Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Magnetic Circuits & Electromagnetic Induction Explained
Загружено:
ashwini patil0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
10 просмотров1 страницаThis document outlines the key topics in magnetic circuits and electromagnetic induction including: the laws of magnetism and magnetic fields; magnetic circuits and their comparison to electric circuits; types of magnets and their applications; Faraday's laws of induction; Lenz's law; inductance; and energy stored in magnetic fields. Key concepts covered are magnetic permeability, flux, reluctance, hysteresis loops, induced EMF, self and mutual inductance, and inductors.
Исходное описание:
magnetic circuit decsription
Оригинальное название
Electrical Magnetic Circuit
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThis document outlines the key topics in magnetic circuits and electromagnetic induction including: the laws of magnetism and magnetic fields; magnetic circuits and their comparison to electric circuits; types of magnets and their applications; Faraday's laws of induction; Lenz's law; inductance; and energy stored in magnetic fields. Key concepts covered are magnetic permeability, flux, reluctance, hysteresis loops, induced EMF, self and mutual inductance, and inductors.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
10 просмотров1 страницаMagnetic Circuits & Electromagnetic Induction Explained
Загружено:
ashwini patilThis document outlines the key topics in magnetic circuits and electromagnetic induction including: the laws of magnetism and magnetic fields; magnetic circuits and their comparison to electric circuits; types of magnets and their applications; Faraday's laws of induction; Lenz's law; inductance; and energy stored in magnetic fields. Key concepts covered are magnetic permeability, flux, reluctance, hysteresis loops, induced EMF, self and mutual inductance, and inductors.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 1
5: Magnetic Circuits & Electromagnetic Induction
5.1 Magnetism: Absolute and Relative Permeabilities of a Medium, Laws of Magnetic
Force, Magnetic field strength, Flux & Flux Density.
5.2 Magnetic Circuit - Ohm’s law of Magnetic Circuit.
5.3 Definitions Concerning Magnetic Circuit. Magneto-Motive-Force (MMF), Ampere
Turns (AT), Reluctance, Permeance, Reluctivity. (simple numerical)
5.4 Comparison Between Electric and Magnetic circuit.
5.5 Concept of Leakage Flux, Useful Flux & Fringing.
5.6 Magnetization Curve (B - H Curve), Magnetic Hysteresis, Hysteresis Loop.
Hysteresis Loops for Hard & Soft Magnetic Materials. Area of Hysteresis Loop,
Hysteresis Loss. (No Derivation and No Numerical)
5.7 Types of Magnets and their applications
5.8 Magnetic effect of electric current, Dot & cross conventions, Right hand thumb rule,
Interaction between magnetic fields, force on current carrying conductors, Fleming’s
left hand rule
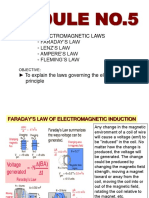
5.9 Faraday’s Laws of Electromagnetic Induction.
5.10 Direction of induced EMF and current, Lenz’s Law, Fleming’s right hand rule,
Induced EMF, Dynamically induced EMF, statically induced EMF, self-Inductance
(L), Mutual Inductance, co-efficient of coupling.
5.11 Inductances in Series and parallel. (No Derivation and No Numerical)
5.12 Types of Inductors and their Applications.
- Air Cored Inductors
- Iron Cored Inductors
- Ferrite Cored Inductors.
5.13 Energy Stored in Magnetic Field
(No Derivation and Simple Numerical)
Вам также может понравиться
- Magnetic CircuitДокумент7 страницMagnetic CircuitjosgauОценок пока нет
- Compared SyllabusДокумент4 страницыCompared SyllabusJerr1 efxОценок пока нет
- 1 Magnetic CircuitsДокумент36 страниц1 Magnetic Circuitssai dharmaОценок пока нет
- Basic Electrical Engineering: (CUTM1057)Документ26 страницBasic Electrical Engineering: (CUTM1057)Yedla Santosh kumarОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic PrinciplesДокумент56 страницElectromagnetic PrinciplesBacha NegeriОценок пока нет
- EEC 125 Note UpdatedДокумент23 страницыEEC 125 Note UpdatedElijah EmmanuelОценок пока нет
- Applied Physics NTCДокумент2 страницыApplied Physics NTCFasih Khan DurraniОценок пока нет
- MCQs On Electrical LawsДокумент6 страницMCQs On Electrical LawsnasimОценок пока нет
- BVGHHДокумент1 страницаBVGHHkultardeepОценок пока нет
- Magnetic reluctance and MMFДокумент3 страницыMagnetic reluctance and MMFAayush KartikОценок пока нет
- Index Faraday's Law ConceptsДокумент4 страницыIndex Faraday's Law ConceptsRajesh SharmaОценок пока нет
- Faraday's & Lenz LawДокумент14 страницFaraday's & Lenz LawPnDeОценок пока нет
- ELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM Lec15Документ40 страницELECTRICITY & MAGNETISM Lec15moonkhan16584Оценок пока нет
- Basics of Electrical MachinesДокумент61 страницаBasics of Electrical MachinesZubair IqbalОценок пока нет
- Magnetic Circuit: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaДокумент8 страницMagnetic Circuit: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediamkbayanОценок пока нет
- Unit I (Magnetic Field and Circuits - Electromagnetic Force and Torque)Документ43 страницыUnit I (Magnetic Field and Circuits - Electromagnetic Force and Torque)UpasnaОценок пока нет
- Magnetism and ElectromagnetismДокумент1 страницаMagnetism and ElectromagnetismMayank Chaudhary 12AОценок пока нет
- Magnetics CH 1Документ55 страницMagnetics CH 1NAHOM ANTENEHОценок пока нет
- Module 5 - DC MachДокумент8 страницModule 5 - DC MachNoel BactonОценок пока нет
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Tehran Split Up Syllabus 2011 - 2012 Class Xii Subject - Physics Month Name of The Topic Detailed Split Up SyllabusДокумент5 страницKendriya Vidyalaya Tehran Split Up Syllabus 2011 - 2012 Class Xii Subject - Physics Month Name of The Topic Detailed Split Up SyllabusCash Cash CashОценок пока нет
- Faraday's LawДокумент9 страницFaraday's LawaliОценок пока нет
- 3.syllabus (Solid State Physics) OptionalДокумент2 страницы3.syllabus (Solid State Physics) OptionalMuhammad Hasan RazaОценок пока нет
- UNIT-1 Electrostatics: Concepts:: Maxwell'S Equations)Документ3 страницыUNIT-1 Electrostatics: Concepts:: Maxwell'S Equations)Sapata KumarОценок пока нет
- Inductance: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchДокумент32 страницыInductance: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchKnight StingrayОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1: Electric Charges and Fields FДокумент3 страницыChapter 1: Electric Charges and Fields FaFОценок пока нет
- AbstractДокумент4 страницыAbstractnipunjangra7Оценок пока нет
- Lenz's Law: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchДокумент7 страницLenz's Law: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchAkarshan WaliaОценок пока нет
- Final SC - Ed. 434. Physics IIIДокумент11 страницFinal SC - Ed. 434. Physics IIItikaram gautamОценок пока нет
- 5.3 ElectromagnetДокумент8 страниц5.3 ElectromagnetYee Jiea PangОценок пока нет
- NEET Physics Checklist - Class 12 by TCДокумент6 страницNEET Physics Checklist - Class 12 by TCanishaОценок пока нет
- Faraday's LawДокумент4 страницыFaraday's LawFarah Bt KhuzaimahОценок пока нет
- EC3452 Electromagnetic Fields Unit I IntroductionДокумент17 страницEC3452 Electromagnetic Fields Unit I IntroductionDivya KishorОценок пока нет
- Wa0003.Документ1 страницаWa0003.Jimmy MachariaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ37 страницChapter 1playerОценок пока нет
- Physics Syllabus SNUCEE 2022Документ3 страницыPhysics Syllabus SNUCEE 2022BalaОценок пока нет
- 1.magnetic Circuits PDFДокумент3 страницы1.magnetic Circuits PDFTanishq MudaliarОценок пока нет
- Physics Syllabus 2022Документ5 страницPhysics Syllabus 2022Ayan AhsanОценок пока нет
- Unit I: Electrostatics: PhysicsДокумент2 страницыUnit I: Electrostatics: PhysicsAyush GaurОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic FieldsДокумент2 страницыElectromagnetic FieldsAnonymous JnvCyu85Оценок пока нет
- Magnetic Flux, Induction, and Faraday's Law - Boundless PhysicsДокумент40 страницMagnetic Flux, Induction, and Faraday's Law - Boundless PhysicsFen XiaОценок пока нет
- MagnetismДокумент11 страницMagnetismObserver of mellinuimОценок пока нет
- B.E. EceДокумент2 страницыB.E. EceJesintha CharlesОценок пока нет
- PHYSICSДокумент5 страницPHYSICSMarion Pierre MateoОценок пока нет
- Unit I: Electrostatics Chapter-1: Electric Charges and FieldsДокумент5 страницUnit I: Electrostatics Chapter-1: Electric Charges and FieldsLungmuaNa RanteОценок пока нет
- Magnetic CircuitsДокумент15 страницMagnetic CircuitsPrianshu JyosyulaОценок пока нет
- Spintronics Swagata Banerjee A4455713019Документ12 страницSpintronics Swagata Banerjee A4455713019Swagata Banerjee100% (1)
- Important Derivations of Physics Class 12 CBSEДокумент11 страницImportant Derivations of Physics Class 12 CBSEPadma kannaОценок пока нет
- Important Derivations of Physics, Class 12 - CBSE: R. K. Malik'S Newton Classes RanchiДокумент11 страницImportant Derivations of Physics, Class 12 - CBSE: R. K. Malik'S Newton Classes RanchiPadma kannaОценок пока нет
- Important Derivations of Physics, Class 12 - CBSE: R. K. Malik'S Newton Classes RanchiДокумент11 страницImportant Derivations of Physics, Class 12 - CBSE: R. K. Malik'S Newton Classes RanchiPadma kannaОценок пока нет
- Syllabus Division of Class XII - 30 Parts: Assignment No Date PhysicsДокумент4 страницыSyllabus Division of Class XII - 30 Parts: Assignment No Date PhysicsRoopa ps murthyОценок пока нет
- RGPV EC 5th Semester Electromagnetic Theory SyllabusДокумент2 страницыRGPV EC 5th Semester Electromagnetic Theory Syllabusrg_0087Оценок пока нет
- EEE-1201 Final Presentation0000Документ31 страницаEEE-1201 Final Presentation0000afshachowdhuryОценок пока нет
- 12th Imp Topics Chapter WiseДокумент4 страницы12th Imp Topics Chapter WiserampriyachinОценок пока нет
- Magnets. Magnetism Four Fundamental Forces Electric CurrentДокумент10 страницMagnets. Magnetism Four Fundamental Forces Electric CurrentJose MzuyuОценок пока нет
- Amie03 Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering: Unit-1 Elementary ConceptsДокумент2 страницыAmie03 Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering: Unit-1 Elementary ConceptsPraveena 27Оценок пока нет
- PhysicsДокумент4 страницыPhysicsAbhinave SОценок пока нет
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Unit - 1 Syllabus: Electrostatics: Chapter - 1: Electric Charges and FieldsДокумент2 страницыCBSE Class 12 Physics Unit - 1 Syllabus: Electrostatics: Chapter - 1: Electric Charges and FieldsRitesh SoniОценок пока нет
- Magnetic Circuits: Magnetic Circuit and Electric Circuit: A ComparisonДокумент13 страницMagnetic Circuits: Magnetic Circuit and Electric Circuit: A ComparisonTrisha SARMIENTOОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetism: Maxwell Equations, Wave Propagation and EmissionОт EverandElectromagnetism: Maxwell Equations, Wave Propagation and EmissionРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (18)
- Principles of Electric Methods in Surface and Borehole GeophysicsОт EverandPrinciples of Electric Methods in Surface and Borehole GeophysicsРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (1)
- Introduction To Electrical Power System and FaultsДокумент229 страницIntroduction To Electrical Power System and FaultsLloyd R. Ponce100% (1)
- Design Optimazation and Simulation of PMSM Based On Maxwell and Twinbuilder For EvsДокумент6 страницDesign Optimazation and Simulation of PMSM Based On Maxwell and Twinbuilder For EvsMayur DeokarОценок пока нет
- Magnetostriction, Barkhausen Noise and Magnetization Processes in Non-Electrical Steels PDFДокумент9 страницMagnetostriction, Barkhausen Noise and Magnetization Processes in Non-Electrical Steels PDFallanromarioОценок пока нет
- Detection of Transformer Winding Displacement by FRSLДокумент6 страницDetection of Transformer Winding Displacement by FRSLKhushbu Thakur100% (2)
- Manual Book Mark 7 ArterionДокумент157 страницManual Book Mark 7 ArterionSyamsul Putra100% (1)
- Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor With Ultrafast Soft Recovery DiodeДокумент17 страницInsulated Gate Bipolar Transistor With Ultrafast Soft Recovery DiodetaynatecОценок пока нет
- Trouble Shooting GuideДокумент18 страницTrouble Shooting GuideDeyan VelikovОценок пока нет
- TL Audio Classic Series 479645Документ14 страницTL Audio Classic Series 479645Nicolas ZuluagaОценок пока нет
- Busworks 900Mb Series Modbus-Rtu I/OДокумент23 страницыBusworks 900Mb Series Modbus-Rtu I/OOmar RobaОценок пока нет
- Project InverterДокумент67 страницProject InverterKeshavGargОценок пока нет
- Solving Circuit ProblemsДокумент33 страницыSolving Circuit Problems19027 PrantoBiswasОценок пока нет
- Air-Conditioner: Service ManualДокумент54 страницыAir-Conditioner: Service ManualsureshchitraОценок пока нет
- Huawei OptiX Metro 1000 Commissioning Guide (V300R007)Документ143 страницыHuawei OptiX Metro 1000 Commissioning Guide (V300R007)Thunder-Link.comОценок пока нет
- Power Transmission, Distribution and Utilization: Lecture# 13 &14: Underground CablesДокумент29 страницPower Transmission, Distribution and Utilization: Lecture# 13 &14: Underground CablesPhD EEОценок пока нет
- Maxwell Stress TensorДокумент8 страницMaxwell Stress Tensorkushaldave227Оценок пока нет
- Amplifier Frequency ResponseДокумент28 страницAmplifier Frequency ResponseBenj MendozaОценок пока нет
- H07RN-F, Enhanced Version: Product InformationДокумент5 страницH07RN-F, Enhanced Version: Product InformationDarwin YupaОценок пока нет
- Hand Book ProteccionesДокумент356 страницHand Book ProteccionesFrozen TgrОценок пока нет
- 3M (TM) Quick Connect 2810 DatasheetДокумент4 страницы3M (TM) Quick Connect 2810 DatasheetNguyễn Ngọc KhánhОценок пока нет
- Push ButtonsДокумент59 страницPush ButtonsTB11SDОценок пока нет
- Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTS) 1Документ19 страницBipolar Junction Transistors (BJTS) 1ጁንታው ነኝОценок пока нет
- PIX-36 Catalogue Schneider 1Документ46 страницPIX-36 Catalogue Schneider 1ARYA JENAОценок пока нет
- DPR - IPDS Jammu - 30.4.2015Документ82 страницыDPR - IPDS Jammu - 30.4.2015Manoj ManhasОценок пока нет
- 2089 340065 Multimeter Mastech Ms8240cДокумент11 страниц2089 340065 Multimeter Mastech Ms8240cFrancisco Javier GuerraОценок пока нет
- Arc Flash and Electrical Safety HazardsДокумент24 страницыArc Flash and Electrical Safety HazardsJulios Charl Panuncialman TagupaОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 4Документ2 страницыTutorial 4Saransh MittalОценок пока нет
- AP Physics 2: Algebra-Based 2015 Free-Response QuestionsДокумент11 страницAP Physics 2: Algebra-Based 2015 Free-Response QuestionsAdam El TohamyОценок пока нет
- Leitura de Corrente Com 0750-050Документ8 страницLeitura de Corrente Com 0750-050wagner_marinaОценок пока нет
- Philips Mcd183Документ29 страницPhilips Mcd183nikola16600% (1)
- Compact Wideband Circularly Polarized Microstrip Antenna Array For 45Ghz ApplicationДокумент5 страницCompact Wideband Circularly Polarized Microstrip Antenna Array For 45Ghz Applicationnguyễn đắc huyОценок пока нет