Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
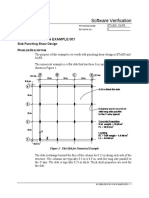
PSIC Receiver (ERAN15.1 - Draft A)
Загружено:
Denmark WilsonОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
PSIC Receiver (ERAN15.1 - Draft A)
Загружено:
Denmark WilsonАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
eRAN
PSIC Receiver Feature Parameter
Description
Issue Draft A
Date 2019-01-05
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD.
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2019. All rights reserved.
No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written
consent of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Trademarks and Permissions
and other Huawei trademarks are trademarks of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
All other trademarks and trade names mentioned in this document are the property of their respective
holders.
Notice
The purchased products, services and features are stipulated by the contract made between Huawei and the
customer. All or part of the products, services and features described in this document may not be within the
purchase scope or the usage scope. Unless otherwise specified in the contract, all statements, information,
and recommendations in this document are provided "AS IS" without warranties, guarantees or
representations of any kind, either express or implied.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Every effort has been made in the
preparation of this document to ensure accuracy of the contents, but all statements, information, and
recommendations in this document do not constitute a warranty of any kind, express or implied.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Address: Huawei Industrial Base
Bantian, Longgang
Shenzhen 518129
People's Republic of China
Website: http://www.huawei.com
Email: support@huawei.com
Issue Draft A (2019-01-05) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. i
eRAN
PSIC Receiver Feature Parameter Description Contents
Contents
1 Change History.............................................................................................................................. 1
1.1 eRAN15.1 Draft A (2019-01-05)................................................................................................................................... 1
2 About This Document.................................................................................................................. 2
2.1 General Statements......................................................................................................................................................... 2
2.2 Applicable RAT.............................................................................................................................................................. 3
2.3 Features in This Document.............................................................................................................................................3
2.4 Feature Differences Between FDD and TDD.................................................................................................................4
3 PSIC Receiver................................................................................................................................. 5
3.1 Principles........................................................................................................................................................................ 5
3.2 Network Analysis........................................................................................................................................................... 5
3.2.1 Benefits........................................................................................................................................................................ 5
3.2.2 Impacts.........................................................................................................................................................................6
3.3 Requirements.................................................................................................................................................................. 6
3.3.1 Licenses....................................................................................................................................................................... 6
3.3.2 Software.......................................................................................................................................................................6
3.3.3 Hardware..................................................................................................................................................................... 7
3.3.4 Others...........................................................................................................................................................................7
3.4 Operation and Maintenance............................................................................................................................................7
3.4.1 Data Configuration...................................................................................................................................................... 7
3.4.1.1 Data Preparation....................................................................................................................................................... 7
3.4.1.2 Using MML Commands........................................................................................................................................... 8
3.4.1.3 Using the CME......................................................................................................................................................... 8
3.4.2 Verification and Monitoring........................................................................................................................................ 8
4 Parameters....................................................................................................................................... 9
5 Counters........................................................................................................................................ 10
6 Glossary......................................................................................................................................... 11
7 Reference Documents................................................................................................................. 12
Issue Draft A (2019-01-05) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. ii
eRAN
PSIC Receiver Feature Parameter Description 1 Change History
1 Change History
This chapter describes changes not included in the "Parameters", "Counters", "Glossary", and
"Reference Documents" chapters. These changes include:
l Technical changes
Changes in functions and their corresponding parameters
l Editorial changes
Improvements or revisions to the documentation
1.1 eRAN15.1 Draft A (2019-01-05)
This issue introduces the following changes to eRAN13.1 01 (2018-04-10).
Technical Changes
None
Editorial Changes
Revised descriptions in the document.
Issue Draft A (2019-01-05) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 1
eRAN
PSIC Receiver Feature Parameter Description 2 About This Document
2 About This Document
2.1 General Statements
Purpose
This document is intended to acquaint readers with:
l The technical principles of features and their related parameters
l The scenarios where these features are used, the benefits they provide, and the impact
they have on networks and functions
l Requirements of the operating environment that must be met before feature activation
l Parameter configuration required for feature activation, verification of feature activation,
and monitoring of feature performance
NOTE
This document only provides guidance for feature activation. Feature deployment and feature
gains depend on the specifics of the network scenario where the feature is deployed. To achieve
the desired gains, contact Huawei professional service engineers.
Software Interfaces
Any parameters, alarms, counters, or managed objects (MOs) described in this document
apply only to the corresponding software release. For future software releases, refer to the
corresponding updated product documentation.
Trial Features
Trial features are features that are not yet ready for full commercial release for certain
reasons. For example, the industry chain (terminals/CN) may not be sufficiently compatible.
However, these features can still be used for testing purposes or commercial network trials.
Anyone who desires to use the trial features shall contact Huawei and enter into a
memorandum of understanding (MoU) with Huawei prior to an official application of such
trial features. Trial features are not for sale in the current version but customers may try them
for free.
Customers acknowledge and undertake that trial features may have a certain degree of risk
due to absence of commercial testing. Before using them, customers shall fully understand not
Issue Draft A (2019-01-05) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2
eRAN
PSIC Receiver Feature Parameter Description 2 About This Document
only the expected benefits of such trial features but also the possible impact they may exert on
the network. In addition, customers acknowledge and undertake that since trial features are
free, Huawei is not liable for any trial feature malfunctions or any losses incurred by using the
trial features. Huawei does not promise that problems with trial features will be resolved in
the current version. Huawei reserves the rights to convert trial features into commercial
features in later R/C versions. If trial features are converted into commercial features in a later
version, customers shall pay a licensing fee to obtain the relevant licenses prior to using the
said commercial features. If a customer fails to purchase such a license, the trial feature(s)
will be invalidated automatically when the product is upgraded.
Feature Differences Between RATs
The feature difference section only describes differences in switches or principles.
Unless otherwise stated, descriptions in this document apply to all RATs. If a description does
not apply to all RATs, the specific RAT that it does apply to will be stated.
For example, in the statement "TDD cells are compatible with enhanced MU-MIMO", "TDD
cells" indicates that this function cannot be used in non-TDD cells.
2.2 Applicable RAT
This document applies to FDD/TDD.
2.3 Features in This Document
This document describes the following FDD feature.
Feature ID Feature Name Section
LOFD-001096 Advanced Receiver 3 PSIC Receiver
(PSIC)
This document describes the PSIC receiver used in TDD.
Issue Draft A (2019-01-05) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 3
eRAN
PSIC Receiver Feature Parameter Description 2 About This Document
2.4 Feature Differences Between FDD and TDD
FDD FDD TDD TDD Difference Section
Feature Feature Feature Feature
ID Name ID Name
LOFD-001 Advanced N/A N/A In FDD, the PSIC 3 PSIC
096 Receiver receiver can be used Receiver
(PSIC) only when uplink
2x2 MU-MIMO is
active.
In TDD, the PSIC
receiver can be used
only when uplink
2x4 MU-MIMO is
active.
Issue Draft A (2019-01-05) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 4
eRAN
PSIC Receiver Feature Parameter Description 3 PSIC Receiver
3 PSIC Receiver
3.1 Principles
The principles of the parallel soft interference cancellation (PSIC) receiver are illustrated in
Figure 3-1. It performs a second iteration based on the soft information provided after the
Turbo decoding for multiple UEs. The receiver reconstructs models for calculating the
channel estimation matrix (H) and equalization matrix (W). It mitigates both inter-UE
interference (IUI) and inter-symbol interference (ISI).
The PSIC receiver can be used only in uplink multi-user multiple-input multiple-output (MU-
MIMO) to improve PUSCH demodulation performance. The PSIC receiver is controlled by
the MumimoPuschPsicSwitch option of the CellAlgoSwitch.PsicSwitch parameter.
In Figure 3-1, y = W(Hx + N), indicating the basic information for channel demodulation.
For details, see MRC and IRC Receivers.
Figure 3-1 Principles of the PSIC receiver
3.2 Network Analysis
3.2.1 Benefits
In FDD, the PSIC receiver can be used only when uplink 2x2 MU-MIMO is active.
In TDD, the PSIC receiver can be used only when uplink 2x4 MU-MIMO is active.
Issue Draft A (2019-01-05) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 5
eRAN
PSIC Receiver Feature Parameter Description 3 PSIC Receiver
The PSIC receiver eliminates IUI to improve post-pairing channel demodulation performance,
increasing the value of Cell Uplink Average Throughput. The higher the correlation
between paired UEs and the higher the signal to interference plus noise ratio (SINR) before
pairing, the higher the PSIC gains.
3.2.2 Impacts
Network Impacts
None
Function Impacts
None
3.3 Requirements
3.3.1 Licenses
The following are FDD license requirements.
Feature ID Feature Name Model Sales Unit
LOFD-001096 Advanced Receiver LT1SARPSIC00 per cell
(PSIC)
The PSIC receiver is not under license control in TDD.
3.3.2 Software
Prerequisite Functions
RAT Function Function Switch Reference
Name
FDD Uplink 2x2 UlVmimoSwitch option of the MIMO
MU-MIMO CellAlgoSwitch.UlSchSwitch
parameter
TDD Uplink 2x4 UlVmimoSwitch option of the MIMO
MU-MIMO CellAlgoSwitch.UlSchSwitch
parameter
Issue Draft A (2019-01-05) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 6
eRAN
PSIC Receiver Feature Parameter Description 3 PSIC Receiver
Mutually Exclusive Functions
RAT Function Function Switch Reference
Name
FDD Short TTI SHORT_TTI_SW option of the Short TTI (FDD)
CellShortTtiAlgo.SttiAlgoSwitch
parameter
TDD N/A N/A N/A
3.3.3 Hardware
Base Station Models
The following base stations support the PSIC receiver:
l 3900 and 5900 series base stations
l DBS3900 LampSite and DBS5900 LampSite
l BTS3911E
Boards
The LBBPc does not support the PSIC receiver in FDD.
Only the UBBP supports the PSIC receiver in TDD.
RF Modules
No requirements
3.3.4 Others
None
3.4 Operation and Maintenance
3.4.1 Data Configuration
3.4.1.1 Data Preparation
Table 3-1 describes the parameters used for function activation.
Issue Draft A (2019-01-05) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 7
eRAN
PSIC Receiver Feature Parameter Description 3 PSIC Receiver
Table 3-1 Parameter related to the PSIC receiver
Parameter Name Parameter ID Option Setting Notes
PSIC algorithm CellAlgoSwitch.PsicSwitc MumimoPusch Select this option.
switch h PsicSwitch
3.4.1.2 Using MML Commands
Activation Command Examples
//Turning on the PSIC receiver
MOD CELLALGOSWITCH: LocalCellId=0,PsicSwitch=MumimoPuschPsicSwitch-1;
Optimization Command Examples
N/A
Deactivation Command Examples
//Turning off the PSIC receiver
MOD CELLALGOSWITCH: LocalCellId=0,PsicSwitch=MumimoPuschPsicSwitch-0;
3.4.1.3 Using the CME
For detailed operations, see CME-based Feature Configuration.
3.4.2 Verification and Monitoring
Activation Verification
None
Network Monitoring
Use the counters listed in Table 3-2 to calculate the uplink cell throughput. The post-
activation throughput should be greater than or equal to the pre-activation throughput.
Uplink cell throughput = L.Thrp.bits.UL / L.Thrp.Time.UL
Table 3-2 Counters related to the uplink cell throughput
Counter ID Counter Name Description
1526728259 L.Thrp.bits.UL Total uplink data volume received at the
PDCP layer in a cell
1526728260 L.Thrp.Time.UL Total uplink data reception duration at the
PDCP layer in a cell
Issue Draft A (2019-01-05) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 8
eRAN
PSIC Receiver Feature Parameter Description 4 Parameters
4 Parameters
The following hyperlinked EXCEL files of parameter reference match the software version
with which this document is released.
l Node Parameter Reference: contains device and transport parameters.
l eNodeBFunction Parameter Reference: contains all parameters related to radio access
functions, including air interface management, access control, mobility control, and radio
resource management.
NOTE
You can find the EXCEL files of parameter reference for the software version on the live network from
the product documentation delivered with that version.
FAQ: How do I find the parameters related to a certain feature from parameter
reference?
Step 1 Open the EXCEL file of parameter reference.
Step 2 On the Parameter List sheet, filter the Feature ID column. Click Text Filters and choose
Contains. Enter the feature ID, for example, LOFD-001016 or TDLOFD-001016.
Step 3 Click OK. All parameters related to the feature are displayed.
----End
Issue Draft A (2019-01-05) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 9
eRAN
PSIC Receiver Feature Parameter Description 5 Counters
5 Counters
The following hyperlinked EXCEL files of performance counter reference match the software
version with which this document is released.
l Node Performance Counter Summary: contains device and transport counters.
l eNodeBFunction Performance Counter Summary: contains all counters related to radio
access functions, including air interface management, access control, mobility control,
and radio resource management.
NOTE
You can find the EXCEL files of performance counter reference for the software version used on the live
network from the product documentation delivered with that version.
FAQ: How do I find the counters related to a certain feature from performance counter
reference?
Step 1 Open the EXCEL file of performance counter reference.
Step 2 On the Counter Summary(En) sheet, filter the Feature ID column. Click Text Filters and
choose Contains. Enter the feature ID, for example, LOFD-001016 or TDLOFD-001016.
Step 3 Click OK. All counters related to the feature are displayed.
----End
Issue Draft A (2019-01-05) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 10
eRAN
PSIC Receiver Feature Parameter Description 6 Glossary
6 Glossary
For the acronyms, abbreviations, terms, and definitions, see Glossary.
Issue Draft A (2019-01-05) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 11
eRAN
PSIC Receiver Feature Parameter Description 7 Reference Documents
7 Reference Documents
1. MIMO
2. MRC and IRC Receivers
Issue Draft A (2019-01-05) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 12
Вам также может понравиться
- A Minimalist Ontology of The Natural World (PDFDrive)Документ189 страницA Minimalist Ontology of The Natural World (PDFDrive)Joseph Hubert Ngon BiramОценок пока нет
- 6 Confidence IntervalsДокумент17 страниц6 Confidence IntervalsLa JeОценок пока нет
- 14 Ships Service GeneratorsДокумент32 страницы14 Ships Service Generatorsdeep4u2009100% (1)
- Nb-Iot Basics (FDD) (Eran15.1 - Draft A)Документ172 страницыNb-Iot Basics (FDD) (Eran15.1 - Draft A)Denmark WilsonОценок пока нет
- Module 2 - Project PlanningДокумент13 страницModule 2 - Project PlanningDenmark WilsonОценок пока нет
- High-Precision TA (GBSS16.0 - 02)Документ21 страницаHigh-Precision TA (GBSS16.0 - 02)Amr Mohamed Abd El-baryОценок пока нет
- Configuration Management (SRAN9.0 02)Документ31 страницаConfiguration Management (SRAN9.0 02)waelq2003Оценок пока нет
- Automatic Congestion Handling (ERAN18.1 - 01)Документ62 страницыAutomatic Congestion Handling (ERAN18.1 - 01)monem777Оценок пока нет
- GSM Carrier Management (GBSS18.1 - 04)Документ199 страницGSM Carrier Management (GBSS18.1 - 04)waelq2003Оценок пока нет
- Performance Management (SRAN7.0 01)Документ21 страницаPerformance Management (SRAN7.0 01)Petson ChirangaraОценок пока нет
- RACH Optimization (ERAN6.0 04)Документ34 страницыRACH Optimization (ERAN6.0 04)theeyanОценок пока нет
- Similarity - Similar Triangles Part 2Документ3 страницыSimilarity - Similar Triangles Part 2Ara Herrera100% (1)
- AS 3600-2018 RC-PN Example 001Документ4 страницыAS 3600-2018 RC-PN Example 001Aashu chaudharyОценок пока нет
- Cell Outage Detection and Compensation (eRAN15.1 - 01)Документ42 страницыCell Outage Detection and Compensation (eRAN15.1 - 01)waelq2003Оценок пока нет
- Air Interface Latency Optimization (ERAN15.1 - 01)Документ37 страницAir Interface Latency Optimization (ERAN15.1 - 01)waelq2003Оценок пока нет
- Module 1 - Project InitiationДокумент21 страницаModule 1 - Project InitiationDenmark WilsonОценок пока нет
- RACH Optimization (ERAN3.0 01)Документ22 страницыRACH Optimization (ERAN3.0 01)Luis Terry TorresОценок пока нет
- Access Class Control (eRAN15.1 - 01) PDFДокумент57 страницAccess Class Control (eRAN15.1 - 01) PDFwaelq2003Оценок пока нет
- Using Multibase Dienes For Basic Six Pupils of Assin NkranДокумент41 страницаUsing Multibase Dienes For Basic Six Pupils of Assin NkranAiman UsmanОценок пока нет
- R12 Oracle Hrms Implement and Use Fastformula: DurationДокумент2 страницыR12 Oracle Hrms Implement and Use Fastformula: DurationAlochiousDassОценок пока нет
- Configuration Management (SRAN16.1 01)Документ22 страницыConfiguration Management (SRAN16.1 01)VVLОценок пока нет
- Northbound Management Feature Description (SRAN15.1)Документ36 страницNorthbound Management Feature Description (SRAN15.1)klajdiОценок пока нет
- Performance Management (SRAN16.1 - 01)Документ26 страницPerformance Management (SRAN16.1 - 01)Didier Sepulveda100% (1)
- Uplink Data Compression (ERAN18.1 - 01)Документ21 страницаUplink Data Compression (ERAN18.1 - 01)monem777Оценок пока нет
- PTT (Eran15.1 Draft A)Документ108 страницPTT (Eran15.1 Draft A)Denmark WilsonОценок пока нет
- RRU PA Efficiency Improvement (SRAN8.0 - 02)Документ23 страницыRRU PA Efficiency Improvement (SRAN8.0 - 02)tadjouaminaОценок пока нет
- Soft Split Resource Duplex (TDD) (eRAN15.1 - Draft A) PDFДокумент55 страницSoft Split Resource Duplex (TDD) (eRAN15.1 - Draft A) PDFDenmark WilsonОценок пока нет
- Soft Split Resource Duplex (TDD) (eRAN15.1 - Draft A) PDFДокумент55 страницSoft Split Resource Duplex (TDD) (eRAN15.1 - Draft A) PDFDenmark WilsonОценок пока нет
- SFN (eRAN15.1 - Draft B) PDFДокумент218 страницSFN (eRAN15.1 - Draft B) PDFDenmark WilsonОценок пока нет
- SFN (eRAN15.1 - Draft B) PDFДокумент218 страницSFN (eRAN15.1 - Draft B) PDFDenmark WilsonОценок пока нет
- Hyper Cell (5G RAN3.1 - Draft A)Документ25 страницHyper Cell (5G RAN3.1 - Draft A)VVL1959100% (1)
- High Speed Mobility (eRAN15.1 - Draft A)Документ160 страницHigh Speed Mobility (eRAN15.1 - Draft A)Denmark WilsonОценок пока нет
- High Speed Mobility (eRAN15.1 - Draft A)Документ160 страницHigh Speed Mobility (eRAN15.1 - Draft A)Denmark WilsonОценок пока нет
- Admission Control (5G RAN6.1 - 01)Документ38 страницAdmission Control (5G RAN6.1 - 01)VVL1959Оценок пока нет
- LTE FDD and NR Spectrum Sharing (SRAN16.1 - 05)Документ70 страницLTE FDD and NR Spectrum Sharing (SRAN16.1 - 05)Bekir OzerОценок пока нет
- AQM (eRAN11.1 02)Документ27 страницAQM (eRAN11.1 02)Yiğit FarukОценок пока нет
- UMTS and LTE Spectrum Sharing (SRAN13.0 01)Документ27 страницUMTS and LTE Spectrum Sharing (SRAN13.0 01)AliNSNОценок пока нет
- Rohc (Eran15.1 Draft A)Документ39 страницRohc (Eran15.1 Draft A)Denmark WilsonОценок пока нет
- MDT (eRAN15.1 - Draft A)Документ26 страницMDT (eRAN15.1 - Draft A)Denmark WilsonОценок пока нет
- Access Control (5G RAN3.1 - 01)Документ15 страницAccess Control (5G RAN3.1 - 01)VVLОценок пока нет
- AQM (eRAN17.1 01)Документ17 страницAQM (eRAN17.1 01)Aklilu AlemayehuОценок пока нет
- 2G, 3G and LTE Co-Transmission (eRAN15.1 - 01)Документ30 страниц2G, 3G and LTE Co-Transmission (eRAN15.1 - 01)Umar MirОценок пока нет
- Configuration Management (SRAN16.1 - 01)Документ24 страницыConfiguration Management (SRAN16.1 - 01)Didier SepulvedaОценок пока нет
- Breathing Pilot (eRAN18.1 - 01)Документ31 страницаBreathing Pilot (eRAN18.1 - 01)monem777Оценок пока нет
- Extended CP (eRAN11.1 - 02)Документ26 страницExtended CP (eRAN11.1 - 02)waelq2003Оценок пока нет
- Performance Management (SRAN13.1 - 01)Документ29 страницPerformance Management (SRAN13.1 - 01)klajdiОценок пока нет
- SRLTE Optimization (ERAN11.1 01)Документ28 страницSRLTE Optimization (ERAN11.1 01)Sameh GalalОценок пока нет
- Access Control Based On 802.1x (SRAN8.0 - 03)Документ33 страницыAccess Control Based On 802.1x (SRAN8.0 - 03)dkmarcОценок пока нет
- Base Station RTOS Security (SRAN15.1 - 01)Документ16 страницBase Station RTOS Security (SRAN15.1 - 01)VVLОценок пока нет
- 2G, 3G and LTE Co-Transmission (ERAN15.1 - Draft A)Документ30 страниц2G, 3G and LTE Co-Transmission (ERAN15.1 - Draft A)Waqas AhmedОценок пока нет
- AQM Feature Parameter Description: Issue DateДокумент20 страницAQM Feature Parameter Description: Issue DateDenmark WilsonОценок пока нет
- Configuration Management (SRAN9.0 01)Документ26 страницConfiguration Management (SRAN9.0 01)mailsianОценок пока нет
- Huawei Lte Outdoor Cpe b2338 168 Product DescriptionДокумент30 страницHuawei Lte Outdoor Cpe b2338 168 Product DescriptionLars-ErikJägardОценок пока нет
- Iu Flex (RAN16.0 - 01)Документ74 страницыIu Flex (RAN16.0 - 01)hekriОценок пока нет
- 01-Library Information (eRAN15.1 - 05)Документ32 страницы01-Library Information (eRAN15.1 - 05)Umar MirОценок пока нет
- Breathing Pilot (eRAN15.1 - 01)Документ32 страницыBreathing Pilot (eRAN15.1 - 01)waelq2003Оценок пока нет
- Access Control Based On 802.1x (SRAN13.1 - 01)Документ34 страницыAccess Control Based On 802.1x (SRAN13.1 - 01)Waqas AhmedОценок пока нет
- BTS3900 V100R010C10SPC120 (NodeB) Release NotesДокумент555 страницBTS3900 V100R010C10SPC120 (NodeB) Release Notesعلي عباسОценок пока нет
- Huawei - RNC - Iu Flex (RAN15.0 - 01)Документ84 страницыHuawei - RNC - Iu Flex (RAN15.0 - 01)Ha Dinh ThanhОценок пока нет
- CE Overbooking (RAN15.0 - 04)Документ163 страницыCE Overbooking (RAN15.0 - 04)dkmarcОценок пока нет
- Transmission Security Overview (SRAN11.1 - 02)Документ21 страницаTransmission Security Overview (SRAN11.1 - 02)waelq2003Оценок пока нет
- Antenna Weight Management ERAN TDD 8 1 02 PDFДокумент26 страницAntenna Weight Management ERAN TDD 8 1 02 PDFdchardwareОценок пока нет
- B 310 S 22Документ21 страницаB 310 S 22firedieselОценок пока нет
- Cloud BB Overview (SRAN10.1 - 02)Документ26 страницCloud BB Overview (SRAN10.1 - 02)DmitryKorovkinОценок пока нет
- Fake Base Station Identification and Detection (eRAN17.1 - Draft A)Документ16 страницFake Base Station Identification and Detection (eRAN17.1 - Draft A)Ahmed YunesОценок пока нет
- B2H (5G Ran2.1 - 01)Документ15 страницB2H (5G Ran2.1 - 01)VVL1959Оценок пока нет
- Channel Management (GBSS17.1 - 01)Документ66 страницChannel Management (GBSS17.1 - 01)goutam4321Оценок пока нет
- Fault Management (SRAN9.0 - 01)Документ46 страницFault Management (SRAN9.0 - 01)dnzgnsОценок пока нет
- Configuration Management (SRAN11.1 02)Документ29 страницConfiguration Management (SRAN11.1 02)waelq2003Оценок пока нет
- Kpi Reference 4Документ53 страницыKpi Reference 4Makki AhmedОценок пока нет
- Base Station OMCH Self-Recovery (SRAN9.0 - 01)Документ26 страницBase Station OMCH Self-Recovery (SRAN9.0 - 01)hekriОценок пока нет
- Turbo Receiver (ERAN12.0 01)Документ31 страницаTurbo Receiver (ERAN12.0 01)Sameh GalalОценок пока нет
- 01-Library Information (ERAN18.1 02)Документ25 страниц01-Library Information (ERAN18.1 02)Abdelbasset AZIZIОценок пока нет
- Ciphering (GBSS18.1 02)Документ58 страницCiphering (GBSS18.1 02)kofi_amoako_amoantwiОценок пока нет
- Ip PM (Ran14.0 - 02)Документ35 страницIp PM (Ran14.0 - 02)bilal_58pkОценок пока нет
- QoS Feature Package Description (ERAN15.1 - Draft A)Документ10 страницQoS Feature Package Description (ERAN15.1 - Draft A)Denmark Wilson100% (1)
- Module 6 - Professional CompetenceДокумент16 страницModule 6 - Professional CompetenceDenmark WilsonОценок пока нет
- Power Supply Management (SRAN15.1 - Draft B)Документ86 страницPower Supply Management (SRAN15.1 - Draft B)Denmark Wilson100% (1)
- AQM Feature Parameter Description: Issue DateДокумент20 страницAQM Feature Parameter Description: Issue DateDenmark WilsonОценок пока нет
- 1.2 MHZ Networking For BCCH TRXs (GBSS21.1 - Draft A)Документ33 страницы1.2 MHZ Networking For BCCH TRXs (GBSS21.1 - Draft A)Denmark WilsonОценок пока нет
- Professional Development Plan TemplateДокумент1 страницаProfessional Development Plan TemplateDenmark WilsonОценок пока нет
- DIPLMBPB15 Assessment 3 Brief 20171101Документ4 страницыDIPLMBPB15 Assessment 3 Brief 20171101Denmark WilsonОценок пока нет
- DIPLMBPB15 Assessment 2 Brief 20171101Документ6 страницDIPLMBPB15 Assessment 2 Brief 20171101Denmark WilsonОценок пока нет
- DIPPMPP15 - Study Guide - For Web PDFДокумент104 страницыDIPPMPP15 - Study Guide - For Web PDFDenmark WilsonОценок пока нет
- Module 4 - Project ScheduleДокумент34 страницыModule 4 - Project ScheduleDenmark WilsonОценок пока нет
- DIPLMBPB15 Assessment 1 Brief 20171101Документ4 страницыDIPLMBPB15 Assessment 1 Brief 20171101Denmark WilsonОценок пока нет
- DIPPMPP15 Assessment 1 Brief 20181017Документ5 страницDIPPMPP15 Assessment 1 Brief 20181017Denmark WilsonОценок пока нет
- Module 4 - Project ScheduleДокумент14 страницModule 4 - Project ScheduleDenmark WilsonОценок пока нет
- Module 6 - Project ReviewДокумент10 страницModule 6 - Project ReviewDenmark WilsonОценок пока нет
- DIPPMPP15 Assessment 3 Brief 20181017Документ5 страницDIPPMPP15 Assessment 3 Brief 20181017Denmark WilsonОценок пока нет
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentДокумент7 страницNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentMangisetty SairamОценок пока нет
- Aea Cookbook Econometrics Module 1Документ117 страницAea Cookbook Econometrics Module 1shadayenpОценок пока нет
- Flint Water Crisis Hypothesis Test: Dan LulsegedДокумент12 страницFlint Water Crisis Hypothesis Test: Dan LulsegedDtwaОценок пока нет
- David Roylance - Mechanics of MaterialsДокумент357 страницDavid Roylance - Mechanics of MaterialsHezi HilikОценок пока нет
- 34ee79a9746d853ef9fa1f44acc55afeДокумент51 страница34ee79a9746d853ef9fa1f44acc55afeSai Pavan MarojuОценок пока нет
- CDMA Simulation: Alison Hightman Elaine Chung Alejandra GalvanДокумент30 страницCDMA Simulation: Alison Hightman Elaine Chung Alejandra GalvanericnaneОценок пока нет
- Download: Coulomb Force (Static) Vocabulary: Prior Knowledge Questions (Do These BEFORE Using The Gizmo.)Документ3 страницыDownload: Coulomb Force (Static) Vocabulary: Prior Knowledge Questions (Do These BEFORE Using The Gizmo.)Xavier McCulloughОценок пока нет
- Marasigan, Christian M. CE-2202 Hydrology Problem Set - Chapter 4 Streamflow MeasurementДокумент10 страницMarasigan, Christian M. CE-2202 Hydrology Problem Set - Chapter 4 Streamflow Measurementchrstnmrsgn100% (1)
- Finite Element Analysis of Hospital BEDДокумент10 страницFinite Element Analysis of Hospital BEDG SATHVIKОценок пока нет
- 5.2 Orthogonal Complements and ProjectionsДокумент17 страниц5.2 Orthogonal Complements and ProjectionsCostalotОценок пока нет
- Adaptive Control Design and AnalysisДокумент45 страницAdaptive Control Design and Analysishind90Оценок пока нет
- Data Structures and Algorithms in Java 6th Edition 201 270Документ70 страницData Structures and Algorithms in Java 6th Edition 201 270longle18704Оценок пока нет
- Chapter2 Sampling Simple Random SamplingДокумент24 страницыChapter2 Sampling Simple Random SamplingDr Swati RajОценок пока нет
- Cis110 12sp MidtermДокумент8 страницCis110 12sp Midtermdodoman666Оценок пока нет
- A K 2 0 0 e R R o R M e S S A G e e X P L A N A T I o N SДокумент142 страницыA K 2 0 0 e R R o R M e S S A G e e X P L A N A T I o N SYatno GomiОценок пока нет
- Chap 1 A - PropositionsДокумент44 страницыChap 1 A - Propositionsعمار الدلال100% (1)
- 8th (0) Physics 9 Weeks DivisionДокумент3 страницы8th (0) Physics 9 Weeks Divisionusama nisarОценок пока нет
- Graph Homomorphisms: Open Problems: L Aszl o Lov Asz June 2008Документ10 страницGraph Homomorphisms: Open Problems: L Aszl o Lov Asz June 2008vanaj123Оценок пока нет
- Handover Parameter 2GДокумент17 страницHandover Parameter 2GSon EricОценок пока нет
- DT Q A DX DT Q KA DX: OverallДокумент193 страницыDT Q A DX DT Q KA DX: OverallHARI B SОценок пока нет
- Representation of Numeric Data in Computer-1Документ3 страницыRepresentation of Numeric Data in Computer-1Anthony LoñezОценок пока нет
- 8 The Chinese Postman ProblemДокумент5 страниц8 The Chinese Postman ProblemWantei Kupar WarjriОценок пока нет