Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
RDC
Загружено:
sindhuАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
RDC
Загружено:
sindhuАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
RDC Design and Verification
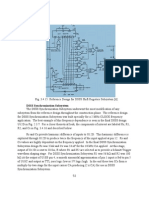
There is a number of design techniques used in reset architecture to mitigate RDC problems. In this
paper, we will discuss a reset staging method and also a RDC synchronization method. The staged reset
synchronization structure enables sequenced removal of resets, minimizing the dangers of
asynchronous and concurrent reset assertion. The staged resets avoid power surges by sequencing the
assertion of resets to design blocks. Staged reset removal structures enforce implicit de-assertion
ordering on data transmitted between adjacent reset domains. For example (Figure 1), if ‘rsta’ is the first
staged synchronizer output and the ‘rstb’ is the second staged synchronizer output, all RDC crossings
from the ‘rsta’ domain to the ‘rstb’ domain are ordered and follow the correct de-assertion sequence.
Automatic verification of the function of such staged reset structures improves the RDC verification
efficiency. Figure 1. Staged Reset Generation. Another technique for sequencing resets is to insert delays
within an asynchronous reset domain. Understanding of the reset architecture also enables the
inference of the reset assertion sequence from insertion of register delays within the same clock
domain. In Figure 2, the assertion of RST will cause DFF2 to reset while DFF1 is still in functional state.
The inconsistent reset delay between adjacent registers causes incorrect data at the downstream logic.
The reset structure assumes that RST is asserted for more than 3 cycles. If RST is only asserted 2 cycles,
then when RST deasserts, DFF2 will be corrupted by DFF1 before DFF1 gets the reset signal. Figure 2.
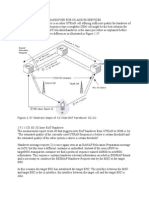
Reset Sequencing. One common RDC synchronization method is to isolate the receiving domain register
from the source domain register. This requires an enable signal to be generated in receiving register’s
clock and reset domain which isolates the receiving register from the transmitting register when the
reset is asserted. Isolation by gating can happen through the data path or the clock path of the receiving
register, as shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4. Specification of A Specification-Driven Methodology for
Reset Domain Crossing Logic 2 the isolation mechanisms for RDC includes the method of
implementation, the source of the isolation enables, the structural details and the possible mapping to
the source and destination reset and clock domains. Figure 3. RDC Clock Isolation Method Figure 4. RDC
Data Isolation Method The RDC verification will verify the reset distribution and verify the RDC paths.
The analysis will check that each RDC path is correctly synchronized and report any RDC path that is
missing a synchronization structure or may be incorrectly synchronized. In addition, any correctly
ordered RDC path will be reported as a correctly synchronized path.
Вам также может понравиться
- From GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandОт EverandFrom GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandОценок пока нет
- A Specification-Driven Methodology For The Design and Verification of Reset Domain Crossing LogicДокумент8 страницA Specification-Driven Methodology For The Design and Verification of Reset Domain Crossing LogicKiran Kumar ParlapalliОценок пока нет
- DSSS Synchronization SubsystemДокумент21 страницаDSSS Synchronization Subsystemapi-26331790Оценок пока нет
- RFC 721Документ15 страницRFC 721NickyNETОценок пока нет
- Huawei Training GuideДокумент5 страницHuawei Training GuidediporufaiОценок пока нет
- vi điều khiểnДокумент4 страницыvi điều khiểnDAO THANH MAIОценок пока нет
- ASIC TimingДокумент54 страницыASIC TimingKrishna MohanОценок пока нет
- Final CDCДокумент4 страницыFinal CDCSrinivas RoaОценок пока нет
- Low Value CSSRДокумент5 страницLow Value CSSRazka100% (1)
- Unit 8 BДокумент105 страницUnit 8 BArvind VishnubhatlaОценок пока нет
- A) Signaling Protocols in GSMДокумент29 страницA) Signaling Protocols in GSMVarun TomarОценок пока нет
- CS Fallback To UMTSДокумент5 страницCS Fallback To UMTSsimish123Оценок пока нет
- WiMAX Channel Simulation Uni ReportДокумент5 страницWiMAX Channel Simulation Uni Reportandygray119Оценок пока нет
- High Speed Clock and Data Recovery For SERDES Applications: October 2012Документ6 страницHigh Speed Clock and Data Recovery For SERDES Applications: October 2012S. Suman Kumar ReddyОценок пока нет
- T Rec Q.712 198811 S!!PDF eДокумент12 страницT Rec Q.712 198811 S!!PDF eDonald TaseОценок пока нет
- ClockDistribution FRIEDMANДокумент28 страницClockDistribution FRIEDMANLionel RiviereОценок пока нет
- S.Kalaivanan N.Sathishkumar K.Ram PrakashДокумент5 страницS.Kalaivanan N.Sathishkumar K.Ram PrakashSaud ManzarОценок пока нет
- RLFДокумент5 страницRLFPritam ModakОценок пока нет
- ROI PAC DocДокумент63 страницыROI PAC DocRayner De RuytОценок пока нет
- A High Estimated Accuracy Random Access Preamble Detection Algorithm For FDD-LTE SystemДокумент8 страницA High Estimated Accuracy Random Access Preamble Detection Algorithm For FDD-LTE Systemevil_dragonОценок пока нет
- Constant Log BCJR Turbo Decoder With Pipelined ArchitectureДокумент5 страницConstant Log BCJR Turbo Decoder With Pipelined ArchitectureInternational Journal of Scientific Research and Engineering StudiesОценок пока нет
- Debug and Testability Features For Multi-Protocol 10G SerdesДокумент5 страницDebug and Testability Features For Multi-Protocol 10G SerdesvelusnОценок пока нет
- Inter Rat Handover GSM UmtsДокумент4 страницыInter Rat Handover GSM UmtsadanakebapОценок пока нет
- 14 Cach Dong Bo Du Lieu - Synchronous TechniquesДокумент8 страниц14 Cach Dong Bo Du Lieu - Synchronous TechniquesNguyễn Thế TuyênОценок пока нет
- SyncДокумент14 страницSyncvishalp6100% (1)
- SRTDivision AlgorithmsДокумент4 страницыSRTDivision AlgorithmsAsif KhanОценок пока нет
- Design of Testable Sequential CircuitsДокумент44 страницыDesign of Testable Sequential CircuitsMahesh S GourОценок пока нет
- 11 RoutingДокумент23 страницы11 Routingketchrajath24Оценок пока нет
- A Low Power VITERBI Decoder Design With Minimum Transition Hybrid Register Exchange Processing For Wireless ApplicationsДокумент9 страницA Low Power VITERBI Decoder Design With Minimum Transition Hybrid Register Exchange Processing For Wireless ApplicationsAnonymous e4UpOQEPОценок пока нет
- Prediction Router: Yet Another Low Latency On-Chip Router ArchitectureДокумент12 страницPrediction Router: Yet Another Low Latency On-Chip Router ArchitectureChih Hsun ChouОценок пока нет
- Leonid, Guerin, Vperis Kumar@ece - Iisc.ernet - inДокумент33 страницыLeonid, Guerin, Vperis Kumar@ece - Iisc.ernet - inChindu KrishОценок пока нет
- RRC Re-EstablishmentДокумент16 страницRRC Re-EstablishmentRaheel ShahzadОценок пока нет
- mnl100 Interface ManualДокумент40 страницmnl100 Interface ManualDavid WalkerОценок пока нет
- Scrambling Code Guidelines For RFI Project v1Документ9 страницScrambling Code Guidelines For RFI Project v1yawer111Оценок пока нет
- Transmission SynchДокумент47 страницTransmission SynchMakarand DereОценок пока нет
- FPGA Implementation of CORDIC-Based QRD-RLS AlgorithmДокумент5 страницFPGA Implementation of CORDIC-Based QRD-RLS Algorithmsappal73asОценок пока нет
- CAN Bus NeuralДокумент6 страницCAN Bus Neuraltssskk1976Оценок пока нет
- Inter Rat Handover GSM Umts PDFДокумент4 страницыInter Rat Handover GSM Umts PDFdearvittОценок пока нет
- Basics of Multicycle Path and Fals PathДокумент11 страницBasics of Multicycle Path and Fals PathMani KandanОценок пока нет
- Traffice Shape ColorДокумент9 страницTraffice Shape ColorSON NGUYEN DUY HAОценок пока нет
- Challenges in Verification of Clock DomainsДокумент8 страницChallenges in Verification of Clock DomainsKi KiОценок пока нет
- RSP 3332 Sistema RedundanteДокумент29 страницRSP 3332 Sistema RedundanteAdan LopezОценок пока нет
- Dynamic Scheduling Framework On An RLC/MAC Layer For General Packet Radio ServiceДокумент9 страницDynamic Scheduling Framework On An RLC/MAC Layer For General Packet Radio ServiceAbdenago RoldanОценок пока нет
- Transcoder Free Operation: Stage 1 RequirementsДокумент12 страницTranscoder Free Operation: Stage 1 RequirementskamalfОценок пока нет
- 2 3 1637833001 1ijcnwmcdec20211Документ8 страниц2 3 1637833001 1ijcnwmcdec20211TJPRC PublicationsОценок пока нет
- GSM Network SDCCH Congestion & Solutions-16Документ15 страницGSM Network SDCCH Congestion & Solutions-16abdullaaОценок пока нет
- LTE Synchronization and Identifiers - PartialДокумент44 страницыLTE Synchronization and Identifiers - PartialManish Kumar100% (1)
- Very High-Level Synthesis of Datapath and Control Structures For Reconfigurable Logic DevicesДокумент5 страницVery High-Level Synthesis of Datapath and Control Structures For Reconfigurable Logic Devices8148593856Оценок пока нет
- RRC EstablishmentДокумент4 страницыRRC Establishmentevil_dragonОценок пока нет
- Serial CommunicationДокумент8 страницSerial CommunicationKrisHnA 2kОценок пока нет
- Picosecond-Accuracy Digital-To-Time Converter For Phase-Interpolation DdsДокумент12 страницPicosecond-Accuracy Digital-To-Time Converter For Phase-Interpolation DdsMark William Sanchez PalaciosОценок пока нет
- Bidirectional Com Spec Ver.1.092Документ43 страницыBidirectional Com Spec Ver.1.092MFОценок пока нет
- A Simple Self-Timed Implementation of A Priority Queue For Dictionary Search ProblemsДокумент6 страницA Simple Self-Timed Implementation of A Priority Queue For Dictionary Search ProblemsSahilYadavОценок пока нет
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksОт EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksОценок пока нет
- Advanced Multicarrier Technologies for Future Radio Communication: 5G and BeyondОт EverandAdvanced Multicarrier Technologies for Future Radio Communication: 5G and BeyondОценок пока нет
- File Extension SДокумент3 страницыFile Extension SSharan Kumar GoudОценок пока нет
- Alignsat 2.4m Earth Station AntennaДокумент4 страницыAlignsat 2.4m Earth Station AntennaVincent Eyada NdjengueОценок пока нет
- Remocon LRT 1Документ2 страницыRemocon LRT 1siluma11Оценок пока нет
- Hearing Is BelievingДокумент1 страницаHearing Is BelievingAntonioPalloneОценок пока нет
- Marquette Cardioserv V4 - Service Manual PDFДокумент113 страницMarquette Cardioserv V4 - Service Manual PDFPablo Millaquén GОценок пока нет
- AC DC AcДокумент3 страницыAC DC AcPhani KumarОценок пока нет
- Gek 106310ahДокумент1 052 страницыGek 106310ahKeli KeyОценок пока нет
- DVDR3570H - SB KL Ex Si - 1221814332Документ54 страницыDVDR3570H - SB KL Ex Si - 1221814332olomouc7267Оценок пока нет
- Parts and Function of A Computer: Name: Anjo Blancada ACT 1-AДокумент5 страницParts and Function of A Computer: Name: Anjo Blancada ACT 1-AJay Mark BlancadaОценок пока нет
- Arduino Modules L298NДокумент4 страницыArduino Modules L298NNermin FejzicОценок пока нет
- Prince PLC & ScadaДокумент46 страницPrince PLC & ScadaPreet ChahalОценок пока нет
- 9200002-QR-T-UNIT SD02 RF Version B08Документ8 страниц9200002-QR-T-UNIT SD02 RF Version B08Cristian RodriguezОценок пока нет
- 1SBP260511R1001 07cr41ac31 PLC 8di 6do Rel 34kb 24vdcДокумент2 страницы1SBP260511R1001 07cr41ac31 PLC 8di 6do Rel 34kb 24vdcSandeep SОценок пока нет
- AC Assignment QuestionsДокумент3 страницыAC Assignment QuestionsSudarshanОценок пока нет
- TS EAMCET 2015 Last RankДокумент54 страницыTS EAMCET 2015 Last RankPranathi BaduguОценок пока нет
- Fieldmaster User ManualДокумент40 страницFieldmaster User ManualArun BalaОценок пока нет
- Lab1 DiodesДокумент4 страницыLab1 DiodesDavid TandjayaОценок пока нет
- Exemplo de Artigo JMOEДокумент13 страницExemplo de Artigo JMOElemuelОценок пока нет
- Radio CommunicationДокумент57 страницRadio CommunicationAhmad Arif Zulfikar100% (1)
- Epox 8RDA3i Mainboard English ManualДокумент90 страницEpox 8RDA3i Mainboard English ManualDan BanОценок пока нет
- Datasheet LTC1298 LTC1286 PDFДокумент24 страницыDatasheet LTC1298 LTC1286 PDFletterniОценок пока нет
- Martin A. Green - Solar Cells Operating Principles Technology and System Applications-Prentice Hall (1982)Документ139 страницMartin A. Green - Solar Cells Operating Principles Technology and System Applications-Prentice Hall (1982)Ahmed SaeedОценок пока нет
- DatasheetДокумент3 страницыDatasheetRahmat Ibnu DahlanОценок пока нет
- QPF4001 Data SheetДокумент21 страницаQPF4001 Data SheetNhat Tran XuanОценок пока нет
- How To Build Advanced ShortWave ReceiversДокумент119 страницHow To Build Advanced ShortWave Receiversiosif_viorelm100% (3)
- CoprocessorДокумент23 страницыCoprocessorsarthakОценок пока нет
- CH 02 FabricationДокумент55 страницCH 02 FabricationUPADHYAY SHIVANSHОценок пока нет
- ARM920T ProcessorДокумент14 страницARM920T ProcessorgpuonlineОценок пока нет
- AVerTV USB2.0 Plus (M036)Документ1 страницаAVerTV USB2.0 Plus (M036)min2bal4uОценок пока нет
- Construction of TransformerДокумент33 страницыConstruction of TransformervurumuuОценок пока нет