Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
NCP #1 Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion
Загружено:
steffi0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
4K просмотров4 страницы1) The patient is a female who suffered a stroke as reported by her daughter, with a GCS of 4 and paralysis of the extremities.
2) The nursing diagnosis is ineffective cerebral tissue perfusion related to interruption of blood flow secondary to hemorrhage from the stroke, as evidenced by a GCS of 4.
3) The goals are for the patient to demonstrate stable vital signs and no further neurological deterioration within 8
Исходное описание:
NCP duy at medical ward
Оригинальное название
Ncp #1 Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документ1) The patient is a female who suffered a stroke as reported by her daughter, with a GCS of 4 and paralysis of the extremities.
2) The nursing diagnosis is ineffective cerebral tissue perfusion related to interruption of blood flow secondary to hemorrhage from the stroke, as evidenced by a GCS of 4.
3) The goals are for the patient to demonstrate stable vital signs and no further neurological deterioration within 8
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
4K просмотров4 страницыNCP #1 Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion
Загружено:
steffi1) The patient is a female who suffered a stroke as reported by her daughter, with a GCS of 4 and paralysis of the extremities.
2) The nursing diagnosis is ineffective cerebral tissue perfusion related to interruption of blood flow secondary to hemorrhage from the stroke, as evidenced by a GCS of 4.
3) The goals are for the patient to demonstrate stable vital signs and no further neurological deterioration within 8
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 4
GOLEZ, Steffi Gabrielle R.
4NUR-2 RLE-2 – Ma’am Dyan Dee Tiongco
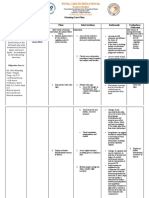
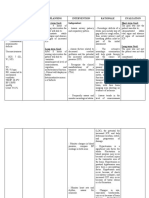
PATIENT CARE RECORD – NURSING CARE PLAN
ASSESSMENT NURSING SCIENTIFIC GOALS/ OBJECTIVES NURSING RATIONALE EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS RATIONALE INTERVENTIONS
Subjective: Ineffective The presence of Short Term: INDEPENDENT: Short Term:
“Na stroke si cerebral partial blockage Within 8 hours of nursing Within 8 hours of
mama.” As tissue of the blood interventions, the client will be -Establish rapport -To promote nursing interventions,
verbalized by perfusion vessel can be able to: cooperation the client was able to:
the client’s related to multifactorial.
daughter. interruption These can be Demonstrate stable -Assess factors -Assessment • Demonstrated stable
of blood due to vital signs and absence related to individual will vital signs and absence
Objectives: flow vasoconstriction, of signs of increased situation for determine and of signs of increased
-GCS: 4 secondary to platelet ICP. decreased cerebral influence the ICP.
-Extremity hemorrhage adherence on Display no further perfusion and choice of • Displayed no further
weakness: as evidenced rough surface, deterioration/recurrence potential for interventions. deterioration/recurrence
paralysis by GCS 4. fat accumulation of deficits increased ICP. of deficits.
and therefore
V/S as decreases -Closely assess and -Assesses Long Term:
follows: elasticity of Long Term: monitor neurological trends in level Within 3 days of
-BP: vessel wall Within 3 days of nursing status frequently and of nursing interventions,
150/90mmHg leading to interventions, the patient will: compare with consciousness the patient was able to:
-PR: 146 alteration of baseline. (LOC) and
Maintain usual or
-RR: 21 blood perfusion potential for • Maintained usual or
-Temp: 37.9C with the improved LOC, increased ICP improved LOC,
initiation of the cognition, and motor and and is useful cognition, and motor
clotting sensory function. in and sensory function.
sequence. This determining
may later lead to location,
the development extent, and
of thrombus progression of
which can be damage.
loosened and
dislodged in Monitor Vital Signs:
some areas of
the brain such as -Changes in blood -Fluctuations
mid cerebral pressure, compare in pressure
carotid artery BP readings in both may occur
that may lead to arms. because of
alteration of cerebral
blood perfusion injury in
and further vasomotor
develop to area of the
cerebral brain.
infarction.
-Heart rate and -Changes in
Source: medical rhythm, assess for rate,
surgical nursing: murmurs. especially
13th Brunner’s bradycardia,
and Suddarath’s can occur
because of the
brain damage.
-Respirations, noting -Irregularities
patterns and rhythm. can suggest
location of
cerebral insult
or increasing
ICP and need
for further
intervention,
including
possible
respiratory
support.
-Position with head -Arterial
slightly elevated and pressure by
in neutral position. promoting
venous
drainage and
may improve
cerebral
perfusion.
-Maintain bedrest, -Continuous
provide quiet and stimulation or
relaxing activity can
environment, restrict increase
visitors and intracranial
activities. pressure
(ICP).
Absolute rest
and quiet may
be needed to
prevent
rebleeding in
the case of
hemorrhage.
-Assess for nuchal -Indicative of
rigidity, twitching, meningeal
increased irritation,
restlessness, especially in
hemorrhage
irritability, onset of disorders.
seizure activity. Seizures may
reflect
increased ICP
or cerebral
injury,
requiring
further
evaluation
and
intervention.
COLLABORATIVE:
-Administer -Reduces
supplemental oxygen hypoxemia
as ordered
-Administer -To promote
medications as wellness
ordered
Вам также может понравиться
- NCP Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion STROKEДокумент3 страницыNCP Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion STROKEMa. Elaine Carla TatingОценок пока нет
- "Mayroong Namuong Dugo Sa Utak Niya Kaya Hindi Maayos Ang Daloy NG Dugo Rito" As Verbalized by The Patient'sДокумент4 страницы"Mayroong Namuong Dugo Sa Utak Niya Kaya Hindi Maayos Ang Daloy NG Dugo Rito" As Verbalized by The Patient'sAllisson BeckersОценок пока нет
- Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related To Interruption of Blood Flow Secondary To Hemorrhage As Evidenced by GCS of 7Документ2 страницыIneffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related To Interruption of Blood Flow Secondary To Hemorrhage As Evidenced by GCS of 7dana100% (4)
- NCP For Subarachnoid HemorrhageДокумент4 страницыNCP For Subarachnoid HemorrhageJoan Rose Rendon-Hung78% (18)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: Short Term: Independent: Short TermДокумент3 страницыAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: Short Term: Independent: Short TermMicaela CrisostomoОценок пока нет
- NCP Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionДокумент2 страницыNCP Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionAngelo ︻╦̵̵͇̿̿̿̿╤── Bulacan50% (6)
- NCP 1: Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related To Interruption of Blood Flow Secondary To Cerebrovascular AccidentДокумент14 страницNCP 1: Ineffective Cerebral Tissue Perfusion Related To Interruption of Blood Flow Secondary To Cerebrovascular AccidentKyle Jingco100% (2)
- NCP-Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionДокумент9 страницNCP-Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionKarel LuОценок пока нет
- Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionДокумент3 страницыIneffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionHanya Bint Potawan88% (25)
- NCP Cva Ineffective Tissue PerfusionДокумент1 страницаNCP Cva Ineffective Tissue Perfusionexcel21121Оценок пока нет
- Impaired Skin DMДокумент3 страницыImpaired Skin DMimnotdatsunny100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plans - Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionДокумент3 страницыNursing Care Plans - Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionKate Cruz75% (8)
- Nursing Care Plan: by The Wife During InterviewДокумент3 страницыNursing Care Plan: by The Wife During InterviewJayson SamonteОценок пока нет
- III. Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Goal Intervention EvaluationДокумент4 страницыIII. Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Goal Intervention EvaluationSTEPHANIE JOSUEОценок пока нет
- Impaired Verbal CommunicationДокумент3 страницыImpaired Verbal CommunicationChenee Mabulay100% (1)
- Ineffective Tissue Perfusion NCPДокумент5 страницIneffective Tissue Perfusion NCPJasmin Calata50% (2)
- CVA-NCPДокумент7 страницCVA-NCPAiza Oronce0% (1)
- NCP AfДокумент3 страницыNCP AfAngelica Mercado SirotОценок пока нет
- IMPAIRED PHYSICAL MOBILITY RT Neuromuscular Involvement (Right Sided Paresthesia Aeb Inability To Purposefully Move Body Parts.Документ2 страницыIMPAIRED PHYSICAL MOBILITY RT Neuromuscular Involvement (Right Sided Paresthesia Aeb Inability To Purposefully Move Body Parts.Senyorita KHaye67% (3)
- NCP CVDДокумент5 страницNCP CVDaejel1889% (9)
- Impaired Verbal CommunicationДокумент2 страницыImpaired Verbal CommunicationEjay Barayuga100% (2)
- CVA NCPДокумент6 страницCVA NCPErika Arboleras0% (1)
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionДокумент2 страницыIneffective Tissue Perfusioniammkrissa33% (3)
- Disturbed Sensory PerceptionДокумент3 страницыDisturbed Sensory PerceptionJashtine JingcoОценок пока нет
- Impaired Verbal CommДокумент3 страницыImpaired Verbal CommKM100% (2)
- Disturbed Thought ProcessДокумент3 страницыDisturbed Thought ProcessAira AlaroОценок пока нет
- NCP Impaired Verbal CommunicationДокумент2 страницыNCP Impaired Verbal CommunicationLovelie Grace GalarpeОценок пока нет
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationДокумент2 страницыAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationCharissa Magistrado De LeonОценок пока нет
- Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA) N C P BY BHERU LALДокумент1 страницаCerebrovascular Accident (CVA) N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalОценок пока нет
- Tissue PerfusionДокумент2 страницыTissue PerfusionMichael John LeandichoОценок пока нет
- Vessel Due FДокумент2 страницыVessel Due Fianecunar88% (8)
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionДокумент1 страницаIneffective Tissue PerfusionEm Castillo50% (2)
- CVA Activity IntoleranceДокумент1 страницаCVA Activity IntoleranceNursesLabs.com75% (4)
- Dec Cardiac Output NCPДокумент2 страницыDec Cardiac Output NCPJoehoney BarreraОценок пока нет
- Impaired Urinary EliminationДокумент3 страницыImpaired Urinary EliminationAgcopra MtchОценок пока нет
- Acute Pain NCPДокумент1 страницаAcute Pain NCPJed AvesОценок пока нет
- NCP - Tissue Perfusion (Cerebral)Документ2 страницыNCP - Tissue Perfusion (Cerebral)moodlayers50% (6)
- NCP Ischemic StrokeДокумент3 страницыNCP Ischemic StrokeLP Benoza100% (3)
- Risk For AspirationДокумент2 страницыRisk For AspirationGly Mtg100% (6)
- NCP Excess Fluid VolumeДокумент3 страницыNCP Excess Fluid VolumeJ.G RОценок пока нет
- NCP - Impaired Verbal Communication Related To Neuromascular Impairment As Manifested by AphaisaДокумент2 страницыNCP - Impaired Verbal Communication Related To Neuromascular Impairment As Manifested by AphaisaKristina Angela CarbonОценок пока нет
- Risk For InjuryДокумент2 страницыRisk For InjuryJoanne Kaye TaylorОценок пока нет
- NCP CvaДокумент3 страницыNCP CvaJey PangilinanОценок пока нет
- NCP STROKE - Impaired Verbal CommДокумент2 страницыNCP STROKE - Impaired Verbal CommCath BrilОценок пока нет
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionДокумент1 страницаIneffective Tissue PerfusionRhae RaynogОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosis Definitio N Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluati ONДокумент5 страницNursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosis Definitio N Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluati ONOphelia Ross Omaña TutanesОценок пока нет
- Icu NCPДокумент8 страницIcu NCPClaire Nicole ApostolОценок пока нет
- Impaired Verbal CommunicationДокумент3 страницыImpaired Verbal CommunicationDesiree Deleon Guerrero0% (2)
- Ischemic Stroke NCPДокумент11 страницIschemic Stroke NCPJohannah DaroОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan For RabiesДокумент1 страницаNursing Care Plan For RabiesAngel VillamorОценок пока нет
- Risk For IneffectiveДокумент6 страницRisk For IneffectiveAce FabrigasОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan Format X1Документ3 страницыNursing Care Plan Format X1Ramiel ChristopherОценок пока нет
- Nanda NCP BasedДокумент14 страницNanda NCP Baseddeliejoyce100% (1)
- Jade R. Dinolan BSN-4: Diagnosi SДокумент5 страницJade R. Dinolan BSN-4: Diagnosi SJhade Relleta100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Artery Blockage May BeДокумент5 страницNursing Care Plan: Artery Blockage May BeDienizs Labini TadenaОценок пока нет
- Patients Nursing PlanДокумент3 страницыPatients Nursing Planmharjoe pulmanoОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan ActivityДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan Activitymharjoe pulmanoОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan For HypertensionДокумент5 страницNursing Care Plan For HypertensionJessy MalloОценок пока нет
- Decreased Cardiac OutputДокумент5 страницDecreased Cardiac Outputshuang81Оценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan For HypertensionДокумент4 страницыNursing Care Plan For HypertensionKathleen Dimacali100% (2)
- University of Santo Tomas College of Nursing NCM 103 Ms Case # 2Документ4 страницыUniversity of Santo Tomas College of Nursing NCM 103 Ms Case # 2steffiОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Breast Cancer: If Not TreatedДокумент1 страницаPathophysiology of Breast Cancer: If Not TreatedsteffiОценок пока нет
- España Boulevard, Sampaloc, Manila, Philippines 1015 Tel. No. 406-1611 Loc. 8241 Telefax: 731-5738 Website: WWW - Ust.edu - PHДокумент4 страницыEspaña Boulevard, Sampaloc, Manila, Philippines 1015 Tel. No. 406-1611 Loc. 8241 Telefax: 731-5738 Website: WWW - Ust.edu - PHsteffiОценок пока нет
- Final NCP Risk For BleedingДокумент2 страницыFinal NCP Risk For Bleedingsteffi100% (1)
- MarcomДокумент4 страницыMarcomsteffiОценок пока нет
- Baby Girl AkitaДокумент25 страницBaby Girl AkitasteffiОценок пока нет
- MemoriesДокумент2 страницыMemoriessteffiОценок пока нет
- Policies For Einc CareДокумент28 страницPolicies For Einc CaresteffiОценок пока нет
- 4 P's of Labor and Birth: Presented By: Ana Laurice R. Nastor & Nerissa N. Natata RLE II-7.2Документ56 страниц4 P's of Labor and Birth: Presented By: Ana Laurice R. Nastor & Nerissa N. Natata RLE II-7.2steffiОценок пока нет
- Source: Operating Room Technique by Nancymarie PhillipsДокумент1 страницаSource: Operating Room Technique by Nancymarie Phillipsnoreen ellieОценок пока нет
- 13 Puspa RamadhaniДокумент182 страницы13 Puspa Ramadhaniewa silverstoneОценок пока нет
- Pedia Drug Study NaproxenparacetamolДокумент3 страницыPedia Drug Study NaproxenparacetamolKuro HanabusaОценок пока нет
- GURPS 4e - Hit Locations V3Документ9 страницGURPS 4e - Hit Locations V3Luca LiperiОценок пока нет
- Patient Age / Sex Referrer 47 Y / Female Prashanth Multi Speciality Hospital (Cash) Branch TondiarpetДокумент1 страницаPatient Age / Sex Referrer 47 Y / Female Prashanth Multi Speciality Hospital (Cash) Branch TondiarpetMeatmaker’s ChennaiОценок пока нет
- Seizures and Epilepsy After Intracerebral Hemorrhage: An UpdateДокумент11 страницSeizures and Epilepsy After Intracerebral Hemorrhage: An UpdateWilfrido Jose Barrios AgamezОценок пока нет
- Approach To Neonatal JaundiceДокумент73 страницыApproach To Neonatal JaundiceG Venkatesh50% (2)
- What Is Legionnaires' Disease?: Patient EducationДокумент2 страницыWhat Is Legionnaires' Disease?: Patient EducationvivaОценок пока нет
- Primary Care DiabetesДокумент5 страницPrimary Care DiabetesKarina Caudillo GamezОценок пока нет
- Skin Care and Management of Pressure UlcerДокумент24 страницыSkin Care and Management of Pressure UlcerchellczyОценок пока нет
- Antiemesis NCCNДокумент79 страницAntiemesis NCCNana salazarОценок пока нет
- Subdural HematomaДокумент3 страницыSubdural HematomaAngga ToragarryОценок пока нет
- Nursing Thesis HypertensionДокумент7 страницNursing Thesis Hypertensioncoawokugg100% (2)
- Transfusion in TraumaДокумент28 страницTransfusion in TraumaSyeda Nasra ShahОценок пока нет
- Concept Map BoxesДокумент2 страницыConcept Map Boxesapi-508174430Оценок пока нет
- Oph 1Документ100 страницOph 1Nishant ShresthaОценок пока нет
- Glucose Tolerance TestДокумент4 страницыGlucose Tolerance TestNikhil KanikaОценок пока нет
- Does A Latissimus Dorsi Flap Improve SurgicalДокумент7 страницDoes A Latissimus Dorsi Flap Improve SurgicalBatista FilhoОценок пока нет
- Assignment GiДокумент14 страницAssignment GiVoid LessОценок пока нет
- 9 - Hepatitis B VaccineДокумент1 страница9 - Hepatitis B VaccineabhivnairОценок пока нет
- UoI Certificate Joining Instruction 2020 21Документ4 страницыUoI Certificate Joining Instruction 2020 21Haason TzОценок пока нет
- Major Haemorrhage ProtocolДокумент2 страницыMajor Haemorrhage ProtocollaurenОценок пока нет
- Oet Official Reading Task Practice Test Part CДокумент5 страницOet Official Reading Task Practice Test Part CSree ShnaОценок пока нет
- Covid-19 Mitigation PlanДокумент8 страницCovid-19 Mitigation PlanEkum EdunghuОценок пока нет
- Disordered Proliferative Endometrium Causes and SymptomsДокумент7 страницDisordered Proliferative Endometrium Causes and SymptomsMuhammad BabarОценок пока нет
- The Rare Disorder of Fibrodysplasia Ossificans ProgressivaДокумент6 страницThe Rare Disorder of Fibrodysplasia Ossificans ProgressivaNoelle NakagakiОценок пока нет
- Gout and Hyperuricemia: PathophysiologyДокумент1 страницаGout and Hyperuricemia: Pathophysiologyسمرة طايبОценок пока нет
- On Brain InjuryДокумент17 страницOn Brain InjuryhumayunОценок пока нет
- Classification of Cerebral PalsyДокумент15 страницClassification of Cerebral PalsypraveenОценок пока нет
- 10 Penyakit Terbanyak JKN 2016Документ2 страницы10 Penyakit Terbanyak JKN 2016RSUD dr. H. Soemarno Sosroatmodjo Kuala KapuasОценок пока нет