Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Describing Quantitative Research
Загружено:
Lawrence Ong Noleal0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
53 просмотров5 страницThe document describes the key characteristics of quantitative research. It outlines the positivist and realist paradigms that quantitative research operates under. The research is objective and seeks to measure variables using tools like questionnaires. It aims to test hypotheses through experimental and manipulative methods like randomization and controlling variables. The goal is to explain causal relationships through empirical examination of measurable and quantifiable data.
Исходное описание:
Describing Quantitaive Research
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThe document describes the key characteristics of quantitative research. It outlines the positivist and realist paradigms that quantitative research operates under. The research is objective and seeks to measure variables using tools like questionnaires. It aims to test hypotheses through experimental and manipulative methods like randomization and controlling variables. The goal is to explain causal relationships through empirical examination of measurable and quantifiable data.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
53 просмотров5 страницDescribing Quantitative Research
Загружено:
Lawrence Ong NolealThe document describes the key characteristics of quantitative research. It outlines the positivist and realist paradigms that quantitative research operates under. The research is objective and seeks to measure variables using tools like questionnaires. It aims to test hypotheses through experimental and manipulative methods like randomization and controlling variables. The goal is to explain causal relationships through empirical examination of measurable and quantifiable data.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 5
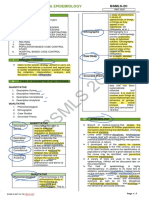
Describing Quantitative Research This frequency refers to frequency
Lesson 1 Numerical distribution percentage, and
Description measures of central tendencies like
mode, median and mean.
To know more about the characteristics of quantitative
research, we should look into what the quantitative paradigm has to
Casual explanation relates to the
say in terms of various orientations. Antwi and Hamza (2015)
highlighted the basic characteristics of quantitative research in each meaning of causality, which refers to
Causal
orientation. A modified version of their presentation is outlined and a concern with establishing causal
Explanation
described in the table below. connections rather than mere
Research
relationships (Bryman 2008)
Characteristics of Purpose
Orientatio (rationale)
Quantitative Description
n Prediction is a statement about the
Research
future based on facts
Prediction
(https://www.vocabulary.com/diction
Positivism - an epistemological
ary/prediction).
position that advocates the
application of methods of the
natural sciences to the study of This refers to "what can be known
social reality and beyond and how. “For examples: Is the
(Bryman 2008 ) Ontology social world patterned and
Paradigm Nature of Social
(assumptio Positivism and Realism - an epistemological (nature of predictable or is the social world
Reality
position that acknowledges a reality) continually being constructed
n about the Realism
reality independent of the senses through human perspective?" (Biber
world)
that is accessible to the and Leavy, 2011)
researcher's tools and theoretical
speculations. It implies that the
categories created by scientists
refer to real objects in the natural
or social world (Bryman, 2008)
Objectivist refers to the notion that Measurement procedure for
Epistemol assigning symbols, letters, or
reality is "objective", "out there",
ogy numbers to empirical properties of
singular and apart from the
(theory of Objectivist variables according to rules
researcher, and it can be measured
knowledge Measurement (web.csulb.edu/~msaintg/ppa696/69
objectively by using a questionnaire
) 6meas.htm). It is also the process of
or an instruments (Cresswell, 1994)
observing and recording the
observations collected as part of a
Refers to a type of quantitative research effort (Trochim 2006)
research where the researchers
Methodolo manipulate one variable and control/
Hypothesis is an informed
gy (aims randomize the rest of the variables.
speculation, which is set up to be
of Experimental / If has a control group and subjects
tested, about the possible
scientific Manipulative have been randomly assigned
Hypothesis relationship between two or more
investigati between the groups. Researcher test
testing variables (Brymab 2008).
on) only one effect at a time.
Hypothesis testing, therefore, of
(https://explorable.
checking if the independent variable
com/experimental-research).
have a relationship.
Empirical explanation is generally
referred to as information that is Randomization is related to random
Research derived through observation or assignment. a term used in
Methods experiment. This may also be linked connection with experiments to refer
Empirical Randomization to the random allocation of research
(technique with empiricism, which is an
examination participants to the experimental
s and approach to the study of reality that
tools) suggest that only knowledge gained group and the control group.
through experience and the senses is
acceptable (Bryman, 2008)
Research protocol is the sequence of
manipulations and measurement
Research
procedures that make up the
Protocol
experiments. Its description should
follow the exact sequence of how the
procedures were executed. This
involves a description of baseline
conditions and any associated
baseline measurements, followed by
the sequence of manipulations of the
independent variable and the
subsequent measurement of changes
in the dependent variable.
A questionnaire is a collection of
Questionnaire questions administered by
respondents (Bryman, 2008)
Deductive - an approach to the
Scientific relationship between theory and
Deductive
Method research in which the latter is
(role of
approach/ testing
of theory
conducted with reference to Differentiating the Quantitative and
theory) hypothesis and ideas inferred from
the former.
Qualitative Research
Lesson 1
A qualitative research is defined as “an inquiry process of
understanding a social or human problem based on building a
complex, holistic picture formed with words, reporting detailed views
of informants, and conducted in a natural setting.” (Creswell, 1994) A
quantitative research, on the other hand, is “an inquiry into a social
or human problem based on testing a theory composed of variables,
measured with numbers, and analyzed with statistical procedures in
order to determine whether the predictive generalizations of the theory
hold true” (Creswell 1994)
Qualitative and Quantitative Research Paradigm Assumptions
situation
Assumption Question Qualitative Quantitative
Axiological What is the Value-laden and Value - free and
Ontological What is the Reality is Reality is role of biased. unbiased,
nature of subjective and "objective”, “out value? Researcher "accomplished
reality? multiple as seen there", singular, "admits the value- through entirely
by participants in apart from the laden nature of omitting
a study. It is researcher, and the study and statements about
'constructed by can be measured actively reports values from a
the individuals in objectively by his or her values written report,
the research using a and biases, as uses impersonal
situation" questionnaire or well as the value language, and
Researcher must an instrument. nature of reports 'facts',
"report faithfully information arguing closely
these realities and gathered from the from the
rely on voices and field." evidence
interpretations of gathered in the
informants" study."
Epistemological What is the Researcher Researcher is Rhetorical What is the Informal Formal
relationship interacts with the independent language of Evolving based on set
of the subject of from the subject research? decisions definitions
researcher research. of research. In Personal voice impersonal
to the Interaction may surveys and Uses accepted voice
subject of be in the form of experiments, for qualitative uses accepted
research? living with or instance, words - quantitative
observing "researchers "understandin words -
informants over a attempt to g, discover, "relationship,
prolonged period control bias, and meaning" comparison,
of time or actual select a and within -
collaboration. systematic group"
sample, and be Methodological What is the nductive process deductive
objective in process of mutual process
assessing a research? simultaneous cause and effect
shaping if factors statis design -
emerging design - categories
categories isolated before
identified during study
research process context - free
context bound generalizations
patterns and lead to
theories prediction,
developed for explanation, and
understanding understanding
accurate and accurate and
reliable through reliable through
verification validity and
reliability.
Adopted from Creswell, J.Research Design. New Delhi: Sage Publications, 1994.5
Вам также может понравиться
- Definition, Characteristics and Types of Quantitative ResearchДокумент47 страницDefinition, Characteristics and Types of Quantitative ResearchRex Michael100% (1)
- Nature of Inquiry and Research RamiscalДокумент24 страницыNature of Inquiry and Research RamiscalAlaizah Gail Luis MatiasОценок пока нет
- M206512 Kasaera S - Research AssignmentДокумент14 страницM206512 Kasaera S - Research Assignmentshingirai kasaeraОценок пока нет
- Abstraction: Lesson 1: Philosophical Worldviews in ResearchДокумент4 страницыAbstraction: Lesson 1: Philosophical Worldviews in ResearchKayla Marie CagoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 Research Methodology (Pretoria University)Документ69 страницChapter 4 Research Methodology (Pretoria University)david100% (3)
- Session 5-6: Understanding Research Philosophies and ApproachesДокумент18 страницSession 5-6: Understanding Research Philosophies and ApproachesNguyen Trung Hau K14 FUG CTОценок пока нет
- Theory Collection Spring 2023Документ40 страницTheory Collection Spring 2023ASHRAFОценок пока нет
- Meta-Ethnography & Theory Building: George Noblit R Dwight HareДокумент42 страницыMeta-Ethnography & Theory Building: George Noblit R Dwight HareInten Dwi Puspa DewiОценок пока нет
- Go Ecological - NatEvolMindsConfДокумент33 страницыGo Ecological - NatEvolMindsConfMiguel Segundo OrtinОценок пока нет
- Chapter Three (RESEARCH METHODOLOGY)Документ127 страницChapter Three (RESEARCH METHODOLOGY)mecca_faiza100% (5)
- 2014PietkiewiczSmith ApracticalguidetousingIPAДокумент9 страниц2014PietkiewiczSmith ApracticalguidetousingIPAtrhonovamartinaОценок пока нет
- Week1 Paradigm ArticleДокумент6 страницWeek1 Paradigm Article秦雪岭Оценок пока нет
- 10 1 1 1072 17Документ7 страниц10 1 1 1072 17TheGilmoreBuddiesОценок пока нет
- (2018) Friston Et Al. - Deep Temporal Models and Active InferenceДокумент16 страниц(2018) Friston Et Al. - Deep Temporal Models and Active InferenceRobert Chis-CiureОценок пока нет
- Qualitative ResearchДокумент61 страницаQualitative Researchrmm0415Оценок пока нет
- Phenomenological Properties of Perceptual Presence: A Constructivist Grounded Theory ApproachДокумент14 страницPhenomenological Properties of Perceptual Presence: A Constructivist Grounded Theory ApproachAjit GhoshОценок пока нет
- EPI 3.6 Qualitative ResearchДокумент5 страницEPI 3.6 Qualitative ResearchJoher MendezОценок пока нет
- Perceptual Ratings of Opposite Spatial Properties - Do They Lie On The Same DimensionДокумент14 страницPerceptual Ratings of Opposite Spatial Properties - Do They Lie On The Same Dimensionlevi nilawatiОценок пока нет
- Descriptive ResearchДокумент9 страницDescriptive ResearchUty AgustiaОценок пока нет
- A Practical Guide To Using Interpretative Phenomenological Analysis in Qualitative Research PsychologyДокумент9 страницA Practical Guide To Using Interpretative Phenomenological Analysis in Qualitative Research PsychologyClau OrellanoОценок пока нет
- Book Reviews: Revisiting Realistic EvaluationДокумент7 страницBook Reviews: Revisiting Realistic EvaluationMuaz JalilОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Business Research Methods Vamsi KrishnaДокумент25 страницIntroduction To Business Research Methods Vamsi KrishnaEng MatanaОценок пока нет
- 03 BiostatДокумент7 страниц03 BiostatDavid MangawilОценок пока нет
- Business Research Method Aljamia-1Документ2 страницыBusiness Research Method Aljamia-1MNK TALK100% (1)
- 2014 Pietkiewicz Smith - A Practical Guide To Using IPA-with-cover-page-v2Документ9 страниц2014 Pietkiewicz Smith - A Practical Guide To Using IPA-with-cover-page-v2dishaa1408Оценок пока нет
- Chapter1 NatureOfInquiryДокумент4 страницыChapter1 NatureOfInquiryAmairani MellОценок пока нет
- Overview of Qualitative Research Designs (9!5!2020)Документ14 страницOverview of Qualitative Research Designs (9!5!2020)MARIFE MUSTACISA-LACABAОценок пока нет
- Paradigm, Theory and MethodsДокумент24 страницыParadigm, Theory and Methodsabrham abagedaОценок пока нет
- Gaze and Eye Contact ResearchДокумент23 страницыGaze and Eye Contact ResearchTomaKlusaitėОценок пока нет
- Flake Pek Hehman SPPSДокумент9 страницFlake Pek Hehman SPPSnilaОценок пока нет
- Virtual Reality in Episodic Memory...Документ26 страницVirtual Reality in Episodic Memory...Laura TorresОценок пока нет
- Conducting Qualitative Research: Writing The MethodologyДокумент30 страницConducting Qualitative Research: Writing The MethodologytamiОценок пока нет
- Stone (2010) - Reserach Strategies in IO Psychology PDFДокумент36 страницStone (2010) - Reserach Strategies in IO Psychology PDFNestor Byron Noguera BejaranoОценок пока нет
- Research Paradigms Full ArticleДокумент14 страницResearch Paradigms Full Articleparwinder1989100% (1)
- Rosenthal QuantifyingConstructДокумент12 страницRosenthal QuantifyingConstructAnjali TiwariОценок пока нет
- A Review of Key Paradigms: Positivism VS InterpretivismДокумент5 страницA Review of Key Paradigms: Positivism VS InterpretivismOmozegie 'OZ1' OtuborОценок пока нет
- Selecting Scientific Procedures and Research MethodsДокумент5 страницSelecting Scientific Procedures and Research MethodsDoãn Phương LinhОценок пока нет
- Practica L Research 2Документ22 страницыPractica L Research 2tan2masОценок пока нет
- 2002 Jong Voordt WaysToStudyDelft6.DescriptiveresearchДокумент9 страниц2002 Jong Voordt WaysToStudyDelft6.Descriptiveresearchantenehkitaw84Оценок пока нет
- The Potential of Hermeneutics in Information System ResearchДокумент14 страницThe Potential of Hermeneutics in Information System Researchgianmarco.campagnolo100% (5)
- Qualitative Inquiry & Research Design - Choosing Among Five Approaches (PDFDrive) - 84-91Документ8 страницQualitative Inquiry & Research Design - Choosing Among Five Approaches (PDFDrive) - 84-91-'aku Cliquers'-Оценок пока нет
- 2.1 Characteristics, Strengths, and Weaknesses of Quantitative ResearchДокумент15 страниц2.1 Characteristics, Strengths, and Weaknesses of Quantitative ResearchBonjovi HajanОценок пока нет
- VC's Final Graduate PresentationДокумент56 страницVC's Final Graduate PresentationCharles ChegeОценок пока нет
- Architectural Research MethodsДокумент1 страницаArchitectural Research MethodsJeri TeОценок пока нет
- CIA1 Psychopathology 22223062Документ9 страницCIA1 Psychopathology 22223062yashita.chhabraОценок пока нет
- Political Science Research MethodsДокумент6 страницPolitical Science Research MethodsZuleira ParraОценок пока нет
- VanWyk Possible (2003) PDFДокумент8 страницVanWyk Possible (2003) PDFLauren BrionesОценок пока нет
- Understanding in Qualitative ResearchДокумент10 страницUnderstanding in Qualitative ResearcharcherselevatorsОценок пока нет
- SOCSCIДокумент3 страницыSOCSCIDianne MenesesОценок пока нет
- Barsalou 2003 Grounding Conceptual Knowledge PDFДокумент8 страницBarsalou 2003 Grounding Conceptual Knowledge PDFFernandaGuimaraesОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Qual Research-1Документ33 страницыIntroduction To Qual Research-1Sewmini KaushalyaОценок пока нет
- Philosophical Paradigms, Grounded Theory, and Perspectives On EmergenceДокумент6 страницPhilosophical Paradigms, Grounded Theory, and Perspectives On EmergenceAlejandro VanegasОценок пока нет
- Research Methods EddieДокумент91 страницаResearch Methods EddieNgonidzaishe DondofemaОценок пока нет
- Barab - Evans - Baek 2001 Activitytheory Characterizing The Participatory UnitДокумент16 страницBarab - Evans - Baek 2001 Activitytheory Characterizing The Participatory UnitMarisol de DiegoОценок пока нет
- 2.1 Characteristics, Strengths, and Weaknesses of Quantitative ResearchДокумент15 страниц2.1 Characteristics, Strengths, and Weaknesses of Quantitative ResearchBonjovi HajanОценок пока нет
- Idiographic Approach (Luthans and Davis, 1982)Документ13 страницIdiographic Approach (Luthans and Davis, 1982)egi radiansyahОценок пока нет
- Universitas Negeri Surabaya Faculty of Economics and Business 2021/2022Документ7 страницUniversitas Negeri Surabaya Faculty of Economics and Business 2021/2022boba milkОценок пока нет
- Topic 1:: Definition and Characteristics of Educational and Social Science ResearchДокумент5 страницTopic 1:: Definition and Characteristics of Educational and Social Science ResearchCharlton Benedict BernabeОценок пока нет
- 1 s2.0 S2211368116301991 MainДокумент6 страниц1 s2.0 S2211368116301991 MainHooba HiibaОценок пока нет
- Convection Transfer EquationsДокумент9 страницConvection Transfer EquationsA.N.M. Mominul Islam MukutОценок пока нет
- Decision Trees For Management of An Avulsed Permanent ToothДокумент2 страницыDecision Trees For Management of An Avulsed Permanent ToothAbhi ThakkarОценок пока нет
- Mosharaf HossainДокумент2 страницыMosharaf HossainRuhul RajОценок пока нет
- Dwnload Full Beckers World of The Cell 9th Edition Hardin Solutions Manual PDFДокумент35 страницDwnload Full Beckers World of The Cell 9th Edition Hardin Solutions Manual PDFgebbielean1237100% (12)
- Guardcam InstructionsДокумент12 страницGuardcam InstructionsCompuFix RepairsОценок пока нет
- Advertising II Marathi VersionДокумент91 страницаAdvertising II Marathi VersionHarsh Sangani100% (1)
- Phylogeny Practice ProblemsДокумент3 страницыPhylogeny Practice ProblemsSusan Johnson100% (1)
- UNCITRAL Guide United Nations Commission On International Trade LawДокумент56 страницUNCITRAL Guide United Nations Commission On International Trade Lawsabiont100% (2)
- Bba VДокумент2 страницыBba VkunalbrabbitОценок пока нет
- Jan 25th 6 TicketsДокумент2 страницыJan 25th 6 TicketsMohan Raj VeerasamiОценок пока нет
- Building and Structural Construction N6 T1 2024 T2Документ9 страницBuilding and Structural Construction N6 T1 2024 T2FranceОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan For Implementing NETSДокумент5 страницLesson Plan For Implementing NETSLisa PizzutoОценок пока нет
- Bank Danamon Organization ChartДокумент4 страницыBank Danamon Organization ChartFaisal Agus NugrahaОценок пока нет
- Walking in Space - Lyrics and Chord PatternДокумент2 страницыWalking in Space - Lyrics and Chord Patternjohn smithОценок пока нет
- Cam 18 Test 3 ListeningДокумент6 страницCam 18 Test 3 ListeningKhắc Trung NguyễnОценок пока нет
- Participants ListДокумент13 страницParticipants Listmailway002Оценок пока нет
- C4 Vectors - Vector Lines PDFДокумент33 страницыC4 Vectors - Vector Lines PDFMohsin NaveedОценок пока нет
- MEd TG G07 EN 04-Oct Digital PDFДокумент94 страницыMEd TG G07 EN 04-Oct Digital PDFMadhan GanesanОценок пока нет
- 788 ManualДокумент16 страниц788 Manualn0rdОценок пока нет
- HFE0106 TraskPart2Документ5 страницHFE0106 TraskPart2arunkr1Оценок пока нет
- Assignment 4Документ5 страницAssignment 4Hafiz AhmadОценок пока нет
- Focus Edition From GC: Phosphate Bonded Investments For C&B TechniquesДокумент35 страницFocus Edition From GC: Phosphate Bonded Investments For C&B TechniquesAlexis De Jesus FernandezОценок пока нет
- Understanding PTS Security PDFДокумент37 страницUnderstanding PTS Security PDFNeon LogicОценок пока нет
- Chinese Paper Cutting Work SheetДокумент4 страницыChinese Paper Cutting Work Sheet黃梓Оценок пока нет
- Cetie Guide No1 EngДокумент55 страницCetie Guide No1 EngJose Manuel Sepulveda RomanОценок пока нет
- Contoh Discussion Text Tentang HomeworkДокумент8 страницContoh Discussion Text Tentang Homeworkg3p35rs6100% (1)
- Dec JanДокумент6 страницDec Janmadhujayan100% (1)
- CiscoДокумент6 страницCiscoNatalia Kogan0% (2)
- Hazardous Locations: C.E.C. ClassificationsДокумент4 страницыHazardous Locations: C.E.C. ClassificationsThananuwat SuksaroОценок пока нет
- Shelly e CommerceДокумент13 страницShelly e CommerceVarun_Arya_8382Оценок пока нет