Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
IFRS 3 Summary
Загружено:
Ashley Estrella0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
25 просмотров4 страницы1) IFRS 3 provides guidance on how to account for business combinations. The acquisition method is used which requires identifying the acquirer, determining the acquisition date, and recognizing and measuring the identifiable assets acquired and liabilities assumed at their acquisition-date fair values.
2) Any excess of the consideration transferred over the net assets acquired is recognized as goodwill. Bargain purchases resulting in negative goodwill are recognized in profit or loss. Contingent consideration is classified as a liability or equity and remeasured at fair value each period.
3) Non-controlling interests are measured at either fair value or their proportionate interest in the assets and liabilities. Subsequent accounting requires goodwill to not be am
Исходное описание:
IFRS 3 Summary
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документ1) IFRS 3 provides guidance on how to account for business combinations. The acquisition method is used which requires identifying the acquirer, determining the acquisition date, and recognizing and measuring the identifiable assets acquired and liabilities assumed at their acquisition-date fair values.
2) Any excess of the consideration transferred over the net assets acquired is recognized as goodwill. Bargain purchases resulting in negative goodwill are recognized in profit or loss. Contingent consideration is classified as a liability or equity and remeasured at fair value each period.
3) Non-controlling interests are measured at either fair value or their proportionate interest in the assets and liabilities. Subsequent accounting requires goodwill to not be am
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
25 просмотров4 страницыIFRS 3 Summary
Загружено:
Ashley Estrella1) IFRS 3 provides guidance on how to account for business combinations. The acquisition method is used which requires identifying the acquirer, determining the acquisition date, and recognizing and measuring the identifiable assets acquired and liabilities assumed at their acquisition-date fair values.
2) Any excess of the consideration transferred over the net assets acquired is recognized as goodwill. Bargain purchases resulting in negative goodwill are recognized in profit or loss. Contingent consideration is classified as a liability or equity and remeasured at fair value each period.
3) Non-controlling interests are measured at either fair value or their proportionate interest in the assets and liabilities. Subsequent accounting requires goodwill to not be am
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 4
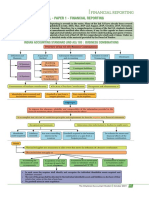
IFRS AT A GLANCE
IFRS 3 Business Combinations
As at 1 July 2018
IFRS 3 Business Combinations Effective Date
Periods beginning on or after 1 July 2009
IDENTIFYING A BUSINESS ACQUISITION METHOD ADDITIONAL GUIDANCE FOR APPLYING
COMBINATION / SCOPE A business combination must be accounted for by applying the acquisition method. THE ACQUISITION METHOD
A business IFRS 3 does not apply to:
combination is: • The accounting for the STEP ACQUISTION
Transaction or event formation of a joint STEP 1: IDENTIFY ACQUIRER STEP 2: DETERMING THE
in which acquirer arrangement in the ACQUISITION DATE • An acquirer sometimes obtains control of an acquiree
obtains control over financial statements of IFRS 10 Consolidated Financial Statements is used to
in which it held an equity interest immediately before
a business (e.g. the joint arrangement identify the acquirer – the entity that obtains control
The date which the acquirer obtains control of the acquisition date. This is known as a business
acquisition of shares itself. of the acquiree.
the acquiree. combination achieved in stages or as a step acquisition
or net assets, legal • Acquisition of an asset • Obtaining control triggers re-measurement of previous
mergers, reverse or group of assets that investments (equity interests)
acquisitions). is not a business. • The acquirer remeasures its previously held equity
• A combination of
entities or businesses
STEP 4: RECOGNITION AND STEP 3: RECOGNITION AND interest in the acquiree at its acquisition-date fair
value (including interests in joint arrangements
under common control. MEASUREMENT OF GOODWILL OR A MEASUREMENT OF ASSETS, classified as joint operations (R)). Any resulting
BARGAIN PURCHASE LIABILITIES AND NON- gain/loss is recognised in profit or loss.
Definition of “control of an investee” • Goodwill is recognised as the excess between: CONTROLLING INTERESTS (NCI)
An investor controls an investee when the investor is - The aggregate of the consideration transferred,
exposed,quantitative
Specific or has rights, todisclosure
variable returns from its
requirements: any non-controlling interest in the acquiree • As of the acquisition date, the acquirer
BUSINESS COMBINATION WITHOUT
involvement with the investee and has the ability to and, in a business combination achieved in recognises, separately from goodwill: TRANSFER OF CONSIDERATION
affect those returns through its power over the stages, the acquisition-date fair value of the - The identifiable assets acquired
investee. acquirer’s previously held equity interest in the - The liabilities assumed • The acquisition method of accounting for a business
acquiree - Any NCI in the acquiree combination also applies if no consideration is
- The identifiable net assets acquired (including • The acquired assets and liabilities are required transferred.
Control (refer to IFRS 10)
any deferred tax balances) to be measured at their acquisition-date fair • Such circumstances include:
• Ownership of more than half the voting right of
• Goodwill can be grossed up to include the values - The acquiree repurchases a sufficient number of its
another entity
amounts attributable to NCI, that is the case • There are certain exceptions to the own shares for an existing investor (the acquirer) to
• Power over more than half of the voting rights by
when NCI is measured at their acquisition date recognition and/or measurement principles obtain control
agreement with investors
fair value. which cover contingent liabilities, income - Minority veto rights lapse that previously kept the
• Power to govern the financial and operating
• A gain from a bargain purchase is immediately taxes, employee benefits, indemnification acquirer from controlling an acquiree in which the
policies of the other entity under statute/
recognised in profit or loss assets, reacquired rights, share-based acquirer held the majority voting rights
agreement
• The consideration transferred in a business payments and assets held for sale. - The acquirer and the acquiree agree to combine
• Power to remove/appoint majority of directors
combination (including any contingent • NCI interests that are present ownership their businesses by contract alone.
• Power to cast majority of votes. consideration) is measured at fair value interests and entitle their holders to a
• Contingent consideration is either classified as a proportionate share of the entity’s net assets
liability or an equity instrument on the basis of in the event of liquidation (e.g. shares) are SUBSEQUENT MEASUREMENT AND
Definition of a “Business” IAS 32 Financial Instruments measured at acquisition-date fair value or at
• Integrated set of activities and assets • Contingent consideration that is within the scope the NCI’s proportionate share in net assets ACCOUNTING
• Capable of being conducted and managed to of IFRS 9 (classified as a financial liability) needs • All other components of NCI (e.g. from IFRS 2
provide return to be remeasured at fair value at each reporting Share-based payments or calls) are required to • In general, after the date of a business combination an
date with changes reported in profit or loss. be measured at their acquisition-date fair acquirer measures and accounts for assets acquired
• Returns include dividends and cost savings.
values. and liabilities assumed or incurred in accordance with
• The acquirer should consider if the consideration
other applicable IFRSs.
includes amounts attributable to other
transactions within the contract (pre-existing • However, IFRS 3 includes accounting requirements for
Acquisition Costs reacquired rights, contingent liabilities, contingent
• Cannot be capitalised, must instead be expensed relationship, arrangements that remunerate
employees etc.). consideration and indemnification assets.
in the period they are incurred
• Costs to issue debt or equity are recognised in
accordance with IAS 32 and IFRS 9.
Вам также может понравиться
- Ifrs at A Glance IFRS 3 Business CombinationsДокумент5 страницIfrs at A Glance IFRS 3 Business CombinationsNoor Ul Hussain MirzaОценок пока нет
- Korean Business Dictionary: American and Korean Business Terms for the Internet AgeОт EverandKorean Business Dictionary: American and Korean Business Terms for the Internet AgeОценок пока нет
- Ifrs 3 AagДокумент5 страницIfrs 3 AagMoses TОценок пока нет
- Business CombinationsДокумент2 страницыBusiness Combinationsssslll2Оценок пока нет
- Summary of Jason A. Scharfman's Private Equity Operational Due DiligenceОт EverandSummary of Jason A. Scharfman's Private Equity Operational Due DiligenceОценок пока нет
- 66705studentjournal-Oct2021a (1) - Removed MadarДокумент20 страниц66705studentjournal-Oct2021a (1) - Removed MadarTimepass MungfuliОценок пока нет
- Factsheet IFRS3 Business CombinationsДокумент15 страницFactsheet IFRS3 Business Combinationsanas khresatОценок пока нет
- Business CombinationsДокумент2 страницыBusiness Combinationsssslll2Оценок пока нет
- Insight To Pfrs 3Документ7 страницInsight To Pfrs 3Elisa ArimasОценок пока нет
- PFRS 3, Business Combination: A) Formation of A Joint Venture - PFRS 11, Joint ArrangementsДокумент7 страницPFRS 3, Business Combination: A) Formation of A Joint Venture - PFRS 11, Joint ArrangementsBhosx KimОценок пока нет
- Profe03 - Chapter 1 Business Combinations Recognition and MeasurementДокумент19 страницProfe03 - Chapter 1 Business Combinations Recognition and MeasurementSteffany Roque100% (1)
- Ifrs 3 IFRS 3 Business Combination: BackgroundДокумент6 страницIfrs 3 IFRS 3 Business Combination: BackgroundKuti KuriОценок пока нет
- Method of Accounting For Business CombinationДокумент13 страницMethod of Accounting For Business CombinationJuliana Stephanie A. ManzanoОценок пока нет
- PFRS 3 Business CombinationsДокумент34 страницыPFRS 3 Business CombinationseiraОценок пока нет
- Concept Map 2Документ8 страницConcept Map 2mike raninОценок пока нет
- Module 13 - BusCom - Forex. - StudentsДокумент13 страницModule 13 - BusCom - Forex. - StudentsLuisito CorreaОценок пока нет
- 2018 Slides Business Combinations EngДокумент42 страницы2018 Slides Business Combinations Engnaomimaboni53Оценок пока нет
- Concept Map 2Документ8 страницConcept Map 2mike raninОценок пока нет
- ADVACC NOTES - Business CombinationДокумент5 страницADVACC NOTES - Business CombinationAlyaОценок пока нет
- Ifrs 3Документ1 страницаIfrs 3Machi KomacineОценок пока нет
- Accounting For Business CombinationsДокумент5 страницAccounting For Business CombinationsJustin RoisОценок пока нет
- Afar 4 - BuscomДокумент2 страницыAfar 4 - Buscomcherish melwinОценок пока нет
- Business CombinationДокумент8 страницBusiness CombinationPhia CustodioОценок пока нет
- Business Combination SummaryДокумент5 страницBusiness Combination SummaryClarice ClaritoОценок пока нет
- Lesson - Business Combinations Part 1 FinalДокумент31 страницаLesson - Business Combinations Part 1 FinalroshandimanthaofficialОценок пока нет
- Edit-XH-H PPT Chap03Документ47 страницEdit-XH-H PPT Chap03An NhiênОценок пока нет
- Ind-AS 103Документ69 страницInd-AS 103amarОценок пока нет
- Ifrs 3 - 2022 SlidesДокумент84 страницыIfrs 3 - 2022 SlidesNolan TitusОценок пока нет
- Business CombinationsДокумент61 страницаBusiness CombinationsGene Joy Villarin100% (1)
- 46355bosfinal p1 cp15Документ105 страниц46355bosfinal p1 cp15aankur97Оценок пока нет
- IndAS 103 AmalgamationДокумент98 страницIndAS 103 AmalgamationadityaОценок пока нет
- Business Combination and Corporate Restructuring: After Studying This Chapter, You Would Be Able ToДокумент98 страницBusiness Combination and Corporate Restructuring: After Studying This Chapter, You Would Be Able ToYUUSDHОценок пока нет
- IAS Plus: IASB Publishes IFRS 3 Business CombinationsДокумент4 страницыIAS Plus: IASB Publishes IFRS 3 Business CombinationsReina EvangelistaОценок пока нет
- Business Combination-Date of AcquisitionДокумент13 страницBusiness Combination-Date of Acquisitionmax pОценок пока нет
- ACCO 30023 - Accounting For Business Combination (IM)Документ74 страницыACCO 30023 - Accounting For Business Combination (IM)rachel banana hammockОценок пока нет
- Ifrs 3 PDFДокумент199 страницIfrs 3 PDFLWQОценок пока нет
- 8 IFRS 3 Business CombinationДокумент21 страница8 IFRS 3 Business Combinationmae acuestaОценок пока нет
- Business CombinationsДокумент44 страницыBusiness CombinationsHimanshu GaurОценок пока нет
- Existence of Control: Prepared By: Angevin B. Acaylar, CpaДокумент2 страницыExistence of Control: Prepared By: Angevin B. Acaylar, CpaCattleyaОценок пока нет
- Buscom Module 2Документ9 страницBuscom Module 2moon binnieОценок пока нет
- Ifrs 3 Business Combinations: Identifying The AcquirerДокумент3 страницыIfrs 3 Business Combinations: Identifying The AcquirerRen NolascoОценок пока нет
- Acquiring A Subsidiary in StagesДокумент19 страницAcquiring A Subsidiary in StagesTokioi OppaОценок пока нет
- Business Combinations Notes: Topic OutlineДокумент4 страницыBusiness Combinations Notes: Topic OutlineMary Jescho Vidal AmpilОценок пока нет
- 4 DP Business Combination - Acquisition DateДокумент6 страниц4 DP Business Combination - Acquisition DateYapi BallersОценок пока нет
- Afar04 Business Combinations Mergers ReviewersДокумент17 страницAfar04 Business Combinations Mergers ReviewersPam G.100% (6)
- Ifrs 3Документ10 страницIfrs 3sayed tarikat ullahОценок пока нет
- Section 19Документ24 страницыSection 19Abata BageyuОценок пока нет
- Accounting For Business Combination - CompressДокумент17 страницAccounting For Business Combination - CompressRonan Ian DinagtuanОценок пока нет
- Accounting For Business Combination Consolidation and Forex Third YearДокумент8 страницAccounting For Business Combination Consolidation and Forex Third YearRosalie Colarte LangbayОценок пока нет
- Prof Elec 1Документ13 страницProf Elec 1Hazel VillanuevaОценок пока нет
- Article On Ifrs 3Документ8 страницArticle On Ifrs 3Yagnesh DesaiОценок пока нет
- Ifrs III - c2 - Ifrs 3 - SVДокумент56 страницIfrs III - c2 - Ifrs 3 - SVPHUC TRAN TRIEU NGUYENОценок пока нет
- Business Combination - Part 1Документ5 страницBusiness Combination - Part 1cpacpacpaОценок пока нет
- Ias 103Документ150 страницIas 103Avani KatheОценок пока нет
- ACC2001 Lecture 8 Business Combinations IIДокумент49 страницACC2001 Lecture 8 Business Combinations IImichael krueseiОценок пока нет
- Prelim Module 1 Introduction To Business Combination StudentДокумент4 страницыPrelim Module 1 Introduction To Business Combination StudentjoshreydugyononОценок пока нет
- Full Ifrs Vs SmeДокумент6 страницFull Ifrs Vs SmeMina ValenciaОценок пока нет
- How Is Inflation Calculated?Документ2 страницыHow Is Inflation Calculated?Omkar SheteОценок пока нет
- UnSigned TVSCS PL ApplicationДокумент13 страницUnSigned TVSCS PL ApplicationArman TamboliОценок пока нет
- Mpb-404 Financial ManagementДокумент6 страницMpb-404 Financial ManagementMohammad Zahirul IslamОценок пока нет
- FRA Endterm QP-Term 1 - PGDM 2023-25Документ4 страницыFRA Endterm QP-Term 1 - PGDM 2023-25elitesquad9432Оценок пока нет
- IC 38 Short Notes (2) 61Документ1 страницаIC 38 Short Notes (2) 61Anil KumarОценок пока нет
- CB Lecture 4Документ17 страницCB Lecture 4Tshepang MatebesiОценок пока нет
- GAC+JD FinalsДокумент3 страницыGAC+JD FinalsAmod JadhavОценок пока нет
- Duties of A Director.: Non-Executive DirectorsДокумент4 страницыDuties of A Director.: Non-Executive DirectorsHitesh ShahОценок пока нет
- CCCR ProjectДокумент17 страницCCCR ProjectVincsОценок пока нет
- REAL 209 Midterm II Study GuideДокумент4 страницыREAL 209 Midterm II Study GuidejuanОценок пока нет
- Dictionary of EconomicsДокумент225 страницDictionary of EconomicsMushtak Shaikh100% (1)
- Invoice 62060270Документ1 страницаInvoice 62060270Chandru PrasathОценок пока нет
- ERP System Functional RequirementsДокумент9 страницERP System Functional RequirementslolitaferozОценок пока нет
- Set 2Документ6 страницSet 2Nicco OrtizОценок пока нет
- Change of BrokerДокумент1 страницаChange of BrokerFiniscope - Investment AdvisorsОценок пока нет
- Retail Trade Liberalization ActДокумент2 страницыRetail Trade Liberalization ActiamdeedattОценок пока нет
- Mba HW Prob 1Документ2 страницыMba HW Prob 1Mercedes JОценок пока нет
- Goals GaloreДокумент15 страницGoals GaloreSandra_ZimmermanОценок пока нет
- Katherine Gaal ResumeДокумент1 страницаKatherine Gaal Resumeapi-302146400Оценок пока нет
- Capital Budgeting: Head, Dept. of Commerce S.D.Jain Girls' College Dimapur: NagalandДокумент13 страницCapital Budgeting: Head, Dept. of Commerce S.D.Jain Girls' College Dimapur: NagalandsantОценок пока нет
- HeatRatesSparkSpreadTolling Dec2010Документ5 страницHeatRatesSparkSpreadTolling Dec2010Deepanshu Agarwal100% (1)
- Income From House Property SEM IVДокумент8 страницIncome From House Property SEM IVThenmozhi RameshОценок пока нет
- Taxguru - In-Schedule II of Companies Act 2013 Depreciation and Practical ImplicationДокумент5 страницTaxguru - In-Schedule II of Companies Act 2013 Depreciation and Practical ImplicationRavi SharmaОценок пока нет
- Case 11-2 SolutionДокумент2 страницыCase 11-2 SolutionArjun PratapОценок пока нет
- Demonetisation The Nielsen ViewДокумент4 страницыDemonetisation The Nielsen ViewShriram SОценок пока нет
- Invoice: Invoice From Invoice To Customer InformationДокумент1 страницаInvoice: Invoice From Invoice To Customer Informationnarsampet stcОценок пока нет
- Planning, Construction and Management of Rural Roads in NepalДокумент17 страницPlanning, Construction and Management of Rural Roads in NepalShambhu SahОценок пока нет
- Departmenatal AccountsДокумент4 страницыDepartmenatal Accountsmanjunatha TKОценок пока нет
- Montes Et Al. (2016)Документ16 страницMontes Et Al. (2016)DiegoPachecoОценок пока нет
- Comparative Study On Financial Analysis of SBI AND HDFC BANK YuiДокумент85 страницComparative Study On Financial Analysis of SBI AND HDFC BANK Yuishshant kashyap50% (4)