Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
AttachmentL14 - Tutorial 3
Загружено:
Joel VazАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
AttachmentL14 - Tutorial 3
Загружено:
Joel VazАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Basic Electrical Technology
[ELE 1002]
Tutorial 3
Lecture 14
Dept. Of Electrical & Electronics Engg., MIT - Manipal 1
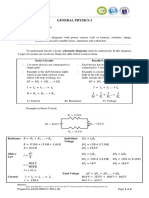
Exercise 1
A magnetic circuit is made of a circular ring of mean circumference of 100 cm. A
saw cut across its cross section is made which is equivalent to an air gap of 2
mm. A coil of 2000 turns, wound on the ring, carries a current of 1 A resulting in
a magnetic flux of 2.5 mWb in the air gap. If the relative permeability of iron is
800, calculate the cross sectional area of iron ring. Neglect fringing effect &
leakage factor.
Ans: 0.32m2
Dept. of Electrical & Electronics Engg., MIT - Manipal 2
Exercise 2
A 1000 turns coils wound on the limb A of the symmetric cast iron steel frame
shown below. Cross-sectional area of the frame is 16 cm2. Find the current
through the coil in order to produce a total flux of 2 mWb in the air gap of the
central limb B. Assume uniform flux density and all the flux lines pass straight
across the air gap. Given air gap thickness 0.1 cm each and all the dimensions are
in centimeters.Assume μr for cast steel is 900.
A B C
4 4
24
18
Ans : 2.68 A
Dept. of Electrical & Electronics Engg., MIT - Manipal 3
Exercise 3
Draw the dotted equivalent circuit and calculate the equivalent inductance of the
coupled circuit shown below where,
L1 = 0.1 H; L2 = 0.2 H; L3 = 0.4 H; k12 = 0.6; k23 = 0.7; k31 = 0.8
Ans : 0.606 H
Dept. of Electrical & Electronics Engg., MIT - Manipal 4
Exercise 4
Find the maximum and minimum inductance possible by connecting the following
magnetically coupled coils wound on the same core in series.
Given the self-inductances of the coils:
L1 = 20 mH; L2 = 30 mH,The coefficient of coupling: K = 0.8
Ans :
Lmax = 89.2 mH
Lmin = 10.8 mH
Dept. of Electrical & Electronics Engg., MIT - Manipal 5
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Mastering HW 1Документ29 страницMastering HW 1hieОценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Chromosome and InheritanceДокумент5 страницChromosome and InheritanceJoel VazОценок пока нет
- TitleДокумент2 страницыTitleJoel VazОценок пока нет
- LetterДокумент1 страницаLetterJoel VazОценок пока нет
- Gram equivalent concept explainedДокумент9 страницGram equivalent concept explained007tsОценок пока нет
- Experiment 2 - Adsorption of Liquids Onto Solid Surfaces: TheoryДокумент3 страницыExperiment 2 - Adsorption of Liquids Onto Solid Surfaces: TheoryfrankjenОценок пока нет
- Project Writeup Guidelines: Cs 239 Section 3: Readable Software Systems Handout 12Документ1 страницаProject Writeup Guidelines: Cs 239 Section 3: Readable Software Systems Handout 12Joel VazОценок пока нет
- mt302 DiffdistДокумент5 страницmt302 DiffdistPinjala AnoopОценок пока нет
- TitleДокумент2 страницыTitleJoel VazОценок пока нет
- Hypothesis-1: Aid in Cancer ResearchДокумент2 страницыHypothesis-1: Aid in Cancer ResearchJoel VazОценок пока нет
- Chapter 19 Angular MomentumДокумент29 страницChapter 19 Angular Momentumgokcen87Оценок пока нет
- Schneider Documentation - Hook-Ups-4Документ1 страницаSchneider Documentation - Hook-Ups-4genih44348Оценок пока нет
- HVT Substation Equipment - Product List PDFДокумент2 страницыHVT Substation Equipment - Product List PDFAmol DeshmukhОценок пока нет
- Katalog PLN 150818Документ48 страницKatalog PLN 150818tuanudinОценок пока нет
- Solving Series and Parallel CircuitsДокумент4 страницыSolving Series and Parallel CircuitsLeonardo PigaОценок пока нет
- CCTV - CVHG780-CN123 - Product ReportДокумент2 страницыCCTV - CVHG780-CN123 - Product ReportTân NguyễnОценок пока нет
- Mission Hydrogen - Siemens - 26th July 2023 - DC SuppliesДокумент21 страницаMission Hydrogen - Siemens - 26th July 2023 - DC Suppliesballa sandyОценок пока нет
- 42 Pbab 399Документ3 страницы42 Pbab 399false mailОценок пока нет
- EMT10 NewДокумент12 страницEMT10 NewzcaptОценок пока нет
- EN3: Introduction To Engineering and Statics: 3. Resultant of Systems of ForcesДокумент6 страницEN3: Introduction To Engineering and Statics: 3. Resultant of Systems of ForceskarthikaОценок пока нет
- CRCW-HP E3: Vishay DraloricДокумент10 страницCRCW-HP E3: Vishay DraloricMohendra PatiОценок пока нет
- MRSM-Physics P2-Trial SPM 2009Документ36 страницMRSM-Physics P2-Trial SPM 2009kamalharmoza100% (3)
- Application Fields of High-Temperature SuperconductorsДокумент14 страницApplication Fields of High-Temperature SuperconductorsMohamed Kather BatchaОценок пока нет
- Ficha Técnica SUPRESOR DE PICOS 40 2 POLOSДокумент2 страницыFicha Técnica SUPRESOR DE PICOS 40 2 POLOSmanuel montero guerraОценок пока нет
- Content Handbook of Energy and Economic Statistics of Indonesia 2021Документ109 страницContent Handbook of Energy and Economic Statistics of Indonesia 2021Richardo DavidОценок пока нет
- Nassim Haramein - The Origin of SpinДокумент16 страницNassim Haramein - The Origin of SpinBogdan Popa100% (1)
- Mock Test-3 CBSEДокумент2 страницыMock Test-3 CBSEAmandeep SinghОценок пока нет
- Methods Predict Added Resistance WavesДокумент66 страницMethods Predict Added Resistance WavesmighalisОценок пока нет
- ISO 9001 AIR-OIL COOLERSДокумент6 страницISO 9001 AIR-OIL COOLERSsuresh muthuramanОценок пока нет
- Die CalculationsДокумент13 страницDie CalculationsDhinakaran R100% (1)
- MATERIALSandMECHANICSmanual CycleiДокумент28 страницMATERIALSandMECHANICSmanual CycleiSrichandОценок пока нет
- Aircraft Electrical Systems (Pallett)Документ192 страницыAircraft Electrical Systems (Pallett)Abolfazl Mazloomi100% (2)
- Study D C Pandey Objective Electrostatics for JEE MainДокумент40 страницStudy D C Pandey Objective Electrostatics for JEE MainAnchitОценок пока нет
- Understanding Shaft Voltage and Grounding Currents of Turbine GeneratorsДокумент12 страницUnderstanding Shaft Voltage and Grounding Currents of Turbine GeneratorsJose PradoОценок пока нет
- Physics Bangla Version PDFДокумент246 страницPhysics Bangla Version PDFDhiman NathОценок пока нет
- Optoelectronics Polarization Optics ChapterДокумент20 страницOptoelectronics Polarization Optics ChapterEngAya R ElmetwallyОценок пока нет
- Equivalence PrincipleДокумент13 страницEquivalence Principlerr1819100% (1)
- Enthalpy Relaxation of Non-Stoichiometric Epoxy-Amine ResinsДокумент13 страницEnthalpy Relaxation of Non-Stoichiometric Epoxy-Amine ResinsOussama El BouadiОценок пока нет
- CBQ Physics XIДокумент2 страницыCBQ Physics XItanmoy bhattacharjeeОценок пока нет