Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
D Mimo
Загружено:
Shashank PrajapatiОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
D Mimo
Загружено:
Shashank PrajapatiАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter
Description
Issue 04
Date 2018-11-07
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD.
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2019. All rights reserved.
No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior written
consent of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Trademarks and Permissions
and other Huawei trademarks are trademarks of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
All other trademarks and trade names mentioned in this document are the property of their respective
holders.
Notice
The purchased products, services and features are stipulated by the contract made between Huawei and the
customer. All or part of the products, services and features described in this document may not be within the
purchase scope or the usage scope. Unless otherwise specified in the contract, all statements, information,
and recommendations in this document are provided "AS IS" without warranties, guarantees or
representations of any kind, either express or implied.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Every effort has been made in the
preparation of this document to ensure accuracy of the contents, but all statements, information, and
recommendations in this document do not constitute a warranty of any kind, express or implied.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Address: Huawei Industrial Base
Bantian, Longgang
Shenzhen 518129
People's Republic of China
Website: http://www.huawei.com
Email: support@huawei.com
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. i
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description Contents
Contents
1 Change History.............................................................................................................................. 1
1.1 eRAN13.1 04 (2018-11-07)............................................................................................................................................1
1.2 eRAN13.1 03 (2018-08-27)............................................................................................................................................1
1.3 eRAN13.1 02 (2018-06-30)............................................................................................................................................2
1.4 eRAN13.1 01 (2018-04-10)............................................................................................................................................2
1.5 eRAN13.1 Draft A (2018-03-30)................................................................................................................................... 2
2 About This Document.................................................................................................................. 4
2.1 Applicable RAT.............................................................................................................................................................. 4
2.2 Features in This Document.............................................................................................................................................4
3 General Principles......................................................................................................................... 6
3.1 Overview........................................................................................................................................................................ 6
3.2 Inter-RRU Channel Calibration......................................................................................................................................9
3.3 Coherent Joint Transmission........................................................................................................................................ 10
4 Intra-Cell D-MIMO.....................................................................................................................16
4.1 Principles...................................................................................................................................................................... 16
4.2 Network Analysis......................................................................................................................................................... 17
4.2.1 Benefits...................................................................................................................................................................... 17
4.2.2 Impacts.......................................................................................................................................................................18
4.3 Requirements................................................................................................................................................................ 22
4.3.1 Licenses..................................................................................................................................................................... 22
4.3.2 Software.....................................................................................................................................................................23
4.3.3 Hardware................................................................................................................................................................... 25
4.3.4 Networking................................................................................................................................................................ 29
4.4 Operation and Maintenance..........................................................................................................................................30
4.4.1 Data Configuration.................................................................................................................................................... 30
4.4.1.1 Data Preparation..................................................................................................................................................... 30
4.4.1.2 Using MML Commands......................................................................................................................................... 36
4.4.1.3 Using the CME....................................................................................................................................................... 38
4.4.2 Activation Observation..............................................................................................................................................38
4.4.3 Network Monitoring.................................................................................................................................................. 39
4.4.4 Possible Issues........................................................................................................................................................... 42
5 Inter-eNodeB D-MIMO..............................................................................................................47
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. ii
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description Contents
5.1 Principles...................................................................................................................................................................... 47
5.2 Network Analysis......................................................................................................................................................... 48
5.2.1 Benefits...................................................................................................................................................................... 48
5.2.2 Impacts.......................................................................................................................................................................49
5.3 Requirements................................................................................................................................................................ 50
5.3.1 Licenses..................................................................................................................................................................... 50
5.3.2 Software.....................................................................................................................................................................50
5.3.3 Hardware................................................................................................................................................................... 50
5.3.4 Networking................................................................................................................................................................ 51
5.4 Operation and Maintenance..........................................................................................................................................51
5.4.1 Data Configuration.................................................................................................................................................... 51
5.4.1.1 Data Preparation..................................................................................................................................................... 52
5.4.1.2 Using MML Commands......................................................................................................................................... 53
5.4.1.3 Using the CME....................................................................................................................................................... 53
5.4.2 Activation Verification.............................................................................................................................................. 53
5.4.3 Network Monitoring.................................................................................................................................................. 53
5.4.4 Possible Issues........................................................................................................................................................... 53
6 Parameters..................................................................................................................................... 54
7 Counters........................................................................................................................................ 98
8 Glossary....................................................................................................................................... 111
9 Reference Documents............................................................................................................... 112
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. iii
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 1 Change History
1 Change History
This chapter describes changes not included in the "Parameters", "Counters", "Glossary", and
"Reference Documents" chapters. These changes include:
l Technical changes
Changes in functions and their corresponding parameters
l Editorial changes
Improvements or revisions to the documentation
1.1 eRAN13.1 04 (2018-11-07)
This issue includes the following changes.
Technical Changes
None
Editorial Changes
Deleted forced switching to beamforming in heavy-load scenarios.
Revised the descriptions in this document.
1.2 eRAN13.1 03 (2018-08-27)
This issue includes the following changes.
Technical Changes
Change Description Parameter Change Base Station Model
Added RRU5258 support for None Macro eNodeBs
D-MIMO. For details, see
4.3.3 Hardware.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 1
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 1 Change History
Editorial Changes
None
1.3 eRAN13.1 02 (2018-06-30)
This issue includes the following changes.
Technical Changes
None
Editorial Changes
Revised the descriptions in this document.
1.4 eRAN13.1 01 (2018-04-10)
This issue includes the following changes.
Technical Changes
None
Editorial Changes
Added deactivation command examples. For details, see the respective "Using MML
Commands" sections.
Added support for cascading between a TDD RRU and an upper-level FDD+TDD RRU in D-
MIMO scenarios. For details, see 4.3.3 Hardware.
Revised descriptions in this document.
1.5 eRAN13.1 Draft A (2018-03-30)
This issue includes the following changes to eRAN TDD 13.0 01 (2017-09-05).
Technical Changes
Change Description Parameter Change Base Station Model
Added support for forced None Macro and LampSite
switching to beamforming in eNodeBs
heavy-load scenarios when D-
MIMO is enabled. For details,
see 4.4.1.1 Data Preparation
and 5.4.1.1 Data Preparation.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 1 Change History
Change Description Parameter Change Base Station Model
Added support for RRU3236E None Macro eNodeBs
in D-MIMO scenarios. For
details, see RF Modules.
Editorial Changes
Reorganized this document using a new template.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 3
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 2 About This Document
2 About This Document
2.1 Applicable RAT
This document applies to TDD.
2.2 Features in This Document
This document describes the following TDD features.
Feature ID Feature Name Section
TDLEOFD-111505 DL D-MIMO 4 Intra-Cell D-
MIMO
TDLEOFD-11150501 Distributed MIMO 4 Intra-Cell D-
MIMO
TDLEOFD-11150502 Intra-BBU D-MIMO 4 Intra-Cell D-
MIMO
TDLEOFD-11150504 D-MIMO by Macro RRUs 4 Intra-Cell D-
MIMO
TDLEOFD-11150505 D-MIMO Within a LampSite Cell 4 Intra-Cell D-
MIMO
TDLEOFD-12050501 D-MIMO with Macro- 4 Intra-Cell D-
Micro(BookRRU) MIMO
TDLEOFD-12050502 D-MIMO with Micro-Micro 4 Intra-Cell D-
(BookRRU) MIMO
TDLEOFD-121501 Inter-eNodeB DL D-MIMO (Trial) 5 Inter-eNodeB D-
MIMO
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 4
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 2 About This Document
The following table lists the mapping between subfeatures and parent features. The license is
deployed on the parent features.
Parent Feature Subfeature Scenario
TDLEOFD-111505 DL D- TDLEOFD-11150501 Basic functions
MIMO Distributed MIMO
TDLEOFD-111505 DL D- TDLEOFD-11150502 Intra- Basic functions
MIMO BBU D-MIMO
TDLEOFD-111505 DL D- TDLEOFD-12050501 D- Outdoor macro-micro
MIMO MIMO with Macro- scenarios
Micro(BookRRU)
TDLEOFD-111505 DL D- TDLEOFD-12050502 D- Outdoor micro-micro
MIMO MIMO with Micro- scenarios
Micro(BookRRU)
TDLEOFD-111505 DL D- TDLEOFD-11150504 D- Outdoor macro-macro
MIMO MIMO by Macro RRUs scenarios
TDLEOFD-111505 DL D- TDLEOFD-11150505 D- Indoor LampSite scenarios
MIMO MIMO Within a LampSite
Cell
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 5
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 3 General Principles
3 General Principles
3.1 Overview
Background
As the number of users and traffic volume increase sharply, the site density rises considerably.
Site densification improves the system capacity. However, it also increases the overlapping
coverage areas of sites, and deteriorates user experience at the cell edge. D-MIMO is
introduced to mitigate interference from neighboring cells in overlapping coverage areas and
improve CEU experience and the downlink user experience of the whole cell.
Introduction
D-MIMO is based on a centralized scheduling+distributed RRU architecture. It uses multiple
physical antennas to transmit data in a coordinated way. The dispersed spatial locations of
antennas illustrated in Figure 3-1 significantly improves the spatial channel resolution. D-
MIMO offers high antenna array gains and interference suppression gains, and improves the
downlink user experience and cell edge user (CEU) experience.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 6
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 3 General Principles
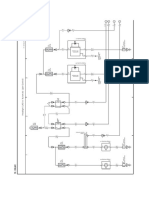
Figure 3-1 D-MIMO
D-MIMO coordinates scheduling based on D-MIMO clusters. A D-MIMO cluster is a set of
multiple physical cells (RRUs) serving a cell or multiple physical cells (RRUs) serving
different cells. D-MIMO requires that D-MIMO cluster data be planned, including the RRUs
in a D-MIMO cluster and the cluster ID. For details about the planning method, contact
Huawei technical support.
Category
Distributed multiple-input multiple-output (D-MIMO) has two networking modes.
Feature Feature Networking Introduced Section
ID Name in...
TDLEOFD DL D-MIMO Multiple RRUs connected eRAN TDD 4 Intra-Cell
-111505 to the same BBU and their 11.1 D-MIMO
corresponding cells form a
logical cell, and a D-
MIMO cluster is set up for
the logical cell. Cells in the
same D-MIMO cluster
must have the same PCI
value.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 7
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 3 General Principles
Feature Feature Networking Introduced Section
ID Name in...
TDLEOFD Inter-eNodeB Inter-eNodeB downlink D- eRAN TDD 5 Inter-
-121501 DL D-MIMO MIMO enables the cells set 12.1 eNodeB D-
(Trial) up on different BBUs but MIMO
on the same Cloud BB
network to form a D-
MIMO cluster.
Working Process
Figure 3-2 shows the working process of the D-MIMO feature.
Figure 3-2 D-MIMO process
1. D-MIMO configuration: includes the configuration of D-MIMO clusters, feature
switches, and related parameters.
2. Inter-RRU channel calibration: D-MIMO adopts the distributed RRU architecture, which
causes the RRUs in different locations to transmit signals with different phases. After
inter-RRU channel calibration, the signals sent by multiple RRU channels in the D-
MIMO cluster can be combined to the UE side in the same phase.
3. Coherent joint transmission: According to a specific algorithm, the eNodeB identifies JT
UEs in a D-MIMO cluster, and performs coherent joint transmission, including SU-JT or
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 8
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 3 General Principles
MU-JT, for UEs in the cluster, improving downlink user experience and edge user
experience.
After a D-MIMO cluster is configured and D-MIMO is enabled, the eNodeB periodically
initiates intra-cluster inter-RRU channel calibration and coherent joint transmission. D-MIMO
is controlled by the following options:
l DmimoJTSwitch option under the CellAlgoSwitch.DMIMOAlgoSwitch parameter
Inter-RRU channel calibration and coherent joint transmission are key technologies for D-
MIMO, which will be described in detail in the following sections.
3.2 Inter-RRU Channel Calibration
In the distributed RRU architecture used by D-MIMO, the RRUs in different locations
transmit signals with different phases. Inter-RRU channel calibration ensures that the RF
channels of a D-MIMO cluster have the same delay so that the signals transmitted over
different RF channels of the RRUs have the same phase on the UE side. With inter-RRU
channel calibration, the eNodeB adjusts the transmit/receive response ratio of each RF
channel of the RRUs to be consistent with that of the reference RF channel.
Figure 3-3 shows the principles of inter-RRU channel calibration.
Figure 3-3 Principles of inter-RRU channel calibration
During inter-RRU channel calibration, the calibration coefficient is calculated so that the
equation is satisfied. In the equation, indicates the transmit/receive
response ratio of the reference RF channel.
NOTE
l For RRU3259 (8T8R) and RRU3235, inter-RRU channel calibration is performed on RF channel A.
l For RRU3259 (4T4R), inter-RRU channel calibration is performed on RF channel B.
The eNodeB performs inter-RRU channel calibration as follows:
1. Performs channel calibration for each RRU using an intra-RRU channel calibration
algorithm.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 9
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 3 General Principles
2. Initiates inter-RRU channel calibration. During inter-RRU channel calibration, the RRUs
transmit calibration sequences to each other over the air interface and then calculate the
calibration coefficient.
3. Implements channel compensation based on the calculation results so that the transmit/
receive response ratios of all RF channels of all the RRUs in the D-MIMO cluster are
consistent.
NOTE
2T2R RRUs and pRRUs do not support intra-RRU channel calibration. Therefore, only steps 2
and 3 are required for 2T2R RRUs and pRRUs.
In inter-RRU channel calibration, the phases of the signals transmitted over different RRU RF
channels are synchronized on the UE side. This increases the strength of the downlink signals
received by the UE. For details about how to check whether inter-RRU channel calibration is
successful, see 4.4.2 Activation Observation.
If a channel calibration fault occurs in a cell in the D-MIMO cluster, the following situations
may occur:
l D-MIMO cells automatically roll back to SFN configurations.
Related Optimization
In eRAN TDD 11.1 or earlier, intra-RRU channel calibration is initiated every 30 minutes. In
eRAN TDD 12.0, intra-RRU channel calibration is initiated every 10s if the
QUICK_CHN_CAL_SWITCH option is selected under the newly added
CellAlgoSwitch.EnhChnCalSwitch parameter. If this option is cleared, intra-RRU channel
calibration is initiated per 30 minutes. It is recommended that this option be selected in D-
MIMO scenarios. 2T2R RRUs and pRRUs do not support intra-RRU channel calibration.
Therefore, the setting of the CellAlgoSwitch.EnhChnCalSwitch parameter does not take
effect on these modules.
3.3 Coherent Joint Transmission
With coherent joint transmission, multiple RRUs jointly transmit signals to the same UE, and
phase synchronization takes place on the UE side. This process increases the downlink RSRP.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 10
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 3 General Principles
Figure 3-4 Coherent joint transmission
The eNodeB performs coherent joint transmission as follows:
1. Identifies joint transmission (JT) UEs. The eNodeB uses sounding reference signals
(SRSs) to obtain the uplink RSRP values of signals arriving at each RRU, and calculates
the downlink equivalent RSRP values. The eNodeB periodically identifies the working
RRU list for a UE. If the working RRU list of a given UE contains two or more RRUs,
the UE is a JT UE.
2. Calculates the beamforming weighting values. The eNodeB obtains the uplink channel
coefficients of uplink signals arriving at each RRU based on the SRSs, and calculates the
joint beamforming weighting values for JT UEs.
If the estimated beamforming weight is inaccurate, beamforming UE pairing
performance will deteriorate. The beamforming weight can be estimated more accurately
by increasing the target SINR of beamforming UEs during SRS power control. When D-
MIMO is enabled, it is recommended that target SINR optimization for beamforming
UEs during SRS power control be enabled to increase the SINR of beamforming UEs.
This function is controlled by the CellPcAlgo.DMSrsPcSinrOffset parameter.
– When this parameter is set to a value greater than 0 and the conditions for triggering
this function are met, the eNodeB sets the target SINR for beamforming UEs during
SRS power control to the value of the CellPcAlgo.SrsPcSinrTarget parameter plus
the value of the CellPcAlgo.DMSrsPcSinrOffset parameter.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 11
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 3 General Principles
– When this parameter is set to 0 or the conditions for triggering this function are not
met, the eNodeB sets the target SINR for beamforming UEs during SRS power
control to the value of the CellPcAlgo.SrsPcSinrTarget parameter.
NOTE
Target SINR optimization for beamforming UEs during SRS power control may slightly increase
the number of RRC Connection Reconfiguration messages and the service drop rate.
3. Performs single-user joint transmission (SU-JT) or multi-user joint transmission (MU-
JT) in each transmission time interval (TTI).
Figure 3-5 JT process
a. SU-JT
In SU-JT, multiple RRUs perform coherent joint transmission to the same UE over
multiple antennas, improving the receive signal quality and strength of the UE.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 12
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 3 General Principles
Figure 3-6 SU-JT
b. MU-JT
In MU-JT, multiple RRUs perform coherent joint transmission to multiple UEs over
multiple antennas, improving the resource reuse efficiency. The weights used for
UEs are orthogonal to each other, which mitigates interference between them.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 13
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 3 General Principles
Figure 3-7 MU-JT
Set the DMIMOCluster.BfWeightNormalizeMode parameter based on site
conditions to achieve optimal MU-JT performance. For details about the setting
notes of this parameter, see 4.4.1.1 Data Preparation.
Figure 3-8 MU-JT example
The following uses Figure 3-8 as an example to describe the MU-JT process. In the
preceding figure, U0 and U1 are the UEs that have been scheduled before MU-JT
pairing, and V0 is the UE to be paired. Before MU-JT pairing, only U0 and U1 can
be scheduled using RBGs 0 to 7 in a subframe. After MU-JT pairing, V0 and U0
are paired in RBGs 0 to 3, and V0 and U1 are paired in RBGs 4 to 7. In this way,
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 14
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 3 General Principles
three UEs, including U0, U1, and V0, can be scheduled on the same frequency
resources, achieving multiplexing and improving spectral efficiency.
When cell-level TMA is enabled in D-MIMO scenarios, more UEs in heavy-load
cells enter the beamforming mode for MU pairing, increasing the system capacity.
This function is controlled by the CellBf.WaitPairingLayerThd parameter.
n If this parameter is set to 0, cell-level adaptive switching between transmission
modes is disabled.
n If this parameter is set to a value greater than 0, the eNodeB initiates cell-level
adaptive switching between transmission modes when both of the following
conditions are met:
○ The downlink PRB usage of the cell is greater than an internally specified
threshold.
○ The number of beamforming UEs to be scheduled in the downlink per
TTI is greater than or equal to the value of the
CellBf.WaitPairingLayerThd parameter multiplied by 0.1.
When D-MIMO is enabled and the DmimoSchAttriOptSwitch option is selected
under the CellAlgoSwitch.DMIMOAlgoSwitch parameter:
n In heavy-load cells, JT can be performed on more beamforming UEs,
achieving SU-JT gains. In addition, the pairing performance of UEs near the
cell center and the MU-JT pairing rate improve.
n In light-load cells, this setting reduces the scheduling delay caused when MU-
JT pairing is unavailable for non-beamforming UEs due to scheduling
conflicts.
The advanced multi-user coordination feature further increases the MU-JT pairing
rate and downlink capacity in downlink D-MIMO scenarios. This feature is
controlled by the MULTI_UE_COORDINATION_OPT_SW option under the
CellAlgoSwitch.CoordinationAlgoSwitch parameter. For details, see Beamforming
(TDD).
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 15
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 4 Intra-Cell D-MIMO
4 Intra-Cell D-MIMO
4.1 Principles
D-MIMO is developed based on SFN. An SFN cell is served by multiple RRUs whose
coverage overlaps between each other. The D-MIMO cluster is equivalent to an SFN cell, and
therefore the number of RRUs within a D-MIMO cluster equals the number of RRUs serving
an SFN cell. There is only one PCI in the D-MIMO cluster.
D-MIMO allows RRUs to connect to the same BBU, as shown in Figure 4-1.
Figure 4-1 Networking diagram of intra-cell D-MIMO
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 16
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 4 Intra-Cell D-MIMO
D-MIMO is suitable for the following SFN scenarios:
l Outdoor macro-macro SFN scenarios
l Outdoor macro-micro SFN scenarios
l Outdoor micro-micro SFN scenarios
l Indoor LampSite SFN scenarios
D-MIMO can be used in the following areas:
l Outdoor hotspot areas, such as densely populated urban areas, central business districts,
and campus
l Indoor densely populated areas, such as stadiums, airports, railway stations, dining halls,
and auditoriums
NOTE
In this document, "macro-macro networking" refers to a combination of macro RRUs, "macro-micro
networking" refers to a combination of macro and micro RRUs, and "micro-micro networking" refers to
a combination of micro RRUs. For details, see RF Modules.
4.2 Network Analysis
4.2.1 Benefits
Most Beneficial Scenarios
D-MIMO is recommended when all of the following conditions are met:
l The inter-site distance does not exceed 150 m in outdoor scenarios or 30 m in LampSite
scenarios, and there is significant coverage overlap between the cells.
l Interference between neighboring cells is severe in LampSite scenarios. D-MIMO is
typically suitable in large open areas where intra-frequency neighboring cells are
deployed, such as transport hubs and exhibition centers.
l There is line-of-sight (LOS) propagation between RRUs.
l The UE speed is lower than 5 km/h.
Benefits
l In outdoor macro-macro SFN scenarios
D-MIMO increases the average downlink UE-perceived rate and the downlink CEU-
perceived rate.
l In outdoor macro-micro SFN scenarios
D-MIMO increases the average downlink UE-perceived rate and the downlink CEU-
perceived rate.
l In outdoor micro-micro SFN scenarios
D-MIMO increases the average downlink UE-perceived rate and the downlink CEU-
perceived rate.
l Benefits of D-MIMO in indoor LampSite SFN scenarios
D-MIMO increases the average downlink UE-perceived rate.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 17
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 4 Intra-Cell D-MIMO
The combination of D-MIMO and advanced multi-user coordination enhances the spatial
multiplexing gains. It increases the downlink cell throughput and spectral efficiency when the
network load is heavy.
4.2.2 Impacts
Network Impacts
l D-MIMO slightly decreases the random access response (RAR) success rate but
increases the UE access delay.
l With D-MIMO, when adaptive transmission mode switching is enabled in SFN cells,
more UEs switch from TM3 to TM8. As a result, a greater proportion of the UEs in the
cell use beamforming, including dual-stream beamforming. UEs working in TM3 rank 2
report separate CQIs for each of the two data streams. However, when such UEs work in
dual-stream beamforming (TM8), they report CQIs for only one data stream. Therefore,
D-MIMO increases the average CQI value reported by the UE.
l UEs working in dual-stream beamforming must switch to single-stream beamforming
before being paired. In this case, the measured value of the KPI BF Rank1 PRB
increases. Therefore, the proportion of dual-stream beamforming UEs is subject to
pairing. When the proportion of dual-stream beamforming UEs participating in pairing is
high, the measured value of the KPI BF Rank2 PRB decreases.
l D-MIMO enables multiple beamforming UEs in SFN cells to be paired for MU-JT. This
enables more UEs to be scheduled within each TTI when many UEs are to be scheduled.
However, successful UE scheduling requires that there be sufficient control channel
elements (CCEs) available.
– If CCE resources are sufficient, the total number of CCEs used by each TTI in the
downlink increases. The increase in the total number of downlink used CCEs
decreases the number of available uplink CCEs, increases the probability of uplink
CCE allocation failures, and affects performance such as the number of uplink
scheduled UEs and MCS indexes.
– If CCE resources are insufficient, an increasing number of CCEs fail to be allocated
in each TTI.
l After D-MIMO is enabled, joint-scheduling UEs receive D-MIMO gains and the overall
D-MIMO pairing rate improves. The BLER may slightly fluctuate due to the changes in
MCS indexes.
l In SFN or D-MIMO scenarios, CRSs are jointly transmitted and PDSCH data is
independently transmitted for independent-scheduling UEs. As a result, there may be a
mismatch between CRS measurement-based rank values and rank values supported by
PDSCH data. For an independent-scheduling UE working in TM3 rank 2 with a small
isolation, RI mismatches lead to consecutive block errors or even the MCS index drop to
0. To solve this problem, the following mechanisms are adopted:
– When the target RRU is a 2T or 4T RRU:
The eNodeB identifies independent-scheduling UEs working in TM3 rank 2
subjected to consecutive block errors caused by RI mismatches and uses rank 1 to
schedule the UEs to ensure UE performance. This function is controlled by the
SfnDlRblerOptSwitch option under the CellAlgoSwitch.SfnAlgoSwitch
parameter. In this scenario, one second is required to identify UEs subjected to RI
mismatches.
– When the target RRU is an 8T RRU:
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 18
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 4 Intra-Cell D-MIMO
UEs working in TM3 rank 2 subjected to consecutive block errors caused by RI
mismatches can be switched to TM8 through TMA to prevent RI mismatches. In
this scenario, approximately two seconds are required to switch UEs subjected to RI
mismatches to TM8.
The MCS index and throughput decrease within the occurrence time of an RI mismatch
issue if the time is shorter than the preceding time (for example, a UE working in TM3
rank 2 switches to independent scheduling and immediately to joint scheduling).
Impacted Functions
Function Name Function Switch Reference Description
RF channel CellRfShutdown.Rf Energy Inter-RRU channel
intelligent shutdown ShutdownSwitch Conservation and calibration will fail
Emission Reduction if RF channel
intelligent shutdown
is enabled.
Intelligent power-off CellShutdown.Cell Energy Inter-RRU channel
of carriers in the ShutdownSwitch Conservation and calibration fails if a
same coverage Emission Reduction cell in the inter-cell
D-MIMO cluster
enters the carrier
intelligent power-off
state.
Low power CellLowPower.Low Energy A cell within the
consumption mode PwrSwitch Conservation and inter-cell D-MIMO
Emission Reduction cluster cannot serve
as the JT
coordinating cell
and inter-RRU
channel calibration
fails when it enters
the low power
consumption mode.
MU beamforming MuBfSwitch option Beamforming (TDD) When D-MIMO is
under the enabled, multi-user
CellAlgoSwitch.Mu spatial multiplexing
BfAlgoSwitch is implemented in a
parameter D-MIMO way, and
the performance
counters and
performance
monitoring items
related to MU
beamforming are no
longer measured.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 19
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 4 Intra-Cell D-MIMO
Function Name Function Switch Reference Description
DRX CellDrxPara.DrxAl DRX and Signaling If DRX is enabled,
gSwitch Control the UE does not
transmit SRSs to the
eNodeB during the
DRX sleep period.
As a result, the
instantaneous
beamforming
weighting values of
D-MIMO UEs
cannot be updated
promptly,
deteriorating D-
MIMO performance.
DRX is enabled
using the
CellDrxPara.DrxAl
gSwitch parameter.
Dynamic power LTE_DYN_POWE Dynamic Power D-MIMO allows
sharing between R_SHARING_SW Sharing Between multiple RF
LTE carriers option under the LTE Carriers modules working on
CellDynPowerShar the same frequency
ing.DynamicPower band in the same
SharingSwitch physical area to
parameter serve the same cell,
while power sharing
between carriers is
performed based on
physical cells that
share one RF
module. When this
function is used with
D-MIMO, dynamic
power sharing
cannot provide
maximum gains.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 20
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 4 Intra-Cell D-MIMO
Function Name Function Switch Reference Description
SFN N/A SFN When D-MIMO is
enabled, interference
suppression between
UEs is implemented
in a D-MIMO way,
and the performance
counters and
performance
monitoring items
related to inter-RRU
coordinated
beamforming are no
longer measured in
SFN scenarios.
Adaptive switching CellBfMimoParaCf Beamforming (TDD) l When the cell
between g.BfMimoAdaptiveS load is light,
beamforming and witch transmission
MIMO mode adaptation
oriented for
optimal single-
link performance
is adopted.
l When the cell
load is heavy,
transmission
mode adaptation
oriented for
optimal single-
link performance
cannot be used to
increase the cell
capacity. Cell-
level
transmission
mode adaptation
is recommended
when the cell
load is heavy and
multiple layers
are available for
pairing.
Preferential use of CellDlschAlgo.Rbg Scheduling When D-MIMO is
resource allocation AllocStrategy set to enabled, preferential
type 1 TYPE1_FIRST use of resource
allocation type 1
does not take effect.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 21
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 4 Intra-Cell D-MIMO
Function Name Function Switch Reference Description
MCS selection for SmallPktMcsSelec- Scheduling MCS selection for
transmission of tAlgoSw option transmission of
small amounts of under the small amounts of
data CellAlgoSwitch.DlS data does not take
chSwitch parameter effect for D-MIMO
UEs in the joint
transmission state.
4.3 Requirements
4.3.1 Licenses
Feature ID Feature Name Model Sales Unit
TDLEOFD-111505 DL D-MIMO LT1SDLMIMO00 per Cell
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 22
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 4 Intra-Cell D-MIMO
4.3.2 Software
Prerequisite Functions
Function Name Function Switch Reference Description
Single-stream BfSwitch option Beamforming (TDD) l D-MIMO
beamforming under the requires single-
CellAlgoSwitch.Bf stream
AlgoSwitch beamforming in
parameter outdoor macro-
macro scenarios.
l D-MIMO
requires single-
stream
beamforming in
outdoor macro-
micro scenarios.
l D-MIMO does
not require
beamforming to
be enabled and
the
corresponding
license control
item to be
purchased in
outdoor micro-
micro or indoor
LampSite
scenarios.
However, the
BfSwitch option
must be selected
under the
CellAlgoSwitch.
BfAlgoSwitch
parameter.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 23
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 4 Intra-Cell D-MIMO
Function Name Function Switch Reference Description
MU beamforming MuBfSwitch option Beamforming (TDD) l D-MIMO
under the requires MU
CellAlgoSwitch.Mu beamforming in
BfAlgoSwitch outdoor macro-
parameter macro scenarios.
l D-MIMO
requires MU
beamforming in
outdoor macro-
micro scenarios.
l D-MIMO does
not require
beamforming to
be enabled and
the
corresponding
license control
item to be
purchased in
outdoor micro-
micro or indoor
LampSite
scenarios.
However, the
MuBfSwitch(M
uBfSwitch)
option must be
selected under
the
CellAlgoSwitch.
MuBfAlgoSwitc
h parameter.
SFN l CellAlgoSwitch. SFN N/A
SfnUlSchSwitch
l CellAlgoSwitch.
SfnDlSchSwitch
Mutually Exclusive Functions
Function Name Function Switch Reference
Extended CP l Cell.UlCyclicPrefix Extended CP
l Cell.DlCyclicPrefix
High speed mobility Cell.HighSpeedFlag High Speed Mobility
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 24
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 4 Intra-Cell D-MIMO
Function Name Function Switch Reference
Out-of-band relay CELLALGOSWITCH.Rel Relay
aySwitch
Massive MIMO introduction Service-based dynamic SRS Massive MIMO (TDD)
allocation is controlled by
the SrvBasedSRSAdjAlgo
option under the
SRSCfg.SrsCfgPolicySwitc
h parameter. Other functions
are free from switch control.
Uplink SU-MIMO CellAlgoSwitch.UlSuMimo MIMO
AlgoSwitch
4.3.3 Hardware
Base Station Models
This feature supports the following base stations:
l 3900 and 5900 series base stations
l DBS3900 LampSite and DBS5900 LampSite
NOTE
l The following sub-features have site type differences:
l TDLEOFD-11150501 Distributed MIMO supports macro and LampSite sites.
l TDLEOFD-11150502 Intra-BBU D-MIMO supports macro sites.
l TDLEOFD-11150504 D-MIMO by Macro RRUs supports macro sites.
l TDLEOFD-11150505 D-MIMO Within a LampSite Cell supports LampSite sites.
l TDLEOFD-12050501 D-MIMO with Macro-Micro(BookRRU) supports macro sites.
l For details about the available bandwidths and configuration restraints in LampSite scenarios, see
DBS3900 LampSite Hardware Description, DBS3900 LampSite Technical Description, DBS5900
LampSite Hardware Description, and DBS5900 LampSite Technical Description.
Boards
l BBP
The UBBPd or UBBPe is required. In eRAN TDD 13.0 or earlier, all cells belonging to
the same D-MIMO cluster must be set up on the same BBP. From eRAN TDD 13.1, cells
belonging to the same D-MIMO cluster must be set up on the same BBU. The BBPs,
however, can be different.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 25
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 4 Intra-Cell D-MIMO
Table 4-1 Cell specifications supported by different types of BBPs
BBP Transmit/ Maximum Number of 10 MHz or 20 MHz
Receive Mode Cells Supported by Each BBP
UBBPd 2T2R or 4T4R l When the BBP does not function as a co-
processing board: 6
l When the BBP also functions as a co-
processing board: 3
8T8R 3
UBBPe 2T2R or 4T4R l When the BBP does not function as a co-
processing board: 12
l When the BBP also functions as a co-
processing board: 6
8T8R l For 10 MHz cells: 6
l For 20 MHz cells:
– When the BBP does not function as a co-
processing board: 6
– When the BBP also functions as a co-
processing board: 6 if CPRI compression is
enabled and 3 if CPRI compression is not
enabled
The outdoor BBU3910A does not support D-MIMO or enhanced channel calibration.
l Co-processing board
This feature requires co-processing boards to calculate D-MIMO co-processing
resources. The co-processing board must be configured based on the following
principles:
– The co-processing board must be a UBBPd or UBBPe.
– Each co-processing board supports a maximum of 72 antennas and 6 clusters when
a UBBPd is used. For example:
n Macro 8T8R scenarios: 8 x 3 D-MIMO clusters x 3 RRUs per D-MIMO
cluster = 72 antennas
n Macro 4T4R scenarios: 4 x 6 D-MIMO clusters x 3 RRUs per D-MIMO
cluster = 72 antennas
n Micro 2T2R scenarios: 2 x 6 D-MIMO clusters x 6 RRUs per D-MIMO cluster
= 72 antennas
4T4R and 8T8R D-MIMO clusters can use the same co-processing resources.
– Each co-processing board supports a maximum of 144 antennas and 12 clusters
when a UBBPe is used. For example:
n Macro 8T8R scenarios: 8 x 6 D-MIMO clusters x 3 RRUs per D-MIMO
cluster = 144 antennas
n Macro 4T4R scenarios: 4 x 12 D-MIMO clusters x 3 RRUs per D-MIMO
cluster = 144 antennas
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 26
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 4 Intra-Cell D-MIMO
n Micro 2T2R scenarios: 2 x 12 D-MIMO clusters x 6 RRUs per D-MIMO
cluster = 144 antennas
4T4R and 8T8R D-MIMO clusters can use the same co-processing resources.
– A co-processing board must be configured in slot 2 or 3 in BBU3900. This restraint
does not apply to BBU3910.
– The co-processing board cannot be used as a dedicated scheduling board.
NOTE
A dedicated scheduling board is a BBP that processes only signaling, instead of service data,
in dedicated scheduling mode. For details, see Cloud BB Overview Feature Parameter
Description.
– A UBBPd cannot be configured as a co-processing board when four or more
physical cells are bound to the board.
– A UBBPe cannot be configured as a co-processing board when four or more 8T8R
20 MHz physical cells are configured on the board and CPRI compression is not
enabled or when seven or more 4T4R or 8T8R physical cells are configured in other
scenarios.
– The FDD+TDD BBP cannot be configured as a co-processing board.
– 4T4R and 8T8R cells cannot be set up simultaneously on a BBP serving as the co-
processing board.
– The co-processing board uses the frame offset of the cell set up on the board. The
frame offset is specified by the CELLFRAMEOFFSET.FrameOffset parameter.
D-MIMO requires that the cell frame offset of the co-processing board be adopted
within the D-MIMO cluster to synchronize coordinated scheduling.
RF Modules
The following table lists the RF modules capable of D-MIMO.
Category RRU Model Number of Supported Scenario
Channels Frequency
Band
Macro RRU RRU3235 4T4R 2.5 GHz l Outdoor
macro-
RRU3259 l 4T4R (non- 2.5 GHz macro
splitting scenarios
scenarios)
l Outdoor
l 8T8R macro-
micro
RRU3279 l 4T4R (non- 3.5 GHz
scenarios
splitting
scenarios)
l 8T8R
RRU5258 8T8R 3.5 GHz
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 27
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 4 Intra-Cell D-MIMO
Category RRU Model Number of Supported Scenario
Channels Frequency
Band
Micro RRU RRU3236E 2T2R 2.5 GHz or 3.5 l Outdoor
GHz macro-
micro
scenarios
l Outdoor
micro-
micro
scenarios
pRRU pRRU3911 2T2R 2.3 GHz, 2.5 Indoor
GHz, or 2.6 LampSite
GHz scenarios
NOTE
D-MIMO is not supported when the RRU3259 or RRU3279 is split into two 4T4R sectors.
The following requirements also need to be satisfied:
l The RRUs incapable of D-MIMO do not support enhanced channel calibration.
l RRUs are not combined.
l Macro RRUs are not cascaded.
l RRUs are not configured using the load sharing topology.
l RRUs are not configured using the ring topology.
l RRUs are not cascaded in macro-macro scenarios.
l The remote RRU deployment distance cannot exceed 20 km. The distance between the
BBU and the last-level RRU cannot exceed 20 km when RRUs are cascaded in macro-
micro scenarios.
l No more than three carriers are configured on the same RRU.
l A TDD RRU can be connected to an FDD+TDD RRU for cascading. However, FDD
RRUs cannot be connected to FDD+TDD RRUs for cascading.
l A maximum of four micro RRUs can be cascaded in macro-micro or micro-micro
scenarios. The cluster IDs must not have the same mod 6 value if multiple cascaded
micro RRUs are configured into different D-MIMO clusters. A maximum of six cluster
IDs with different mod 6 values can be configured on a cascaded micro RRU chain. A
maximum of three micro RRUs can be cascaded when two carriers are configured on a
micro RRU and D-MIMO is enabled on all carriers belonging to different D-MIMO
clusters
Cells
l The cell bandwidth must be 10 MHz or 20 MHz.
l The 2.5 GHz band is supported in indoor LampSite scenarios.
l The 2.5 GHz and 3.5 GHz bands are supported in outdoor scenarios.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 28
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 4 Intra-Cell D-MIMO
Configuration Restraints in LampSite Scenarios
l D-MIMO cannot be used in pRRU combination scenarios.
l pRRUs belonging to the same D-MIMO cluster must be connected to the same RHUB or
connected to two neighboring RHUBs on the same CPRI link.
l No extender is used to extend the Ethernet cable connecting the RHUB to the pRRU.
Other Requirements
Beamforming is not supported in micro-micro scenarios when D-MIMO is disabled. Joint-
scheduling UEs must reaccess the network after D-MIMO is enabled so that such UEs can
enter beamforming. Independent-scheduling UEs do not support beamforming in 2T2R
scenarios when D-MIMO is enabled.
4.3.4 Networking
Planning of SFN Networking
l In SFN scenarios, D-MIMO can be deployed directly.
l In non-SFN scenarios, networking must be planned using a D-MIMO cluster planning
tool.
Planning of D-MIMO Cluster IDs
D-MIMO cluster IDs need to be planned using a D-MIMO cluster planning tool, which can be
obtained from Huawei engineers.
D-MIMO cluster planning must meet the following requirements:
l Basic requirements
– Two or more RRUs or more than three pRRUs form a D-MIMO cluster.
– Each cluster ID must have a unique mod 6 value for each RRU in multi-carrier
scenarios.
– The D-MIMO cluster ID must be unique within a BBU.
– The IDs of physically neighboring D-MIMO clusters must not have the same mod
24 value.
l Macro-macro scenarios
Each D-MIMO cluster supports two to four RRUs.
l Macro-micro scenarios
– Each D-MIMO cluster supports up to seven RRUs, including macro and micro
RRUs. There can be no more than four macro RRUs and no more than 32 antennas
in total.
– If more than four RRUs are configured, the D-MIMO cluster ID must be an even
number.
– The difference between D-MIMO cluster ID mod 6 values for different carriers
cannot be less than or equal to 1 if there are more than four RRUs in a D-MIMO
cluster and an RRU supports multi-carrier networking.
– If multiple micro RRUs are cascaded and are configured in different D-MIMO
clusters, the mod 6 values of the D-MIMO cluster IDs must be unique.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 29
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 4 Intra-Cell D-MIMO
l Micro-micro scenarios
– Each D-MIMO cluster supports up to seven book RRUs.
– If more than four RRUs are configured, the D-MIMO cluster ID must be an even
number.
– The difference between D-MIMO cluster ID mod 6 values for different carriers
cannot be less than or equal to 1 if there are more than four RRUs in a D-MIMO
cluster and an RRU supports multi-carrier networking.
– If multiple micro RRUs are cascaded and are configured in different D-MIMO
clusters, the mod 6 values of the D-MIMO cluster IDs must be unique.
l LampSite scenarios
– Each D-MIMO cluster supports three to six pRRUs.
– If multiple carriers are configured, both the number of LTE TDD carriers and the
LTE TDD bandwidth must be the same for all the pRRUs belonging to the same D-
MIMO cluster, regardless of whether D-MIMO is enabled for all the carriers.
– If more than four pRRUs are configured, the D-MIMO cluster ID must be an even
number.
4.4 Operation and Maintenance
4.4.1 Data Configuration
4.4.1.1 Data Preparation
Parameters Used for Activation
For details about data preparation for an SFN cell, see SFN. The following tables describe the
data preparations for setting up a D-MIMO cluster.
Table 4-2 Parameters in the CoProcRes MO
Parameter Parameter ID Setting Notes
Name
Coordinate CoProcRes.CoProcResId Set this parameter to a value from
Process 0 to 12.
Resource ID
BaseBand CoProcRes.BaseBandEqmId Set this parameter to the ID of the
Equipment ID baseband equipment on which the
co-processing board is configured.
Set this parameter to 255 or to a
value from 0 to 23.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 30
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 4 Intra-Cell D-MIMO
Parameter Parameter ID Setting Notes
Name
Work Mode CoProcRes.WorkMode l If D-MIMO is the only
coordination feature enabled,
leave this parameter blank.
l If D-MIMO is enabled with
other coordination features,
select the
COORDINATING_PROCES
SING option.
Bundling CoProcRes.BundlingClusterType l If D-MIMO is the only
Cluster Type coordination feature enabled,
set this parameter to DMIMO.
l If D-MIMO is enabled with
other coordination features, set
this parameter to ADAPTIVE.
Table 4-3 Parameters in the DMIMOCluster MO
Parameter Parameter ID Setting Notes
Name
D-MIMO DMIMOCluster.DMIMOCluster Set this parameter to a value
Cluster ID ID ranging from 0 to 65535.
l The D-MIMO cluster ID must
be an even number if more than
four RRUs, including macro
and micro RRUs, are
configured in macro-micro
scenarios.
l The D-MIMO cluster ID must
be an even number if more than
four pRRUs are configured in
LampSite scenarios.
l Each cluster ID must have a
unique mod 6 value for an
RRU in multi-carrier scenarios.
l The D-MIMO cluster ID must
be unique within a BBU.
Coordinate DMIMOCluster.CoProcResId Set this parameter to a value
Process ranging from 0 to 12 or to 255.
Resource ID No co-processing resources are
specified when this parameter is
set to 255.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 31
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 4 Intra-Cell D-MIMO
Parameter Parameter ID Setting Notes
Name
Beamforming DMIMOCluster.BfWeightNorma l If this parameter is set to
Weight lizeMode NEBF, paired beamforming
Normalized UEs achieve optimal
Mode performance when residing at
the D-MIMO cell edge.
l If this parameter is set to
PEBF, paired beamforming
UEs achieve optimal
performance when not residing
at the D-MIMO cell edge.
Set this parameter to NEBF in
commercial use scenarios.
Table 4-4 Parameters in the DMIMOClusterCell MO
Parameter Parameter ID Setting Notes
Name
D-MIMO DMIMOClusterCell.DMIMOClu Set this parameter to a value
Cluster ID sterID ranging from 0 to 65535.
Cell ID DMIMOClusterCell.CellID Set this parameter to a value
ranging from 0 to 255.
eNodeB ID DMIMOClusterCell.eNodeBID Set this parameter to a value
ranging from 0 to 1048575.
Mobile Country DMIMOClusterCell.Mcc Set this parameter to a value
Code ranging from 000 to 999.
Mobile DMIMOClusterCell.Mnc Set this parameter to a value
Network Code ranging from 00 to 99 or from 000
to 999.
NOTE
l Only SFN cells and pRRU aggregation cells can be added to a D-MIMO cluster. Only one cell can
be added to each D-MIMO cluster.
l The same cell cannot be added to different D-MIMO clusters.
l A given cell can be added to a D-MIMO cluster by the primary operator ID or secondary operator ID
but not both. It is recommended that the cell be added to a D-MIMO cluster by the primary operator
ID.
l A cell cannot be added to a D-MIMO cluster by both the primary operator ID and the secondary
operator ID.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 32
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 4 Intra-Cell D-MIMO
Table 4-5 Parameters in the CellAlgoSwitch MO
Parameter Parameter ID Setting Notes
Name
BF algorithm CellAlgoSwitch.BfAlgoSwitch Select the BfSwitch option under
switch this parameter.
MUBF CellAlgoSwitch.MuBfAlgoSwitch Select the MuBfSwitch option
algorithm under this parameter.
switch
D-MIMO CellAlgoSwitch.DMIMOAlgoSwi Inter-RRU channel calibration and
Algorithm tch D-MIMO JT are enabled when the
Switch DmimoJTSwitch option is
selected under this parameter.
It is recommended that the
DmimoSchAttriOptSwitch
option be selected under this
parameter when D-MIMO is
enabled.
Enhanced CellAlgoSwitch.EnhChnCalSwitc Optional. It is recommended that
Channel h the
Calibration QUICK_CHN_CAL_SWITCH
Switch option be selected under this
parameter when D-MIMO is
enabled.
Coordination CellAlgoSwitch.CoordinationAlg It is recommended that the
Algorithm oSwitch MULTI_UE_COORDINATION
Switch _OPT_SW option be selected
under this parameter when D-
MIMO is enabled.
Joint-scheduling UEs served by 2T2R target RRUs support beamforming only when D-
MIMO is enabled. Therefore, the parameters listed in Table 4-6 need to be set in macro-micro
or micro-micro scenarios.
Table 4-6 Parameters in the CellBfMimoParaCfg MO
Parameter Parameter ID Setting Notes
Name
Initial CellBfMimoParaCfg.InitialBfMi Set this parameter to TM3.
BFMIMO moType
Mode
Bf Mimo CellBfMimoParaCfg.BfMimoAd Set this parameter to ON.
Adaptive apWithoutTm2
Without Tm2
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 33
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 4 Intra-Cell D-MIMO
Table 4-7 Parameters in the CellPcAlgo MO
Parameter Parameter ID Setting Notes
Name
D-MIMO Srs CellPcAlgo.DMSrsPcSinrOffset Optional. It is recommended that
Power Control this parameter be set to 5 when D-
Offset for Sinr MIMO is enabled and to 0 when
Target D-MIMO is disabled.
Table 4-8 Parameters in the CellBf MO
Parameter Parameter ID Setting Notes
Name
Wait Pairing CellBf.WaitPairingLayerThd l Set this parameter to 30 when
Layer Number the cell load is heavy and the
Threshold multi-layer pairing rate is high.
l Set this parameter to 0 in other
situations.
Table 4-9 Parameters in the CellPdcchAlgo MO
Parameter Parameter ID Setting Notes
Name
PDCCH CellPdcchAlgo.PdcchBfGainOffs Set this parameter to 0 when the
Beamforming et PDCCHAggLvlAdaptStrage
Gain Offset parameter is set to
STRATEGYBASEDONCO-
VERAGE(Coverage-based
Selection Strategy) and D-MIMO
is enabled. Set this parameter to –
127 when D-MIMO is disabled.
Table 4-10 Parameters in the CellBfMimoParaCfg MO
Parameter Parameter ID Setting Notes
Name
Transmission CellBfMimoParaCfg.TmAcceler Set this parameter to
Mode ationSwitch INITIAL_ACCESS_TO_BF
Acceleration when D-MIMO is enabled.
Switch Set this parameter to OFF when
D-MIMO is disabled.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 34
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 4 Intra-Cell D-MIMO
To encourage more UEs to use beamforming and improve D-MIMO gains in heavy-load
micro-micro scenarios, set the DlHighLoadSdmaThdOffset parameter based on the setting
notes in Table 4-11.
Table 4-11 Parameters in the CellDlschAlgo MO
Parameter Parameter ID Setting Notes
Name
Downlink High CellDlSchAlgo.DlHighLoadSdma Set this parameter to 10 if both D-
Load SDMA ThdOffset MIMO and quick entry into
Threshold beamforming are enabled and to 5
Offset if only D-MIMO is enabled in
micro-micro scenarios.
Retain the default value 0 when
both D-MIMO and quick entry
into beamforming are disabled in
micro-micro scenarios.
Leave this parameter blank in
macro-macro or macro-micro
scenarios.
Parameters Used for Optimization
l SRS resource allocation optimization
The SRS resource optimization function is supported in micro-micro and LampSite
scenarios to improve D-MIMO performance. This function increases the proportion of
UEs allocated short-period SRS resources, improving beamforming performance for the
UEs and enhancing the downlink spectral efficiency of the cell.
The SRSCfg.SrsResOptSwitch parameter controls this function. It is valid only when all
of the following conditions are met:
– D-MIMO is enabled.
– UBBP boards are manually bound.
– The SRSCfg.TddSrsCfgMode parameter is set to ACCESS_ENHANCED.
– The Cell.MultiRruCellMode parameter is set to MPRU_AGGREGATION.
l Modifying the SRSCfg.SrsResOptSwitch parameter is a high-risk operation.
Therefore, perform this operation with caution.
l The SRS resource optimization function requires the UBBPd or UBBPe.
l The LBBPd does not support SRS resource optimization. If this function is enabled
on the LBBPd, physical cells on the board cannot be activated, and ALM-29243 Cell
Capability Degraded or ALM-29240 Cell Unavailable is reported. In this situation,
the value of the Work Status parameter is The BBP configuration does not
support SRS resource optimization in the DSP CELL command output.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 35
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 4 Intra-Cell D-MIMO
4.4.1.2 Using MML Commands
Activation Command Examples
This section describes MML command examples for enabling D-MIMO for an SFN cell
whose local cell ID is 0.
In this example:
UBBP boards are installed in slots 0 to 3, and the UBBP in slot 3 functions as the co-
processing board.
l Four pieces of sector equipment are configured for the cell in LampSite scenarios.
l Three pieces of sector equipment are configured for the SFN cell on a macro eNodeB
and are bound to UBBP boards in slots 0 to 2.
Adding and activating the SFN cell. For details, see SFN.
//Specifying baseband equipment for the BBP and co-processing board
ADD BASEBANDEQM: BASEBANDEQMID=0, BASEBANDEQMTYPE=ULDL, UMTSDEMMODE=NULL, SN1=0;
ADD BASEBANDEQM: BASEBANDEQMID=1, BASEBANDEQMTYPE=ULDL, UMTSDEMMODE=NULL, SN1=1;
ADD BASEBANDEQM: BASEBANDEQMID=2, BASEBANDEQMTYPE=ULDL, UMTSDEMMODE=NULL, SN1=2;
ADD BASEBANDEQM: BASEBANDEQMID=3, BASEBANDEQMTYPE=ULDL, UMTSDEMMODE=NULL, SN1=3;
//(Only for macro eNodeBs) Adding sector equipment and binding baseband equipment for
physical cells in SFN scenarios
ADD EUCELLSECTOREQM: LocalCellId=0, SectorEqmId=0, BASEBANDEQMID=0;
ADD EUCELLSECTOREQM: LocalCellId=0, SectorEqmId=1, BASEBANDEQMID=1;
ADD EUCELLSECTOREQM: LocalCellId=0, SectorEqmId=2, BASEBANDEQMID=2;
//(Only for LampSite eNodeBs) Adding sector equipment groups for LampSite cells and
adding sector equipment to the sector equipment groups
ADD EUSECTOREQMGROUP: LocalCellId=0, SectorEqmGroupId=0;
ADD EUSECTOREQMGROUP: LocalCellId=0, SectorEqmGroupId=1;
ADD EUSECTOREQMGROUP: LocalCellId=0, SectorEqmGroupId=2;
ADD EUSECTOREQMGROUP: LocalCellId=0, SectorEqmGroupId=3;
ADD EUSECTOREQMID2GROUP: LocalCellId=0, SectorEqmGroupId=0, SectorEqmId=0;
ADD EUSECTOREQMID2GROUP: LocalCellId=0, SectorEqmGroupId=1, SectorEqmId=1;
ADD EUSECTOREQMID2GROUP: LocalCellId=0, SectorEqmGroupId=2, SectorEqmId=2;
ADD EUSECTOREQMID2GROUP: LocalCellId=0, SectorEqmGroupId=3, SectorEqmId=3;
//Adding the D-MIMO co-processing resource
ADD COPROCRES: CoProcResId=0, BaseBandEqmId=3, BundlingClusterType=DMIMO;
//Adding a D-MIMO cluster
ADD DMIMOCLUSTER: DMIMOClusterId=0, CoProcResId=0;
//Adding the SFN cell to the D-MIMO cluster
ADD DMIMOCLUSTERCELL: DMIMOClusterId=0, CellId=0, eNodeBId=0, Mcc="100", Mnc="01";
//(Optional) Enabling target SINR optimization for beamforming UEs during SRS power
control
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 36
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 4 Intra-Cell D-MIMO
MOD CELLPCALGO: LocalCellId=0, DMSrsPcSinrOffset=5;
//Turning on the beamforming, MU beamforming, D-MIMO, and enhanced channel
calibration switches
MOD CELLALGOSWITCH: LocalCellId=0, BFAlgoSwitch=BFSwitch-1,
MuBfAlgoSwitch=MuBfSwitch-1, DMIMOAlgoSwitch=DmimoJTSwitch-1,
EnhChnCalSwitch=QUICK_CHN_CAL_SWITCH-1;
//(Optional) Enabling advanced multi-user coordination
MOD CELLALGOSWITCH: LocalCellId=0, CoordinationAlgoSwitch=
MULTI_UE_COORDINATION_OPT_SW-1;
//(Optional) Setting the PDCCH beamforming gain offset to 0 and enabling CCE aggregation
level selection optimization for joint-transmission beamforming UEs in coverage-based
PDCCH scenarios
MOD CELLPDCCHALGO: LocalCellId=0, PdcchBfGainOffset=0;
//(Optional) Configuring adaptive switching between beamforming and MIMO in macro-
micro or micro-micro scenarios
MOD CELLBFMIMOPARACFG: LocalCellId=0, BfMimoAdaptiveswitch=MIMO_BF_ADAPTIVE,
BfMimoAdapWithoutTm2=ON, InitialBfMimoType=TM3;
//(Optional) Setting the number of layers to be paired to 30 and enabling cell-level adaptive
switching between transmission modes when the cell load is heavy and the multi-layer pairing
rate is high
MOD CELLBF: LocalCellId=0, WaitPairingLayerThd=30;
//(Optional) Enabling quick entry into beamforming during initial access
MOD CELLBFMIMOPARACFG: LocalCellId=0, TmAccelerationSwitch = INITIAL_ACCESS_TO_BF;
//Setting the downlink high load SDMA threshold offset to 10 dB when quick entry into
beamforming during initial access is enabled in micro-micro scenarios
MOD CELLDLSCHALGO: LocalCellId=0, DlHighLoadSdmaThdOffset = 10;
//(Optional) Enabling D-MIMO scheduling attribute optimization
MOD CELLALGOSWITCH: LocalCellId=0, DMIMOAlgoSwitch= DmimoSchAttriOptSwitch-1;
Deactivation Command Examples
//(Optional) Disabling target SINR optimization for beamforming UEs during SRS power
control
MOD CELLPCALGO: LocalCellId=0, DMSrsPcSinrOffset=0;
//Turning off the beamforming, MU beamforming, D-MIMO, and enhanced channel
calibration switches
MOD CELLALGOSWITCH: LocalCellId=0, BFAlgoSwitch=BFSwitch-0,
MuBfAlgoSwitch=MuBfSwitch-0, DMIMOAlgoSwitch=DmimoJTSwitch-0,
EnhChnCalSwitch=QUICK_CHN_CAL_SWITCH-0;
//(Optional) Enabling advanced multi-user coordination
MOD CELLALGOSWITCH: LocalCellId=0, CoordinationAlgoSwitch=
MULTI_UE_COORDINATION_OPT_SW-0;
//Removing the SFN cell from the D-MIMO cluster
RMV DMIMOCLUSTERCELL: DMIMOClusterId=0, CellId=0, eNodeBId=0, Mcc="100", Mnc="01";
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 37
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 4 Intra-Cell D-MIMO
//Removing a D-MIMO cluster
RMV DMIMOCLUSTER: DMIMOClusterId=0;
//(Optional) Restoring the PDCCH beamforming gain offset and disabling CCE aggregation
level selection optimization for joint-transmission beamforming UEs in coverage-based
PDCCH scenarios
MOD CELLPDCCHALGO: LocalCellId=0, PdcchBfGainOffset=-127;
//(Optional) Restoring the parameter settings in the CellBfMimoParaCfg MO to those used
before D-MIMO is enabled in macro-micro or micro-micro scenarios
MOD CELLBFMIMOPARACFG: LocalCellId=0, BfMimoAdapWithoutTm2=OFF,
InitialBfMimoType=TM2;
//(Optional) Restoring the threshold for the number of layers to be paired to the value used
before D-MIMO is enabled when the cell load is heavy and the multi-layer pairing rate is high
MOD CELLBF: LocalCellId=0, WaitPairingLayerThd=0;
//(Optional) Disabling quick entry into beamforming during initial access
MOD CELLBFMIMOPARACFG: LocalCellId=0, TmAccelerationSwitch = OFF;
//Setting the downlink high load SDMA threshold offset to the value used before D-MIMO is
enabled in micro-micro scenarios, when quick entry into beamforming during initial access is
disabled in micro-micro scenarios
MOD CELLDLSCHALGO: LocalCellId=0, DlHighLoadSdmaThdOffset = 0;
//(Optional) Disabling D-MIMO scheduling attribute optimization
MOD CELLALGOSWITCH: LocalCellId=0, DMIMOAlgoSwitch= DmimoSchAttriOptSwitch-0;
4.4.1.3 Using the CME
For detailed operations, see CME-based Feature Configuration.
4.4.2 Activation Observation
Step 1 Run the DSP CELL and LST CELL commands to check the cell status of the D-MIMO
cluster. The cells in the D-MIMO cluster are working properly if all of the following
conditions are met in the command outputs:
l The value of the Mode of Multi-RRU Cell parameter is SFN or
MPRU_AGGREGATION in the LST CELL command output, indicating that the cell
is a multi-sector cell.
l The value of the Work Status parameter is Normal in the DSP CELL command output
for all the RRUs, indicating that the RRUs are working properly.
l The value of the Cell instance state parameter is Normal in the DSP CELL command
output, indicating that the cells have been activated.
Step 2 Run the DSP DMIMOCLUSTERCELL command to check the cell status of the D-MIMO
cluster. The D-MIMO cluster is working properly if the value of the D-MIMO Cluster Cell
Status parameter is Normal.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 38
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 4 Intra-Cell D-MIMO
Step 3 Run the DSP DMIMOCALIBRATION command to check the channel calibration status of
the D-MIMO cluster. Channel calibration is successful in the D-MIMO cluster if the value of
the D-MIMO Calibration Result parameter is Succeeded.
----End
4.4.3 Network Monitoring
Monitoring Whether D-MIMO Takes Effect
The following counters can be used on the eNodeB side to check whether D-MIMO has taken
effect.
Table 4-12 Counters used to observe UE pairing for D-MIMO
Counter Description
L.ChMeas.DMIMO.1Layer.PRB Average number of PRBs that can be paired
for D-MIMO
L.ChMeas.DMIMO.2Layer.PairPRB Average number of PRBs paired for D-
MIMO at layer 2
L.ChMeas.DMIMO.3Layer.PairPRB Average number of PRBs paired for D-
MIMO at layer 3
L.ChMeas.DMIMO.4Layer.PairPRB Average number of PRBs paired for D-
MIMO at layer 4
L.ChMeas.DMIMO.5Layer.PairPRB Average number of PRBs paired for D-
MIMO at layer 5
L.ChMeas.DMIMO.6Layer.PairPRB Average number of PRBs paired for D-
MIMO at layer 6
L.ChMeas.DMIMO.7Layer.PairPRB Average number of PRBs paired for D-
MIMO at layer 7
L.ChMeas.DMIMO.8Layer.PairPRB Average number of PRBs paired for D-
MIMO at layer 8
Remarks
l The L.ChMeas.DMIMO.1Layer.PRB counter measures the number of PRBs that can
be paired for D-MIMO. D-MIMO takes effect if the value of this counter is greater than
0.
l The other counters measure the number of PRBs paired for D-MIMO at the
corresponding layers.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 39
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 4 Intra-Cell D-MIMO
Table 4-13 Counters used to observe the proportion and scope of UEs on which D-MIMO
takes effect
Counter Description
L.ChMeas.DMIMO.JT.User.Avg Number of D-MIMO joint-transmission
UEs in the downlink
L.ChMeas.DMIMO.JTUser.RRU.Avg Average number of working RRUs for D-
MIMO joint-transmission UEs in the
downlink
Monitoring the Working Status and Channel Calibration Status of the D-MIMO
Cluster
The external CHR counter PERIOD_CELL_DMIMO_MR is used to monitor the working
status and the channel calibration status of the D-MIMO cluster.
This counter periodically measures the invalidity duration of the D-MIMO cluster. Based on
the invalidity duration, the working status of the D-MIMO cluster can be determined. The
default measurement period is 15 minutes.
Field Description
>DmimoClusterID ID of the D-MIMO cluster to which the logical cells
performing MR reporting belong
>ClusterAbnormallatency Invalidity duration of the D-MIMO cluster
>CalibrationAbnormallatency Channel calibration invalidity duration of the D-
MIMO cluster
Monitoring the Pairing Status of the D-MIMO Cell
On the U2000, the following items can be monitored under MIMO (Cell) Monitoring to
observe the number of RBs paired in a D-MIMO cell.
Monitoring Item Unit Description
Number of Enable Numb Number of RBs that can be paired for D-MIMO in a
DMIMO Pairing RB er cell within a monitoring period. The total number of
available RBs that can be paired for D-MIMO during
all transmission time intervals (TTIs) is averaged at
the end of the monitoring period.
Number of successful Numb Number of RBs that are successfully paired for D-
DMIMO Pairing TM7 er MIMO in TM7 at layer N within a monitoring period.
RB(Num) with N Layers The total number of available RBs that are
successfully paired for D-MIMO during all TTIs is
averaged at the end of the monitoring period.
N = {2,3,4,5,6,7,8}
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 40
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 4 Intra-Cell D-MIMO
Monitoring Item Unit Description
Number of successful Numb Number of RBs that are successfully paired for D-
DMIMO Pairing TM8 er MIMO in TM8 at layer N within a monitoring period.
RB(Num) with N Layers The total number of available RBs that are
successfully paired for D-MIMO during all TTIs is
averaged at the end of the monitoring period.
N = {2,3,4,5,6,7,8}
Number of successful Numb Number of RBs that are successfully paired for D-
DMIMO Pairing TM9 er MIMO in TM9 at layer N within a monitoring period.
RB(Num) with N Layers The total number of available RBs that are
successfully paired for D-MIMO during all TTIs is
averaged at the end of the monitoring period.
N = {2,3,4,5,6,7,8}
Monitoring the Pairing Status of a Single UE in a D-MIMO Cell
On the U2000, the following items can be monitored under MIMO (User) Monitoring to
observe the number of PRBs paired for a single UE in a D-MIMO cell.
Monitoring Item Unit Description
Number of Enable Numb Number of RBs that can be paired for a D-MIMO UE
DMIMO Pairing RB er within a monitoring period. The total number of
available RBs that can be paired for D-MIMO during
all TTIs is averaged at the end of the monitoring
period.
This item is measured only when the Test Items
parameter is set to DMIMO.
Number of successful Numb Number of RBs for UEs successfully paired for D-
DMIMO Pairing er MIMO at layer N within a monitoring period. The
RB(Num) with N Layers total number of RBs for UEs successfully paired for
D-MIMO at layer N during all TTIs is averaged as a
cell-level value (including all RRUs) at the end of a
monitoring period.
N = {2,3,4,5,6,7,8}
This item is measured only when the Test Items
parameter is set to DMIMO.
Value range: 0-1000
Monitoring CEU Performance
The following counters can be used to monitor CEU performance on the eNodeB side.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 41
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 4 Intra-Cell D-MIMO
Counter Description
L.Thrp.bits.UL.BorderUE.Joint Total uplink PDCP-layer traffic volume jointly
Reception received for CEUs in a cell
L.Thrp.bits.UL.SmallPkt.Border PDCP-layer traffic volume scheduled for uplink small
UE.JointReception packets jointly received for CEUs in a cell
L.Thrp.Time.UL.RmvSmallPkt. Transmission duration of uplink data except small
BorderUE.JointReception packets jointly received for CEUs in a cell
L.Thrp.Time.UL.BorderUE.Join Total duration of jointly receiving data from CEUs in
tReception the uplink at the PDCP layer in a cell
L.Thrp.bits.DL.BorderUE.Joint Total downlink PDCP-layer traffic volume jointly
Transmit transmitted for CEUs in a cell
L.Thrp.bits.DL.LastTTI.Border Downlink PDCP traffic volume jointly transmitted
UE.JointTransmit for CEUs in the last TTI before the buffer is empty
L.Thrp.Time.DL.RmvLastTTI.B Data transmission duration for joint-transmission
orderUE.JointTransmit CEUs except the last TTI before the downlink buffer
is empty
L.Thrp.Time.DL.BorderUE.Join Total duration of jointly transmitting data to CEUs in
tTransmit the downlink at the PDCP layer in a cell
L.ChMeas.PRB.PUSCH.Avg.Bo Average number of PUSCH PRBs used by CEUs for
rderUE.JointReception joint reception in a cell
L.ChMeas.PRB.PDSCH.Avg.Bo Average number of PDSCH PRBs used by CEUs for
rderUE.JointTransmit joint transmission in a cell
4.4.4 Possible Issues
D-MIMO cells automatically revert to SFN configurations if there is a fault related to channel
calibration, D-MIMO cluster cell activation, or RRUs.
Channel Calibration Failures
A user-defined performance threshold alarm can be configured on the U2000. The alarm is
reported when the duration of the channel calibration failure exceeds the configured threshold.
The alarm helps O&M personnel more quickly identify channel calibration failures.
NOTE
The L.CellSectorEqpt.UNA.Dur.Cali counter measures the channel calibration failure duration.
To define a channel calibration failure alarm, perform the following operations on the U2000:
Step 1 On the U2000, choose Performance > Threshold Management > Threshold Settings. The
Threshold Settings tab page is displayed.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 42
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 4 Intra-Cell D-MIMO
Step 2 Choose eNodeB > Measurement of CellSectorEQUIP Performance from the navigation
tree, and then click Add at the bottom right part of the tab page. The Add Threshold dialog
box is displayed.
Step 3 Select one or more NEs in the Object tab of the Add Threshold dialog box.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 43
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 4 Intra-Cell D-MIMO
Step 4 On the Basic tab page, set Name, Period, and Activation time.
Step 5 On the Advanced tab page, perform the following operations and then click OK.
An alarm is reported if the duration of the channel calibration failure is greater than or equal
to the threshold plus the offset. It is cleared if the duration falls below the threshold minus the
offset.
l Set Direction to Ascending.
l Set Function subset to Network / Measurements Related to Algorithm(LTE) / Cell
Sector Algorithm Measurement.
l Set Counter name to L.CellSectorEqpt.UNA.Dur.Cali.
l Set Threshold based on the calculation result of Period set on the Basic tab page
multiplied by 80% minus the offset. In the example, set Threshold to 9, namely 15 x
80% – 3.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 44
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 4 Intra-Cell D-MIMO
l Set Offset based on the calculation result of Period set on the Basic tab page multiplied
by 20%. In the example, set Offset to 3, namely 15 x 20%.
----End
Channel Calibration-related Troubleshooting
If a user-defined performance threshold alarm is not reported on the U2000, run the DSP
DMIMOCALIBRATION command to query the channel calibration status.
l If the value is Exception occurred in internal calibration, intra-RRU channel
calibration has failed. Run the DSP CELLCALIBRATION command to identify the
faulty RRU and then contact Huawei technical support for fault handling.
l If the value is Route search failed, no appropriate routing path has been found between
RRUs due to external interference. The interference needs to be eliminated.
l If the value is Reciprocity calibration failed, the intra-cluster route search was
successful but inter-RRU reciprocity calibration failed due to the failure to reach
specified thresholds. Obtain the values of the Calibration Signal CINR and
Calibration Signal RSSI parameters and then contact Huawei technical support for
troubleshooting.
Abnormal D-MIMO Cluster Cell Status
The value of the D-MIMO Cluster Cell Status parameter is not Normal in the DSP
DMIMOCLUSTERCELL command output.
l If the value is Incorrect configurations or unavailable licenses, check whether the
following conditions are met:
– The D-MIMO switch is turned on.
– The number of RRUs is configured properly.
– The D-MIMO cluster is configured properly.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 45
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 4 Intra-Cell D-MIMO
– The license has been activated.
l If the value is Limited hardware capacity, check whether the cell is set up on a UBBPd
or UBBPe.
l If the value is Route application failures, check whether the routing bandwidth is
sufficient.
l If the value is Cell abnormal, run the DSP CELL command to verify the cell status.
l If the value is Insufficient co-processing resources, check whether co-processing board
configurations meet the requirements provided in 4.3.3 Hardware.
l If the value is Channel calibration failures, run the DSP DMIMOCALIBRATION
command to identify the cause.
l If the value is Cluster ID conflicts, check whether the D-MIMO cluster ID is configured
according to the restraints provided in 4.3.4 Networking.
l If the value is Clusters being established, wait until the cluster is set up successfully.
Others
When the DmimoJTSwitch option is selected under the
CellAlgoSwitch.DMIMOAlgoSwitch parameter, consecutive block errors arise during dual-
stream beamforming, even leading to network exits. For details about the workarounds, see
Beamforming (TDD).
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 46
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 5 Inter-eNodeB D-MIMO
5 Inter-eNodeB D-MIMO
5.1 Principles
Inter-eNodeB downlink D-MIMO enables the cells set up on different BBUs but on the same
Cloud BB network to form a D-MIMO cluster. Inter-eNodeB downlink D-MIMO uses inter-
eNodeB inter-RRU channel calibration and coherent JT. For details about inter-RRU channel
calibration and coherent JT, see 3 General Principles.
Figure 5-1 shows inter-eNodeB D-MIMO networking. Inter-BBU RRU networking is
supported and inter-BBU frequency synchronization is required. If RGPS functions as the
clock source of the entire Cloud BB network, the BBU on which the RGPS device is
configured is available only for intra-eNodeB D-MIMO. This restriction does not apply when
a GPS clock functions as the clock source of the entire Cloud BB network.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 47
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 5 Inter-eNodeB D-MIMO
Figure 5-1 Networking diagram of inter-eNodeB D-MIMO
The inter-BBU clock solution is implemented as follows:
1. BBU 1 connects to the clock reference source (for example, RGPS), locks the reference
clock source, and shares the clock source with the USUs.
2. The USUs generate a system clock source.
– If two levels of USUs are configured, the second-level USU is selected as the root
node to generate the system clock.
– If only one level of USUs is configured, the first-level USU is selected as the root
node to generate the system clock.
3. The hardware synchronization modules of other BBUs are locked to the system clock
source generated in step 2.
5.2 Network Analysis
5.2.1 Benefits
This feature offers the same benefits as downlink D-MIMO. For details, see 4.2.1 Benefits.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 48
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 5 Inter-eNodeB D-MIMO
5.2.2 Impacts
Network Impacts
l D-MIMO slightly decreases the random access response (RAR) success rate but
increases the UE access delay.
l With D-MIMO, when adaptive transmission mode switching is enabled in SFN cells,
more UEs switch from TM3 to TM8. As a result, a greater proportion of the UEs in the
cell use beamforming, including dual-stream beamforming. UEs working in TM3 rank 2
report separate CQIs for each of the two data streams. However, when such UEs work in
dual-stream beamforming (TM8), they report CQIs for only one data stream. Therefore,
D-MIMO increases the average CQI value reported by the UE.
l UEs working in dual-stream beamforming must switch to single-stream beamforming
before being paired. In this case, the measured value of the KPI BF Rank1 PRB
increases. Therefore, the proportion of dual-stream beamforming UEs is subject to
pairing. When the proportion of dual-stream beamforming UEs participating in pairing is
high, the measured value of the KPI BF Rank2 PRB decreases.
l D-MIMO enables multiple beamforming UEs in SFN cells to be paired for MU-JT. This
enables more UEs to be scheduled within each TTI when many UEs are to be scheduled.
However, successful UE scheduling requires that there be sufficient control channel
elements (CCEs) available.
– If CCE resources are sufficient, the total number of CCEs used by each TTI in the
downlink increases. The increase in the total number of downlink used CCEs
decreases the number of available uplink CCEs, increases the probability of uplink
CCE allocation failures, and affects performance such as the number of uplink
scheduled UEs and MCS indexes.
– If CCE resources are insufficient, an increasing number of CCEs fail to be allocated
in each TTI.
l After D-MIMO is enabled, joint-scheduling UEs receive D-MIMO gains and the overall
D-MIMO pairing rate improves. The BLER may slightly fluctuate due to the changes in
MCS indexes.
l In SFN or D-MIMO scenarios, CRSs are jointly transmitted and PDSCH data is
independently transmitted for independent-scheduling UEs. As a result, there may be a
mismatch between CRS measurement-based rank values and rank values supported by
PDSCH data. For an independent-scheduling UE working in TM3 rank 2 with a small
isolation, RI mismatches lead to consecutive block errors or even the MCS index drop to
0. To solve this problem, the following mechanisms are adopted:
– When the target RRU is a 2T or 4T RRU:
The eNodeB identifies independent-scheduling UEs working in TM3 rank 2
subjected to consecutive block errors caused by RI mismatches and uses rank 1 to
schedule the UEs to ensure UE performance. This function is controlled by the
SfnDlRblerOptSwitch option under the CellAlgoSwitch.SfnAlgoSwitch
parameter. In this scenario, one second is required to identify UEs subjected to RI
mismatches.
– When the target RRU is an 8T RRU:
UEs working in TM3 rank 2 subjected to consecutive block errors caused by RI
mismatches can be switched to TM8 through TMA to prevent RI mismatches. In
this scenario, approximately two seconds are required to switch UEs subjected to RI
mismatches to TM8.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 49
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 5 Inter-eNodeB D-MIMO
The MCS index and throughput decrease within the occurrence time of an RI mismatch
issue if the time is shorter than the preceding time (for example, a UE working in TM3
rank 2 switches to independent scheduling and immediately to joint scheduling).
Function Impacts
None
5.3 Requirements
5.3.1 Licenses
Feature ID Feature Name Model Sales Unit
TDLEOFD-121501 Inter-eNodeB DL D- LT1STDLDMC00 per eNodeB
MIMO (Trial)
5.3.2 Software
Prerequisite Functions
Function Name Function Switch Reference Description
Downlink D-MIMO DmimoJTSwitch D-MIMO (TDD) Inter-eNodeB
option under the downlink D-MIMO
CellAlgoSwitch.D requires downlink
MIMOAlgoSwitch D-MIMO.
parameter
Mutually Exclusive Functions
None
5.3.3 Hardware
Base Station Models
3900 and 5900 series base stations are compatible with this feature.
Boards
The requirements for BBPs and co-processing boards are the same as those of downlink D-
MIMO. For details, see Boards. This feature also has the following constraints:
l For the main control board:
– If a USU3900 is used as the only USU for BBU interconnection, only one switch
main processing and transmission unit (SMPT) can be configured.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 50
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 5 Inter-eNodeB D-MIMO
– If a USU3900 is used and there are two levels of USUs configured, only one SMPT
can be configured for each level.
– The main control board must be a UMPTe, UMPTa, or UMPTe+UMPTa.
l The D-MIMO cluster and co-processing board must be configured on the BBU where
the layer-2 cells of the SFN cell are configured in inter-eNodeB D-MIMO scenarios.
NOTE
An SMPT functions as the main control board of the USU3900. It provides functions such as O&M and
resource management for other boards. For details, see USU3900 Product Documentation.
RF Modules
This feature requires downlink D-MIMO to be activated, and has the same AAU requirements
as intra-eNodeB D-MIMO. For details, see RF Modules.
Cells
This feature requires downlink D-MIMO to be activated, and has the same cell requirements
as intra-eNodeB D-MIMO. For details, see Cells.
5.3.4 Networking
This feature requires downlink D-MIMO. For details about the networking requirements of
downlink D-MIMO, see 4.3.4 Networking.
Planning of D-MIMO Cluster IDs
D-MIMO cluster IDs need to be planned using a D-MIMO cluster planning tool, which can be
obtained from Huawei engineers.
D-MIMO cluster planning must meet the following requirements:
l Basic requirements
– Two or more RRUs or more than three pRRUs form a D-MIMO cluster.
– Each cluster ID must have a unique mod 6 value for each RRU in multi-carrier
scenarios. The value of the D-MIMO Calibration Result parameter is Channel
calibration failures in inter-eNodeB scenarios if multiple cluster IDs
corresponding to multiple carriers of the same RRU have the same mod 6 value.
– The D-MIMO cluster ID must be unique within a BBU.
– The IDs of physically neighboring D-MIMO clusters must not have the same mod
24 value.
5.4 Operation and Maintenance
5.4.1 Data Configuration
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 51
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 5 Inter-eNodeB D-MIMO
5.4.1.1 Data Preparation
Parameters Used for Activation
Inter-eNodeB D-MIMO is deployed by performing the following operations:
l Enable downlink D-MIMO.
l Set clock parameters for inter-eNodeB services.
For details about the parameters required for enabling downlink D-MIMO, see 4.4.1.1 Data
Preparation.
The following clock parameters for inter-eNodeB services need to be configured.
Table 5-1 Parameters used for activation
Parameter Parameter ID Setting Notes
Name
Clock Working TASM.MODE Set this parameter for the USU
Mode according to the following
principles:
l This parameter must not be set
to FREE for top-level USUs.
l This parameter can be set to
FREE for lower-level USUs.
Locked System TASM.SYSCLKSRC Set this parameter according to the
Clock Source following principles when one
level of USU is configured:
l Set this parameter to LOCAL
for first-level USUs.
l Set the Tasm.SYSCLKSRC
parameter to
INTER_SYSCLK for the
BBU.
Set this parameter according to the
following principles when two
levels of USUs are configured:
l Set this parameter to LOCAL
for the second-level USU.
l Set this parameter to
INTER_SYSCLK for first-
level USUs.
l Set the Tasm.SYSCLKSRC
parameter to
INTER_SYSCLK for the
BBU.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 52
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 5 Inter-eNodeB D-MIMO
The following requirements also need to be satisfied during inter-eNodeB D-MIMO
deployment:
l If RGPS is used as the clock source for the entire Cloud BB network, the BBU on which
the RGPS clock is configured is available only for intra-eNodeB D-MIMO, not for inter-
eNodeB D-MIMO. This restriction does not apply when a GPS clock functions as the
clock source of the entire Cloud BB network.
l Inter-eNodeB D-MIMO is not supported when there is a backup for the first-level USU
or second-level USU.
NOTE
For details about clock configurations for inter-eNodeB services, see USU3900-based Multi-BBU
Interconnection or USU3910-based Multi-BBU Interconnection.
5.4.1.2 Using MML Commands
Inter-eNodeB D-MIMO is deployed by performing the following operations:
l Enable inter-eNodeB downlink D-MIMO.
l Set clock parameters for inter-eNodeB services.
For details about MML command configurations required for downlink D-MIMO
deployment, see 4.4.1.2 Using MML Commands. For details about clock configurations for
inter-eNodeB services, see USU3900-based Multi-BBU Interconnection or USU3910-based
Multi-BBU Interconnection.
5.4.1.3 Using the CME
For detailed operations, see CME-based Feature Configuration.
5.4.2 Activation Verification
This function requires downlink D-MIMO to be activated. It has the same activation
observation methods as downlink D-MIMO. For details, see 4.4.2 Activation Observation.
5.4.3 Network Monitoring
This feature requires downlink D-MIMO to be activated. It has the same network monitoring
methods as downlink D-MIMO. For details, see 4.4.3 Network Monitoring.
5.4.4 Possible Issues
The value of the D-MIMO Cluster Cell Status parameter is not Normal in the DSP
DMIMOCLUSTERCELL command output.
l If the value is Clock exceptions, run the DSP SYSCLKSRC command to check
whether the value of the Locked System Clock Source parameter is Interconnection
System Clock and the value of the ESN of the NE where the locked source is located
parameter is the same for all BBUs and USUs. If not, check clock configurations.
l If the value is Incorrect configurations or unavailable licenses, check whether the
inter-eNodeB link is functional.
If there are other faults, see 4.4.4 Possible Issues.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 53
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
6 Parameters
Table 6-1 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
CellAlg DMIMO MOD TDLEO DL D- Meaning:
oSwitch AlgoSwi CELLA FD-1115 MIMO Indicates whether to enable D-MIMO algorithms. This
tch LGOSW 05 Inter- parameter applies only to LTE TDD.
ITCH TDLEO Cell DL
LST FD-130 D- DmimoJTSwitch: Indicates whether to enable D-
CELLA 501 MIMO MIMO joint transmission. If this option is selected, D-
LGOSW MIMO joint transmission is enabled. If this option is
TDLEO Inter- deselected, D-MIMO joint transmission is disabled.
ITCH FD-121 eNodeB This option applies only to LTE TDD.
501 DL D-
MIMO DmimoSchAttriOptSwitch: Indicates whether to
enable scheduling attribute optimization for D-MIMO
UEs. If this option is selected, scheduling attribute
optimization is enabled for D-MIMO UEs. If this
option is deselected, scheduling attribute optimization
is disabled for D-MIMO UEs. This option applies
only to LTE TDD.
InterCellDmimoJTSwitch: Indicates whether to enable
inter-cell D-MIMO. If this option is selected, inter-cell
D-MIMO is enabled. If this option is deselected, inter-
cell D-MIMO is disabled. This option applies only to
LTE TDD.
GUI Value Range:
DmimoJTSwitch(DmimoJTSwitch),
DmimoSchAttriOptSwitch(DmimoSchAttriOptS-
witch), InterCellDmimoJTS-
witch(InterCellDmimoJTSwitch)
Unit: None
Actual Value Range: DmimoJTSwitch,
DmimoSchAttriOptSwitch, InterCellDmimoJTSwitch
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 54
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
Default Value: DmimoJTSwitch:Off,
DmimoSchAttriOptSwitch:Off, InterCellDmimoJTS-
witch:Off
CellAlg EnhChn MOD None None Meaning:
oSwitch CalSwit CELLA Indicates whether to enable enhanced channel
ch LGOSW calibration.
ITCH
LST QUICK_CHN_CAL_SWITCH: Indicates whether to
CELLA enable fast channel calibration. If this option is
LGOSW selected, fast channel calibration is enabled. If this
ITCH option is deselected, fast channel calibration is
disabled. This option takes effect only when UBBP
boards are used and does not take effect in the case of
LBBP boards or in massive MIMO scenarios. This
option applies only to LTE TDD.
TDD_PASSIVE_PORT_CAL_SWITCH: Indicates
whether to enable channel calibration for passive ports
of LTE TDD AAUs. If this option is selected, channel
calibration takes effect for passive ports of LTE TDD
AAUs. If this option is deselected, channel calibration
does not take effect for passive ports of LTE TDD
AAUs. This option applies only to LTE TDD.
GUI Value Range:
QUICK_CHN_CAL_SWITCH(QUICK_CHN_CAL_
SWITCH),
TDD_PASSIVE_PORT_CAL_SWITCH(TDD_PASSI
VE_PORT_CAL_SWITCH)
Unit: None
Actual Value Range: QUICK_CHN_CAL_SWITCH,
TDD_PASSIVE_PORT_CAL_SWITCH
Default Value: QUICK_CHN_CAL_SWITCH:Off,
TDD_PASSIVE_PORT_CAL_SWITCH:Off
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 55
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
CellPcA DMSrsP MOD TDLBF Uplink Meaning: Indicates the offset to the target SINR for
lgo cSinrOff CELLP D-00202 Power beamforming UEs during SRS power control in D-
set CALGO 6 Control MIMO scenarios. If this parameter is set to 0, the
LST TDLEO DL D- target SINR of SRS power control for beamforming
CELLP FD-1115 MIMO UEs is not adjusted. If this parameter is set to another
CALGO 05 value, the target SINR of SRS power control for
Distribut beamforming UEs equals the configured target SINR
TDLEO ed plus this offset. This parameter applies only to LTE
FD-1115 MIMO TDD.
0501 Intra- GUI Value Range: 0~10
TDLEO BBU D-
FD-1115 MIMO Unit: dB
0502 D- Actual Value Range: 0~10
TDLEO MIMO Default Value: 0
FD-1115 by
0504 Macro
TDLEO RRUs
FD-1115 D-
0505 MIMO
TDLEO Within a
FD-121 LampSit
501 e Cell
Inter-
eNodeB
DL D-
MIMO
CellPcA SrsPcSi MOD TDLBF Uplink Meaning: Indicates the target SINR for SRS power
lgo nrTarget CELLP D-00202 Power control. If this parameter is set to a large value, the
CALGO 6 Control transmit power of UEs increases, causing interference
LST to neighboring cells. If this parameter is set to a small
CELLP value, the transmit power of UEs decreases, causing
CALGO poor uplink SRS receive performance in the local cell.
If inter-cell interference is strong, set this parameter to
a small value. If SRS receive performance in the local
cell is poor, set this parameter to a large value. This
parameter applies only to LTE TDD.
GUI Value Range: -50~50
Unit: dB
Actual Value Range: -50~50
Default Value: 1
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 56
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
DMIMO BfWeig ADD TDLEO Distribut Meaning: Indicates the beamforming weight
Cluster htNorma DMIMO FD-1115 ed normalization mode. If this parameter is set to
lizeMod CLUST 0501 MIMO NEBF(NEBF), all physical antennas consume the
e ER TDLEO D- same amount of transmit power, but the orthogonality
MOD FD-1115 MIMO among paired UEs is affected. If this parameter is set
DMIMO 0505 Within a to PEBF(PEBF), the orthogonality among paired UEs
CLUST LampSit is not affected, but physical antennas consume
ER e Cell different amount of transmit power. In this case, the
power resources of certain physical antennas are not
LST efficiently used. This parameter applies only to LTE
DMIMO TDD.
CLUST
ER GUI Value Range: NEBF(NEBF), PEBF(PEBF)
Unit: None
Actual Value Range: NEBF, PEBF
Default Value: NEBF(NEBF)
CellBf WaitPair MOD TDLOF MU- Meaning: Indicates the threshold of the number of
ingLaye CELLB D-00107 Beamfor pairing layers. This parameter is used to identify
rThd F 7 ming heavy-load and multi-layer pairing scenarios and
LST TDLEO DL D- adapt the transmission mode for each cell, facilitating
CELLB FD-1115 MIMO multi-user pairing and improving system capacity. If
F 05 this parameter is set to 0, heavy-load scenarios are not
Single identified and the transmission mode is not adapted
TDLOF Streami for each cell. This parameter applies only to LTE
D-00104 ng TDD.
9 Beamfor
ming GUI Value Range: 0~640
TDLOF
D-00106 Dual Unit: None
1 Streami Actual Value Range: 0~64, step: 0.1
ng Default Value: 0
Beamfor
ming
CellAlg Coordin MOD TDLOF Advance Meaning:
oSwitch ationAlg CELLA D-13020 d Multi- Indicates whether to enable coordination algorithms.
oSwitch LGOSW 4 User
ITCH Coordin MULTI_UE_COORDINATION_OPT_SW: Indicates
LST ation whether to optimize multi-user coordination. This
CELLA option applies only to LTE TDD.
LGOSW GUI Value Range:
ITCH MULTI_UE_COORDINATION_OPT_SW(MULTI_
UE_COORDINATION_OPT_SW)
Unit: None
Actual Value Range:
MULTI_UE_COORDINATION_OPT_SW
Default Value:
MULTI_UE_COORDINATION_OPT_SW:Off
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 57
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
CellAlg SfnAlgo MOD LOFD-0 Adaptiv Meaning:
oSwitch Switch CELLA 70205/ e SFN/ Indicates whether to enable algorithms related to
LGOSW TDLOF SDMA single frequency networks (SFNs).
ITCH D-00200 Super
LST 8 Combin SfnPdcchDcsSwitch: Indicates whether to enable
CELLA LOFD-0 ed Cell selective transmission of PDCCH data for an SFN
LGOSW 81221 cell. This option applies only to LTE TDD.
SFN
ITCH LOFD-0 If this option is selected, selective transmission of
PDCCH
03029/ DCS in PDCCH data is performed when adaptive SFN/SDMA
TDLOF SFN is enabled.
D-00107
5/ PDCCH If this option is deselected, joint transmission or
MLOFD SDMA SDMA-based transmission of PDCCH data is
-121204 in SFN performed when adaptive SFN/SDMA is enabled.
TDLOF SfnUll2SelectiveRcvSwitch: Indicates whether to
D-07022 enable selective reception of L2 data for an SFN cell.
7 This option applies only to LTE TDD.
TDLOF If this option is selected, one of the working RRUs
D-08122 serving a UE is selected to receive L2 data of this UE.
1
If this option is deselected, only the target RRU of a
UE is fixedly used to receive L2 data of this UE.
SfnPdcchSdmaSwitch: Indicates whether to enable
SDMA-based transmission of PDCCH data for an
SFN cell. This option applies only to LTE TDD.
If this option is selected, SDMA-based transmission
of PDCCH data is performed when adaptive SFN/
SDMA is enabled.
If this option is deselected, joint transmission or
selective transmission of PDCCH data is performed
when adaptive SFN/SDMA is enabled.
SfnPucchAckSdmaSwitch: Indicates whether to
enable SDMA-based transmission and reception of
dynamic ACK over the PUCCH for an SFN cell. This
option applies only to LTE TDD.
If this option is selected, SDMA-based transmission
and reception of dynamic ACK over the PUCCH can
be performed when adaptive SFN/SDMA is enabled.
If this option is deselected, SDMA-based transmission
and reception of dynamic ACK over the PUCCH
cannot be performed when adaptive SFN/SDMA is
enabled.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 58
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
SuperCombCellSwitch: Indicates whether to enable
the super combined cell feature. This option applies
only to LTE FDD and LTE TDD.
If this option is selected, the super combined cell
feature is enabled. If this option is deselected, the
super combined cell feature is disabled.
SfnDl2LoadLevelAdptSwitch: Indicates whether to
enable downlink two-load-level adaptation for an SFN
cell. This option applies only to LTE TDD.
If this option is selected, downlink two-load-level
adaptation is enabled when adaptive SFN/SDMA is
enabled.
If this option is deselected, downlink two-load-level
adaptation is disabled when adaptive SFN/SDMA is
enabled.
SfnDlSchAttriAdjsSwitch: Indicates whether to adjust
downlink scheduling attributes for an SFN cell. This
option applies only to LTE FDD and LTE TDD.
If this option is selected, downlink scheduling
attributes are adjusted when adaptive SFN/SDMA is
enabled.
If this option is deselected, downlink scheduling
attributes are not adjusted when adaptive SFN/SDMA
is enabled.
SfnCbfSwitch: Indicates whether to enable
coordinated beamforming (CBF) for an SFN cell. This
option applies only to LTE TDD.
If this option is selected, CBF is performed when
adaptive SFN/SDMA is enabled.
If this option is deselected, CBF is not performed
when adaptive SFN/SDMA is enabled.
SfnVoLteDlJSchSwitch: Indicates whether to jointly
schedule VoLTE UEs in the downlink in an adaptive
SFN cell. This option applies only to LTE FDD and
LTE TDD.
If this option is selected, VoLTE UEs are always
jointly scheduled when adaptive SFN/SDMA is
enabled.
If this option is deselected, VoLTE UEs are adaptively
scheduled when adaptive SFN/SDMA is enabled.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 59
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
SfnTarRruSelEnhSwitch: Indicates whether to
enhance the selection of an uplink target RRU. This
function is enabled when the distance between
physical cells of an SFN cell exceeds 500 m. This
option applies only to LTE FDD and LTE TDD.
If this option is selected, the physical layer calibrates
received uplink signals based on TA measurements so
that a more appropriate target RRU can be selected.
If this option is deselected, the physical layer does not
calibrate received uplink signals for target RRU
selection.
SfnTarRruAdptSelSwitch: Indicates whether to enable
adaptive use of uplink SINR and uplink RSRP for
target RRU selection. This option applies only to LTE
FDD and LTE TDD.
If this option is selected, the eNodeB chooses either
the uplink SINR or the uplink RSRP based on the UE
location for target RRU selection.
If this option is deselected, the eNodeB always uses
the uplink SINR for target RRU selection.
SfnVoLteUlJSchSwitch: Indicates whether to jointly
schedule VoLTE UEs in the uplink in an adaptive SFN
cell. This option applies only to LTE FDD and LTE
TDD.
If this option is selected, VoLTE UEs are always
jointly scheduled in the uplink when adaptive SFN/
SDMA is enabled.
If this option is deselected, VoLTE UEs are adaptively
scheduled in the uplink when adaptive SFN/SDMA is
enabled.
SfnDlRblerOptSwitch: Indicates whether to enable the
optimization to resolve consecutive downlink bit
errors. This option applies only to LTE FDD and LTE
TDD.
If this option is selected, the optimization is enabled to
resolve consecutive downlink bit errors or even an
MCS index decrease to 0.
If this option is deselected, the optimization is
disabled.
SfnJtSwitch: Indicates whether to enable joint
transmission for TM9/TM10 UEs in the overlapping
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 60
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
areas of an SFN cell. This option applies only to LTE
FDD and LTE TDD.
If this option is selected, the SFN joint transmission
function is enabled.
If this option is deselected, the SFN joint transmission
function is disabled.
GUI Value Range:
SfnPdcchDcsSwitch(SFNPDCCHDCSSWITCH),
SfnUll2SelectiveRcvSwitch(SfnUll2SelectiveRcvSwit
ch),
SfnPdcchSdmaSwitch(SFNPDCCHSDMASWITCH),
SfnPucchAckSdmaS-
witch(SFNPUCCHACKSDMASWITCH),
SuperCombCellSwitch(SuperCombCellSwitch),
SfnDl2LoadLevelAdptSwitch(SfnDl2LoadLevelAdpt
Switch), SfnDlSchAttriAdjsS-
witch(SfnDlSchAttriAdjsSwitch),
SfnCbfSwitch(SfnCbfSwitch), SfnVoLteDlJSchS-
witch(SfnVoLteDlJSchSwitch), SfnTarRruSelEnhS-
witch(SfnTarRruSelEnhSwitch), SfnTarRruAdptSelS-
witch(SfnTarRruAdptSelSwitch), SfnVoLteUlJSchS-
witch(SfnVoLteUlJSchSwitch),
SfnDlRblerOptSwitch(SfnDlRblerOptSwitch),
SfnJtSwitch(SfnJtSwitch)
Unit: None
Actual Value Range: SfnPdcchDcsSwitch,
SfnUll2SelectiveRcvSwitch, SfnPdcchSdmaSwitch,
SfnPucchAckSdmaSwitch, SuperCombCellSwitch,
SfnDl2LoadLevelAdptSwitch, SfnDlSchAttriAdjsS-
witch, SfnCbfSwitch, SfnVoLteDlJSchSwitch,
SfnTarRruSelEnhSwitch, SfnTarRruAdptSelSwitch,
SfnVoLteUlJSchSwitch, SfnDlRblerOptSwitch,
SfnJtSwitch
Default Value: SfnPdcchDcsSwitch:Off,
SfnUll2SelectiveRcvSwitch:Off,
SfnPdcchSdmaSwitch:Off, SfnPucchAckSdmaS-
witch:Off, SuperCombCellSwitch:Off,
SfnDl2LoadLevelAdptSwitch:Off,
SfnDlSchAttriAdjsSwitch:Off, SfnCbfSwitch:Off,
SfnVoLteDlJSchSwitch:Off, SfnTarRruSelEnhS-
witch:Off, SfnTarRruAdptSelSwitch:Off,
SfnVoLteUlJSchSwitch:Off,
SfnDlRblerOptSwitch:Off, SfnJtSwitch:Off
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 61
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
CellRfS RfShutd MOD LOFD-0 RF Meaning: Indicates whether to enable intelligent RF
hutdown ownSwit CELLR 01039/ Channel channel shutdown. The eNodeB can perform
ch FSHUT TDLOF Intellige intelligent RF channel shutdown when specific
DOWN D-00103 nt criterion is met only if this parameter is set to
LST 9 Shutdow ON(On). If this parameter is set to
CELLR n DETECTION(DETECTION), the eNodeB only
FSHUT detects and measures the duration when intelligent RF
DOWN channel shutdown can be triggered, but does not
perform intelligent RF channel shutdown. This
parameter applies only to LTE FDD and LTE TDD.
GUI Value Range: OFF(Off), ON(On),
DETECTION(DETECTION)
Unit: None
Actual Value Range: OFF, ON, DETECTION
Default Value: OFF(Off)
CellShut CellShut MOD LOFD-0 Intellige Meaning: Indicates whether to enable or disable
down downSw CELLS 01042/ nt intelligent power-off of carriers in the same coverage.
itch HUTDO TDLOF Power- Intelligent power-off of carriers in the same coverage
WN D-00104 Off of can be performed only when this parameter is set to
LST 2 Carriers ON and specific conditions are met. For intelligent
CELLS in the power-off of carriers in the same coverage, each basic
HUTDO Same cell must have its intelligent power-off of carriers
WN Coverag switch enabled and the UL or DL PRB usage
e threshold set to 0. This parameter applies only to LTE
FDD and LTE TDD.
GUI Value Range: OFF(Off), ON(On)
Unit: None
Actual Value Range: OFF, ON
Default Value: OFF(Off)
CellLow LowPwr MOD LOFD-0 Low Meaning: Indicates the switch for the functionality of
Power Switch CELLL 01040/ Power the low power consumption mode. The cell can enter
OWPO TDLOF Consum the low power consumption mode only when this
WER D-00104 ption parameter is set to ON and specific conditions are
LST 0 Mode met. This parameter applies only to LTE FDD and
CELLL LTE TDD.
OWPO GUI Value Range: OFF(Off), ON(On)
WER Unit: None
Actual Value Range: OFF, ON
Default Value: OFF(Off)
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 62
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
CellAlg MuBfAl MOD TDLOF MU- Meaning:
oSwitch goSwitc CELLA D-00107 Beamfor Indicates whether to enable multi-user beamforming
h LGOSW 7 ming (MU beamforming). This parameter is valid only if
ITCH TDLOF DL 4- the BfSwitch option of the BfAlgoSwitch parameter is
LST D-11022 Layer selected.
CELLA 1 MU-
LGOSW Beamfor MuBfSwitch: Indicates whether to enable MU
TDLEO beamforming in the downlink for a cell. If this option
ITCH FD-121 ming
is selected, MU beamforming in the downlink is
604 DL 8- enabled for a cell (or an SFN physical cell). If this
TDLEO Layer option is deselected, MU beamforming in the
FD-121 MU- downlink is disabled for a cell (or an SFN physical
605 Beamfor cell). This option applies only to LTE TDD.
ming
TDLOF TM9MuBfSwitch: Indicates whether to enable MU
D-13020 DL 16-
Layer beamforming in the downlink for closed-loop TM9
2 UEs in a cell. The setting of this option takes effect
MU-
TDLEO Beamfor only when the MuBfSwitch option of this parameter
FD-131 ming or the SfnCbfSwitch option of the SfnAlgoSwitch
612 parameter is selected. If this option is selected, the
WTTx MuBfSwitch option of this parameter or the
Turbo SfnCbfSwitch option of the SfnAlgoSwitch parameter
Beamfor is selected, and the TM9Switch option of the
ming EnhMIMOSwitch parameter is selected, MU
Multi- beamforming in the downlink is enabled for closed-
User loop TM9 UEs in a cell. If this option is deselected in
Split non-multi-user split SDMA scenarios, MU
SDMA beamforming in the downlink is disabled for closed-
in loop TM9 UEs in a cell. This option applies only to
Massive LTE TDD.
MIMO
HighOrderMubfSwitch: Indicates whether to enable
high-order MU beamforming for a cell. The setting of
this option takes effect only when the MuBfSwitch
option of this parameter or the SfnCbfSwitch option
of the SfnAlgoSwitch parameter is selected. If this
option is selected and the MuBfSwitch option of this
parameter or the SfnCbfSwitch option of the
SfnAlgoSwitch parameter is selected, high-order MU
beamforming in the downlink is enabled for a cell. If
this option is deselected, high-order MU beamforming
is disabled for a cell.
MubfResAdjSwitch: Indicates whether to enable MU
beamforming resource adjustment. The setting of this
option takes effect only when the MuBfSwitch option
of this parameter or the SfnCbfSwitch option of the
SfnAlgoSwitch parameter is selected. If this option is
selected and the MuBfSwitch option of this parameter
or the SfnCbfSwitch option of the SfnAlgoSwitch
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 63
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
parameter is selected, downlink resource adjustment
for MU beamforming is enabled for the cell. If this
option is deselected, downlink resource adjustment for
MU beamforming is disabled for the cell. This option
applies only to LTE TDD.
HarqRetranPairSwitch: Indicates whether to enable
MU beamforming for UEs subjected to HARQ
retransmissions. This option is valid only if the
MuBfSwitch option of this parameter is selected. If
both the MuBfSwitch option and this option are
selected, MU beamforming is enabled for UEs
subjected to HARQ retransmissions in the cell. If this
option is deselected, MU beamforming is disabled for
UEs subjected to HARQ retransmissions in the cell.
This option applies only to LTE TDD.
SplitSdmaSwitch: Indicates whether to enable split
SDMA for massive MIMO cells. If this option is
selected, adaptation between MU beamforming and
split SDMA for the PDSCH is supported. If this
option is deselected, split SDMA for the PDSCH is
not supported. This option applies only to LTE TDD.
TurboBfSwitch: Indicates whether to enable turbo
beamforming in WTTx scenarios. If both this option
and the MuBfSwitch option of this parameter are
selected, turbo beamforming takes effect in 8T8R
normal cells.
GUI Value Range: MuBfSwitch(MuBfSwitch),
TM9MuBfSwitch(TM9MuBfSwitch),
HighOrderMubfSwitch(HighOrderMubfSwitch),
MubfResAdjSwitch(MubfResAdjSwitch),
HarqRetranPairSwitch(HarqRetranPairSwitch),
SplitSdmaSwitch(SplitSdmaSwitch),
TurboBfSwitch(TurboBfSwitch)
Unit: None
Actual Value Range: MuBfSwitch, TM9MuBfSwitch,
HighOrderMubfSwitch, MubfResAdjSwitch,
HarqRetranPairSwitch, SplitSdmaSwitch,
TurboBfSwitch
Default Value: MuBfSwitch:Off,
TM9MuBfSwitch:Off, HighOrderMubfSwitch:Off,
MubfResAdjSwitch:Off, HarqRetranPairSwitch:Off,
SplitSdmaSwitch:Off, TurboBfSwitch:Off
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 64
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
CellDrx DrxAlg MOD LBFD-0 DRX Meaning: Indicates whether to enable DRX. This
Para Switch CELLD 02017/ Breathin parameter does not control dynamic DRX. In FDD
RXPAR TDLBF g Pilot and TDD cells, DRX takes effect on a CA UE only
A D-00201 when this parameter is set to ON for eNodeBs serving
LST 7/ both the PCell and SCells of the CA UE. In NB-IoT
CELLD MLBFD cells, DRX takes effect when this parameter is set to
RXPAR -120002 ON.
A 36 GUI Value Range: OFF(Off), ON(On)
LEOFD- Unit: None
111306/
TDLOF Actual Value Range: OFF, ON
D-12020 Default Value: OFF(Off)
5
CellDyn Dynami MOD LCOFD Cross Meaning:
PowerS cPowerS CELLD -131311 LTE Indicates whether to enable dynamic power sharing.
haring haringS YNPO TDLCO Carriers This parameter consists of the following options:
witch WERSH FD-131 Dynami
ARING 311 c Power LTE_DYN_POWER_SHARING_SW:controls power
LST Sharing sharing between LTE carriers. These LTE carriers can
MRFD- (LTE be FDD carriers or TDD carriers, but cannot be any
CELLD 131222
YNPO FDD) combination of FDD and TDD carriers. When this
WERSH Cross option is selected, power can be shared between LTE
ARING LTE carriers. This option applies only to LTE FDD and
Carriers LTE TDD.
Dynami UMTS_LTE_DYN_POWER_SHARING_SW:control
c Power s power sharing between LTE and UMTS carriers.
Sharing When this option is selected, power can be shared
(LTE between LTE and UMTS carriers. This option applies
TDD) only to LTE FDD.
UMTS GUI Value Range:
and LTE LTE_DYN_POWER_SHARING_SW(LTE_DYN_PO
Dynami WER_SHARING_SW),
c Power UMTS_LTE_DYN_POWER_SHARING_SW(UMTS
Sharing _LTE_DYN_POWER_SHARING_SW)
(LTE
FDD) Unit: None
Actual Value Range:
LTE_DYN_POWER_SHARING_SW,
UMTS_LTE_DYN_POWER_SHARING_SW
Default Value:
LTE_DYN_POWER_SHARING_SW:Off,
UMTS_LTE_DYN_POWER_SHARING_SW:Off
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 65
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
CellBfM BfMimo MOD TDLOF DL 2x2 Meaning:
imoPara Adaptiv CELLB D-00100 MIMO Indicates the type of adaptive selection between
Cfg eSwitch FMIMO 1 DL 4x4 beamforming and MIMO for a multi-antenna eNodeB.
PARAC TDLOF MIMO The values are described as follows:
FG D-00106 Single NO_ADAPTIVE: A fixed beamforming or MIMO
LST 0 Streami
CELLB transmission mode is used. That is, transmission mode
TDLOF ng switching is not supported.
FMIMO D-00104 Beamfor
PARAC 9 ming TxD_BF_ADAPTIVE: The transmission mode
FG changes adaptively between TM2 and TM7 or
TDLOF Dual
D-00106 Streami between TM2 and TM8, depending on the 3GPP
1 ng release with which UEs comply.
TDLAO Beamfor MIMO_BF_ADAPTIVE: The transmission mode
FD-001 ming changes adaptively among TM2, TM3, and TM7,
00115 Beamfor among TM2, TM3, and TM8, or among TM2, TM3,
TDLAO ming in TM8, and TM9, depending on the 3GPP release with
FD-081 Scell which UEs comply. The TM9Switch option must be
409 DL 4- selected if the TM9 mode is required. This parameter
Layer applies only to LTE TDD.
MIMO GUI Value Range:
Based NO_ADAPTIVE(NO_ADAPTIVE),
on TM9 TxD_BF_ADAPTIVE(TxD_BF_ADAPTIVE),
MIMO_BF_ADAPTIVE(MIMO_BF_ADAPTIVE)
Unit: None
Actual Value Range: NO_ADAPTIVE,
TxD_BF_ADAPTIVE, MIMO_BF_ADAPTIVE
Default Value:
MIMO_BF_ADAPTIVE(MIMO_BF_ADAPTIVE)
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 66
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
CellDlsc RbgAllo MOD LBFD-0 Basic Meaning:
hAlgo cStrateg CELLD 02025/ Scheduli For services whose QoS class identifier (QCI) is not 1:
y LSCHA TDLBF ng
LGO D-00202 Dynami When this parameter is set to ROUND_DOWN: (1) If
LST 5 c the number of required resource block groups (RBGs)
CELLD LBFD-0 Scheduli is less than 1, the actual required number of RBs are
LSCHA 0101502 ng allocated to UEs in the current transmission time
LGO / interval (TTI); (2) If the number of required RBGs is
TDLBF greater than N but less than N+1 (N is an integer
D-00101 greater than or equal to 1), N RBGs are allocated to
502 UEs in the current TTI and the other required RBs are
allocated to UEs in subsequent TTIs. Setting this
parameter to ROUND_DOWN ensures full utilization
of RBs, but increases scheduling times and decreases
the downlink UE data rate.
When this parameter is set to ROUND_UP and the
number of required RBGs is greater than N but less
than N+1 (N is an integer greater than or equal to 0),
N+1 RBGs are allocated to UEs in the current TTI.
Setting this parameter to ROUND_UP wastes a few
RBs, but decreases scheduling times and increases the
downlink UE data rate.
When this parameter is set to ADAPTIVE: (1) If the
number of required RBGs is less than 1, the actual
required number of RBs are allocated to UEs in the
current TTI; (2) If the number of required RBGs is
greater than N but less than N+1 (N is an integer
greater than or equal to 1), N+1 RBGs are allocated to
UEs in the current TTI. Compared with setting this
parameter to ROUND_UP, setting this parameter to
ADAPTIVE does not waste RBs when the number of
required RBGs is less than 1.
When this parameter is set to TYPE1_FIRST and the
number of required RBs is less than or equal to the
maximum number of RBs that can be allocated in type
1 allocation mode, type 1 allocation mode is
preferentially used to allocate RBs.
If the conditions for using type 1 allocation mode are
not met, the parameter value ADAPTIVE takes effect.
This value applies only to LTE TDD.
For services whose QCI is 1 (such as VoIP services):
When this parameter is set to ROUND_DOWN: (1) If
the number of required RBGs is less than 1, the actual
required number of RBs are allocated to UEs in the
current TTI; (2) If the number of required RBGs is
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 67
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
greater than N but less than N+1 (N is an integer
greater than or equal to 1), N+1 RBGs are allocated to
UEs in the current TTI.
If this parameter is set to ROUND_UP or
ADAPTIVE, RBs are allocated to UEs in the same
way as they are allocated when this parameter is set to
ROUND_UP or ADAPTIVE for non-QCI-1 services,
respectively.
If this parameter is set to TYPE1_FIRST, RBs are
allocated to UEs in the same way as they are allocated
when this parameter is set to ADAPTIVE.
For ping services:
If this parameter is set to ROUND_DOWN,
ROUND_UP, or ADAPTIVE and the number of
required RBs is greater than N but less than N+1
RBGs (N is an integer greater than or equal to 0), N+1
RBGs are allocated to UEs in the current TTI.
If this parameter is set to TYPE1_FIRST, RBs are
allocated to UEs in the same way as they are allocated
when this parameter is set to TYPE1_FIRST for non-
QCI-1 services.
This parameter applies only to LTE FDD and LTE
TDD.
GUI Value Range: ROUND_DOWN(Round Down),
ROUND_UP(Round Up), ADAPTIVE(Adaptive),
TYPE1_FIRST(Type1 First)
Unit: None
Actual Value Range: ROUND_DOWN, ROUND_UP,
ADAPTIVE, TYPE1_FIRST
Default Value: ADAPTIVE(Adaptive)
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 68
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
CellAlg DlSchS MOD LOFD-1 Traffic Meaning:
oSwitch witch CELLA 10205/ Model Indicates whether to enable downlink scheduling
LGOSW TDLOF Based algorithms in a cell. This parameter includes the
ITCH D-11022 Perform following options:
LST 7 ance
CELLA LOFD-0 Optimiz FreqSelSwitch: Indicates whether to enable
LGOSW 01016/ ation frequency-selective scheduling. If this option is
ITCH TDLOF VoIP selected, data is transmitted on the frequency band of
D-00101 Semi- high channel quality. This option applies only to LTE
6 persisten FDD and LTE TDD.
LBFD-0 t
SpsSchSwitch: Indicates whether to enable semi-
0101502 Scheduli
persistent scheduling during talk spurts of VoLTE
/ ng
services. If this option is selected, semi-persistent
TDLBF Dynami scheduling is applied during talk spurts of VoLTE
D-00101 c services. If this option is deselected, dynamic
502 Scheduli scheduling is applied during talk spurts of VoLTE
ng services. This option applies only to LTE FDD and
LOFD-0
01109/ DL LTE TDD.
TDLOF Non-
MBSFNShutDownSwitch: Indicates whether to
D-00110 GBR
enable Multimedia Broadcast multicast service Single
9 Packet
Frequency Network (MBSFN) subframe shutdown. If
Bundlin
LOFD-0 this option is selected, MBSFN subframe shutdown is
g
01070/ applied. If this option is deselected, MBSFN subframe
TDLOF Symbol shutdown is not applied. This option takes effect only
D-00107 Power if the SymbolShutdownSwitch option of the
0 Saving PowerSaveSwitch parameter is selected. If the
TDLOF Scheduli MBSFNShutDownSwitch option is selected, the
D-07022 ng setting of the switch for mapping SIBs to SI messages
2/ Based becomes invalid. If the MBSFNShutDownSwitch
LOFD-1 on Max option is deselected, the setting of the switch for
31213 Bit Rate mapping SIBs to SI messages becomes valid. The
MBSFNShutDownSwitch option applies only to LTE-
LBFD-0 Basic
only base stations. This option applies only to LTE
02025/ Scheduli
FDD and LTE TDD.
TDLBF ng
D-00202 Aperiodi NonGbrBundlingSwitch: Indicates whether to enable
5 c CQI downlink non-GBR packet bundling. If this option is
LBFD-0 Reportin selected, delay of non-GBR services can be controlled
02031/ g in non-congestion scenarios. If this option is
TDLBF MBR>G deselected, delay of non-GBR services cannot be
D-00203 BR controlled. This option applies only to LTE FDD and
1 Configu LTE TDD.
LBFD-0 ration EnAperiodicCqiRptSwitch: Indicates whether to
70102/ Enhance enable enhanced aperiodic channel quality indicator
TDLBF d DL (CQI) reporting. If this option is selected, the eNodeB
D-07010 Frequen triggers aperiodic CQI reporting for a UE based on
2 cy downlink services of the UE and the interval at which
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 69
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
LBFD-0 Selectiv the UE sends periodic CQI reports. If this option is
60103 e deselected, UEs under non-frequency-selective
LOFD-0 Scheduli scheduling do not trigger aperiodic CQI reporting
81218 ng based on downlink services and trigger an aperiodic
Enhance CQI reporting if no valid periodic CQI reports are sent
LTROF in eight consecutive periodic CQI reporting periods.
D-11120 d
Extende This option applies only to LTE FDD and LTE TDD.
4/
TDLOF d QCI DlMbrCtrlSwitch: Indicates whether to enable
D-12110 MCPTT downlink scheduling based on the maximum bit rate
6 Voice (MBR) and guaranteed bit rate (GBR) on GBR
TDLBF Manage bearers. If this option is selected, the eNodeB
D-00200 ment performs downlink scheduling on GBR bearers based
5 DL on the MBR and GBR. If this option is deselected, the
Asynchr eNodeB performs downlink scheduling on GBR
LBFD-0 bearers based on the GBR only. This option applies
60101 onous
HARQ only to LTE FDD and LTE TDD.
LBFD-0
60103/ Optimiz MbrDlSchSwitch: Indicates whether the eNodeB
TDLBF ation of performs downlink scheduling based on MBR. If this
D-08010 CQI option is selected, the eNodeB prioritizes UEs based
2 Reportin on the MBRs during downlink scheduling. This
g parameter applies only to LTE FDD and LTE TDD.
LEOFD-
111305 Enhance UeAmbrDlSchSwitch: Indicates whether the eNodeB
d DL performs downlink scheduling based on per UE
LEOFD- Frequen aggregate maximum bit rates (UE-AMBRs). If this
111307 cy option is selected, the eNodeB prioritizes UEs based
TDLOF Selectiv on the UE-AMBRs during downlink scheduling. This
D-12110 e option applies only to LTE FDD and LTE TDD.
5 Scheduli
ng EpfEnhancedSwitch: Indicates whether to enable
enhanced proportional fair (EPF) enhancement for
Virtual
scheduling. EPF enhancement for scheduling is
4T4R
enabled only if this option is selected. This option
eMIMO applies only to LTE FDD and LTE TDD.
RRC AperiodicCqiTrigOptSwitch: Indicates whether to
and optimize triggering of aperiodic CQI reporting. If this
DRX option is selected, a UE performing initial access
Policy triggers aperiodic CQI reporting based on related
for trigger conditions after the DLMAC instance has been
Public established for 200 ms and the eNodeB receives
Safety MSG5. Consider that aperiodic CQI reporting is
triggered by invalid CQI reports in eight consecutive
CQI reporting periods. If cyclic redundancy check
(CRC) on aperiodic CQI reports fails, aperiodic CQI
reporting is not repeatedly triggered when DRX is
enabled; or aperiodic CQI reporting is triggered after
eight TTIs when DRX is disabled. If this option is
deselected, a UE performing initial access triggers
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 70
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
aperiodic CQI reporting based on related trigger
conditions after the DLMAC instance has been
established for 200 ms. Consider that aperiodic CQI
reporting is triggered by invalid CQI reports in eight
consecutive CQI reporting periods. If CRC on
aperiodic CQI reports fails, aperiodic CQI reporting is
triggered after eight TTIs, regardless of the DRX
status. This option applies only to LTE FDD and LTE
TDD.
VoipTbsBasedMcsSelSwitch: Indicates whether the
modulation and coding scheme (MCS) index is
selected based on the transport block size (TBS) in
downlink scheduling for VoLTE services. The MCS
index is selected based on the TBS in downlink
dynamic scheduling for VoLTE services only if this
option is selected. This option applies only to LTE
FDD and LTE TDD.
PagingInterfRandSwitch: Indicates whether to enable
interference randomization for paging messages. If
this option is selected, interference randomization is
enabled for paging messages. This option applies only
to LTE FDD and LTE TDD.
DlSingleUsrMcsOptSwitch: Indicates conditions for
lowering the MCS index for a single UE. If this option
is selected, the MCS index can be lowered for a UE if
the UE is the only UE to be scheduled in a
transmission time interval (TTI). If this option is
deselected, the MCS index can be lowered for a UE if
the threshold for the function of lowering the MCS
index to increase the number of RBs is reached and
the UE is the only UE to be scheduled in a TTI. This
option applies only to LTE FDD and LTE TDD.
UeSigMcsEnhanceSwitch: Indicates whether to
enable MCS optimization for UE signaling. If this
option is selected, MCS optimization for UE signaling
is enabled. For LTE FDD, the MCS index for UE
signaling is the same as the MCS index for data. For
LTE TDD, the MCS index for UE signaling is lowered
based on the MCS index for data. If this option is
deselected, a fixed low MCS index is used for UE
signaling. This option applies only to LTE FDD and
LTE TDD.
SubframeSchDiffSwitch: For TDD cells, this option
indicates whether to perform scheduling in subframes
3 and 8 based on the policy of increasing the number
of UEs scheduled in the uplink when uplink-downlink
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 71
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
configuration 2 is used. If this option is selected,
scheduling in subframes 3 and 8 is performed based
on the policy of increasing the number of UEs
scheduled in the uplink when uplink-downlink
configuration 2 is used. If this option is deselected, the
scheduling policy used in subframes 3 and 8 is the
same as that used in other downlink subframes when
uplink-downlink configuration 2 is used. For NB-IoT
cells, this option indicates whether to enable
scheduling priority optimization. If this option is
deselected, the scheduling priority of downlink
services is higher than that of uplink services for UEs
for which control plane CIoT EPS optimization is
used. If this option is selected, the scheduling priority
of downlink services is the same as that of uplink
services for UEs for which control plane CIoT EPS
optimization is used. This option applies only to LTE
TDD and NB-IoT.
TailPackagePriSchSwitch: Indicates whether to enable
scheduling of downlink connected tail packages in the
bearer. If this option is selected, the connected tail
package is scheduled preferentially in the next TTI,
which reduces the delay and increases the
transmission rate. If this option is deselected, the
scheduling policy of the connected tail package is the
same as other downlink subframes. This option
applies only to LTE TDD.
SIB1InterfRandSwitch: Indicates whether to enable
SIB1 interference randomization. If this option is
selected, interference randomization is enabled for
SIB1. This option applies only to LTE TDD.
FreqSelJudgeIgnorDopplerSwitch: Indicates whether
to ignore Doppler conditions. If this option is selected,
Doppler conditions are ignored during frequency
selective channel determination. If this option is
deselected, Doppler conditions are considered during
frequency selective channel determination. This
parameter applies only to LTE FDD and LTE TDD.
EnhExtQCISpsSchSwitch: Indicates whether to
enable semi-persistent scheduling during talk spurts of
PTT services with standardized QCI 65, standardized
QCI 66, or an enhanced extended QCI. If this option
is selected, semi-persistent scheduling is applied. If
this option is deselected, dynamic scheduling is
applied. This option applies only to LTE FDD and
LTE TDD.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 72
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
DlVoipBundlingSwitch: Indicates whether to enable
active packet bundling for downlink VoLTE services.
Active packet bundling is enabled for downlink
VoLTE services only if this option is selected. If this
option is selected, PDCCH resources can be saved for
downlink data services or uplink services, thereby
increasing the VoLTE capacity for VoLTE services or
increasing the throughput of data services in mixed
service scenarios. However, the delay in VoLTE voice
packet scheduling will increase in the downlink and
MOSs may decrease. You are advised to deselect this
option if you prefer VoLTE performance and do not
expect MOS reduction. This option applies only to
LTE FDD and LTE TDD.
DlPacketLenAwareSchSw: Indicates whether to
enable packet length awareness performance
optimization in the downlink. Packet length awareness
performance optimization is enabled in the downlink
only if this option is selected. This option applies only
to LTE FDD and LTE TDD.
RLCArqFeedbackEnhancedSwitch: Indicates whether
to modify HARQ feedback results based on RLC
status reports when uplink-downlink configuration 2
is used. If this option is selected, the eNodeB modifies
HARQ feedback results based on RLC status reports
after receiving the reports. This prevents unnecessary
HARQ retransmissions. This option applies only to
LTE TDD.
PaReconfigOptSwitch: Indicates whether to enable PA
reconfiguration optimization. The optimization is
enabled when this option is selected. This option
applies only to LTE FDD and LTE TDD.
RankRapidRptSwitch: Indicates whether to enable fast
rank reporting. If this option is selected, an aperiodic
CQI reporting is immediately triggered after
successful network access. If this option is deselected,
an aperiodic CQI reporting is not immediately
triggered after successful network access. This option
applies only to LTE FDD and LTE TDD.
DlRLCStateReportSchDelaySw: Indicates whether to
enable optimization on the delay-based scheduling of
downlink RLC status reports. The optimization is
enabled when this option is selected. This option
applies only to LTE FDD and LTE TDD.
SmallPktMcsSelectAlgoSw: Indicates whether to
enable MCS selection for small packets. If this option
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 73
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
is selected, the scheduler selects an MCS with a lower
index based on the amount of data to be initially
transmitted and the allocated TBS in each TTI on
condition that the allocated TB can carry the data. The
function is enabled only if this option is selected. This
option applies only to LTE FDD and LTE TDD.
SRB0SplitSchSw: Indicates whether to enable
separate scheduling of SRB0 and contention
resolution MCE. If this option is selected, SRB0 and
contention resolution MCE are separately scheduled.
This option applies only to LTE FDD and LTE TDD.
BfUserPairPriorSwitch: Indicates whether to
preferentially allocate resources to paired
beamforming UEs for UE pairing features such as MU
beamforming and D-MIMO. If this option is selected,
the eNodeB preferentially allocates resources to
paired beamforming UEs for UE pairing features such
as MU beamforming and D-MIMO. This option
applies only to LTE TDD.
HarqAllocOptSwitch: Indicates whether to optimize
the allocation of HARQ processes. If this option is
selected, the downlink UE rate increases. This option
takes effect only when D-MIMO or massive MIMO is
enabled. This option applies only to LTE TDD.
Pusch32Switch: Indicates whether to enable the
PUSCH 3-2 feedback mode. If this option is selected,
UEs that support the PUSCH 3-2 feedback mode use
this mode to aperiodically report CQIs. If this option
is deselected, the mode cannot be used. This option
applies only to LTE FDD.
DlPreciseAmbrCtrlSwitch: Indicates whether to
enable precise downlink AMBR control. If this option
is selected, a more accurate optimization algorithm
applies to the AMBR control, which achieves more
accurate AMBR control. If this option is deselected,
the original AMBR control algorithm is used. This
option applies only to LTE FDD and LTE TDD.
GUI Value Range: FreqSelSwitch(FreqSelSwitch),
SpsSchSwitch(SpsSchSwitch),
MBSFNShutDownSwitch(MBSFNShutDownSwitch),
NonGbrBundlingSwitch(NonGbrBundlingSwitch),
EnAperiodicCqiRptSwitch(EnAperiodicCqiRptS-
witch), DlMbrCtrlSwitch(DlMbrCtrlSwitch),
MbrDlSchSwitch(MbrDlSchSwitch),
UeAmbrDlSchSwitch(UeAmbrDlSchSwitch),
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 74
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
EpfEnhancedSwitch(EpfEnhancedSwitch),
AperiodicCqiTrigOptSwitch(AperiodicCqiTrigOptS-
witch), VoipTbsBasedMcsSelS-
witch(VoipTbsBasedMcsSelSwitch),
PagingInterfRandSwitch(PagingInterfRandSwitch),
DlSingleUsrMcsOptSwitch(DlSingleUsrMcsOptS-
witch), SubframeSchDiffSwitch(SubframeSchDiffS-
witch), TailPackagePriSchS-
witch(TailPackagePriSchSwitch),
UeSigMcsEnhanceSwitch(UeSigMcsEnhanceSwitch),
FreqSelJudgeIgnorDopplerSwitch(FreqSelJudgeIgnor-
DopplerSwitch),
SIB1InterfRandSwitch(SIB1InterfRandSwitch),
EnhExtQCISpsSchSwitch(EnhExtQCISpsSchSwitch),
DlVoipBundlingSwitch(DlVoipBundlingSwitch),
DlPacketLenAwareSchSw(DlPacketLenAwar-
eSchSw), RLCArqFeedbackEnhanced-
Switch(RLCArqFeedbackEnhancedSwitch),
PaReconfigOptSwitch(PaReconfigOptSwitch),
RankRapidRptSwitch(RankRapidRptSwitch),
DlRLCStateReportSchDe-
laySw(DlRLCStateReportSchDelaySw),
SmallPktMcsSelectAlgoSw(SmallPktMcsSelectAl-
goSw), SRB0SplitSchSw(SRB0SplitSchSw),
BfUserPairPriorSwitch(BfUserPairPriorSwitch),
HarqAllocOptSwitch(HarqAllocOptSwitch),
Pusch32Switch(Pusch32Switch),
DlPreciseAmbrCtrlSwitch(DlPreciseAmbrCtrlSwitch)
Unit: None
Actual Value Range: FreqSelSwitch, SpsSchSwitch,
MBSFNShutDownSwitch, NonGbrBundlingSwitch,
EnAperiodicCqiRptSwitch, DlMbrCtrlSwitch,
MbrDlSchSwitch, UeAmbrDlSchSwitch,
EpfEnhancedSwitch, AperiodicCqiTrigOptSwitch,
VoipTbsBasedMcsSelSwitch, PagingInterfRand-
Switch, DlSingleUsrMcsOptSwitch,
SubframeSchDiffSwitch, TailPackagePriSchSwitch,
UeSigMcsEnhanceSwitch, FreqSelJudgeIgnorDop-
plerSwitch, SIB1InterfRandSwitch,
EnhExtQCISpsSchSwitch, DlVoipBundlingSwitch,
DlPacketLenAwareSchSw, RLCArqFeedbackEnhan-
cedSwitch, PaReconfigOptSwitch,
RankRapidRptSwitch, DlRLCStateReportSchDe-
laySw, SmallPktMcsSelectAlgoSw, SRB0SplitSchSw,
BfUserPairPriorSwitch, HarqAllocOptSwitch,
Pusch32Switch, DlPreciseAmbrCtrlSwitch
Default Value: FreqSelSwitch:Off, SpsSchSwitch:Off,
MBSFNShutDownSwitch:Off, NonGbrBundlingS-
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 75
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
witch:Off, EnAperiodicCqiRptSwitch:Off,
DlMbrCtrlSwitch:Off, MbrDlSchSwitch:Off,
UeAmbrDlSchSwitch:Off, EpfEnhancedSwitch:Off,
AperiodicCqiTrigOptSwitch:On, VoipTbsBasedMcs-
SelSwitch:On, PagingInterfRandSwitch:Off,
DlSingleUsrMcsOptSwitch:Off, SubframeSchDiffS-
witch:Off, TailPackagePriSchSwitch:Off,
UeSigMcsEnhanceSwitch:Off, FreqSelJudgeIgnor-
DopplerSwitch:Off, SIB1InterfRandSwitch:On,
EnhExtQCISpsSchSwitch:Off, DlVoipBundlingS-
witch:Off, DlPacketLenAwareSchSw:Off,
RLCArqFeedbackEnhancedSwitch:Off,
PaReconfigOptSwitch:Off, RankRapidRptSwitch:Off,
DlRLCStateReportSchDelaySw:Off,
SmallPktMcsSelectAlgoSw:Off,
SRB0SplitSchSw:Off, BfUserPairPriorSwitch:Off,
HarqAllocOptSwitch:Off, Pusch32Switch:Off,
DlPreciseAmbrCtrlSwitch:Off
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 76
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
CellAlg BfAlgoS MOD TDLOF Single Meaning:
oSwitch witch CELLA D-00104 Streami BfSwitch: Indicates whether to enable the
LGOSW 9 ng beamforming algorithm. If this option is selected, the
ITCH TDLOF Beamfor beamforming algorithm is enabled for all UEs in a
LST D-00106 ming cell. If this option is deselected, the beamforming
CELLA 1 Dual algorithm is disabled for all UEs in the cell. This
LGOSW TDLOF Streami option is deselected by default. If a cell supporting
ITCH D-13020 ng beamforming is established, manually select this
2 Beamfor option. This option applies only to LTE TDD.
ming
TDLEO LongSrsPeriodBfSwitch: Indicates whether to perform
FD-121 WTTx beamforming for UEs with the SRS period longer than
615 Turbo 40 ms in non-massive MIMO cells. If this option is
Beamfor selected, the eNodeB can perform beamforming for
ming UEs with the SRS period longer than 40 ms in non-
DL massive MIMO cells. If this option is deselected, the
Flexible eNodeB cannot perform beamforming for such UEs.
3D- This option takes effect only when the beamforming
Beamfor algorithm is enabled. This option applies only to LTE
ming TDD.
AntSelEnhanceBfSwitch: Indicates whether four
antennas can send SRSs in turn. If this option is
selected, four antennas can send SRSs in turn. If this
option is deselected, four antennas cannot send SRSs
in turn. This option applies only to LTE TDD.
GUI Value Range: BfSwitch(BfSwitch),
LongSrsPeriodBfSwitch(LongSrsPeriodBfSwitch),
AntSelEnhanceBfSwitch(AntSelEnhanceBfSwitch)
Unit: None
Actual Value Range: BfSwitch, LongSrsPeriodBfS-
witch, AntSelEnhanceBfSwitch
Default Value: BfSwitch:Off, LongSrsPeriodBfS-
witch:Off, AntSelEnhanceBfSwitch:Off
CellAlg SfnUlSc MOD LOFD-0 SFN Meaning: Indicates the SFN uplink scheduling mode.
oSwitch hSwitch CELLA 03029/ Adaptiv The uplink scheduling modes include the joint
LGOSW TDLOF e SFN/ scheduling mode, and the auto-selection mode
ITCH D-00107 SDMA between joint scheduling and independent scheduling.
LST 5/ This parameter applies only to LTE FDD and LTE
CELLA MLOFD TDD.
LGOSW -121204 GUI Value Range: ADAPTIVE(Adaptive scheduling),
ITCH LOFD-0 JOINT(Joint scheduling)
70205/ Unit: None
TDLOF
D-00200 Actual Value Range: ADAPTIVE, JOINT
8 Default Value: JOINT(Joint scheduling)
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 77
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
CellAlg SfnDlSc MOD LOFD-0 SFN Meaning: Indicates the SFN downlink scheduling
oSwitch hSwitch CELLA 03029/ Adaptiv mode. The downlink scheduling modes include the
LGOSW TDLOF e SFN/ joint scheduling mode, and the auto-selection mode
ITCH D-00107 SDMA between joint scheduling and independent scheduling.
LST 5/ This parameter applies only to LTE FDD and LTE
MLOFD Inter- TDD.
CELLA eNodeB
LGOSW -121204 GUI Value Range: ADAPTIVE(Adaptive scheduling),
SFN
ITCH LOFD-0 Based JOINT(Joint scheduling)
70205/ on Unit: None
TDLOF Coordin
D-00200 Actual Value Range: ADAPTIVE, JOINT
ated
8 eNodeB Default Value: JOINT(Joint scheduling)
TDLOF Inter-
D-00108 eNodeB
0 Adaptiv
TDLOF e SFN/
D-00108 SDMA
2 Based
on
Coordin
ated
eNodeB
Cell UlCycli ADD LBFD-0 Normal Meaning: Indicates the UL cyclic prefix length of a
cPrefix CELL 0100401 CP cell. A cyclic prefix can be a common or extended
MOD / Extende cyclic prefix. An extended cyclic prefix is generally
CELL TDLBF d CP used in a complex environment with a strong multi-
D-00100 path effect and long delay. In a cell, the UL cyclic
LST 401 Broadca prefix length can be different from the DL one. In
CELL st of addition, the UL or DL cyclic prefix length of a cell
LOFD-0 system
01031/ must be the same as that of the cell using the same
informat BBP. For details, see 3GPP TS 36.211.
TDLOF ion
D-00103 GUI Value Range: NORMAL_CP(Normal),
1 EXTENDED_CP(Extended)
LBFD-0 Unit: None
02009/ Actual Value Range: NORMAL_CP,
TDLBF EXTENDED_CP
D-00200
9/ Default Value: NORMAL_CP(Normal)
MLBFD
-120002
29
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 78
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
Cell DlCycli ADD LBFD-0 Normal Meaning: Indicates the length of the DL cyclic prefix
cPrefix CELL 0100401 CP of a cell. A DL cyclic prefix can be a common or
MOD / Extende extended cyclic prefix. An extended cyclic prefix is
CELL TDLBF d CP generally used in a complex environment with a
D-00100 strong multi-path effect and long delay. In a cell, the
LST 401 eMTC UL cyclic prefix length can be different from the DL
CELL Introduc one. In addition, the UL or DL cyclic prefix length of
LOFD-0 tion
01031/ a cell must be the same as that of the cell using the
TDLOF same BBP. For details, see 3GPP TS 36.211.
D-00103 GUI Value Range: NORMAL_CP(Normal),
1 EXTENDED_CP(Extended)
TDLEO Unit: None
FD-121 Actual Value Range: NORMAL_CP,
611 EXTENDED_CP
Default Value: NORMAL_CP(Normal)
Cell HighSpe ADD LOFD-0 High Meaning: Indicates the speed flag of the cell. Set this
edFlag CELL 01007/ Speed parameter to HIGH_SPEED if the cell is used to
MOD TDLOF Mobility provide coverage for a high-speed railway. Set this
CELL D-00100 Ultra parameter to LOW_SPEED in other scenarios. TDD
7 High cells with a bandwidth of 5 MHz or in 8T8R mode can
LST only be configured as low-speed cells. TDD cells
CELL LOFD-0 Speed
01008 Mobility cannot be configured as ultra-high-speed cells. This
parameter applies only to LTE FDD and LTE TDD.
GUI Value Range: LOW_SPEED(Low speed cell
flag), HIGH_SPEED(High speed cell flag),
ULTRA_HIGH_SPEED(Ultra high speed cell flag),
EXTRA_HIGH_SPEED(Extra high speed cell flag)
Unit: None
Actual Value Range: LOW_SPEED, HIGH_SPEED,
ULTRA_HIGH_SPEED, EXTRA_HIGH_SPEED
Default Value: LOW_SPEED(Low speed cell flag)
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 79
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
CellAlg RelayS MOD LAOFD Out of Meaning:
oSwitch witch CELLA -111202/ Band Indicates whether to enable relay-related functions.
LGOSW TDLAO Relay
ITCH FD-080 In-Band OutOfBandRelaySwitch: Indicates whether to enable
LST 405 Relay out-of-band relay. If this option is selected, out-of-
CELLA LAOFD band relay is enabled. If this option is deselected, out-
LGOSW -131208 of-band relay is disabled. This option applies only to
ITCH / LTE FDD and LTE TDD.
TDLAO InBandRelayDeNbSwitch: Indicates whether to
FD-131 enable in-band relay for the DeNB. If this option is
406 selected, in-band relay is enabled for the DeNB. If this
option is deselected, in-band relay is disabled for the
DeNB. This option applies only to LTE FDD and LTE
TDD.
InBandRelayReNbSwitch: Indicates whether to enable
in-band relay for the ReNB. If this option is selected,
in-band relay is enabled for the ReNB. If this option is
deselected, in-band relay is disabled for the ReNB.
This option applies only to LTE FDD and LTE TDD.
InBandRelayDistantDeploySw: Indicates whether to
allow the first-hop ReNB to be deployed less than 20
km from the DeNB in in-band relay scenarios. If this
option is selected, the first-hop ReNB can be deployed
less than 20 km from the DeNB in in-band relay
scenarios. If this option is deselected, the first-hop
ReNB cannot be deployed less than 20 km from the
DeNB in in-band relay scenarios. This option applies
only to LTE FDD and LTE TDD.
GUI Value Range:
OutOfBandRelaySwitch(OutOfBandRelaySwitch),
InBandRelayDeNbSwitch(InBandRelayDeNbSwitch),
InBandRelayReNbSwitch(InBandRelayReNbSwitch),
InBandRelayDistantDeploySw(InBandRelayDistant-
DeploySw)
Unit: None
Actual Value Range: OutOfBandRelaySwitch,
InBandRelayDeNbSwitch, InBandRelayReNbSwitch,
InBandRelayDistantDeploySw
Default Value: OutOfBandRelaySwitch:Off,
InBandRelayDeNbSwitch:Off, InBandRelayReNbS-
witch:Off, InBandRelayDistantDeploySw:Off
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 80
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
SRSCfg SrsCfgP MOD TDLOF Single Meaning: Indicates the SRS configuration policy. This
olicySwi SRSCF D-00104 Streami parameter applies only to LTE TDD.
tch G 9 ng SRSPolicyforUL2LayersMIMO: Indicates the two-
LST TDLOF Beamfor antenna-port SRS configuration policy if two antenna
SRSCF D-00106 ming ports are configured for a UE in the uplink. If this
G 1 Dual option is deselected, the eNodeB preferentially
Streami allocates short-term SRSs (including single-antenna-
TDLOF port SRSs). If this option is selected, the eNodeB
D-12020 ng
Beamfor preferentially allocates two-antenna-port SRSs
1 (including long-term SRSs). SrvBasedSRSAdjAlgo:
ming
TDLEO Indicates whether to enable service-based SRS
FD-121 UL SU- adjustment. If this option is selected, the eNodeB can
601 MIMO adjust SRSs for UEs based on the identified UE
Massive services for SRS adjustment. If this option is
MIMO deselected, the eNodeB does not identify UE services
Introduc for SRS adjustment. This option applies only to LTE
tion TDD.
GUI Value Range:
SRSPolicyforUL2LayersMIMO(SRSPolicyforUL2La
yersMIMO), SrvBasedSRSAdjAl-
go(SrvBasedSRSAdjAlgo)
Unit: None
Actual Value Range: SRSPolicyforUL2LayersMIMO,
SrvBasedSRSAdjAlgo
Default Value: SRSPolicyforUL2LayersMIMO:Off,
SrvBasedSRSAdjAlgo:Off
CellAlg UlSuMi MOD LOFD-1 UL SU- Meaning:
oSwitch moAlgo CELLA 30201/ MIMO Indicates whether to enable single-user MIMO in the
Switch LGOSW TDLOF uplink for the cell.
ITCH D-12020
LST 1 ULSUMIMO2LayersSwitch: If this option is
CELLA deselected, uplink SU MIMO is disabled, and single-
LGOSW codeword scheduling is performed for all UEs. If this
ITCH option is selected, uplink single-user MIMO is
enabled, and the eNodeB performs dual-codeword
scheduling for SU-MIMO-capable UEs. This option
applies only to LTE FDD and LTE TDD.
GUI Value Range:
ULSUMIMO2LayersSwitch(ULSUMIMO2LayersSw
itch)
Unit: None
Actual Value Range: ULSUMIMO2LayersSwitch
Default Value: ULSUMIMO2LayersSwitch:Off
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 81
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
CellFra FrameO ADD None None Meaning: Indicates the offset of the start time of a cell
meOffse ffset CELLF frame against a reference clock source.
t RAME GUI Value Range: 0~261120,275943~307200
OFFSE
T Unit: Ts
MOD Actual Value Range: 0~261120,275943~307200
CELLF Default Value: 0
RAME
OFFSE
T
LST
CELLF
RAME
OFFSE
T
CoProc CoProc ADD None None Meaning: Indicates a co-processing resource index.
Res ResId COPRO This parameter applies only to LTE FDD and LTE
CRES TDD.
LST GUI Value Range: 0~12
COPRO Unit: None
CRES
Actual Value Range: 0~12
MOD
COPRO Default Value: None
CRES
RMV
COPRO
CRES
CoProc BaseBan ADD None None Meaning: Indicates the ID of the baseband equipment
Res dEqmId COPRO providing coordinated processing resources. When
CRES this parameter is set to 255, no baseband equipment is
MOD specified. In this scenario, the eNodeB selects
COPRO baseband processing units (BBPs) for providing
CRES coordinated processing resources among all BBPs in
the eNodeB. When this parameter is set to a value
LST other than 255, the eNodeB selects BBPs contained in
COPRO the specified baseband equipment for providing
CRES coordinated processing resources. This parameter
applies only to LTE FDD and LTE TDD.
GUI Value Range: 0~23,255
Unit: None
Actual Value Range: 0~23,255
Default Value: 255
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 82
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
CoProc WorkM ADD TDLOF Coordin Meaning:
Res ode COPRO D-08020 ated Indicates the working mode of co-processing
CRES 3 Scheduli resources. This parameter includes the following
MOD TDLOF ng based options:
COPRO D-11120 Power
CRES 8 Control BASEBAND_PROCESSING: Indicates that the
Uplink baseband equipment performs general baseband
LST TDLAO processing.
COPRO FD-081 Interfere
CRES 411 nce COORDINATING_PROCESSING: Indicates that the
Coordin baseband equipment performs coordination
LOFD-0 ation
70208 processing.
Inter-
TDLEO eNodeB CLUSTER_MANAGEMENT: Indicates that the
FD-1115 DL baseband equipment performs cluster management.
05 CoMP Only one piece of baseband equipment can be
Based configured in an eNodeB for cluster management.
on This option applies only to LTE FDD and LTE TDD.
Relaxed
GUI Value Range:
Backhau
BASEBAND_PROCESSING(BASEBAND_PROCE
l
SSING),
Coordin COORDINATING_PROCESSING(COORDINATIN
ated G_PROCESSING),
Scheduli CLUSTER_MANAGEMENT(CLUSTER_MANAGE
ng based MENT)
Power
Unit: None
Control
Actual Value Range: BASEBAND_PROCESSING,
DL D-
COORDINATING_PROCESSING,
MIMO
CLUSTER_MANAGEMENT
Default Value: BASEBAND_PROCESSING:Off,
COORDINATING_PROCESSING:Off,
CLUSTER_MANAGEMENT:Off
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 83
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
CoProc Bundlin ADD TDLOF Coordin Meaning: Indicates the cluster type bound to co-
Res gCluster COPRO D-08020 ated processing resources. If this parameter is set to
Type CRES 3 Scheduli ADAPTIVE, no cluster type is specified and the
MOD TDLOF ng based eNodeB adaptively specifies a cluster type based on
COPRO D-11120 Power the coordination processing requirements of
CRES 8 Control coordination features. This parameter applies only to
Uplink LTE FDD and LTE TDD.
LST TDLAO
COPRO FD-081 Interfere GUI Value Range: ADAPTIVE(ADAPTIVE),
CRES 411 nce CSPC(CSPC), DL_COMP(DL_COMP),
Coordin UL_ICS(UL_ICS), DMIMO(DMIMO)
LOFD-0 ation
70208 Unit: None
Inter- Actual Value Range: ADAPTIVE, CSPC, DL_COMP,
TDLEO eNodeB
FD-1115 UL_ICS, DMIMO
DL
05 CoMP Default Value: ADAPTIVE(ADAPTIVE)
Based
on
Relaxed
Backhau
l
Coordin
ated
Scheduli
ng based
Power
Control
DL D-
MIMO
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 84
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
DMIMO DMIMO ADD TDLEO DL D- Meaning: Indicates the D-MIMO static cluster index.
Cluster ClusterI DMIMO FD-1115 MIMO This parameter applies only to LTE TDD.
d CLUST 05 GUI Value Range: 0~65535
ER
Unit: None
DSP
DMIMO Actual Value Range: 0~65535
CALIB Default Value: None
RATIO
N
LST
DMIMO
CLUST
ER
MOD
DMIMO
CLUST
ER
RMV
DMIMO
CLUST
ER
DMIMO CoProc ADD TDLEO DL D- Meaning: Identifies a co-processing resource. If this
Cluster ResId DMIMO FD-1115 MIMO parameter is set to 255, no co-processing resource is
CLUST 05 Distribut specified for the cluster. This parameter applies only
ER TDLEO ed to LTE TDD.
MOD FD-1115 MIMO GUI Value Range: 0~12,255
DMIMO 0501 Intra- Unit: None
CLUST TDLEO BBU D-
ER Actual Value Range: 0~12,255
FD-1115 MIMO
LST 0502 Default Value: 255
D-
DMIMO TDLEO MIMO
CLUST FD-1115 by
ER 0504 Macro
TDLEO RRUs
FD-1115 D-
0505 MIMO
TDLEO Within a
FD-121 LampSit
501 e Cell
Inter-
eNodeB
DL D-
MIMO
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 85
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
DMIMO DMIMO ADD None None Meaning: Indicates the D-MIMO static cluster index.
ClusterC ClusterI DMIMO This parameter applies only to LTE TDD.
ell d CLUST GUI Value Range: 0~65535
ERCEL
L Unit: None
DSP Actual Value Range: 0~65535
DMIMO Default Value: None
CLUST
ERCEL
L
LST
DMIMO
CLUST
ERCEL
L
RMV
DMIMO
CLUST
ERCEL
L
DMIMO CellId ADD None None Meaning: Indicates the unique ID of a cell. The 28-bit
ClusterC DMIMO E-UTRAN cell identity is comprised of the cell ID
ell CLUST (represented by the least significant 8 bits) and the
ERCEL eNodeB ID. The cell global identity (CGI) of an E-
L UTRAN cell is comprised of the E-UTRAN cell
LST identity and the PLMN ID. For details, see 3GPP TS
DMIMO 36.413. This parameter applies only to LTE TDD
CLUST cells.
ERCEL GUI Value Range: 0~255
L Unit: None
RMV Actual Value Range: 0~255
DMIMO
CLUST Default Value: None
ERCEL
L
DSP
DMIMO
CLUST
ERCEL
L
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 86
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
DMIMO eNodeB ADD None None Meaning: Indicates the ID of an eNodeB. The 28-bit
ClusterC Id DMIMO E-UTRAN cell ID is comprised of the cell ID and the
ell CLUST eNodeB ID (represented by the most significant 20
ERCEL bits). The CGI of an E-UTRAN cell is comprised of
L the E-UTRAN cell ID and the PLMN ID. For details,
LST see 3GPP TS 36.413. This parameter applies only to
DMIMO LTE TDD.
CLUST GUI Value Range: 0~1048575
ERCEL Unit: None
L
Actual Value Range: 0~1048575
RMV
DMIMO Default Value: None
CLUST
ERCEL
L
DSP
DMIMO
CLUST
ERCEL
L
DMIMO Mcc ADD None None Meaning: Indicates the MCC of a D-MIMO cluster
ClusterC DMIMO cell. A PLMN ID is comprised of an MCC and an
ell CLUST MNC. The MCC consists of three digits. The MNC
ERCEL consists of two or three digits. For example, if the
L MCC is 123 and the MNC is 45, the PLMN ID is
LST 12345. This parameter applies only to LTE TDD.
DMIMO GUI Value Range: 3 characters
CLUST Unit: None
ERCEL
L Actual Value Range: 000~999
RMV Default Value: None
DMIMO
CLUST
ERCEL
L
DSP
DMIMO
CLUST
ERCEL
L
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 87
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
DMIMO Mnc ADD None None Meaning: Indicates the MNC of a D-MIMO cluster
ClusterC DMIMO cell. A PLMN ID is comprised of an MCC and an
ell CLUST MNC. The MCC consists of three digits. The MNC
ERCEL consists of two or three digits. For example, if the
L MCC is 123 and the MNC is 45, the PLMN ID is
LST 12345. This parameter applies only to LTE TDD.
DMIMO GUI Value Range: 2~3 characters
CLUST Unit: None
ERCEL
L Actual Value Range: 00~99,000~999
RMV Default Value: None
DMIMO
CLUST
ERCEL
L
DSP
DMIMO
CLUST
ERCEL
L
CellBfM InitialBf MOD TDLOF DL 2x2 Meaning: Indicates the beamforming and MIMO
imoPara MimoTy CELLB D-00100 MIMO mode used during initial network access. This
Cfg pe FMIMO 1 DL 4x4 parameter applies only to LTE TDD. When the
PARAC TDLOF MIMO CrsPortNum parameter in the Cell MO is set to
FG D-00106 CRS_PORT_4(4 ports) and the
Single BfMimoAdapWithTm4Switch parameter in the
LST 0 Streami
CELLB CellBfMimoParaCfg MO is set to ON(On), the value
TDLOF ng TM3(TM3) of this parameter does not take effect. If
FMIMO D-00104 Beamfor
PARAC this value is set in this case, TM2 is used as the
9 ming beamforming and MIMO mode during initial network
FG
TDLOF Dual access.
D-00106 Streami GUI Value Range: TM2(TM2), TM3(TM3)
1 ng
Beamfor Unit: None
ming Actual Value Range: TM2, TM3
Default Value: TM2(TM2)
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 88
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
CellBfM BfMimo MOD TDLOF DL 2x2 Meaning:
imoPara AdapWi CELLB D-00100 MIMO Indicates whether TM2 can be selected during
Cfg thoutTm FMIMO 1 DL 4x4 adaptation between beamforming and MIMO when
2 PARAC TDLOF MIMO the BfMimoAdaptiveSwitch parameter is set to
FG D-00106 MIMO_BF_ADAPTIVE. This parameter applies only
Single
LST 0 Streami to LTE TDD.
CELLB TDLOF ng
FMIMO If this parameter is set to ON and the
D-00104 Beamfor BfMimoAdaptiveSwitch parameter is set to
PARAC 9 ming
FG MIMO_BF_ADAPTIVE:
TDLOF Dual
D-00106 Streami 1. When the BfMimoAdapWithTm4Switch parameter
1 ng in the CellBfMimoParaCfg MO is set to OFF, TM3 is
Beamfor initially used for handovers in the cell, and then the
ming transmission mode is adaptively selected between
TM3 and TM7, between TM3 and TM8, or among
TM3, TM8, and TM9 based on the version of 3GPP
release that UEs comply with. If TM9 needs to be
adaptively selected, the TM9Switch option of the
EnhMIMOSwitch parameter must be selected.
2. When the BfMimoAdapWithTm4Switch parameter
in the CellBfMimoParaCfg MO is set to ON, TM4 is
initially used for handovers in the cell, and then the
transmission mode is adaptively selected among TM2,
TM4, and TM7, among TM2, TM4, and TM8, or
among TM2, TM4, TM7, and TM8 based on the
version of 3GPP release that UEs comply with.
If this parameter is set to OFF and the
BfMimoAdaptiveSwitch parameter is set to
MIMO_BF_ADAPTIVE:
1. When the BfMimoAdapWithTm4Switch parameter
in the CellBfMimoParaCfg MO is set to OFF, TM2 is
initially used for handovers in the cell, and then the
transmission mode is adaptively selected among TM2,
TM3, and TM7, among TM2, TM3, and TM8, or
among TM2, TM3, TM8, and TM9 based on the
version of 3GPP release that UEs comply with. If
TM9 needs to be adaptively selected, the TM9Switch
option of the EnhMIMOSwitch parameter must be
selected.
2. When the BfMimoAdapWithTm4Switch parameter
in the CellBfMimoParaCfg MO is set to ON, TM2 is
initially used for handovers in the cell, and then the
transmission mode is adaptively selected among TM2,
TM4, and TM7, among TM2, TM4, and TM8, or
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 89
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
among TM2, TM4, TM7, and TM8 based on the
version of 3GPP release that UEs comply with.
GUI Value Range: OFF(Off), ON(On)
Unit: None
Actual Value Range: OFF, ON
Default Value: OFF(Off)
CellPdc PdcchBf MOD TDLBF Physical Meaning: Indicates the PDCCH beamforming gain
chAlgo GainOff CELLP D-00200 Channel offset for D-MIMO cells when the PDCCH
set DCCHA 3 Manage aggregation level is selected based on coverage. If this
LGO TDLEO ment parameter is set to –127, optimization of PDCCH
LST FD-1115 DL D- beamforming gain offset is disabled. If this parameter
CELLP 05 MIMO is set to a value ranging from –10 to 10, optimization
DCCHA of PDCCH beamforming gain offset is enabled, and
TDLEO Distribut the offset is specified by this parameter. This
LGO FD-1115 ed parameter applies only to LTE TDD.
0501 MIMO
GUI Value Range: -127,-10~10
TDLEO Intra-
FD-1115 BBU D- Unit: None
0502 MIMO Actual Value Range: -127,-10~10
TDLEO D- Default Value: -127
FD-1115 MIMO
0504 by
TDLEO Macro
FD-1115 RRUs
0505 D-
TDLEO MIMO
FD-121 Within a
501 LampSit
e Cell
Inter-
eNodeB
DL D-
MIMO
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 90
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
CellBfM TmAcce MOD TDLOF DL 2x2 Meaning:
imoPara leration CELLB D-00100 MIMO Indicates whether to accelerate the determination of
Cfg Switch FMIMO 1 Single transmission mode switching for UEs when adaptation
PARAC TDLOF Streami between beamforming and MIMO is enabled. If this
FG D-00104 ng parameter is set to ON, the eNodeB adaptively
LST 9 Beamfor accelerates the determination of transmission mode
CELLB TDLOF ming switching for all UEs based on their signal quality. In
FMIMO D-00106 Dual this way, the spectral efficiency improves in scenarios
PARAC 1 Streami with traffic burst. If it is set to OFF, the acceleration
FG ng function is disabled. If it is set to
TDLAO INITIAL_ACCESS_TO_BF, the eNodeB accelerates
FD-081 Beamfor
ming the determination of the switching from MIMO to
409 beamforming during initial network access and
DL 4- accelerates the first update of the working RRU
Layer attribute of UEs after initial network access or
MIMO incoming handovers in D-MIMO or SFN scenarios.
Based
on TM9 This parameter applies only to LTE TDD.
GUI Value Range: OFF(OFF), ON(ON),
INITIAL_ACCESS_TO_BF(INITIAL_ACCESS_TO
_BF)
Unit: None
Actual Value Range: OFF, ON,
INITIAL_ACCESS_TO_BF
Default Value: OFF(OFF)
CellDlsc DlHigh MOD TDLOF Adaptiv Meaning: Indicates the offset to the high load isolation
hAlgo LoadSd CELLD D-00200 e SFN/ threshold in the downlink of an adaptive SFN cell.
maThdO LSCHA 8/ SDMA This parameter applies only to LTE FDD and LTE
ffset LGO LOFD-0 TDD.
LST 70205 GUI Value Range: -25~25
CELLD Unit: dB
LSCHA
LGO Actual Value Range: -25~25
Default Value: 0
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 91
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
SRSCfg SrsResO MOD TDLEO DL D- Meaning: Indicates whether to optimize SRS resource
ptSwitch SRSCF FD-1115 MIMO allocation for 2R access enhancement. If this
G 05 parameter is set to ON(On), quadruple code division
LST can be used for SRS resource allocation to enhance 2R
SRSCF access. If this parameter is set to OFF(Off), quadruple
G code division cannot be used for SRS resource
allocation to enhance 2R access. This parameter
applies only to LTE TDD.
GUI Value Range: OFF(Off), ON(On)
Unit: None
Actual Value Range: OFF, ON
Default Value: OFF(Off)
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 92
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
SRSCfg TddSrsC MOD TDLBF Physical Meaning: Indicates the SRS configuration for LTE
fgMode SRSCF D-00200 Channel TDD. If this parameter is set to ACCESS_FIRST, the
G 3 Manage SRS configuration designed to preferentially
LST TDLAO ment guarantee the number of accessed UEs and BHCA is
SRSCF FD-081 DL 4- used. If this parameter is set to
G 409 Layer EXPERIENCE_FIRST, the SRS configuration
MIMO designed to preferentially guarantee user experience
TDLEO (for example, beamforming performance) is used. If
FD-121 Based
on TM9 this parameter is set to EXPERIENCE_ENHANCED,
615 downlink experience improves compared with that
TDLOF DL obtained when this parameter is set to
D-00104 Flexible ACCESS_FIRST. If this parameter is set to
9 3D- ACCESS_ENHANCED, more UEs can access the
Beamfor network compared with that obtained when this
ming parameter is set to EXPERIENCE_ENHANCED. The
Single values EXPERIENCE_ENHANCED and
Streami ACCESS_ENHANCED are not supported by the
ng LBBPc. If this parameter is set to
Beamfor EXPERIENCE_ENHANCED or
ming ACCESS_ENHANCED for a cell established on an
LBBPc board, the value is automatically changed to
ACCESS_FIRST when this parameter takes effect.
This parameter applies only to LTE TDD.
GUI Value Range: ACCESS_FIRST(Access First),
EXPERIENCE_FIRST(Experience First),
EXPERIENCE_ENHANCED(Experience Enhanced),
ACCESS_ENHANCED(Access Enhanced)
Unit: None
Actual Value Range: ACCESS_FIRST,
EXPERIENCE_FIRST,
EXPERIENCE_ENHANCED,
ACCESS_ENHANCED
Default Value: ACCESS_ENHANCED(Access
Enhanced)
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 93
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
Cell MultiRr ADD LOFD-0 SFN Meaning: Indicates the type of the multi-RRU cell.
uCellMo CELL 03029/ Adaptiv GUI Value Range: SFN(SFN),
de MOD TDLOF e SFN/ CELL_COMBINATION(Cell Combination),
CELL D-00107 SDMA TWO_RRU_COMBINATION(TWO RRU
5 Combination), DIGITAL_COMBINATION(Cell
LST Inter-
CELL LOFD-0 BBP Digital Combination),
70205/ SFN MPRU_AGGREGATION(MPRU_AGGREGATION)
TDLOF Unit: None
D-00200 Inter-
8 eNodeB Actual Value Range: SFN, CELL_COMBINATION,
SFN TWO_RRU_COMBINATION,
TDLOF Based DIGITAL_COMBINATION,
D-00109 on MPRU_AGGREGATION
8 Coordin Default Value: SFN(SFN)
TDLOF ated
D-00108 eNodeB
0 Inter-
TDLOF BBP
D-00108 Adaptiv
1 e SFN/
TDLOF SDMA
D-00108 Inter-
2 eNodeB
Adaptiv
e SFN/
SDMA
Based
on
Coordin
ated
eNodeB
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 94
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
TASM MODE SET MRFD- BTS Meaning: Indicates the working mode of the system
CLKM 210501 Clock clock. Manual indicates that a clock source must be
ODE specified by the user. Auto indicates that the system
LBFD-0 Synchro automatically selects a clock source based on the
DSP 03005 nization priority and availability of the clock source. Free
CLKST
AT LBFD-0 Clock indicates that the system clock works in free-running
0300501 Source mode, that is, the system clock does not trace any
LST reference clock source.
LBFD-0 Switchin
CLKM
0300502 g GUI Value Range: AUTO(Auto), MANUAL(Manual),
ODE
LBFD-0 Manuall FREE(Free)
0300503 y or
Unit: None
Automat
LBFD-0 ically Actual Value Range: AUTO, MANUAL, FREE
0300504 Default Value: FREE(Free)
Free-
LBFD-0 running
0300505 Mode
LBFD-0
Synchro
0300506
nization
LOFD-0 with
03013 GPS
LOFD-0 Synchro
0301301 nization
LOFD-0 with
0301302 BITS
LOFD-0 Synchro
0301303 nization
LOFD-0 with
03023 1PPS
MRFD- Synchro
121117 nization
with
MRFD- E1/T1
121127
Enhance
MRFD-
d
121137
Synchro
MRFD- nization
121147
Synchro
MRFD- nization
121157 with
Ethernet
(ITU-T
G.8261)
IEEE15
88 V2
Clock
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 95
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
Synchro
nization
Clock
over IP
(Huawei
propriet
ary)
IEEE
1588v2
over
IPv6
Multi-
mode
BS
Commo
n
Referen
ce
Clock(G
BTS)
Multi-
mode
BS
Commo
n
Referen
ce
Clock(N
odeB)
Multi-
mode
BS
Commo
n
Referen
ce
Clock(e
NodeB)
Multi-
mode
BS
Commo
n
Referen
ce Clock
(LTE
TDD)
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 96
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 6 Parameters
MO Parame MML Feature Feature Description
ter ID Comma ID Name
nd
Multi-
mode
BS
Commo
n
Referen
ce
Clock(N
B-IoT)
TASM SYSCL SET WRFD- Uplink Meaning: Indicates the locked system clock source,
KSRC CLKSY 151207 CoMP which is obtained from the local standard clock or
NCMO (Joint interconnection system clock. The local standard
DE Receptio clock is a clock synchronized with the reference clock
DSP n) Based of the local NE or multimode base station. The
SYSCL on interconnection system clock is the standard clock
KSRC Coordin obtained from the interconnection port.
ated GUI Value Range: LOCAL(Local Standard Clock),
LST BBU
CLKSY INTER_SYSCLK(Interconnection System Clock)
NCMO Unit: None
DE Actual Value Range: LOCAL, INTER_SYSCLK
Default Value: LOCAL(Local Standard Clock)
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 97
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 7 Counters
7 Counters
Table 7-1 Counters
Counter ID Counter Name Counter Feature ID Feature Name
Description
1526742035 L.ChMeas.DMIMO Average number of Multi-mode: None Inter-BBP Adaptive
.1Layer.PRB PRBs that can be GSM: None SFN/SDMA
paired for D-MIMO
UMTS: None
LTE:
TDLOFD-001081
NR: None
1526742036 L.ChMeas.DMIMO Average number of Multi-mode: None Inter-BBP Adaptive
.2Layer.PairPRB PRBs paired for D- GSM: None SFN/SDMA
MIMO at layer 2
UMTS: None
LTE:
TDLOFD-001081
NR: None
1526742037 L.ChMeas.DMIMO Average number of Multi-mode: None Inter-BBP Adaptive
.3Layer.PairPRB PRBs paired for D- GSM: None SFN/SDMA
MIMO at layer 3
UMTS: None
LTE:
TDLOFD-001081
NR: None
1526742038 L.ChMeas.DMIMO Average number of Multi-mode: None Inter-BBP Adaptive
.4Layer.PairPRB PRBs paired for D- GSM: None SFN/SDMA
MIMO at layer 4
UMTS: None
LTE:
TDLOFD-001081
NR: None
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 98
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 7 Counters
Counter ID Counter Name Counter Feature ID Feature Name
Description
1526742039 L.ChMeas.DMIMO Average number of Multi-mode: None Inter-BBP Adaptive
.5Layer.PairPRB PRBs paired for D- GSM: None SFN/SDMA
MIMO at layer 5
UMTS: None
LTE:
TDLOFD-001081
NR: None
1526742040 L.ChMeas.DMIMO Average number of Multi-mode: None Inter-BBP Adaptive
.6Layer.PairPRB PRBs paired for D- GSM: None SFN/SDMA
MIMO at layer 6
UMTS: None
LTE:
TDLOFD-001081
NR: None
1526742041 L.ChMeas.DMIMO Average number of Multi-mode: None Inter-BBP Adaptive
.7Layer.PairPRB PRBs paired for D- GSM: None SFN/SDMA
MIMO at layer 7
UMTS: None
LTE:
TDLOFD-001081
NR: None
1526742042 L.ChMeas.DMIMO Average number of Multi-mode: None Inter-BBP Adaptive
.8Layer.PairPRB PRBs paired for D- GSM: None SFN/SDMA
MIMO at layer 8
UMTS: None
LTE:
TDLOFD-001081
NR: None
1526742043 L.ChMeas.DMIMO Number of D- Multi-mode: None Inter-BBP Adaptive
.JT.User.Avg MIMO JT UEs in GSM: None SFN/SDMA
the downlink
UMTS: None
LTE:
TDLOFD-001081
NR: None
1526742044 L.ChMeas.DMIMO Average number of Multi-mode: None Inter-BBP Adaptive
.JTUser.RRU.Avg working RRUs for GSM: None SFN/SDMA
D-MIMO JT UEs in
the downlink UMTS: None
LTE:
TDLOFD-001081
NR: None
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 99
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 7 Counters
Counter ID Counter Name Counter Feature ID Feature Name
Description
1526743758 L.Thrp.bits.UL.Bor Total uplink traffic Multi-mode: None SFN
derUE.JointRecepti volume of PDCP GSM: None Adaptive SFN/
on PDUs for joint SDMA
reception CEUs in a UMTS: None
cell LTE: Virtual 4T4R
LOFD-003029 SFN
LOFD-070205 Adaptive SFN/
LEOFD-111305 SDMA
TDLOFD-001075 Inter-BBP SFN
TDLOFD-002008 Inter-BBP Adaptive
SFN/SDMA
TDLOFD-001098
Inter-eNodeB SFN
TDLOFD-001081 Based on
TDLOFD-001080 Coordinated
TDLOFD-001082 eNodeB
TDLOFD-070227 Inter-eNodeB
Adaptive SFN/
TDLOFD-081221 SDMA Based on
TDLEOFD-111505 Coordinated
NR: None eNodeB
PDCCH DCS in
SFN
PDCCH SDMA in
SFN
DL D-MIMO
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 100
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 7 Counters
Counter ID Counter Name Counter Feature ID Feature Name
Description
1526743759 L.Thrp.bits.DL.Bor Total downlink Multi-mode: None SFN
derUE.JointTransmi traffic volume of GSM: None Adaptive SFN/
t PDCP SDUs for SDMA
joint transmission UMTS: None
CEUs in a cell LTE: Virtual 4T4R
LOFD-003029 SFN
LOFD-070205 Adaptive SFN/
LEOFD-111305 SDMA
TDLOFD-001075 Inter-BBP SFN
TDLOFD-002008 Inter-BBP Adaptive
SFN/SDMA
TDLOFD-001098
Inter-eNodeB SFN
TDLOFD-001081 Based on
TDLOFD-001080 Coordinated
TDLOFD-001082 eNodeB
TDLOFD-070227 Inter-eNodeB
Adaptive SFN/
TDLOFD-081221 SDMA Based on
TDLEOFD-111505 Coordinated
NR: None eNodeB
PDCCH DCS in
SFN
PDCCH SDMA in
SFN
DL D-MIMO
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 101
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 7 Counters
Counter ID Counter Name Counter Feature ID Feature Name
Description
1526743760 L.Thrp.bits.UL.Sma Traffic volume of Multi-mode: None SFN
llPkt.BorderUE.Joi PDCP PDUs GSM: None Adaptive SFN/
ntReception scheduled for SDMA
uplink small UMTS: None
packets for joint LTE: Virtual 4T4R
reception CEUs in a LOFD-003029 SFN
cell LOFD-070205 Adaptive SFN/
LEOFD-111305 SDMA
TDLOFD-001075 Inter-BBP SFN
TDLOFD-002008 Inter-BBP Adaptive
SFN/SDMA
TDLOFD-001098
Inter-eNodeB SFN
TDLOFD-001081 Based on
TDLOFD-001080 Coordinated
TDLOFD-001082 eNodeB
TDLOFD-070227 Inter-eNodeB
Adaptive SFN/
TDLOFD-081221 SDMA Based on
TDLEOFD-111505 Coordinated
NR: None eNodeB
PDCCH DCS in
SFN
PDCCH SDMA in
SFN
DL D-MIMO
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 102
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 7 Counters
Counter ID Counter Name Counter Feature ID Feature Name
Description
1526743761 L.Thrp.Time.UL.R Duration of Multi-mode: None SFN
mvSmallPkt.Border transmitting uplink GSM: None Adaptive SFN/
UE.JointReception data except small SDMA
packets for joint UMTS: None
reception CEUs in a LTE: Virtual 4T4R
cell LOFD-003029 SFN
LOFD-070205 Adaptive SFN/
LEOFD-111305 SDMA
TDLOFD-001075 Inter-BBP SFN
TDLOFD-002008 Inter-BBP Adaptive
SFN/SDMA
TDLOFD-001098
Inter-eNodeB SFN
TDLOFD-001081 Based on
TDLOFD-001080 Coordinated
TDLOFD-001082 eNodeB
TDLOFD-070227 Inter-eNodeB
Adaptive SFN/
TDLOFD-081221 SDMA Based on
TDLEOFD-111505 Coordinated
NR: None eNodeB
PDCCH DCS in
SFN
PDCCH SDMA in
SFN
DL D-MIMO
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 103
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 7 Counters
Counter ID Counter Name Counter Feature ID Feature Name
Description
1526743762 L.Thrp.bits.DL.Last Downlink traffic Multi-mode: None SFN
TTI.BorderUE.Joint volume of PDCP GSM: None Adaptive SFN/
Transmit SDUs sent in the SDMA
last TTI before the UMTS: None
buffer of the UE is LTE: Virtual 4T4R
empty for joint LOFD-003029 SFN
transmission CEUs LOFD-070205 Adaptive SFN/
in a cell SDMA
LEOFD-111305
TDLOFD-001075 Inter-BBP SFN
TDLOFD-002008 Inter-BBP Adaptive
SFN/SDMA
TDLOFD-001098
Inter-eNodeB SFN
TDLOFD-001081 Based on
TDLOFD-001080 Coordinated
TDLOFD-001082 eNodeB
TDLOFD-070227 Inter-eNodeB
Adaptive SFN/
TDLOFD-081221 SDMA Based on
TDLEOFD-111505 Coordinated
NR: None eNodeB
PDCCH DCS in
SFN
PDCCH SDMA in
SFN
DL D-MIMO
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 104
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 7 Counters
Counter ID Counter Name Counter Feature ID Feature Name
Description
1526743763 L.Thrp.Time.DL.R Duration of Multi-mode: None SFN
mvLastTTI.Border transmitting data GSM: None Adaptive SFN/
UE.JointTransmit for joint SDMA
transmission CEUs UMTS: None
in a cell except the LTE: Virtual 4T4R
last TTI before the LOFD-003029 SFN
downlink buffer of LOFD-070205 Adaptive SFN/
the UE is empty SDMA
LEOFD-111305
TDLOFD-001075 Inter-BBP SFN
TDLOFD-002008 Inter-BBP Adaptive
SFN/SDMA
TDLOFD-001098
Inter-eNodeB SFN
TDLOFD-001081 Based on
TDLOFD-001080 Coordinated
TDLOFD-001082 eNodeB
TDLOFD-070227 Inter-eNodeB
Adaptive SFN/
TDLOFD-081221 SDMA Based on
TDLEOFD-111505 Coordinated
NR: None eNodeB
PDCCH DCS in
SFN
PDCCH SDMA in
SFN
DL D-MIMO
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 105
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 7 Counters
Counter ID Counter Name Counter Feature ID Feature Name
Description
1526743764 L.Thrp.Time.UL.Bo Total duration of Multi-mode: None SFN
rderUE.JointRecept receiving PDCP GSM: None Adaptive SFN/
ion PDUs from joint SDMA
reception CEUs in a UMTS: None
cell LTE: Virtual 4T4R
LOFD-003029 SFN
LOFD-070205 Adaptive SFN/
LEOFD-111305 SDMA
TDLOFD-001075 Inter-BBP SFN
TDLOFD-002008 Inter-BBP Adaptive
SFN/SDMA
TDLOFD-001098
Inter-eNodeB SFN
TDLOFD-001081 Based on
TDLOFD-001080 Coordinated
TDLOFD-001082 eNodeB
TDLOFD-070227 Inter-eNodeB
Adaptive SFN/
TDLOFD-081221 SDMA Based on
TDLEOFD-111505 Coordinated
NR: None eNodeB
PDCCH DCS in
SFN
PDCCH SDMA in
SFN
DL D-MIMO
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 106
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 7 Counters
Counter ID Counter Name Counter Feature ID Feature Name
Description
1526743765 L.Thrp.Time.DL.Bo Total duration of Multi-mode: None SFN
rderUE.JointTrans sending PDCP GSM: None Adaptive SFN/
mit SDUs to joint SDMA
transmission CEUs UMTS: None
in a cell LTE: Virtual 4T4R
LOFD-003029 SFN
LOFD-070205 Adaptive SFN/
LEOFD-111305 SDMA
TDLOFD-001075 Inter-BBP SFN
TDLOFD-002008 Inter-BBP Adaptive
SFN/SDMA
TDLOFD-001098
Inter-eNodeB SFN
TDLOFD-001081 Based on
TDLOFD-001080 Coordinated
TDLOFD-001082 eNodeB
TDLOFD-070227 Inter-eNodeB
Adaptive SFN/
TDLOFD-081221 SDMA Based on
TDLEOFD-111505 Coordinated
NR: None eNodeB
PDCCH DCS in
SFN
PDCCH SDMA in
SFN
DL D-MIMO
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 107
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 7 Counters
Counter ID Counter Name Counter Feature ID Feature Name
Description
1526743766 L.ChMeas.PRB.PU Average number of Multi-mode: None SFN
SCH.Avg.BorderU PRBs used by the GSM: None Adaptive SFN/
E.JointReception PUSCH for joint SDMA
reception CEUs in a UMTS: None
cell LTE: Virtual 4T4R
LOFD-003029 SFN
LOFD-070205 Adaptive SFN/
LEOFD-111305 SDMA
TDLOFD-001075 Inter-BBP SFN
TDLOFD-002008 Inter-BBP Adaptive
SFN/SDMA
TDLOFD-001098
Inter-eNodeB SFN
TDLOFD-001081 Based on
TDLOFD-001080 Coordinated
TDLOFD-001082 eNodeB
TDLOFD-070227 Inter-eNodeB
Adaptive SFN/
TDLOFD-081221 SDMA Based on
TDLEOFD-111505 Coordinated
NR: None eNodeB
PDCCH DCS in
SFN
PDCCH SDMA in
SFN
DL D-MIMO
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 108
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 7 Counters
Counter ID Counter Name Counter Feature ID Feature Name
Description
1526743767 L.ChMeas.PRB.PD Average number of Multi-mode: None SFN
SCH.Avg.BorderU PRBs used by the GSM: None Adaptive SFN/
E.JointTransmit PDSCH for joint SDMA
transmission CEUs UMTS: None
in a cell LTE: Virtual 4T4R
LOFD-003029 SFN
LOFD-070205 Adaptive SFN/
LEOFD-111305 SDMA
TDLOFD-001075 Inter-BBP SFN
TDLOFD-002008 Inter-BBP Adaptive
SFN/SDMA
TDLOFD-001098
Inter-eNodeB SFN
TDLOFD-001081 Based on
TDLOFD-001080 Coordinated
TDLOFD-001082 eNodeB
TDLOFD-070227 Inter-eNodeB
Adaptive SFN/
TDLOFD-081221 SDMA Based on
TDLEOFD-111505 Coordinated
NR: None eNodeB
PDCCH DCS in
SFN
PDCCH SDMA in
SFN
DL D-MIMO
1526745707 L.ChMeas.DL.Succ Number of TTIs Multi-mode: None MU-Beamforming
.Pair.TTI during which UEs GSM: None DL 4-Layer MU-
are successfully Beamforming
paired in the UMTS: None
downlink LTE: DL 8-Layer MU-
TDLOFD-001077 Beamforming
TDLOFD-110221 DL 16-Layer MU-
Beamforming
TDLEOFD-121604
DL D-MIMO
TDLEOFD-121605
Inter-eNodeB DL
TDLEOFD-111505 D-MIMO
TDLEOFD-121501 Inter-Cell DL D-
TDLEOFD-130501 MIMO
NR: None
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 109
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 7 Counters
Counter ID Counter Name Counter Feature ID Feature Name
Description
1526746695 L.Traffic.User.CoM Maximum number Multi-mode: None Inter-Cell DL D-
easSRS.Max of UEs performing GSM: None MIMO
coordinated SRS
measurement for a UMTS: None
cell LTE:
TDLEOFD-130501
NR: None
1526746766 L.CellSectorEqpt.U Duration in which None None
NA.Dur.Cali the channel
calibration function
for a set of cell
sector equipment is
unavailable
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 110
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 8 Glossary
8 Glossary
For the acronyms, abbreviations, terms, and definitions, see Glossary.
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 111
eRAN
D-MIMO (TDD) Feature Parameter Description 9 Reference Documents
9 Reference Documents
1. SFN
2. Energy Conservation and Emission Reduction
3. Beamforming (TDD)
4. DRX and Signaling Control
5. Extended CP
6. High Speed Mobility
7. Relay
8. Massive MIMO (TDD)
9. Scheduling
10. Uplink Coordinated Scheduling
11. Carrier Aggregation
12. RAN Sharing
13. Dynamic Power Sharing Between LTE Carriers
14. 3900 & 5900 Series Base Station Initial Configuration Guide
15. USU3900 Product Documentation
16. USU3910 Product Documentation
17. MIMO
18. DBS3900 LampSite Hardware Description
19. DBS5900 LampSite Hardware Description
20. Cloud BB Overview
21. USU3900-based Multi-BBU Interconnection
22. USU3910-based Multi-BBU Interconnection
Issue 04 (2018-11-07) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 112
Вам также может понравиться
- Affidavit of Undertaking - TransferДокумент2 страницыAffidavit of Undertaking - TransferGracelyn Enriquez Bellingan100% (2)
- Video Accelerator (RAN19.0 - Draft A)Документ46 страницVideo Accelerator (RAN19.0 - Draft A)Abdel SbeitiОценок пока нет
- DL CoMP (eRAN12.1 - 02)Документ57 страницDL CoMP (eRAN12.1 - 02)CosminDОценок пока нет
- PDSCH Power Configuration Tool V1 4 Optimization Enhanced Version English Dec15 7Документ12 страницPDSCH Power Configuration Tool V1 4 Optimization Enhanced Version English Dec15 7Shashank PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Huawei Lampsite Solution Overview 01Документ10 страницHuawei Lampsite Solution Overview 01Roberto TRОценок пока нет
- Drive Test Analysis 1Документ16 страницDrive Test Analysis 1Shashank PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Intelligent 5g l2 Mac Scheduler Powered by Capgemini Netanticipate 5g On Intel Architecture v13Документ17 страницIntelligent 5g l2 Mac Scheduler Powered by Capgemini Netanticipate 5g On Intel Architecture v13b prashanthОценок пока нет
- Piping Latest Aramco QuestionsДокумент2 страницыPiping Latest Aramco Questionschandu666creator0% (1)
- Wholesale (TDD) (eRAN15.1 - 01) PDFДокумент63 страницыWholesale (TDD) (eRAN15.1 - 01) PDFFaizal JamaludeenОценок пока нет
- Beam Management (5G RAN3.1 - 02)Документ49 страницBeam Management (5G RAN3.1 - 02)VVL100% (1)
- Huawei U2000 Data Collection - UpdateДокумент54 страницыHuawei U2000 Data Collection - UpdateShashank Prajapati0% (1)
- Mimo (FDD) (5g Ran6.1 - Draft A)Документ54 страницыMimo (FDD) (5g Ran6.1 - Draft A)VVLОценок пока нет
- Uplink Interference Cancellation (ERAN12.1 - 06)Документ42 страницыUplink Interference Cancellation (ERAN12.1 - 06)waelq2003Оценок пока нет
- Capacity Dimensioning For 5G Mobile Heterogeneous NetworksДокумент164 страницыCapacity Dimensioning For 5G Mobile Heterogeneous NetworksCarlosRivasОценок пока нет
- 10q Poster LH EnglishДокумент1 страница10q Poster LH EnglishTri Sumadya Aditya100% (1)
- TCSP10403R0Документ30 страницTCSP10403R0BADRI VENKATESHОценок пока нет
- Huawei SingleRAN Hardware Roadmap (2016Q4)Документ44 страницыHuawei SingleRAN Hardware Roadmap (2016Q4)MiradoniainaRakotoarimananaОценок пока нет
- Anr (5g Ran6.1 - Draft A)Документ105 страницAnr (5g Ran6.1 - Draft A)VVLОценок пока нет
- NG and XN Self-Management (5G RAN3.1 - Draft A) PDFДокумент83 страницыNG and XN Self-Management (5G RAN3.1 - Draft A) PDFVVL1959Оценок пока нет
- FAQ - 5G NR Carrier Bandwidth Part BWPДокумент15 страницFAQ - 5G NR Carrier Bandwidth Part BWPmohamed fadlОценок пока нет
- GasesДокумент102 страницыGasesLya EscoteОценок пока нет
- Uplink Experience Intelligent Acceleration (ERAN16.1 - 01)Документ27 страницUplink Experience Intelligent Acceleration (ERAN16.1 - 01)monem777Оценок пока нет
- CPRI Compression (5G RAN6.1 - Draft A)Документ41 страницаCPRI Compression (5G RAN6.1 - Draft A)VVLОценок пока нет
- Access Class Control (eRAN15.1 - 01) PDFДокумент57 страницAccess Class Control (eRAN15.1 - 01) PDFwaelq2003Оценок пока нет
- Dynamic Power Sharing Between LTE Carriers (ERAN16.1 - 03)Документ52 страницыDynamic Power Sharing Between LTE Carriers (ERAN16.1 - 03)VVLОценок пока нет
- Requirements For Pressure Vessel Basic Engineering DesignДокумент6 страницRequirements For Pressure Vessel Basic Engineering DesignLDM Man. e Mont. Ind. EIRELIОценок пока нет
- VoLTE and ViLTE: Voice and Conversational Video Services over the 4G Mobile NetworkОт EverandVoLTE and ViLTE: Voice and Conversational Video Services over the 4G Mobile NetworkОценок пока нет
- LTE FDD and NR Spectrum Sharing (SRAN18.1 - Draft A)Документ228 страницLTE FDD and NR Spectrum Sharing (SRAN18.1 - Draft A)VVLОценок пока нет
- Uplink Interference Cancellation (FDD) (ERAN18.1 - 01)Документ28 страницUplink Interference Cancellation (FDD) (ERAN18.1 - 01)monem777Оценок пока нет
- NB-IoT Radio and Performance Basics (ERAN12.1 - 05)Документ435 страницNB-IoT Radio and Performance Basics (ERAN12.1 - 05)CosminD100% (3)
- MIMO (eRAN13.1 02)Документ274 страницыMIMO (eRAN13.1 02)Shashank PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Comp (Low-Frequency TDD) (5g Ran3.1 - 02)Документ37 страницComp (Low-Frequency TDD) (5g Ran3.1 - 02)VVLОценок пока нет
- WTTX (5G RAN3.1 - Draft A) PDFДокумент19 страницWTTX (5G RAN3.1 - Draft A) PDFVVL1959Оценок пока нет
- Comp (5g Ran6.1 - Draft A)Документ68 страницComp (5g Ran6.1 - Draft A)VVLОценок пока нет
- Interference Avoidance (5G RAN6.1 - Draft A)Документ57 страницInterference Avoidance (5G RAN6.1 - Draft A)VVL100% (1)
- DRX (5G Ran3.1 - 02)Документ40 страницDRX (5G Ran3.1 - 02)VVLОценок пока нет
- 5G RAN3.1 Basic Feature DescriptionДокумент93 страницы5G RAN3.1 Basic Feature DescriptionDawood MayarОценок пока нет
- Cell Combination (5G RAN6.1 - 02)Документ60 страницCell Combination (5G RAN6.1 - 02)VVL1959Оценок пока нет
- Massive MIMO (FDD) (eRAN13.1 - 05)Документ154 страницыMassive MIMO (FDD) (eRAN13.1 - 05)Shashank Prajapati100% (2)
- Energy Conservation and Emission Reduction (5G RAN3.1 - 01)Документ100 страницEnergy Conservation and Emission Reduction (5G RAN3.1 - 01)VVLОценок пока нет
- Guide To Features (5G RAN2.1 - Draft B)Документ12 страницGuide To Features (5G RAN2.1 - Draft B)Mohammed Mokhtar50% (2)
- Configuration Management (SRAN16.1 01)Документ22 страницыConfiguration Management (SRAN16.1 01)VVLОценок пока нет
- eCPRI V 1 0 2017 08 22Документ15 страницeCPRI V 1 0 2017 08 22Nguyễn Trọng CôngОценок пока нет
- LTE eRAN2.1 Power Control Feature: Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without PermissionДокумент39 страницLTE eRAN2.1 Power Control Feature: Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without PermissionAhmed GamalОценок пока нет
- Beamforming Overview DL and UL Beamforming Performance ConclusionsДокумент37 страницBeamforming Overview DL and UL Beamforming Performance ConclusionsAhed AlhamadeenОценок пока нет
- CPRI MUX (LampSite) (SRAN16.1 - 01)Документ73 страницыCPRI MUX (LampSite) (SRAN16.1 - 01)VVLОценок пока нет
- 1-5 BTS Hardware Quality Standard-20120922-EMTS Project TrainingДокумент97 страниц1-5 BTS Hardware Quality Standard-20120922-EMTS Project Trainingengr_dandayo1Оценок пока нет
- Lte L2 RLC MacДокумент113 страницLte L2 RLC MacShashank PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- CPRI Compression (5G RAN2.1 - 02)Документ30 страницCPRI Compression (5G RAN2.1 - 02)waelq200350% (2)
- DRX (5g Ran6.1 - Draft A)Документ51 страницаDRX (5g Ran6.1 - Draft A)VVLОценок пока нет
- 2023-Nokia 5G EvolutionДокумент109 страниц2023-Nokia 5G EvolutionJОценок пока нет
- Neutral Host Models in 4G & 5G Architecture: Dr. Wenbing Yao VP, Business Development & PartnershipsДокумент17 страницNeutral Host Models in 4G & 5G Architecture: Dr. Wenbing Yao VP, Business Development & PartnershipscopslockОценок пока нет
- Coordinated Interference Management (Low-Frequency TDD) (5G RAN6.1 - Draft A)Документ28 страницCoordinated Interference Management (Low-Frequency TDD) (5G RAN6.1 - Draft A)VVLОценок пока нет
- EXn Self-Management (5G RAN6.1 - Draft A)Документ42 страницыEXn Self-Management (5G RAN6.1 - Draft A)VVLОценок пока нет
- CPRI Compression (5G RAN3.1 - 02)Документ35 страницCPRI Compression (5G RAN3.1 - 02)VVLОценок пока нет
- Keysight 5G Field Measurements Feb2019Документ38 страницKeysight 5G Field Measurements Feb2019NenadОценок пока нет
- Hyper Cell (5G RAN3.1 - Draft A)Документ25 страницHyper Cell (5G RAN3.1 - Draft A)VVL1959100% (1)
- 00-Guide To Features (5G RAN6.1 - Draft A)Документ23 страницы00-Guide To Features (5G RAN6.1 - Draft A)VVL100% (1)
- 5G Basic Service Capabilities and ApplicationsДокумент92 страницы5G Basic Service Capabilities and ApplicationsTiago SouzaОценок пока нет
- SRAN SolutionДокумент38 страницSRAN SolutionMochamad Guntur Hady PutraОценок пока нет
- Cell Combination (5G RAN6.1 - Draft A)Документ67 страницCell Combination (5G RAN6.1 - Draft A)VVLОценок пока нет
- Radio Security (5G RAN3.1 - Draft A)Документ56 страницRadio Security (5G RAN3.1 - Draft A)VVL1959100% (1)
- Huawei NodeB Data ConfigurationДокумент57 страницHuawei NodeB Data Configurationอะไรๆก็เรา ทั้งเพ100% (3)
- 5G RAN Capacity Management Guide (V100R016C10 - 01) (PDF) - ENДокумент22 страницы5G RAN Capacity Management Guide (V100R016C10 - 01) (PDF) - ENMohammed ShakilОценок пока нет
- 3.5 GHZ 5G TDD SynchronisationДокумент20 страниц3.5 GHZ 5G TDD SynchronisationjuliosantanaОценок пока нет
- Parameter DescriptionДокумент769 страницParameter DescriptionShashank Prajapati100% (1)
- 5G RAN3.1 Trial Feature Description PDFДокумент17 страниц5G RAN3.1 Trial Feature Description PDFchowdary100% (1)
- DRX and Signaling Control (eRAN12.1 - 03) PDFДокумент189 страницDRX and Signaling Control (eRAN12.1 - 03) PDFKhin Nyein ThuОценок пока нет
- SRAN13.1&15.0 NSA Networking Based On EPC-20180905Документ24 страницыSRAN13.1&15.0 NSA Networking Based On EPC-20180905Mohammed Babar Ahmed100% (2)
- 5G Link Budget: Best Partner For InnovationДокумент6 страниц5G Link Budget: Best Partner For InnovationSpam SpamОценок пока нет
- B2H (5G Ran2.1 - 01)Документ15 страницB2H (5G Ran2.1 - 01)VVL1959Оценок пока нет
- L2, L3 Protocol Testing Training in Chennai PDFДокумент2 страницыL2, L3 Protocol Testing Training in Chennai PDFShashank PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- SOS MobilityДокумент35 страницSOS MobilityShashank Prajapati100% (1)
- Invoice 20170731 Sheet1Документ1 страницаInvoice 20170731 Sheet1Shashank PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- 2G Short Call Dropped Cause 16Документ4 страницы2G Short Call Dropped Cause 16Shashank PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Query - R 2.0 4G Perfomance - PCI RETUNE - HourlyДокумент215 страницQuery - R 2.0 4G Perfomance - PCI RETUNE - HourlyShashank PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Handover GSMДокумент33 страницыHandover GSMShashank Prajapati0% (1)
- Implemented 3G Cells So FarДокумент4 страницыImplemented 3G Cells So FarShashank PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- LTE Worst Cell ListДокумент5 страницLTE Worst Cell ListShashank PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Sept ExtSCДокумент10 страницSept ExtSCShashank PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Analysis Report On KPI DegradeДокумент6 страницAnalysis Report On KPI DegradeShashank PrajapatiОценок пока нет
- Office Automation & Attendance System Using IoTДокумент4 страницыOffice Automation & Attendance System Using IoTAnonymous kw8Yrp0R5rОценок пока нет
- Google Assistant Home Automation CodeДокумент3 страницыGoogle Assistant Home Automation CodeStjepan BartolovićОценок пока нет
- 14 Fine Tuned Assembly LineДокумент4 страницы14 Fine Tuned Assembly LineSadhish KannanОценок пока нет
- VSL 2024 Course List and Loan Caps (Students)Документ14 страницVSL 2024 Course List and Loan Caps (Students)ashishkumar777Оценок пока нет
- 02 February 1990Документ108 страниц02 February 1990Monitoring TimesОценок пока нет
- Jeppesen Charts LegendsДокумент34 страницыJeppesen Charts LegendsFatih OguzОценок пока нет
- Single Phase Induction MotorДокумент5 страницSingle Phase Induction MotorSridhar SridharОценок пока нет
- Manual de Parts ES16D6Документ36 страницManual de Parts ES16D6Eduardo CortezОценок пока нет
- BME Joining ProcessesДокумент11 страницBME Joining ProcessesalysonmicheaalaОценок пока нет
- DLP Sample Detailed Lesson PlanДокумент4 страницыDLP Sample Detailed Lesson PlanJaydie PalОценок пока нет
- IBM Flex System p270 Compute Node Planning and Implementation GuideДокумент630 страницIBM Flex System p270 Compute Node Planning and Implementation GuideAnonymous Qvouxg2aОценок пока нет
- KNS2163 Week1Документ32 страницыKNS2163 Week1Nurul QurratuОценок пока нет
- Co Linear Antenna DesignДокумент2 страницыCo Linear Antenna DesignAhmed JafarОценок пока нет
- Experiment 1Документ5 страницExperiment 1Cheng BauzonОценок пока нет
- Specification For Piping MaterialДокумент9 страницSpecification For Piping MaterialAgus SupriadiОценок пока нет
- CSC204 - Chapter 3.1Документ30 страницCSC204 - Chapter 3.1Alif HaiqalОценок пока нет
- ColorCells CC784 ProgrammingGuideДокумент20 страницColorCells CC784 ProgrammingGuideTom SteinhauerОценок пока нет
- Overall EWD Vehicle Exterior Rear Fog LightДокумент10 страницOverall EWD Vehicle Exterior Rear Fog Lightgabrielzinho43Оценок пока нет
- Int. J. Miner. Process.: Emin Cafer CilekДокумент10 страницInt. J. Miner. Process.: Emin Cafer CilekJose Patricio VelardeОценок пока нет
- Voice Recognition Using MatlabДокумент10 страницVoice Recognition Using MatlabSneha Muralidharan100% (1)
- TIOut Brickwork 1Документ4 страницыTIOut Brickwork 1kevin smithОценок пока нет
- GRE Sentence CompletionДокумент3 страницыGRE Sentence Completionapi-3699142Оценок пока нет
- QUBEДокумент2 страницыQUBEJován MéridaОценок пока нет
- CAL-ST-070!17!01 Rev01 Shipping Saddles CalculationДокумент11 страницCAL-ST-070!17!01 Rev01 Shipping Saddles CalculationgiubelloОценок пока нет