Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Immunologic derangement and immune activation in scleroderma
Загружено:
Aye0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
18 просмотров2 страницыThe document discusses systemic sclerosis (SSc), a chronic autoimmune connective tissue disease. It notes that activation of the immune system is a hallmark feature of SSc. The document outlines the clinical manifestations and treatment approaches for SSc and differentiates between the localized and systemic forms of the disease. Key characteristics of limited and diffuse cutaneous SSc are also summarized.
Исходное описание:
Scleroderma
Оригинальное название
Scleroderma
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThe document discusses systemic sclerosis (SSc), a chronic autoimmune connective tissue disease. It notes that activation of the immune system is a hallmark feature of SSc. The document outlines the clinical manifestations and treatment approaches for SSc and differentiates between the localized and systemic forms of the disease. Key characteristics of limited and diffuse cutaneous SSc are also summarized.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
18 просмотров2 страницыImmunologic derangement and immune activation in scleroderma
Загружено:
AyeThe document discusses systemic sclerosis (SSc), a chronic autoimmune connective tissue disease. It notes that activation of the immune system is a hallmark feature of SSc. The document outlines the clinical manifestations and treatment approaches for SSc and differentiates between the localized and systemic forms of the disease. Key characteristics of limited and diffuse cutaneous SSc are also summarized.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
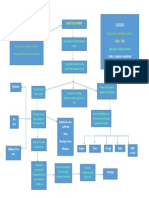
Cellular and humoral immunologic
derangement
Activation of the immune system
is an outstanding disease feature
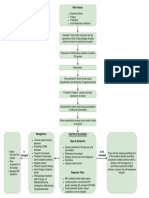
Clinical Manifestation Treatment Diagnostic Investigations
Vascular abnormalities No therapy has been shown • Serumauto-antibodies,
Skin involvement significantly to alter the upper GI endoscopy
Musculoskeletal system natural history SSc till date. • FBC, CT scan of chest
Intestinal Involvement Multiple interventions are • Urea &’ serum creatinine
Lungs
available in allevating the • ESR, serum muscle
Heart
symptoms- slowly progression enzymes
Kidney
Exocrine Glands of organ damage.
Treatment approaches to be
individually tailored.
Optimal management-
prompt, accurate diagnosis,
classification, risk stratify,early
recognition of organ based
complications, regular
monitoring of progression,
disease activity, response to
treatment, patient education
Holistic approach
Combination of drugs are
used
Physician- pt. relationship to
be maintained
Disease Modifying Treatment:
• Immunosuppressive agents
• Glucocorticoids
• Cyclophosphamide
• Methotrexate
• Mycophenolate mofetil
• Immunomodulation
• Immune ablation
• Stem cell transplantations
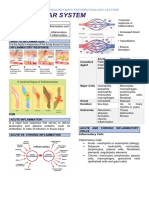
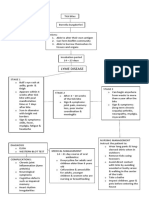
SCLERODERMA
-a chronic connective tissue disease generally
classified as one of the autoimmune rheumatic
diseases.
Localized Scleroderma- found Systemic Sclerosis- is a multi-
systemic, autoimmune disease
onlya few places on the skin or
affecting small arteries, micro-
muscles and rarely spread
vessels and fibroblasts resulting in
elsewhere. (MILD)
vascular obliteration, collagen
accumulation and scarring (fibrosis)
of skin and internal organs.
Morphea waxy Linear Scleroderma
patches on the skin of starts as a streak or line
varying sizes, shapes & of hardened, waxy skin DIFFUSE CUTANEOUS LIMITED CUTANEOUS
color. Usually appears on crease on the head or cutaneous scleroderma - skin induration limited to
the age’s 20 & 50 but neck referred to as en begins with symmetrical hands, feet, face. CREST
often seen in young coup de sabre. Usually widespread thickening Calsinosis: Calcium
children. develops in childhood of the skin on the deposits in the tissues.
extremeties, the face Raynaud’s Phenomenon:
and the trunk. Intermittent vasospasm
Plaque
In the early stages of the of finger tips.
Guttate
disease: bilateral Esophageal hardening:
Generalized
symmetrical swelling of Sclerosis of the
Bulous
the fingers, face & feet esophagus
Deep
-Skin has a tense, wrinkle- Sclerodactyly:
free appearance, more Scleroderma of the digits
thickened, hidebound & Telangiectasias: Capillary
shiny dilations that form
vascular lesions on the
face, lips, and fingers.
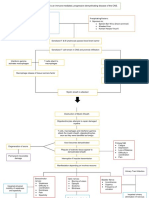
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Endothelial cell injury
Fibroblast activation
Вам также может понравиться
- Myopathies: Presented By, Dr. Chandan N Intern, Department of Medicine, MIMS, MandyaДокумент42 страницыMyopathies: Presented By, Dr. Chandan N Intern, Department of Medicine, MIMS, MandyaShafira WidiaОценок пока нет
- Multiple Sclerosis PDFДокумент1 страницаMultiple Sclerosis PDFAcey TfОценок пока нет
- Care of Preschoolers With Health ProblemsДокумент5 страницCare of Preschoolers With Health ProblemsmajoodhОценок пока нет
- Drug Study PrednisoloneДокумент2 страницыDrug Study Prednisoloneunnamed personОценок пока нет
- 4.penyembuhan LukaДокумент52 страницы4.penyembuhan LukaFajar Satria Rahmaditya100% (1)
- 4.penyembuhan LukaДокумент52 страницы4.penyembuhan LukaazisaaidrОценок пока нет
- Ms Orv Trans Cruz202002012Документ115 страницMs Orv Trans Cruz202002012Julienne HernandezОценок пока нет
- Connective Tissue FinalsДокумент3 страницыConnective Tissue FinalsVon HippoОценок пока нет
- Aging PhysiologicalДокумент37 страницAging PhysiologicalNico WirawanОценок пока нет
- Dermatomyositis: Morphology, Etiology, Pathogenesis, Treatment, and PrognosisДокумент3 страницыDermatomyositis: Morphology, Etiology, Pathogenesis, Treatment, and PrognosisRiena Austine Leonor NarcillaОценок пока нет
- Wound Healing SummaryДокумент9 страницWound Healing Summarybarb gОценок пока нет
- Race Dermatology 2024 by Dr AshishДокумент29 страницRace Dermatology 2024 by Dr AshishdrshekarforyouОценок пока нет
- Chapter 64:: Morphea and Lichen SclerosusДокумент21 страницаChapter 64:: Morphea and Lichen Sclerosuss02579Оценок пока нет
- HAPP-PICO Tissue Pathology Journal ResearchДокумент4 страницыHAPP-PICO Tissue Pathology Journal ResearchArlynn MartinezОценок пока нет
- Lamb 2017Документ6 страницLamb 2017Carolina González RiveraОценок пока нет
- LABORATORY ASSESSMENT ON IMMUNE SYSTEM DYSFUNCTION AND INFLAMMATION IN CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE - Dr. Dian Ariningrum, M.Kes., SP - PK (K)Документ24 страницыLABORATORY ASSESSMENT ON IMMUNE SYSTEM DYSFUNCTION AND INFLAMMATION IN CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE - Dr. Dian Ariningrum, M.Kes., SP - PK (K)EllenОценок пока нет
- An Overview of Muscle Histopathology in Myositis: Differentiating Subtypes of MyositisДокумент35 страницAn Overview of Muscle Histopathology in Myositis: Differentiating Subtypes of MyositisIsaac MaderoОценок пока нет
- DermatomyositisДокумент4 страницыDermatomyositisLakshya J BasumataryОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology and Management of Multiple SclerosisДокумент6 страницPathophysiology and Management of Multiple SclerosisJoyce Ann CumlatОценок пока нет
- Environmental Factors and Clinical Manifestations of Systemic Lupus ErythematosusДокумент1 страницаEnvironmental Factors and Clinical Manifestations of Systemic Lupus ErythematosusMel Izhra N. MargateОценок пока нет
- Scleroderma: Chuah Wei HongДокумент33 страницыScleroderma: Chuah Wei HongChuah Wei HongОценок пока нет
- Medical Basic Science III Mechanisms of DiseaseДокумент16 страницMedical Basic Science III Mechanisms of Diseaseakun internetОценок пока нет
- Hallmark: Thickened Skin: Green Book and Additional NotesДокумент6 страницHallmark: Thickened Skin: Green Book and Additional NotesVon HippoОценок пока нет
- 7.2 Muscular System: Human Anatomy and Physiology With Pathophysiology LectureДокумент3 страницы7.2 Muscular System: Human Anatomy and Physiology With Pathophysiology LectureRamea LamanoОценок пока нет
- Wound Care Management TechniquesДокумент104 страницыWound Care Management TechniquesriaastrianiОценок пока нет
- 1 Autoimmune DeseasesДокумент9 страниц1 Autoimmune DeseasesHiromi CarterОценок пока нет
- Cellulitis Treatment and SymptomsДокумент37 страницCellulitis Treatment and SymptomswindhymonicaОценок пока нет
- Dermatology Revision E6.5 @theboggusdocДокумент36 страницDermatology Revision E6.5 @theboggusdockhushi koliОценок пока нет
- Sirs 2013Документ96 страницSirs 2013wildan acalipha wilkensiaОценок пока нет
- Systemic lupus erythematosusДокумент3 страницыSystemic lupus erythematosussaranya amuОценок пока нет
- Leukoderma and VitiligoДокумент82 страницыLeukoderma and VitiligoBahaa ShaabanОценок пока нет
- PIIS0092867421005067Документ2 страницыPIIS0092867421005067Carlos CostaОценок пока нет
- Lesiones Cutaneas y Enfermedad Sistemica en Felinos Sep 2017Документ13 страницLesiones Cutaneas y Enfermedad Sistemica en Felinos Sep 2017dayana rodriguezОценок пока нет
- Rheumatology - Other Connective TissueДокумент1 страницаRheumatology - Other Connective TissueJasmine Kang100% (2)
- FEU-NRMF Pathology A Lecture on Inflammation and Tissue RepairДокумент13 страницFEU-NRMF Pathology A Lecture on Inflammation and Tissue RepairkristineОценок пока нет
- NCP 2 - CellulitisДокумент4 страницыNCP 2 - CellulitisROSHANNEDANICA VERGARAОценок пока нет
- MBR 2019 - Pathology HandoutsДокумент98 страницMBR 2019 - Pathology HandoutsRgm UyОценок пока нет
- His To PathologyДокумент7 страницHis To PathologyDessa MartinezОценок пока нет
- Tea-Colored Urine and Impetigo: A Case of Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisДокумент5 страницTea-Colored Urine and Impetigo: A Case of Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisSean Dominique Cruz MaghinayОценок пока нет
- Hordeolum: Acute Abscess Within An Eyelid Sebaceous Gland: The Clinical PictureДокумент3 страницыHordeolum: Acute Abscess Within An Eyelid Sebaceous Gland: The Clinical PictureCamОценок пока нет
- @acute Nephritic SyndromeДокумент3 страницы@acute Nephritic SyndromeMazlia FarzanaОценок пока нет
- Pathology of Urinary SystemДокумент384 страницыPathology of Urinary SystemNzau MuangeОценок пока нет
- Stevens Johnson SyndromeДокумент13 страницStevens Johnson SyndromeMimi SyakilaОценок пока нет
- Lichen MyxedematosusДокумент4 страницыLichen MyxedematosusRiena Austine Leonor NarcillaОценок пока нет
- Clinical Use and Molecular Action of Corticosteroids in The Pediatric AgeДокумент25 страницClinical Use and Molecular Action of Corticosteroids in The Pediatric AgeLailОценок пока нет
- Burn Wound CareДокумент53 страницыBurn Wound CarenikinikkoОценок пока нет
- Wound Healing ProcessДокумент34 страницыWound Healing ProcessoctyvaniОценок пока нет
- Geria MidtermsДокумент4 страницыGeria Midtermswieka mawieОценок пока нет
- Wound Healing, Tissue Repair, and FibrosisДокумент28 страницWound Healing, Tissue Repair, and FibrosisRibka TheodoraОценок пока нет
- Understanding Autoimmune Disorders and Rheumatoid ArthritisДокумент7 страницUnderstanding Autoimmune Disorders and Rheumatoid Arthritisfebie pachecoОценок пока нет
- Pathology IMP Questions Cell Injury InflammationДокумент20 страницPathology IMP Questions Cell Injury InflammationALI HASSANОценок пока нет
- Multiple Sclerosis - Is An Immune-Mediated, Progressive Demyelinating Disease of The CNSДокумент4 страницыMultiple Sclerosis - Is An Immune-Mediated, Progressive Demyelinating Disease of The CNSJarod HembradorОценок пока нет
- Rheumatoid ArthritisДокумент14 страницRheumatoid ArthritisLorebell100% (5)
- Immunologic DisordersДокумент3 страницыImmunologic DisordersMarie Antionette MondragonОценок пока нет
- Five Cardinal Signs of InflammationДокумент4 страницыFive Cardinal Signs of Inflammationmanny danielОценок пока нет
- Clipp 11 PDFДокумент6 страницClipp 11 PDFPrashant MishraОценок пока нет
- Systemic Lupus ErythematosusДокумент3 страницыSystemic Lupus ErythematosusKim Mae ComendadorОценок пока нет
- GPHT1 InflammationДокумент5 страницGPHT1 InflammationRachel ManaloОценок пока нет
- Genitourinary CancersДокумент58 страницGenitourinary CancersAyeОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care of Patients With Cardiac ProblemsДокумент125 страницNursing Care of Patients With Cardiac ProblemsAyeОценок пока нет
- Low Sodium Diet Foods List PDFДокумент3 страницыLow Sodium Diet Foods List PDFAye100% (1)
- Blood TransfusionДокумент39 страницBlood TransfusionAyeОценок пока нет
- PhilhealthДокумент15 страницPhilhealthAyeОценок пока нет
- Burns Definition Classification Pathophysiology and Initial Approach 2327 5146 1000298Документ5 страницBurns Definition Classification Pathophysiology and Initial Approach 2327 5146 1000298Alexandra Ançã PiresОценок пока нет
- Pulmonary Function TestsДокумент8 страницPulmonary Function TestsAyeОценок пока нет
- Alzheimers Disease Causes Treatment A ReviewДокумент8 страницAlzheimers Disease Causes Treatment A ReviewPaul HartingОценок пока нет
- Near Drowning: Pediatric Critical Care Medicine Emory University Children's Healthcare of AtlantaДокумент35 страницNear Drowning: Pediatric Critical Care Medicine Emory University Children's Healthcare of AtlantaAyeОценок пока нет
- Liver Abscess PDFДокумент11 страницLiver Abscess PDFFendra WicianОценок пока нет
- Neardrowning: Prehospital and Emergency Department ManagementДокумент34 страницыNeardrowning: Prehospital and Emergency Department ManagementAyeОценок пока нет
- Hypertension Nursing Care PlanДокумент2 страницыHypertension Nursing Care PlanCee SanchezОценок пока нет
- Pulmonary Function TestingДокумент53 страницыPulmonary Function TestingAyeОценок пока нет
- Genitourinary CancersДокумент58 страницGenitourinary CancersAyeОценок пока нет
- IMCI Knowledge Post-Test Answer KeyДокумент8 страницIMCI Knowledge Post-Test Answer KeyCarissa De Luzuriaga-BalariaОценок пока нет
- Helium Dilution Technique Rakesh Oct 2016Документ61 страницаHelium Dilution Technique Rakesh Oct 2016AyeОценок пока нет
- E Static Lung Volumes and CapacitiesДокумент5 страницE Static Lung Volumes and CapacitiesAyeОценок пока нет
- Data Analysis and Health ProfileДокумент8 страницData Analysis and Health ProfileAyeОценок пока нет
- Giant Cell ArteritisДокумент1 страницаGiant Cell ArteritisAyeОценок пока нет
- SchizopreniaДокумент19 страницSchizopreniaAyeОценок пока нет
- Nursing Diagnosis Goals Short-Term: Interventions Rationale EvaluationДокумент2 страницыNursing Diagnosis Goals Short-Term: Interventions Rationale EvaluationAyeОценок пока нет
- Pamphlet CDДокумент5 страницPamphlet CDAyeОценок пока нет
- DepressionДокумент1 страницаDepressionAyeОценок пока нет
- Drowning and Near Drowning: KH Naghibi MDДокумент64 страницыDrowning and Near Drowning: KH Naghibi MDAyeОценок пока нет
- Lyme DiseaseДокумент1 страницаLyme DiseaseAyeОценок пока нет
- Transfusion Medicine QuestionsДокумент31 страницаTransfusion Medicine QuestionsJhoanie Sanggoy Tauli100% (1)
- Champs Englishqxn 26dec02Документ10 страницChamps Englishqxn 26dec02AyeОценок пока нет
- NCP - Risk For Decreased Cardiac OutputДокумент2 страницыNCP - Risk For Decreased Cardiac Outputmikelbalagat80% (5)
- Other - Learning - Strategies - Docx Filename - UTF-8''other Learning StrategiesДокумент4 страницыOther - Learning - Strategies - Docx Filename - UTF-8''other Learning StrategiesAyeОценок пока нет
- Improving Oncology Trials Through Adaptive Trial Design - ACT-Oncology-eBook-2016-MayДокумент7 страницImproving Oncology Trials Through Adaptive Trial Design - ACT-Oncology-eBook-2016-MayRaviprakash MadhyasthaОценок пока нет
- Jim Humble Newsletter 10 New MMS ProtocolДокумент6 страницJim Humble Newsletter 10 New MMS Protocolgio_co64Оценок пока нет
- Iugr FinalДокумент35 страницIugr Finalsanthiyasandy100% (4)
- Florendo V Philam PlansДокумент2 страницыFlorendo V Philam Plansange ManagaytayОценок пока нет
- Abs Wabco ManutecДокумент56 страницAbs Wabco ManutecBom_Jovi_681Оценок пока нет
- DH 0604Документ16 страницDH 0604The Delphos HeraldОценок пока нет
- البروفيل الديمغرافي لمرضى سرطان القولون و المستقيم بمركز مكافحة السرطان سطيفДокумент14 страницالبروفيل الديمغرافي لمرضى سرطان القولون و المستقيم بمركز مكافحة السرطان سطيفsaraОценок пока нет
- Some Important Plants Used in Electro-Homeopathic System of MedicineДокумент1 страницаSome Important Plants Used in Electro-Homeopathic System of MedicineDev SarovaОценок пока нет
- MSDS Af 11 PDFДокумент6 страницMSDS Af 11 PDFIseng 19Оценок пока нет
- Saturn-Moon Link to CancerДокумент10 страницSaturn-Moon Link to CancerjanakrajchauhanОценок пока нет
- Postpartal Thrombophlebitis: Client Assessment Data Base Activity/RestДокумент8 страницPostpartal Thrombophlebitis: Client Assessment Data Base Activity/RestLei OrtegaОценок пока нет
- Beyond Magenta Press ReleaseДокумент3 страницыBeyond Magenta Press ReleaseCandlewick PressОценок пока нет
- Week 5 CSL Notes Session 1Документ4 страницыWeek 5 CSL Notes Session 1kevОценок пока нет
- Silica Flour D66Документ4 страницыSilica Flour D66georgenzОценок пока нет
- Despite Changes, Live Auctions Are Still Popular: Speakers Announced For Relay For Life Community ReceptionДокумент10 страницDespite Changes, Live Auctions Are Still Popular: Speakers Announced For Relay For Life Community ReceptionKristina HicksОценок пока нет
- Organic PollutantsДокумент14 страницOrganic PollutantsM.SohailОценок пока нет
- 2017 @radproflib Hariqbal Singh, Shailendra Savale Textbook of Radiology PDFДокумент295 страниц2017 @radproflib Hariqbal Singh, Shailendra Savale Textbook of Radiology PDFHesty Syahputri NababanОценок пока нет
- شريحه 1 مصطلحات طبيةДокумент37 страницشريحه 1 مصطلحات طبيةMohamed WahidОценок пока нет
- Myles Textbook For Midwives, 15th Edition: Journal of Obstetrics and GynaecologyДокумент3 страницыMyles Textbook For Midwives, 15th Edition: Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecologyintan wahyuОценок пока нет
- NP 1 To 5 Focus210-D WITHOUT AnswersДокумент5 страницNP 1 To 5 Focus210-D WITHOUT AnswersMarkie CubosОценок пока нет
- Fred Gallo PHD and Harry VincenziEdD Energy TappingДокумент203 страницыFred Gallo PHD and Harry VincenziEdD Energy Tappingthomist36100% (1)
- Diverticulum DiseaseДокумент6 страницDiverticulum Diseasen_robinОценок пока нет
- Sub District Sub Divisional HospitalДокумент102 страницыSub District Sub Divisional HospitalGanesh SoniОценок пока нет
- Functional Foods - Processing & Biochemicals Aspects PDFДокумент436 страницFunctional Foods - Processing & Biochemicals Aspects PDFJoseane Biso de Carvalho100% (3)
- Jurnal GLIKOSIDA ALKOHOL White Willow Bark (Salix Alba)Документ12 страницJurnal GLIKOSIDA ALKOHOL White Willow Bark (Salix Alba)Akhmad NgafifОценок пока нет
- Comp ReДокумент8 страницComp RervanguardiaОценок пока нет
- At The Gates of Despair, Beginning of Hope (English Translation) by Florica IchimДокумент72 страницыAt The Gates of Despair, Beginning of Hope (English Translation) by Florica IchimDumitru Ichim100% (1)
- Path 2Документ2 страницыPath 2SREE NITHINОценок пока нет
- Cytotoxicity of Snake Plant IntroДокумент3 страницыCytotoxicity of Snake Plant IntroSean Ezekiel SalvadorОценок пока нет
- Rectal Bleeding OverviewДокумент7 страницRectal Bleeding OverviewYanceHanzieОценок пока нет