 страницаConjugação Do Verbo To Be em Inglês - Conjugador de Verbos Bab - LaLéo Primoroso Dos SantosОценок пока нет
- 1 Reglas Gramaticales Realizada en CuadroДокумент14 страниц1 Reglas Gramaticales Realizada en CuadrojuanОценок пока нет
- Conjugarea Verbului A Fi La Toate TimpurileДокумент4 страницыConjugarea Verbului A Fi La Toate TimpurileDrima Edi100% (1)
- Conjugaison Tous Temps AnglaisДокумент3 страницыConjugaison Tous Temps AnglaisLFolОценок пока нет
- Basic TensesДокумент3 страницыBasic TensesSyafqhОценок пока нет
- 1 PAST SIMPLE - TeoríaДокумент2 страницы1 PAST SIMPLE - TeoríaMateo GonzalezОценок пока нет
- BarryДокумент1 страницаBarryMamadou Alpha BarryОценок пока нет
- Tenses ChartДокумент2 страницыTenses ChartantonsuwantoОценок пока нет
- Mme Chenk (Livre D'anglais1Документ191 страницаMme Chenk (Livre D'anglais1wahiba16Оценок пока нет
- Ilovepdf MergedДокумент37 страницIlovepdf MergedmarracheОценок пока нет
- There Is/there AreДокумент23 страницыThere Is/there ArePris FeversaniОценок пока нет
- Verbo em Inglês TubeДокумент2 страницыVerbo em Inglês TubeJosé franciscoОценок пока нет
- Verb Tenses ReviewДокумент29 страницVerb Tenses ReviewRocío García100% (1)
- Verb 3 Form Verb 3 Form. Verb 3 Form.: ¿ Had He/s He/it Walked?Документ2 страницыVerb 3 Form Verb 3 Form. Verb 3 Form.: ¿ Had He/s He/it Walked?Adriizz Kennedy100% (1)
- Formas Verbales:: 1.-Infinitivo: Watch Es Un InfinitivoДокумент5 страницFormas Verbales:: 1.-Infinitivo: Watch Es Un InfinitivoJoswphОценок пока нет
- Past Simple: Form: V - Ed + - Did Not (Didn't) Play ? Did Play?Документ2 страницыPast Simple: Form: V - Ed + - Did Not (Didn't) Play ? Did Play?Bot StefanОценок пока нет
- The Progressive TensesДокумент22 страницыThe Progressive TensesSajitha PashaОценок пока нет
- How Do We Make The Simple Present Tense?Документ24 страницыHow Do We Make The Simple Present Tense?Noelia Nancy PonceОценок пока нет
- Bahan Ujian Akhir Semester 2 Kelas 10 Bahasa InggrisДокумент12 страницBahan Ujian Akhir Semester 2 Kelas 10 Bahasa InggrisIngrid ChristyОценок пока нет
- Past Simple and ContinuousДокумент3 страницыPast Simple and ContinuousIggnaciio MooraОценок пока нет
- PAD 082 Intensive English Grammar Review - Freebies About EricДокумент7 страницPAD 082 Intensive English Grammar Review - Freebies About EricErik PieceОценок пока нет
- Review - Units 1 - 6Документ32 страницыReview - Units 1 - 6Rolando Aparicio Cueto OsorioОценок пока нет
- Sample ConjugationДокумент3 страницыSample Conjugationgiovanni mОценок пока нет
- Simple Present TenseДокумент8 страницSimple Present Tenseapostuadrian01Оценок пока нет
- Lecciones de InglesДокумент7 страницLecciones de InglesLizRamirezMorenoОценок пока нет
- Grammar Reference B.1 U2Документ2 страницыGrammar Reference B.1 U2Iván DomingoОценок пока нет
- B1.1 U2 GrammarReference-3983837Документ2 страницыB1.1 U2 GrammarReference-3983837Jennifer bcОценок пока нет
- TensesДокумент10 страницTensesShyamala KrishnamurthyОценок пока нет
- Kimia B.inggrisДокумент16 страницKimia B.inggriskhairiyatiОценок пока нет
- Past Perfect SimpleДокумент4 страницыPast Perfect SimpleDr. Amr AboelmagdОценок пока нет
- Past ProgressiveДокумент7 страницPast ProgressiveMilagros irene Montalvan rodriguezОценок пока нет
- Resumen Final de Ingles IIДокумент14 страницResumen Final de Ingles IIDi CasellaОценок пока нет
- Combination TableДокумент12 страницCombination TableVenkatesh WaranОценок пока нет
- Future Forms Will Shall Be Going ToДокумент3 страницыFuture Forms Will Shall Be Going ToMiriamОценок пока нет
- Conjugación Verbal. Adjetivo. Genitivo Sajón: InglésДокумент24 страницыConjugación Verbal. Adjetivo. Genitivo Sajón: InglésMichel MartinezОценок пока нет
- Verbe Auxiliare in Engleza: Verbul To Be - A FiДокумент23 страницыVerbe Auxiliare in Engleza: Verbul To Be - A FiCatalina Miron100% (1)
- Present SimpleДокумент3 страницыPresent SimpletetianaОценок пока нет
- Inglês Módulo 04 Cbmerj: Verb To Be (Am/is/are)Документ2 страницыInglês Módulo 04 Cbmerj: Verb To Be (Am/is/are)Vitor GreyОценок пока нет
- (Full Form) : I, You, We, They She, He, ItДокумент33 страницы(Full Form) : I, You, We, They She, He, ItSilvana NuñezОценок пока нет
- Serbian: Vocabulary Practice A1 to the Book “Idemo dalje 1” - Latin Script: Serbian ReaderОт EverandSerbian: Vocabulary Practice A1 to the Book “Idemo dalje 1” - Latin Script: Serbian ReaderОценок пока нет
- Harold Bloom Sylvia Plath Blooms Modern Critical Views 2007Документ259 страницHarold Bloom Sylvia Plath Blooms Modern Critical Views 2007AndreeaMatei86% (7)
- Def7g H5 Ije61e 9 5 Def7g H5 Ije61e 9 5Документ1 страницаDef7g H5 Ije61e 9 5 Def7g H5 Ije61e 9 5AndreeaMateiОценок пока нет
- Authorial Presence in PoetryДокумент32 страницыAuthorial Presence in PoetryAndreeaMateiОценок пока нет
- Nfi VM NQ Fe FSKQ F H - M HNM MKP (M - M G M M: de FG Hijklm Jkifnfe Om Fmfi FPQ e M PF KKR Hnsi Kttuv Wwi FM X Yz (Документ1 страницаNfi VM NQ Fe FSKQ F H - M HNM MKP (M - M G M M: de FG Hijklm Jkifnfe Om Fmfi FPQ e M PF KKR Hnsi Kttuv Wwi FM X Yz (AndreeaMateiОценок пока нет
- ?@ABCD E FGE Hbiajk @LGCMG: Ji JCDДокумент1 страница?@ABCD E FGE Hbiajk @LGCMG: Ji JCDAndreeaMateiОценок пока нет
- Pag04 PDFДокумент1 страницаPag04 PDFAndreeaMateiОценок пока нет
- Qrstuvrwxyz (TW - ) Ty V) (TSR S Tvu ( VXV (: % Jji KДокумент1 страницаQrstuvrwxyz (TW - ) Ty V) (TSR S Tvu ( VXV (: % Jji KAndreeaMateiОценок пока нет
- Moody - History of English Lit. - Chapter 1 SummaryДокумент4 страницыMoody - History of English Lit. - Chapter 1 SummaryAndreeaMateiОценок пока нет
- Present ContinuousДокумент44 страницыPresent ContinuoushootanОценок пока нет
- Structural Analysis of English SyntaxДокумент26 страницStructural Analysis of English SyntaxremovableОценок пока нет
- Ks2 English 2019 Grammar Punctuation Spelling Paper 1 Short Answer QuestionsДокумент32 страницыKs2 English 2019 Grammar Punctuation Spelling Paper 1 Short Answer QuestionsBharat Manjibhai BhadaniОценок пока нет
- Mod 3, Lesson 4Документ9 страницMod 3, Lesson 4Chrisna Ian Lou EneroОценок пока нет
- Ingles-3ºtrim-7º AnoДокумент8 страницIngles-3ºtrim-7º AnomarcosОценок пока нет
- Engleza Clasa A 5 A 2021-2022Документ6 страницEngleza Clasa A 5 A 2021-2022Elena GheorgheОценок пока нет
- English Functional Literacy EssayДокумент3 страницыEnglish Functional Literacy Essayapi-357571395Оценок пока нет
- Week/Date/ Theme/Topic Content Standard Learning Standard Performance Standard Remarks Basic Content Additional ContentДокумент13 страницWeek/Date/ Theme/Topic Content Standard Learning Standard Performance Standard Remarks Basic Content Additional ContentqaaisarazhafirОценок пока нет
- 36 892153bcrytbxcxbДокумент3 страницы36 892153bcrytbxcxbRiqii PerezОценок пока нет
- Met. It Is Probable That A Determinated Result Might Happen. in Other WordsДокумент7 страницMet. It Is Probable That A Determinated Result Might Happen. in Other WordsDaniela EscalanteОценок пока нет
- Myths Lies and Half-Truths of Language Usage (Starter Materials)Документ3 страницыMyths Lies and Half-Truths of Language Usage (Starter Materials)eo112Оценок пока нет
- Takeaway Hello!: Let's TartДокумент5 страницTakeaway Hello!: Let's TartSonia Alejandra Guevara DuarteОценок пока нет
- Anna-Maria de Cesare, D. Garassino 2015 Exhaustiveness in Cleft Sentences: An Empirical and Cross-Linguistic StudyДокумент56 страницAnna-Maria de Cesare, D. Garassino 2015 Exhaustiveness in Cleft Sentences: An Empirical and Cross-Linguistic StudySergio De Moura MenuzziОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 - Student's BookДокумент14 страницUnit 1 - Student's BookJoey MontanaОценок пока нет
- The Development of Speech ProductionДокумент24 страницыThe Development of Speech ProductionNadia TurRahmiОценок пока нет
- Eastern Armenian Comprehensive Self Study Language CourseДокумент221 страницаEastern Armenian Comprehensive Self Study Language CourseL77% (13)
- Phrases With Prepositions + Ing Form: First Bimester TEACHER: Nila Inés Núñez AlmonacidДокумент2 страницыPhrases With Prepositions + Ing Form: First Bimester TEACHER: Nila Inés Núñez AlmonacidKuniОценок пока нет
- Kelompok 5 - Simple Past Tense Nominal & VerbaДокумент8 страницKelompok 5 - Simple Past Tense Nominal & VerbaMuhamad DullapОценок пока нет
- Verb To Be: Negative / Short Form Affirmative / Short Form InterrogativeДокумент1 страницаVerb To Be: Negative / Short Form Affirmative / Short Form InterrogativeFrancisca Belen VillafrancaОценок пока нет
- 9 TH English Mock TestДокумент6 страниц9 TH English Mock Testpramila monteiroОценок пока нет
- Pie Chart RubricДокумент1 страницаPie Chart RubricJoshua Peregrina100% (1)
- (9783110438444 - Case Studies From Austronesia, The Pacific, The Americas, and Theoretical Outlook) Contents PDFДокумент6 страниц(9783110438444 - Case Studies From Austronesia, The Pacific, The Americas, and Theoretical Outlook) Contents PDFMaxwell MirandaОценок пока нет
- English Course s3 Modal Verb 1Документ20 страницEnglish Course s3 Modal Verb 1Razak AliОценок пока нет
- Guide Number 2 Activities: Get Go Like Meet Start WatchДокумент2 страницыGuide Number 2 Activities: Get Go Like Meet Start Watchvalentina Tao PeñaОценок пока нет
- Read The Article and Choose The Best AnswerДокумент1 страницаRead The Article and Choose The Best AnswerTsvetelina NikolovaОценок пока нет
- Michael Esteban Gomez Taborda-11-4-PHRASAL VERBSДокумент4 страницыMichael Esteban Gomez Taborda-11-4-PHRASAL VERBSmichael gomez tabordaОценок пока нет
- TezeДокумент10 страницTezeTatiana SclifosОценок пока нет
- 2022 Unilorin Post Utme Secret Guide-1Документ12 страниц2022 Unilorin Post Utme Secret Guide-1Agbaje SimiloluwaОценок пока нет
- Quiz#1 ModalsДокумент1 страницаQuiz#1 ModalsJoy YengyenganОценок пока нет
- 800 Phrasal VerbДокумент33 страницы800 Phrasal VerbNgân Nguyễn100% (1)