Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
IonicPotential04P PDF
Загружено:
Gajanan HegdeОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
IonicPotential04P PDF
Загружено:
Gajanan HegdeАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
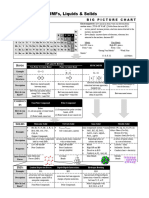
Railsback's Some Fundamentals of Mineralogy and Geochemistry
Ionic potential mediate ionic potential like Al3+ have sufficient density of
One important way to characterize ions is by their charge to bond strongly to O2- but not such dense
ionic potential. Ionic potential is an ion's charge divided charge as to repel each other, and so they make stable
by its radius, and it is thus a measure of density of oxides and/or hydroxides and thus are insoluble. The
charge. Ionic potential gives a sense of how strongly or cations of intermediate ionic potential also enter into
weakly the ion will be electrostatically attracted to ions of solids at high temperatures.
opposite charge, and to what extent the ion will repel The diagrams here show the effect of these trends in
other ions of like charge. Ionic potential varies greatly for the melting temperatures and solubilites of oxides. The
cations, from 0.75 for K+ to 45 for N5+. Earth Scientist's Periodic Table of the Elements and
Ionic potential is very useful in understanding the Their Ions shows many more geoscience trends that
behavior of relatively hard cations (see below). Cations result from variation in ionic potential. In addition, this
of low ionic potential like Na+ are typically soluble and book's page on "A bit of the Earth Scientist's Periodic
enter into solids only at relatively low temperatures, Table of the Elements and Their Ions as a cross-section
because they make weak bonds to O2-. On the other of the Earth" shows the implications of these trends at
hand, cations of high ionic potential, like S6+, bond so even larger scale, the pages on Bowen's Reaction Series
well to O2- that they make oxocomplexes like SO42- shows how ionic potential affects igneous crystallization,
(sulfate) that are soluble. Repulsions between S6+ ions, the pages on solutions and aqueous speciation show
and between the S66+ ion and other highly charged how ionic potential controls the behavior of catons in
cations, make most sulfate minerals relatively soluble, solution, and the page on "The Special Siituation of
and S6+ thus is an incompatible or volatile ion in high- Silicon" shows the implications of ionic potential for one
temperature systems. In between, cations of inter- important element.
Contours of ionic potential: Conceptual model of the behavior of
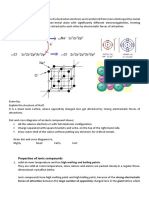
Example: oxides of hard (and intermediate) cations
Ca2+ Li N
charge = 2 Li + Be2+ B3+ C4+ N5+ Cations
radius = 1.0 Å 32 H+ 1Å
ionic potential
= 2.0
Na+ Mg2+ Al 3+ Si4+ P5+ S6+
16
K+ Ca2+ Sc3+ Ti 4+ V5+ Cr 6+ High z/r
Strong
Rb O2– bonds, but
charge
Rb+ Sr 2+ Y 3+ Zr 4+ Nb5+ Mo6+ Intermediate
Low z/r cation-cation
radius z/r repulsion
Weak cation-
= ionic Cs+ Ba2+ La3+ Hf4+ Ta5+ W 6+ oxygen bonds
Strong cation- Thus less
potential oxygen bonds stable solids
1 2 4 8 Thus less stable
Thus stable solids
solids
+ 2+
Li
+
Be 2+ B 3+ C 4+ N 5+ Li4.4 Be–7.4 3+
B2.77 C 4+ N 5+
1700 2681 723 216 Bromellite
500
Melting + 2+ 4+ 5+
Na
+
Mg 2+
Al 3+ Si 4+
P 5+ S 6+ temperature Na9.9 Mg –2.4 Al 3+ Si –3.9
–8.1
P–1.37 S 6+
1193 3125 2345 1996 855 290 Periclase
of oxides of Corundum Quartz
hard cations
+
K
+
Ca2+ Sc 3+ Ti 4+ V 5+ Cr 6+ K14.0 Ca2+ Sc3+ Ti 4+ 5+
V –7.6 Cr 6+
3200 Lime 1.4 –9.7
2103 943 Rutile Shcherbinaite
10
00
Solubility + 2+
Rb
+
Sr 2+
Y 3+
Zr 4+
Nb 5+
Mo6+ Rb Sr4.3 Y 3+ Zr 4+ Nb5+ Mo6+
673 2938 3123 1785 1074
of oxide 28.9 Baddeleyite
Molybdite
minerals
of hard
Cs
+
Ba2+ La 3+ Hf 4+ Ta 5+ W 6+
cations 2+
Ba6.7 La 3+ Hf 4+ Ta 5+ W 6+
1500
2286 2580 3173 2058 1745 Mineral Tantite
2000
1500
2500
200
2500
–9.7
4+
3000
300
Th 4+ Th Thorianite
0
Log of activity of cation species
Temperatures in Kelvins in distilled water at 25 °C LBR 2/2007
0
3493
IonicPotential04
Вам также может понравиться
- Alkaline Earth Metals and Their PropertiesДокумент8 страницAlkaline Earth Metals and Their PropertiesH.r. IndiketiyaОценок пока нет
- Bowens Reaction SeriesДокумент9 страницBowens Reaction SeriesManfinflaОценок пока нет
- Reactions of Period 3 Elements With Chlorine, Oxygen and WaterДокумент13 страницReactions of Period 3 Elements With Chlorine, Oxygen and WaterTony GonzalezОценок пока нет
- S-Block Elements & Compounds: Group - IДокумент46 страницS-Block Elements & Compounds: Group - Iविशाल जायसवालОценок пока нет
- s-Block Elements GuideДокумент7 страницs-Block Elements Guideإدريس أل أذهري100% (1)
- 11 S Block Revision Notes QuizrrДокумент30 страниц11 S Block Revision Notes QuizrrÃrjït ShûklãОценок пока нет
- S Block ElementsДокумент59 страницS Block Elementsanikesh JainОценок пока нет
- Chem 1 FrontДокумент1 страницаChem 1 Frontvighneshdp174Оценок пока нет
- Fajans RuleДокумент9 страницFajans RuleRishabh ChaudhariОценок пока нет
- Chemical Bonding SummaryДокумент8 страницChemical Bonding SummaryKiara LimОценок пока нет
- S Block ElementsДокумент31 страницаS Block ElementsMuhammad AsgharОценок пока нет
- Watermark Chemistry Igcse Notes 2 PDFДокумент15 страницWatermark Chemistry Igcse Notes 2 PDFMeerab ShahОценок пока нет
- S-Block Class 11Документ27 страницS-Block Class 11sumitchauhan100000Оценок пока нет
- Topic 1 The S Block Elements Group 1 2 Part 1Документ34 страницыTopic 1 The S Block Elements Group 1 2 Part 1A/P SUPAYA SHALINIОценок пока нет
- S-Block Notes-1Документ26 страницS-Block Notes-1Kishore SurampalliОценок пока нет
- S Block-1Документ46 страницS Block-1Jeevan KumarОценок пока нет
- 11 Chemistry Notes - The S-Block ElementsДокумент21 страница11 Chemistry Notes - The S-Block ElementsAishwary yadav100% (1)
- Interatomic Bonding PDFДокумент14 страницInteratomic Bonding PDFFaysal Qadeer KhanОценок пока нет
- 3 StructEngMatДокумент43 страницы3 StructEngMatM Thoriq BhadrikaОценок пока нет
- S Block ElementsДокумент8 страницS Block ElementsSwati Jadhav100% (3)
- Chemistry of s-Block and p-Block ElementsДокумент26 страницChemistry of s-Block and p-Block ElementsNatish JaglanОценок пока нет
- 3 Fajan's RuleДокумент13 страниц3 Fajan's RuleNazmi LatifОценок пока нет
- 1.3 Revision Guide Bonding AqaДокумент3 страницы1.3 Revision Guide Bonding AqaPragna AnanthОценок пока нет
- Chemical Bonding & Molecular StructureДокумент14 страницChemical Bonding & Molecular StructureAYUSH GOSWAMIОценок пока нет
- S-Block Lecture NotesДокумент43 страницыS-Block Lecture NotesIchhpilani KabirОценок пока нет
- The S-Block ElementsДокумент51 страницаThe S-Block ElementsDiksha TОценок пока нет
- S Block (Landscape)Документ8 страницS Block (Landscape)Drastic Pranksters Inc.Оценок пока нет
- S BlockДокумент18 страницS BlockHEОценок пока нет
- PDF Document 5Документ25 страницPDF Document 5miriam harriottОценок пока нет
- Chemistry 9th CH 8Документ16 страницChemistry 9th CH 8Ahmad mehmoodОценок пока нет
- Subject: Chemistry Class: XI Chapter: The S-Block Elements Top ConceptsДокумент10 страницSubject: Chemistry Class: XI Chapter: The S-Block Elements Top ConceptsRISHI KEJRIWALОценок пока нет
- Periodic Properties - Part 4Документ31 страницаPeriodic Properties - Part 4Bhavesh GargОценок пока нет
- S - Block Elements, Class 11Документ13 страницS - Block Elements, Class 11Ashish kumarОценок пока нет
- Continued:: More On Ionic BondingДокумент37 страницContinued:: More On Ionic BondingArdhy Biker'sОценок пока нет
- Bonding Summary ChartДокумент1 страницаBonding Summary ChartКанат ТютеновОценок пока нет
- S&P Block PDFДокумент1 страницаS&P Block PDFvrtbhgmngfОценок пока нет
- Occurrence & Abundance 2. Electronic Configuration 3. Physical State 4. DensityДокумент3 страницыOccurrence & Abundance 2. Electronic Configuration 3. Physical State 4. DensityAmit YadavОценок пока нет
- Ionic or Electrovalent Bond:: Chemical Bonding-VДокумент8 страницIonic or Electrovalent Bond:: Chemical Bonding-VwanderedОценок пока нет
- 1.6 CHEM FINAL Chapter6 ElectrolysisДокумент41 страница1.6 CHEM FINAL Chapter6 ElectrolysisSudhanshuОценок пока нет
- New Fou 1&2 Nagratoli S - BlockДокумент19 страницNew Fou 1&2 Nagratoli S - BlockAnamikaОценок пока нет
- Trends in Periodic Table ChemДокумент56 страницTrends in Periodic Table ChemShazira AllyОценок пока нет
- S BlockДокумент7 страницS BlockpushpОценок пока нет
- Jee S BlockДокумент129 страницJee S BlockAmirtha RajОценок пока нет
- Lecture 14. Chemistry of Groups I, II, III and IV: (Cyclic Polyether)Документ27 страницLecture 14. Chemistry of Groups I, II, III and IV: (Cyclic Polyether)Ramesh KatkamОценок пока нет
- The S-Block ElementsДокумент34 страницыThe S-Block ElementsPrakhar TandonОценок пока нет
- Bonding Structures & PropertiesДокумент23 страницыBonding Structures & PropertiesRuha VОценок пока нет
- 15.1. Group 1 Elements: Li He 2s RB KR 5sДокумент33 страницы15.1. Group 1 Elements: Li He 2s RB KR 5sDurgeshTiwariОценок пока нет
- Interatomic Bonds: Prof. H. K. Khaira Hod, Msme Deptt. Manit, BhopalДокумент81 страницаInteratomic Bonds: Prof. H. K. Khaira Hod, Msme Deptt. Manit, Bhopalraj kumarОценок пока нет
- S BlockДокумент53 страницыS BlockhappyОценок пока нет
- Rules FajansДокумент1 страницаRules FajansLilian PaesОценок пока нет
- S-Block ElementsДокумент1 страницаS-Block ElementsRishabhОценок пока нет
- Alkali and Alkali Earth Metals - SRДокумент20 страницAlkali and Alkali Earth Metals - SRMuzahidul IslamОценок пока нет
- Reactions PDFДокумент6 страницReactions PDFAnshu MovvaОценок пока нет
- 2-HASB Ralph Pearson1968Документ6 страниц2-HASB Ralph Pearson1968Vasu NagpalОценок пока нет
- DFFHMДокумент9 страницDFFHMyaswanthОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 Material ScienceДокумент69 страницChapter 1 Material ScienceFadhli JapryОценок пока нет
- Ionic Bonding ExplainedДокумент2 страницыIonic Bonding ExplainedChanupa YanethОценок пока нет
- Properties and Reactions of S-Block ElementsДокумент55 страницProperties and Reactions of S-Block ElementsAVR BroZОценок пока нет
- The S-Block Elements: Dr. Vatsala Soni PGGC Sector - 11 ChandigarhДокумент55 страницThe S-Block Elements: Dr. Vatsala Soni PGGC Sector - 11 ChandigarhNagendra MadineniОценок пока нет
- Inorganic Hydrides: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionОт EverandInorganic Hydrides: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionОценок пока нет
- Duke Univ Study Uranium in India SupplementДокумент35 страницDuke Univ Study Uranium in India SupplementGajanan HegdeОценок пока нет
- Jataka BharanamДокумент10 страницJataka BharanamElampoorananОценок пока нет
- Government Details Uranium Levels in Groundwater Across StatesДокумент4 страницыGovernment Details Uranium Levels in Groundwater Across StatesGajanan HegdeОценок пока нет
- Duke Univ Study Uranium in India SupplementДокумент35 страницDuke Univ Study Uranium in India SupplementGajanan HegdeОценок пока нет
- Ancient WisdomДокумент29 страницAncient WisdomGajanan HegdeОценок пока нет
- Geochemical Survey - An Overview - ScienceDirect TopicsДокумент15 страницGeochemical Survey - An Overview - ScienceDirect TopicsGajanan HegdeОценок пока нет
- Uttara KalamritaДокумент1 страницаUttara Kalamritanavinsabharwal0% (2)
- Special Method For Ore Beneficiation - TummalapalleДокумент7 страницSpecial Method For Ore Beneficiation - TummalapalleGajanan HegdeОценок пока нет
- Tips For Geochemical ExplorationДокумент5 страницTips For Geochemical ExplorationGajanan HegdeОценок пока нет
- Ganapathi Saharanamavali - Powerful MantraДокумент42 страницыGanapathi Saharanamavali - Powerful MantraGajanan HegdeОценок пока нет
- Jataka ChandrikaДокумент16 страницJataka Chandrikaapi-3708513100% (4)
- Chamatkar Chintamani PDFДокумент17 страницChamatkar Chintamani PDFGunanidhi SharmaОценок пока нет
- Swami Shivanand Baba BanarasДокумент5 страницSwami Shivanand Baba BanarasGajanan HegdeОценок пока нет
- Ionic PotentialДокумент1 страницаIonic PotentialGajanan HegdeОценок пока нет
- Geochemical Survey - An Overview - ScienceDirect TopicsДокумент15 страницGeochemical Survey - An Overview - ScienceDirect TopicsGajanan HegdeОценок пока нет
- Aspects in Vedic ChartsДокумент2 страницыAspects in Vedic ChartsGajanan HegdeОценок пока нет
- Cancellation of Deviation Signs in AstrologyДокумент1 страницаCancellation of Deviation Signs in AstrologyGajanan HegdeОценок пока нет
- Books On AstrologyДокумент10 страницBooks On AstrologyAli Muhammad Khan100% (1)
- Vayu Putra Vandana PDFДокумент6 страницVayu Putra Vandana PDFGajanan HegdeОценок пока нет
- Opening RitualДокумент17 страницOpening RitualTracy CrockettОценок пока нет
- ID Kajian Hukum Perjanjian Perkawinan Di Kalangan Wni Islam Studi Di Kota Medan PDFДокумент17 страницID Kajian Hukum Perjanjian Perkawinan Di Kalangan Wni Islam Studi Di Kota Medan PDFsabila azilaОценок пока нет
- Alice Hoffman - Green AngelДокумент24 страницыAlice Hoffman - Green AngelHristiyana Yotova71% (14)
- Two Sides of Effective Oral CommunicationДокумент17 страницTwo Sides of Effective Oral CommunicationSharath KumarОценок пока нет
- 05 Mesina v. PeopleДокумент7 страниц05 Mesina v. PeopleJason ToddОценок пока нет
- Casalla vs. PeopleДокумент2 страницыCasalla vs. PeopleJoan Eunise FernandezОценок пока нет
- 9851 BCG Vaccine Professional HCWДокумент4 страницы9851 BCG Vaccine Professional HCWIuliana PanaitОценок пока нет
- ChaseDream Business School Guide LBS - ZH-CN - enДокумент27 страницChaseDream Business School Guide LBS - ZH-CN - enRafael LimaОценок пока нет
- Coordinates: Primary Practice QuestionsДокумент10 страницCoordinates: Primary Practice QuestionsJames KeruОценок пока нет
- The Base-Catalyzed-Hydrolysis and Condensation-Reactions of Dilute and Concentrated Teos SolutionsДокумент7 страницThe Base-Catalyzed-Hydrolysis and Condensation-Reactions of Dilute and Concentrated Teos SolutionscoloreyeОценок пока нет
- Fraud under Indian Contract Act - Essentials and Exceptions to Mere SilenceДокумент6 страницFraud under Indian Contract Act - Essentials and Exceptions to Mere SilenceabhilashОценок пока нет
- California Clothing Vs QuinonesДокумент4 страницыCalifornia Clothing Vs QuinonesLily MondaragonОценок пока нет
- Demand Letter Jan 16Документ8 страницDemand Letter Jan 16jhean0215Оценок пока нет
- Individual Assignment I Google Search Network CampaignДокумент15 страницIndividual Assignment I Google Search Network CampaignMokshita VajawatОценок пока нет
- Chapter 8 SQL Complex QueriesДокумент51 страницаChapter 8 SQL Complex QueriesJiawei TanОценок пока нет
- Function Point and Cocomo ModelДокумент31 страницаFunction Point and Cocomo ModelParinyas SinghОценок пока нет
- TQM 2 MARKSДокумент12 страницTQM 2 MARKSMARIYAPPANОценок пока нет
- Contact Resistance Between Gas Diffusion Layer and CatalystДокумент5 страницContact Resistance Between Gas Diffusion Layer and Catalystp.designОценок пока нет
- A Project Report On Market Research & Brand Activation: Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of The RequirementsДокумент55 страницA Project Report On Market Research & Brand Activation: Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirementskartik chauhan100% (1)
- Atmakaraka PDFДокумент46 страницAtmakaraka PDFrohitsingh_8150% (4)
- MedicineДокумент19 страницMedicineSarah100% (1)
- A Practice Teaching Narrative of Experience in Off Campus InternshipДокумент84 страницыA Practice Teaching Narrative of Experience in Off Campus InternshipClarenz Jade Magdoboy MonserateОценок пока нет
- Tugas BHS InggrisДокумент2 страницыTugas BHS InggrisJust NestОценок пока нет
- What Is Link AdaptationДокумент4 страницыWhat Is Link AdaptationAshutosh SinghОценок пока нет
- Semaphore Twinsoft Manual PDFДокумент101 страницаSemaphore Twinsoft Manual PDFReza AnantoОценок пока нет
- United States v. Calvin Antonio Spencer, 68 F.3d 462, 4th Cir. (1995)Документ4 страницыUnited States v. Calvin Antonio Spencer, 68 F.3d 462, 4th Cir. (1995)Scribd Government DocsОценок пока нет
- Treasures Book 1 Unit 1Документ33 страницыTreasures Book 1 Unit 1Janinne AbuegОценок пока нет
- Bobby Joe Public NoticeДокумент3 страницыBobby Joe Public NoticeUpscale International InvestmentsОценок пока нет
- Alesco User GuideДокумент20 страницAlesco User GuideXHo D. King Jr.90% (10)
- Minimizing Dose Is DR PDFДокумент4 страницыMinimizing Dose Is DR PDFYamuna GovindarajОценок пока нет