Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Anomaly Program Data Buffer: Buffer Overflow: Buffer Overflow, or Buffer Overrun, Is An
Загружено:
mansamratОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Anomaly Program Data Buffer: Buffer Overflow: Buffer Overflow, or Buffer Overrun, Is An
Загружено:
mansamratАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
IP Spoofing: The term IP address spoofing or IP spoofing refers to the creation of Internet Protocol (IP)
packets with a forged source IP address, called spoofing, with the purpose of concealing the identity of
the sender or impersonating another computing system. IP spoofing is most frequently used in denial-of-
service attacks
buffer overflow : buffer overflow, or buffer overrun, is an anomaly where a program, while
writing data to a buffer, overruns the buffer's boundary and overwrites adjacent memory. Buffer
overflows can be triggered by inputs that are designed to execute code, or alter the way the
program operates. This may result in erratic program behavior, including memory access errors,
incorrect results, a crash, or a breach of system security. Programming languages commonly
associated with buffer overflows include C and C++, which provide no built-in protection against
accessing or overwriting data in any part of memory and do not automatically check that data
written to an array is within the boundaries of that array.
Session hijack: session hijacking is the exploitation of a valid computer session—sometimes also called a
session key—to gain unauthorized access to information or services in a computer system. In particular, it
is used to refer to the theft of a magic cookie used to authenticate a user to a remote server. It has
particular relevance to web developers, as the HTTP cookies used to maintain a session on many web
sites can be easily stolen by an attacker using an intermediary computer or with access to the saved
cookies on the victim's computer
Frame spoofing: Basically, the Frames Spoof is a "spoofing" attack that allows attackers to insert
unauthorized content into the frames of other Websites. Every frames-based Website is vulnerable.
D-DOS -> a denial-of-service attack (DoS attack) or distributed denial-of-service attack (DDoS attack) is
an attempt to make a machine or network resource unavailable to its intended users. One common
method of attack involves saturating the target machine with external communications requests, so
much so that it cannot respond to legitimate traffic.
DNS Spoofing: DNS spoofing (or DNS cache poisoning) is a computer hacking attack, whereby
data is introduced into a Domain Name System (DNS) name server's cache database, causing the
name server to return an incorrect IP address, diverting traffic to another computer (often the
attacker's).
Cross-site scripting: The expression "cross-site scripting" originally referred to the act of loading the
attacked, third-party web application from an unrelated attack site, in a manner that executes a fragment
of JavaScript prepared by the attacker in the security context of the targeted domain
Brute Force: Such an attack might be utilized when it is not possible to take advantage of other
weaknesses in an encryption system (if any exist) that would make the task easier. It consists of
systematically checking all possible keys until the correct key is found. In the worst case, this
would involve traversing the entire search space.
Вам также может понравиться
- Denial of ServiceДокумент11 страницDenial of ServiceKaycee Morauda SindacОценок пока нет
- Hacking TerminologyДокумент18 страницHacking Terminologymemeavelo4746Оценок пока нет
- Dos & DDos Attack For BegineersДокумент18 страницDos & DDos Attack For BegineersAgung Dwi LaksonoОценок пока нет
- Security AttackДокумент6 страницSecurity Attackarif18bariОценок пока нет
- Lectre 11Документ4 страницыLectre 11AkRajОценок пока нет
- Network Threat, Crime TermsДокумент4 страницыNetwork Threat, Crime TermsSwathi KandulaОценок пока нет
- Ethical Hacking - TerminologiesДокумент4 страницыEthical Hacking - TerminologiesmihirmmbОценок пока нет
- Cyber Security IA 2Документ15 страницCyber Security IA 2Shivam PandeyОценок пока нет
- Buffer OverflowДокумент4 страницыBuffer OverflowNoel Cobo GuzonОценок пока нет
- 2-Tools and Methods Used in Cybercrime Stages of An Attack On NetworkДокумент16 страниц2-Tools and Methods Used in Cybercrime Stages of An Attack On NetworkUDxОценок пока нет
- Tools and Methods Used in Cybercrime: Unit 4Документ93 страницыTools and Methods Used in Cybercrime: Unit 4Divya TGОценок пока нет
- IP SpoofingДокумент3 страницыIP SpoofingajeeshcreativeОценок пока нет
- Networks and Network SecurityДокумент10 страницNetworks and Network SecurityashishОценок пока нет
- Cyber Sec 05Документ10 страницCyber Sec 05Jacques MegaptcheОценок пока нет
- Categories of AttacksДокумент4 страницыCategories of AttacksQais Saif QassimОценок пока нет
- Security of OSДокумент25 страницSecurity of OSUmyt GurbanovОценок пока нет
- Cyber Security ItДокумент4 страницыCyber Security ItIfrat ZawarОценок пока нет
- Computer Fundamentals: Lecture # 9: Cyber CrimeДокумент34 страницыComputer Fundamentals: Lecture # 9: Cyber CrimeHina ZahirОценок пока нет
- Information Security: Muhammad Aon BalouchДокумент8 страницInformation Security: Muhammad Aon BalouchBilal Khan RindОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6: Protection & SecurityДокумент38 страницChapter 6: Protection & SecurityGeeta DalviОценок пока нет
- What Is Buffer Overflow?Документ5 страницWhat Is Buffer Overflow?bethlehemshewakena000Оценок пока нет
- Computer Network and Security: 1) What Is Security Threat? List Out Threats and Explain Any One in DetailДокумент27 страницComputer Network and Security: 1) What Is Security Threat? List Out Threats and Explain Any One in DetailParshw PatelОценок пока нет
- IDS EvadesДокумент35 страницIDS EvadesjagdishОценок пока нет
- 3.2 Web Application AttacksДокумент23 страницы3.2 Web Application AttacksLEOBERT CANALES JR.Оценок пока нет
- Experiment No 7: Aim Theory: Denial-of-Service (Dos)Документ3 страницыExperiment No 7: Aim Theory: Denial-of-Service (Dos)Kaitlyn beckhamОценок пока нет
- Computer Security Risks2Документ29 страницComputer Security Risks2bhemteodosioОценок пока нет
- Unit-Iii Tools and Methods Used in Cybercrime:: Cyber and Network SecurityДокумент19 страницUnit-Iii Tools and Methods Used in Cybercrime:: Cyber and Network SecurityayushОценок пока нет
- Information Security PracticalДокумент21 страницаInformation Security PracticalDeepak Kumar Rajak67% (6)
- Ip SpoofingДокумент25 страницIp SpoofingKanwar KakkarОценок пока нет
- Server Side Web Applications AttacksДокумент25 страницServer Side Web Applications AttacksBasharat AliОценок пока нет
- Summary CH.6 Computer Fraud and Abuse TechniquesДокумент6 страницSummary CH.6 Computer Fraud and Abuse TechniquesBrittany Elisabeth MahaОценок пока нет
- 2.1 14 Most Common Network Protocols and Their Vulnerabilities (AutoRecovered)Документ12 страниц2.1 14 Most Common Network Protocols and Their Vulnerabilities (AutoRecovered)kndnew guadeОценок пока нет
- Infrastructure SecurityДокумент107 страницInfrastructure SecurityDoctor LyricsОценок пока нет
- Securing Web PortalsДокумент12 страницSecuring Web PortalsPietro VivoliОценок пока нет
- Report KunoДокумент36 страницReport Kunoferdinand mayolОценок пока нет
- Web Server Misconfiguration: Figure 13-03 RobotsДокумент1 страницаWeb Server Misconfiguration: Figure 13-03 RobotsKaren GarzaОценок пока нет
- Cyber Security Unit - VДокумент67 страницCyber Security Unit - VDeepak kumarОценок пока нет
- Network Security: Presented By: Dr. Munam Ali ShahДокумент32 страницыNetwork Security: Presented By: Dr. Munam Ali ShahNadeem ShoukatОценок пока нет
- Section 1: Basic Introduction To Cyber Security and Information SecurityДокумент5 страницSection 1: Basic Introduction To Cyber Security and Information SecuritynadaОценок пока нет
- Unit 5 - Cyber SecurityДокумент9 страницUnit 5 - Cyber SecurityDraxОценок пока нет
- Network Security: MSC Course byДокумент9 страницNetwork Security: MSC Course bymheba11Оценок пока нет
- Data Centre Security Lecture 16 MarchДокумент8 страницData Centre Security Lecture 16 MarchchamunorwaОценок пока нет
- Different Types of Network Attacks and Security Threats and Counter MeasuresДокумент6 страницDifferent Types of Network Attacks and Security Threats and Counter MeasuresSimar Chauhan100% (1)
- Web Server Application Attacks 1Документ12 страницWeb Server Application Attacks 1Red DragonОценок пока нет
- Cyber Security !Документ3 страницыCyber Security !kavya keerthiОценок пока нет
- Ping of DeathДокумент7 страницPing of DeathManish Jangid100% (1)
- EHДокумент3 страницыEHamii.vikrantОценок пока нет
- AttacksДокумент6 страницAttacksvshukla989Оценок пока нет
- Title of Assignment: Security Vulnerabilities and Countermeasures inДокумент19 страницTitle of Assignment: Security Vulnerabilities and Countermeasures inErwinFunaОценок пока нет
- Security+ Notes v.2Документ69 страницSecurity+ Notes v.2Avo Andrinantenaina100% (1)
- Computer System Security (KNC-301) Unit-IДокумент17 страницComputer System Security (KNC-301) Unit-IATEEN DUBEYОценок пока нет
- FALLSEM2022-23 CSE3501 ETH VL2022230103403 Reference Material I 01-08-2022 Lect 4Документ21 страницаFALLSEM2022-23 CSE3501 ETH VL2022230103403 Reference Material I 01-08-2022 Lect 4Rajarshi BoseОценок пока нет
- A.1 Cross-Site ScriptingДокумент7 страницA.1 Cross-Site ScriptingJastine AnneОценок пока нет
- Security+ Notes v.2Документ70 страницSecurity+ Notes v.2sabiyОценок пока нет
- Information Security Week 01Документ17 страницInformation Security Week 01Danish KhanОценок пока нет
- Cyber CrimeДокумент101 страницаCyber Crimeyesreplynow36Оценок пока нет
- Web Definitions: Example For Active and Passive AttackДокумент7 страницWeb Definitions: Example For Active and Passive AttackJanaka VidurindaОценок пока нет
- Imp Security Concepts - 2Документ24 страницыImp Security Concepts - 2RahulОценок пока нет
- Group 8Документ23 страницыGroup 8Menberu MunyeОценок пока нет
- Teachers Work BookДокумент130 страницTeachers Work Bookagha zahidОценок пока нет
- Video Provides A Powerful Way To Help You Prove Your PointДокумент457 страницVideo Provides A Powerful Way To Help You Prove Your PointderpОценок пока нет
- 413 Channel ListДокумент4 страницы413 Channel ListmansamratОценок пока нет
- Law & Practice of Banking, Priority Sector Lending, Current Trends and Developments in BankingДокумент1 страницаLaw & Practice of Banking, Priority Sector Lending, Current Trends and Developments in BankingmansamratОценок пока нет
- Model Paper For IT Specialist Officer ExamДокумент8 страницModel Paper For IT Specialist Officer ExamAjit JenaОценок пока нет
- RBI Doc - Report On Trend and Banking ProgressДокумент191 страницаRBI Doc - Report On Trend and Banking ProgressChandan AgarwalОценок пока нет
- MCQ m1Документ16 страницMCQ m1kndunaОценок пока нет
- Information System Integration After Merger and Acquisition in The Banking IndustryДокумент5 страницInformation System Integration After Merger and Acquisition in The Banking IndustrymansamratОценок пока нет
- Go DigitalДокумент2 страницыGo DigitalmansamratОценок пока нет
- It Officer General Awareness Andhra Bank PaperДокумент2 страницыIt Officer General Awareness Andhra Bank PapermansamratОценок пока нет
- IBPS Computer Knowledge Paper I IДокумент8 страницIBPS Computer Knowledge Paper I ISyb KhanОценок пока нет
- IBPS Computer Knowledge Paper IДокумент5 страницIBPS Computer Knowledge Paper ISunny ChauhanОценок пока нет
- It Officer Central Bank of IndiaДокумент6 страницIt Officer Central Bank of IndiaMondar DebОценок пока нет
- Digital & Tech Integration Top Agenda Post MergerДокумент1 страницаDigital & Tech Integration Top Agenda Post MergermansamratОценок пока нет
- Digital & Tech Integration Top Agenda Post MergerДокумент1 страницаDigital & Tech Integration Top Agenda Post MergermansamratОценок пока нет
- ProductДокумент1 страницаProductmansamratОценок пока нет
- ProductДокумент1 страницаProductmansamratОценок пока нет
- JolphoringДокумент1 страницаJolphoringmansamratОценок пока нет
- History of BankingДокумент54 страницыHistory of BankingmansamratОценок пока нет
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightДокумент593 страницыHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- Kol SouthДокумент1 страницаKol SouthmansamratОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4: Thermal ComfortДокумент16 страницChapter 4: Thermal ComfortWengelОценок пока нет
- Clinical Skills TrainingДокумент12 страницClinical Skills TrainingSri Wahyuni SahirОценок пока нет
- Forensic IR-UV-ALS Directional Reflected Photography Light Source Lab Equipment OR-GZP1000Документ3 страницыForensic IR-UV-ALS Directional Reflected Photography Light Source Lab Equipment OR-GZP1000Zhou JoyceОценок пока нет
- Zero Tolerance 2010Документ16 страницZero Tolerance 2010Adrian KozelОценок пока нет
- Ultimate Trading Guide - Flash FUT 2023Документ33 страницыUltimate Trading Guide - Flash FUT 2023marciwnw IОценок пока нет
- Linux ProgramДокумент131 страницаLinux ProgramsivashaОценок пока нет
- Flight Data Recorder Rule ChangeДокумент7 страницFlight Data Recorder Rule ChangeIgnacio ZupaОценок пока нет
- 2022 AMR Dashboard Funding Opportunity Announcement 11.18.2022Документ16 страниц2022 AMR Dashboard Funding Opportunity Announcement 11.18.2022Tuhin DeyОценок пока нет
- Extraction of Mangiferin From Mangifera Indica L. LeavesДокумент7 страницExtraction of Mangiferin From Mangifera Indica L. LeavesDaniel BartoloОценок пока нет
- Tenses English Grammar PresentationДокумент14 страницTenses English Grammar PresentationMaz Gedi60% (5)
- Vq40de Service ManualДокумент257 страницVq40de Service Manualjaumegus100% (4)
- The One With The ThumbДокумент4 страницыThe One With The Thumbnoelia20_09Оценок пока нет
- DBM Uv W ChartДокумент2 страницыDBM Uv W ChartEddie FastОценок пока нет
- Oil List: Audi Front Axle DriveДокумент35 страницOil List: Audi Front Axle DriveAska QianОценок пока нет
- Less Homework More TroubleДокумент7 страницLess Homework More Troubleg697a0mw100% (1)
- This Is A Short Presentation To Explain The Character of Uncle Sam, Made by Ivo BogoevskiДокумент7 страницThis Is A Short Presentation To Explain The Character of Uncle Sam, Made by Ivo BogoevskiIvo BogoevskiОценок пока нет
- Microsoft Powerpoint BasicsДокумент20 страницMicrosoft Powerpoint BasicsJonathan LocsinОценок пока нет
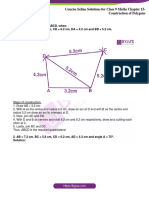
- Concise Selina Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 15 Construction of PolygonsДокумент31 страницаConcise Selina Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 15 Construction of Polygonsbhaskar51178Оценок пока нет
- Formato MultimodalДокумент1 страницаFormato MultimodalcelsoОценок пока нет
- OBOE GougerДокумент2 страницыOBOE GougerCarlos GaldámezОценок пока нет
- Acceptable Use Policy 08 19 13 Tia HadleyДокумент2 страницыAcceptable Use Policy 08 19 13 Tia Hadleyapi-238178689Оценок пока нет
- Caroline Coady: EducationДокумент3 страницыCaroline Coady: Educationapi-491896852Оценок пока нет
- Air Blower ManualДокумент16 страницAir Blower ManualshaiknayeemabbasОценок пока нет
- CHN Nutri LabДокумент4 страницыCHN Nutri LabMushy_ayaОценок пока нет
- GrenTech Express Communication System Introduction 1.0Документ30 страницGrenTech Express Communication System Introduction 1.0Son NguyenОценок пока нет
- SY22-23+Annual+Report FinalДокумент47 страницSY22-23+Annual+Report FinalNorus LizaОценок пока нет
- Gobekli TepeДокумент2 страницыGobekli TepeCarl Feagans100% (1)
- Sage TutorialДокумент115 страницSage TutorialChhakuli GiriОценок пока нет
- Role of Communication at Mahabharatha WarДокумент19 страницRole of Communication at Mahabharatha WarAmit Kalita50% (2)
- Developpments in OTC MarketsДокумент80 страницDeveloppments in OTC MarketsRexTradeОценок пока нет