Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Questions
Загружено:
Madhura Bhashitha0%(1)0% нашли этот документ полезным (1 голос)
86 просмотров1 страницаThis document provides parameters for NMOS and PMOS transistors including mobility, threshold voltage, and capacitances. It describes an inverter circuit and lists 17 calculations to perform using the provided transistor parameters and circuit information. The calculations include gate overdrive, drain current, various voltages, capacitances, transconductance, output conductance, and what will happen if the drain currents do not match.
Исходное описание:
Set of question in economics
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThis document provides parameters for NMOS and PMOS transistors including mobility, threshold voltage, and capacitances. It describes an inverter circuit and lists 17 calculations to perform using the provided transistor parameters and circuit information. The calculations include gate overdrive, drain current, various voltages, capacitances, transconductance, output conductance, and what will happen if the drain currents do not match.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0%(1)0% нашли этот документ полезным (1 голос)
86 просмотров1 страницаQuestions
Загружено:
Madhura BhashithaThis document provides parameters for NMOS and PMOS transistors including mobility, threshold voltage, and capacitances. It describes an inverter circuit and lists 17 calculations to perform using the provided transistor parameters and circuit information. The calculations include gate overdrive, drain current, various voltages, capacitances, transconductance, output conductance, and what will happen if the drain currents do not match.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 1
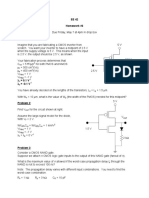
Homework 1
EEE 433/591 Allee, Fall 2015
PARAMETER NMOS PMOS
uCox/2 (uA/V2) 120 40
Vth (V) 0.5 -0.5
Lambda (V-1) 0.15 0.2
(for L=0.5um)
Cgdo (F/m) 2x10-10 2x10-10
Cjo (F/m2 ) 10-3 10-3
Vdd = 2.5V
Phi = 0.7V (built in potential of pn junction)
Cjo = 0 bias capacitance of pn junction Fig. 1
Gate dielectric: SiO2, 10nm thick
Calculate the following both for the NMOS and PMOS transistors in the inverter circuit
shown (Fig.1). The gate widths are 2um and lengths are 0.5um. The voltage at each node is
marked. Note the N-well is at Vdd.
1. Gate overdrive or Veff for NMOS
2. Drain current of NMOS
3. Gate overdrive or Veff for PMOS
4. Drain current of PMOS
5. Voltage between source and bulk for NMOS.
6. Source to bulk capacitance for the NMOS. Note: the area of a source or drain is
device width times 0.5um.
7. Voltage between drain and bulk for NMOS.
8. Drain to bulk capacitance for NMOS.
9. Voltage between source and well for PMOS.
10. Source to well capacitance for the PMOS. Note: the area of a source or drain is
device width times 0.5um.
11. Voltage between drain and well for PMOS.
12. Drain to well capacitance for PMOS.
13. Gate to source capacitance for NMOS and PMOS. Note the gate area is device width
times length.
14. Gate to drain capacitance for NMOS and PMOS.
15. Region of operation for each device – linear or saturation.
16. Transconductance of NMOS and PMOS.
17. Output conductance of NMOS and PMOS.
18. If the two drain currents do not match explain what will happen to the output
voltage.
Вам также может понравиться
- Characteristics: EXPERIMENT 08: SPICE Simulation of and Implementation For MOSFETДокумент11 страницCharacteristics: EXPERIMENT 08: SPICE Simulation of and Implementation For MOSFETJohnny NadarОценок пока нет
- Vlsi 2-Marks With AnswerДокумент23 страницыVlsi 2-Marks With Answerk poornimaОценок пока нет
- DLC LAB - 08 - Student - ManualДокумент10 страницDLC LAB - 08 - Student - ManualImtiaj SajinОценок пока нет
- UNIT 3: Transistor Sizing in CMOS: Aims and ObjectivesДокумент12 страницUNIT 3: Transistor Sizing in CMOS: Aims and ObjectivesGirish Kv50% (2)
- ECE429 Laboratory 4 NAND Schematic: Bapu A20489420 21/09/2021Документ14 страницECE429 Laboratory 4 NAND Schematic: Bapu A20489420 21/09/2021Prasanna NalawarОценок пока нет
- Physical DesignДокумент45 страницPhysical DesignMalka RavikrishnaОценок пока нет
- ECE429 Laboratory 3 Inverter Layout: Prasanna N A20489739 21/09/2021Документ14 страницECE429 Laboratory 3 Inverter Layout: Prasanna N A20489739 21/09/2021Prasanna NalawarОценок пока нет
- ECE429 Laboratory 2 Inverter Schematic: Prasanna Nalawar A20489739 21/09/2021Документ14 страницECE429 Laboratory 2 Inverter Schematic: Prasanna Nalawar A20489739 21/09/2021Prasanna NalawarОценок пока нет
- Pid00050 2 CmosДокумент8 страницPid00050 2 CmosSaurabh ChakravartyОценок пока нет
- Lect12 InverterДокумент17 страницLect12 InverterVimala PriyaОценок пока нет
- Physical DesignДокумент45 страницPhysical DesignSameer Badachi100% (10)
- EI2403 - VLSI Design 2 Marks With AnswersДокумент23 страницыEI2403 - VLSI Design 2 Marks With AnswersAnand GvphОценок пока нет
- Microelectronics Lab ReportsДокумент75 страницMicroelectronics Lab ReportsAmArbir SinghОценок пока нет
- Dec Exp 3 Student ManualДокумент7 страницDec Exp 3 Student ManualSakib MahmudОценок пока нет
- American International University-Bangladesh: Faculty of Engineering (EEE)Документ7 страницAmerican International University-Bangladesh: Faculty of Engineering (EEE)SifatОценок пока нет
- 2marks Unit1Документ4 страницы2marks Unit1Sinan SinanОценок пока нет
- Level 1 IdsДокумент46 страницLevel 1 IdsDavid Montoya MoralesОценок пока нет
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer ScienceДокумент7 страницMassachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer ScienceFernando Sánchez HernándezОценок пока нет
- Vlsi QBДокумент34 страницыVlsi QBKaviya dharshini S -ECE-028Оценок пока нет
- Design, Characterization and Use of Custom Standard CellsДокумент18 страницDesign, Characterization and Use of Custom Standard CellsAlamgir MohammedОценок пока нет
- Mosfet Using Tanner ToolДокумент20 страницMosfet Using Tanner ToolParmeet SinghОценок пока нет
- Spice Parameter CalculatorДокумент14 страницSpice Parameter Calculatorhamid_kh_56Оценок пока нет
- U18ec038 - Vlsi - Lab 2Документ9 страницU18ec038 - Vlsi - Lab 2Timir PatelОценок пока нет
- BD180 - A New 0.18 Ȝm BCD (Bipolar-CMOS-DMOS)Документ4 страницыBD180 - A New 0.18 Ȝm BCD (Bipolar-CMOS-DMOS)samactrangОценок пока нет
- Op-Amps and Startup Circuits For CMOS Bandgap References With Near 1-V SupplyДокумент5 страницOp-Amps and Startup Circuits For CMOS Bandgap References With Near 1-V Supplynivia25Оценок пока нет
- CMOS Interview QAДокумент14 страницCMOS Interview QAarammartОценок пока нет
- VLSI Design TechniquesДокумент119 страницVLSI Design Techniquesrajesh26julyОценок пока нет
- Mosfet I-V Characteristic Curve LaboratoryДокумент13 страницMosfet I-V Characteristic Curve LaboratoryCheka CurativoОценок пока нет
- Exp-1Документ3 страницыExp-1asОценок пока нет
- Topic 3Документ48 страницTopic 3Saiful NizamОценок пока нет
- Effects of On Resistance RON To An Analog SwitchДокумент3 страницыEffects of On Resistance RON To An Analog SwitchVăn CôngОценок пока нет
- ECE 4141-Experiment 3 - CMOS NAND Transistors Sizing Simulation Using PSPICEДокумент6 страницECE 4141-Experiment 3 - CMOS NAND Transistors Sizing Simulation Using PSPICEAnwar Zainuddin100% (2)
- 12 Steps For Designing SMPS TransformersДокумент11 страниц12 Steps For Designing SMPS TransformersRnDES1 CMLОценок пока нет
- The State-of-the-Art of Silicon-on-Sapphire CMOS RF SwitchesДокумент4 страницыThe State-of-the-Art of Silicon-on-Sapphire CMOS RF SwitchesAhmed AtefОценок пока нет
- Voltage References and Biasing: KT/Q, For Example) - Similarly, Any Current We Produce Must Depend On Parameters ThatДокумент15 страницVoltage References and Biasing: KT/Q, For Example) - Similarly, Any Current We Produce Must Depend On Parameters ThatmaheshsamanapallyОценок пока нет
- (EE476) (Lab 1) 09ece - Group8Документ20 страниц(EE476) (Lab 1) 09ece - Group8Trung LyamОценок пока нет
- Lpvlsi - V Unit Q & AДокумент17 страницLpvlsi - V Unit Q & ANarasimhulu MaddireddyОценок пока нет
- A Report: Verilog-A Implementation of The EKV v2.6 Long and Short Channel MOSFET ModelsДокумент43 страницыA Report: Verilog-A Implementation of The EKV v2.6 Long and Short Channel MOSFET ModelsDilan ByteОценок пока нет
- Unit 1.2 VLSI NotesДокумент16 страницUnit 1.2 VLSI NotesElston RyanОценок пока нет
- Dual Op Amp, LDO Regulator With Power Supply Gain Suppression For CMOS Smart Sensors and MicrosystemsДокумент4 страницыDual Op Amp, LDO Regulator With Power Supply Gain Suppression For CMOS Smart Sensors and Microsystemssukumar78Оценок пока нет
- Ec 302Документ1 страницаEc 302gauravkumartech0Оценок пока нет
- Lecture8 MOS TransistorДокумент21 страницаLecture8 MOS TransistorKartika MunirОценок пока нет
- Dheeraj ReportДокумент15 страницDheeraj ReportGirdhar Gopal GautamОценок пока нет
- HW 6Документ2 страницыHW 6Shimaa BarakatОценок пока нет
- Mos Transistor TheoryДокумент144 страницыMos Transistor TheorymailtolokiОценок пока нет
- EMDmod 2Документ28 страницEMDmod 2SuprithaОценок пока нет
- Iscas06 Curr RefДокумент4 страницыIscas06 Curr Refkareka_ccОценок пока нет
- How To Buffer An Op-Amp Output For Higher Current Part 3Документ8 страницHow To Buffer An Op-Amp Output For Higher Current Part 3adalberto soplatetasОценок пока нет
- VO3120 2.5 A Output Current IGBT and MOSFET Driver: Vishay SemiconductorsДокумент10 страницVO3120 2.5 A Output Current IGBT and MOSFET Driver: Vishay Semiconductorsfadapow4uОценок пока нет
- Problems MOSFET Operation and IVДокумент1 страницаProblems MOSFET Operation and IVahsanhabib2572003Оценок пока нет
- A 32nm Tunnel FET SRAM For Ultra Low LeakageДокумент4 страницыA 32nm Tunnel FET SRAM For Ultra Low LeakageNITHINОценок пока нет
- dk7zb LiniarДокумент6 страницdk7zb LiniarBelea Stelu'Оценок пока нет
- Service Manual: CFS-515SДокумент5 страницService Manual: CFS-515SAndre BaezОценок пока нет
- VLSI Design Unit-2 Mosfet TransistorДокумент5 страницVLSI Design Unit-2 Mosfet Transistorselvi0412Оценок пока нет
- ECE2274 Pre-Lab For MOSFET Logic NAND Gate, NOR Gate, and CMOS Inverter 1. Nmos Nand GateДокумент6 страницECE2274 Pre-Lab For MOSFET Logic NAND Gate, NOR Gate, and CMOS Inverter 1. Nmos Nand GateRudra MishraОценок пока нет
- LTspice AssignmentДокумент7 страницLTspice Assignmentsudhakar kethanaОценок пока нет
- Characterization of A Generic 90nm CMOS Technology: DS DS DS GSДокумент10 страницCharacterization of A Generic 90nm CMOS Technology: DS DS DS GSgill6335Оценок пока нет
- Semiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsОт EverandSemiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsОценок пока нет
- MatcadДокумент3 страницыMatcadMadhura BhashithaОценок пока нет
- AaaaaДокумент1 страницаAaaaaMadhura BhashithaОценок пока нет
- 1.cellular SystemsДокумент79 страниц1.cellular SystemsMadhura BhashithaОценок пока нет
- Simulation Exercises 1 and 2: M.B.Sondarangalla 120636AДокумент18 страницSimulation Exercises 1 and 2: M.B.Sondarangalla 120636AMadhura BhashithaОценок пока нет
- Kithsiri Meditation Course UOM P7Документ18 страницKithsiri Meditation Course UOM P7Madhura Bhashitha100% (1)