Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Biochem
Загружено:
Nicole AquinoОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Biochem
Загружено:
Nicole AquinoАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
AQUINO, NICOLE M.
BIOCHEMISTRY LECTURE
MEDICINE 1A AUGUST 15, 2019
1. What is the most common etiology for COPD?
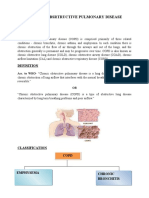
COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)
-a progressive disease that makes it hard to breath.
-associated with group of breathing conditions:
Chronic bronchitis (Chronic mucus production)
Asthma I COPD
Emphysema (destruction of airsacs)
CAUSES:
Smoking
Long term exposure to irritants: (Second hand smoke, air pollution, dust, workplace fumes,
biomass exposure)
Alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency
RESPIRATORY INFECTIONS THAT CAN WORSEN COPD:
Influenza
Pneumonia
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS:
Shortness of breath
Wheezing
Chest tightness
Ongoing (chest) cough
Difficulty with routine activities
Fatigue
Weight loss
Muscle loss
In COPD:
Airways become thick and inflamed
Produce more mucus that clog airways
Damage airsacs- lost their elasticity; become floppy and broken
2. What is the acid base abnormality in this patient?
Hypercapnia- (hypercarbia) condition arising from too much carbon dioxide in the blood.
Caused by hypoventilation or disordered breathing where not enough oxygen enters the lungs
and not enough carbon dioxide emitted.
Respiratory Acidosis- condition that occurs when the lungs can’t remove enough of the carbon
dioxide produced by the body. Excess carbon dioxide causes the pH of blood and other bodily
fluids to decrease, making them too acidic.
3. What is “partial pressure of dissolve gas”?
Partial pressure- the rate of diffusion of each of the gas is directly proportional to the pressure caused
by the gas alone.
Example: The total pressure of air at sea level averages 760mmHg. The pressure that each gas
contributes to the total pressure in direct proportion to its concentration.
-79%nof 760mmHg is caused by Nitrogen (600mmHg)
-21% by oxygen (160mmHg)
The partial pressure of Nitrogen in the mixture is 600mmHg and the partial pressure of Oxygen is
160mmHg.
4. Explain biochemically the pathogenesis of hypercapnia.
In COPD:
CO2 + H2O H2CO3 -HCO3 +H
o In hypercapnia, carbon dioxide is hydrated and forms carbonic acid that subsequently
dissociate into bicarbonate and hydrogen ions.
o There is an increase of hydrogen ion concentration which leads to development of
respiratory acidosis, called hypercapnic acidosis.
5. Explain biochemically how may the body compensate to the acid-base abnormality.
Вам также может понравиться
- Asthma: Symptoms, Treatments, and Medication for Asthma and BronchitisОт EverandAsthma: Symptoms, Treatments, and Medication for Asthma and BronchitisОценок пока нет
- Medical Mnemonic Sketches : Pulmonary DiseasesОт EverandMedical Mnemonic Sketches : Pulmonary DiseasesОценок пока нет
- Biochemical Case 1Документ2 страницыBiochemical Case 1Affie SaikolОценок пока нет
- SL NO Content NOДокумент12 страницSL NO Content NOPdianghunОценок пока нет
- COPD NotesДокумент4 страницыCOPD NotesjisooОценок пока нет
- COPD AsthmaДокумент16 страницCOPD Asthma09172216507Оценок пока нет
- Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (Copd)Документ32 страницыChronic Obstructive Lung Disease (Copd)manal at100% (1)
- CopdДокумент60 страницCopdRizqy Shofianingrum100% (1)
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseДокумент3 страницыChronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseJessica Corona - MarianoОценок пока нет
- Chronic Obsrtructive Pulmonary DiseaseДокумент11 страницChronic Obsrtructive Pulmonary Diseasepreeti sharmaОценок пока нет
- Assignment: Applied MedicineДокумент17 страницAssignment: Applied MedicineKhadija BakhtawarОценок пока нет
- Copd 200412082048Документ139 страницCopd 200412082048Richard ArceОценок пока нет
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseДокумент4 страницыChronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseAudrey Nicole GabianaОценок пока нет
- NCLEX Review NotesДокумент36 страницNCLEX Review NotesKyla Patricia RibanoОценок пока нет
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseДокумент33 страницыChronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseiyhcorОценок пока нет
- Onchi & CopdДокумент8 страницOnchi & CopdAngellene GraceОценок пока нет
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseДокумент10 страницChronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseZinya RobinsonОценок пока нет
- Copd ScriptДокумент17 страницCopd ScriptHydie Mae AlcabedosОценок пока нет
- Copd NotesДокумент11 страницCopd NotesAgnes Jeane EnriquezОценок пока нет
- Chronic Obstructive Pulamonary DiseaseДокумент12 страницChronic Obstructive Pulamonary Diseaseanamika sharmaОценок пока нет
- 1 CopdДокумент37 страниц1 CopdnaturehalwestОценок пока нет
- Order 2763068Документ9 страницOrder 2763068skylineco4Оценок пока нет
- Resp Lung Diseases eДокумент24 страницыResp Lung Diseases eYudi Aryasena Radhitya PurnomoОценок пока нет
- CopdДокумент30 страницCopdsalmanhabeebekОценок пока нет
- DR Ambreen Shams NephrologistДокумент58 страницDR Ambreen Shams NephrologistAamer NaeemОценок пока нет
- Copd: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Information For PatientsДокумент8 страницCopd: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Information For PatientsNrupal PatelОценок пока нет
- Asthma and The COPDsДокумент133 страницыAsthma and The COPDsShania robertsОценок пока нет
- Copd Davidson + OsmosisДокумент3 страницыCopd Davidson + OsmosisElyas MehdarОценок пока нет
- Mostafa 33 2Документ12 страницMostafa 33 2Ahmed AshrafОценок пока нет
- Tina ThankachanДокумент50 страницTina ThankachanBharat JamodОценок пока нет
- COPD PTДокумент49 страницCOPD PTSathish RathnamОценок пока нет
- COPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease REVISEDДокумент37 страницCOPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease REVISEDSonny AgultoОценок пока нет
- Care of Patient With Copd: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseДокумент32 страницыCare of Patient With Copd: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseJesselle LasernaОценок пока нет
- COPD Case StudyДокумент10 страницCOPD Case Studyskylineco4Оценок пока нет
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseДокумент12 страницChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseasejisoo100% (1)
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) : Presented By: Melody Jane Cerbito Cen Janber CabrillosДокумент17 страницChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) : Presented By: Melody Jane Cerbito Cen Janber CabrillosAlecОценок пока нет
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DeseaseДокумент30 страницChronic Obstructive Pulmonary DeseaseShinta DewiОценок пока нет
- CopdДокумент29 страницCopdRidha SyahputraОценок пока нет
- Chronic Obstructive Lung DiseaseДокумент31 страницаChronic Obstructive Lung DiseaseKrizdan PaguioОценок пока нет
- COPD Treatment and ManagementДокумент3 страницыCOPD Treatment and ManagementHydie Mae AlcabedosОценок пока нет
- COPDДокумент26 страницCOPDburjay100% (3)
- Plasma University: Guriel-Galgadud RegionДокумент17 страницPlasma University: Guriel-Galgadud RegionDr AbdulkadirОценок пока нет
- Respiratory DisordersДокумент8 страницRespiratory DisordersDonna DayudayОценок пока нет
- PBL 1 (Pneumonia)Документ11 страницPBL 1 (Pneumonia)Rakeesh VeeraОценок пока нет
- PN21 Health and Healing - Pre-Class Activities - Test 2 PDFДокумент33 страницыPN21 Health and Healing - Pre-Class Activities - Test 2 PDFRachel HomesОценок пока нет
- COPD, or Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseДокумент18 страницCOPD, or Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseemilliansОценок пока нет
- COPDДокумент73 страницыCOPDBroken OreosОценок пока нет
- Medical Management: Chronic Obstructive PulmonaryДокумент1 страницаMedical Management: Chronic Obstructive PulmonaryNuha AlshareefОценок пока нет
- Non-Communicable Disease - COPDДокумент4 страницыNon-Communicable Disease - COPDCamilogsОценок пока нет
- Oxygen InsufficiencyДокумент25 страницOxygen InsufficiencyAnusha Verghese38% (8)
- 2copd FinalДокумент2 страницы2copd FinaluikapuОценок пока нет
- CopdДокумент5 страницCopdapi-719803017Оценок пока нет
- COPDДокумент12 страницCOPDlojainmohamed253Оценок пока нет
- #6 Copd 11 PDFДокумент11 страниц#6 Copd 11 PDFOmar BasimОценок пока нет
- Module 4 - Topic 2 CopdДокумент6 страницModule 4 - Topic 2 CopdZEITAIMEОценок пока нет
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Документ36 страницChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)GLORY MI SHANLEY CARUMBAОценок пока нет
- COPD Case PresentationДокумент15 страницCOPD Case PresentationBola Kwentua29% (7)
- Respiratory Acidosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОт EverandRespiratory Acidosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОценок пока нет
- LAB ActivityДокумент2 страницыLAB ActivityNicole AquinoОценок пока нет
- Aquino, Nicole Miguel Biochemistry Cmed-1A: Heme + Globin Hemoglobin Heme SynthesisДокумент4 страницыAquino, Nicole Miguel Biochemistry Cmed-1A: Heme + Globin Hemoglobin Heme SynthesisNicole AquinoОценок пока нет
- What Is The Most Common Etiology For COPD?: Aquino, Nicole M. Biochemistry Lecture Medicine 1A AUGUST 15, 2019Документ2 страницыWhat Is The Most Common Etiology For COPD?: Aquino, Nicole M. Biochemistry Lecture Medicine 1A AUGUST 15, 2019Nicole AquinoОценок пока нет
- What Is The Most Common Etiology For COPD?: Aquino, Nicole M. Biochemistry Lecture Medicine 1A AUGUST 15, 2019Документ2 страницыWhat Is The Most Common Etiology For COPD?: Aquino, Nicole M. Biochemistry Lecture Medicine 1A AUGUST 15, 2019Nicole AquinoОценок пока нет
- 5000 MCQs in BiochemistryДокумент301 страница5000 MCQs in BiochemistryZia Ashraf Chaudhary94% (17)
- Gross Anatomy IntroductionДокумент4 страницыGross Anatomy IntroductionNicole AquinoОценок пока нет
- TS Nicaragua Health System RPTДокумент74 страницыTS Nicaragua Health System RPTAlcajОценок пока нет
- Referat Smile FixfixДокумент24 страницыReferat Smile FixfixarumОценок пока нет
- Cataract Refract Surg, 35 (2), 273-276.: NISITA SURYANTO, Prof. Dr. Suhardjo, SU., SP.M (K) . Dr. Hartono, SP.M (K)Документ4 страницыCataract Refract Surg, 35 (2), 273-276.: NISITA SURYANTO, Prof. Dr. Suhardjo, SU., SP.M (K) . Dr. Hartono, SP.M (K)peachandmintsОценок пока нет
- Application of Eye Patch, Shield and Bandage.Документ19 страницApplication of Eye Patch, Shield and Bandage.yaraОценок пока нет
- Post Test AtlsДокумент6 страницPost Test Atlsnurul huda85% (62)
- Acu-Stim For RecoveryДокумент4 страницыAcu-Stim For Recoverycare_e_genОценок пока нет
- Pi Is 0022347617311927Документ1 страницаPi Is 0022347617311927Umesh BabuОценок пока нет
- Diabetes Care in Nigeria - 2015 - Annals of Global Health PDFДокумент9 страницDiabetes Care in Nigeria - 2015 - Annals of Global Health PDFarmanОценок пока нет
- Multiple SclerosisДокумент44 страницыMultiple SclerosisVijaya LakshmiОценок пока нет
- Auerbach's Wilderness Medicine PDFДокумент1 672 страницыAuerbach's Wilderness Medicine PDFKieran D90% (10)
- Focus Charting of FДокумент12 страницFocus Charting of FLester GonzalesОценок пока нет
- Chapter7 B and T Cell Activation (1) ImmunologyДокумент21 страницаChapter7 B and T Cell Activation (1) ImmunologyIka BakarОценок пока нет
- Science: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsДокумент42 страницыScience: Modified Strategic Intervention Materialsmichelle sumatОценок пока нет
- PBL 4 - Acyanotic Heart DiseaseДокумент27 страницPBL 4 - Acyanotic Heart DiseaseNadiah Abdul HalimОценок пока нет
- Mock SurgeryДокумент7 страницMock SurgeryElegant Dental clinicОценок пока нет
- Straumann Catalogue Cementatble AbutmentsДокумент35 страницStraumann Catalogue Cementatble AbutmentstzuquinoОценок пока нет
- DrugsДокумент2 страницыDrugsJeff MarekОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 - NT2Документ25 страницChapter 2 - NT2Kathlene GamitОценок пока нет
- Efficacy of A Harvest Graft Substitute For Recession Coverage and Soft Tissue Volume Augmentation. A Randomized Controlled TrialДокумент21 страницаEfficacy of A Harvest Graft Substitute For Recession Coverage and Soft Tissue Volume Augmentation. A Randomized Controlled TrialGabriela Lou GomezОценок пока нет
- Medical Microbiology Made MemorableДокумент113 страницMedical Microbiology Made MemorableParna Praveen90% (10)
- Notes in Human Anatomy and PhysiologyДокумент9 страницNotes in Human Anatomy and PhysiologyRikki Mae Bueno100% (3)
- Muscular DystrophyДокумент64 страницыMuscular DystrophysridharОценок пока нет
- Lesson 1: Health and Skill Related FitnessДокумент2 страницыLesson 1: Health and Skill Related FitnessCrhystal Joy ReginioОценок пока нет
- World Journal of Radiology PDFДокумент8 страницWorld Journal of Radiology PDFniluhОценок пока нет
- Insulin Resistance and PCOS-dr. Hilma Final 11 Juli 2021 FIXДокумент48 страницInsulin Resistance and PCOS-dr. Hilma Final 11 Juli 2021 FIXputrihealthirezaОценок пока нет
- Comparison of Health-Related Quality of Life of Elderly With Hypertension Living in Long-Term Facility vs. CommunityДокумент82 страницыComparison of Health-Related Quality of Life of Elderly With Hypertension Living in Long-Term Facility vs. CommunityEllah ChristineОценок пока нет
- Cardiac Risk AssessmentДокумент4 страницыCardiac Risk Assessmentmonir61Оценок пока нет
- Full Report-Disinfectant and SanitizerДокумент19 страницFull Report-Disinfectant and Sanitizermohd addinОценок пока нет
- Barry S. Fogel, Donna B. Greenberg-Psychiatric Care of The Medical Patient-Oxford University Press (2015) PDFДокумент1 813 страницBarry S. Fogel, Donna B. Greenberg-Psychiatric Care of The Medical Patient-Oxford University Press (2015) PDFhalamadrid77100% (2)
- TransplantДокумент30 страницTransplantLoshi ChandrasekarОценок пока нет