Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
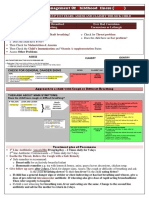
A Forecast On The Textile Processing Industry in 21C
Загружено:
huyngИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
A Forecast On The Textile Processing Industry in 21C
Загружено:
huyngАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
A forecast on the textile processing industry in 21C 1.Classification of fib...dification technology - IS Co., Ltd. Senshoku Keizai Shimbun textileinfo.
com
Search pages from texitileinfo Google Search
A forecast on the textile processing industry in 21C
Editor of textileinfo
Technology IS Co., Ltd.
Contents 1.Classification of fiber surface modification technology
A forecast on the
textile processing Many kinds of functional finishes are increasingly processed in Japanese textile
industry in 21C industries. The aim of these finishes is to produce textiles which are comfortable
1. Classification of for the consumer. Such functional finishes to realize comfort are divided into
fiber surface two categories, that is “Physically based technology” and “Chemically based
modification technology”.
technology
2. Functional finish
Recently, the number of developments in physically based technology, which
to make textile
can harmonize the environment and production, have increased because
like human skin
regulations on chemical substances have become stricter.
3. Design of fabrics
for functional
At present, although chemically based technology is still major, its combination
finishes
with physically based technology is steadily increasing (Figure-1).
4. Functional finish
and new
Figure-1 Classification of fiber surface modification technology1)
technology in
future
One example of physically based technology, which is not included in Figure-1,
is the shrink proofing of wool without using chlorine. This new technology was
developed first in the world by the wool department of Kurabo (Japan) and
commercialized under the name of ECO-WASH 21. This technology adopts
special ozone treatment instead of chlorine treatment, and was developed on
the supposition that regulations on chlorine use would become globally stricter
(Photo-1).
Prof.Inagaki in the Faculty of Engineering of Shizuoka Univ. (Japan)is also
http://textileinfo.com/en/tech/21c/01.html (1 of 3)12/22/2006 6:12:42 PM
A forecast on the textile processing industry in 21C 1.Classification of fib...dification technology - IS Co., Ltd. Senshoku Keizai Shimbun textileinfo.com
working on the shrink proofing of wool employing low temperature plasma2).
Prof. Takagishi in Tokyo Kasei Univ. is studying the same theme using
potassium hydrogen persulfate (PMS) and Keratinase (enzyme for hydrolysis of
keratin), and evaluating the dyeing behavior of the treated wool3).
Photo-1 Comparison of the surface of wool (electron microscope)
The reason for the increase in such research is that strict controls have started
to be imposed on the amounts used of halogens, such as fluorine, chlorine,
bromine and iodine.
HBCD (hexabromocyclododecane), a flame retardant has proved to be toxic,
and its use is carefully controlled.
Although the flame retardant effect of DBDE is expected to be higher by
incorporating antimony trioxide, recently the generation of highly toxic dioxins
has been confirmed, thus the regulation of those chemicals has become stricter.
At present, flame retardants are widely applied to curtains and flags etc., and
recently new flame retardants for polyester fiber based on phosphates have
been developed to solve this problem.
As a topic in Japan, the generation of dioxins in the bleaching process in the
pulp industry is confirmed, although the situation is different in the bleaching of
cotton. Thus, in Japanese dyehouses, they check the content of AOX and
halomethane in their effluent, and some are employing further treatment such
as activated carbon. But it pushes the costs up so much that new technology
which uses light irradiation for cotton bleaching is progressing.
The organizations who are studying this technology are Sangyo Sougo
Kenkyusho (Japan) and Nisshinbo. They are making joint efforts to accelerate
the research. Their work named “light bleaching” aims to make only the colored
http://textileinfo.com/en/tech/21c/01.html (2 of 3)12/22/2006 6:12:42 PM
A forecast on the textile processing industry in 21C 1.Classification of fib...dification technology - IS Co., Ltd. Senshoku Keizai Shimbun textileinfo.com
contamination absorb the light and activate it then to react with rather mild
chemicals to decompose the color at room temperature4).
The special feature of this method is that the cellulose itself can be bleached
with almost no damage. For bulk production, a new pilot plant was installed,
and tests for commercialization have been continuing. We are expecting
successful results for light irradiation bleaching based on physical technology,
because the state of bleached cotton influences the effectiveness of functional
finishing.
The above-mentioned research is the ultimate example of “the harmonization of
the environment and production” although research along that course is also
increasing. The research forwards the establishment of ultimate new technology
can be helpful indeed, in the establishment of that new technology.
Reference
1)K.Joukou: presented in the discussion at Japan Dyers’ Association meeting
2-4)From the annual meeting of The Society of Fiber Science and Technology,
Japan 2005
Copyright (c) 1999-2006, IS Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved. net@textileinfo.com
No reproduction or republication without written permission.
http://textileinfo.com/en/tech/21c/01.html (3 of 3)12/22/2006 6:12:42 PM
A forecast on the textile processing industry in 21C 2.Functional finish to ...xtile like human skin - IS Co., Ltd. Senshoku Keizai Shimbun textileinfo.com
Search pages from texitileinfo Google Search
A forecast on the textile processing industry in 21C
Editor of textileinfo
Technology IS Co., Ltd.
Contents 2.Functional finish to make textile like human skin
A forecast on the
textile processing In Japan, functional finishes to textiles for apparel and technical use are
industry in 21C increasing, and the requirement for apparel use is the sensitivity and the
1. Classification of compatibility to surrounding circumstances.
fiber surface
modification
The human skin has moisture absorbency and repellency to water, oil and
technology
soiling, and release them easily. To give such performance to the textiles is a
2. Functional finish strong research sector for Japanese technical experts.
to make textile
like human skin
Reviewing the history of the development of functional finishes on textiles in
3. Design of fabrics Japan, we have cultivated the advantages and covered the disadvantages of
for functional natural and synthetic fibers to meet the customers’ needs. One of the defects of
finishes 100% cotton woven fabric is a high tendency to crease, then its blends with
4. Functional finish washable polyester were developed competing with overseas textile
and new manufactures.
technology in
future Since 1945, wash and wear finish and permanent press finish for preventing
creasing in cotton woven fabrics has become popular, but these technologies
were first developed in the US. However, shape stabilizing finishes on cotton
developed in Japan are globally accepted in the apparel industry.
On the other hand, new synthetic fibers which give the advantages of natural
fibers, such as good hand, appearance and water and sweat absorbency, have
been progressively developed, still keeping their inherent properties.
One of the examples is called “Bionature” developed by Kurabo (Japan). This
fiber consists of hydrolysable/biodegradable polyester, and its characteristic is
beyond the classification between natural and synthetic fibers. This fiber has
been put on sale for 2006 Spring/Summer apparel.
Bionature is made from “Biomax” hydrolysable/biodegradable polyester resin
(Du Pont) and can be blended with cotton or wool to produce polyester/cotton
or polyester/wool environment-friendly textiles. This may be a profound
collaboration of ideas both from DuPont and Kurabo.
This technology belongs to a chemically based one.
▽ Characteristics of Bionature
http://textileinfo.com/en/tech/21c/02.html (1 of 3)12/22/2006 6:12:56 PM
A forecast on the textile processing industry in 21C 2.Functional finish to ...xtile like human skin - IS Co., Ltd. Senshoku Keizai Shimbun textileinfo.com
・ hydrolysable/biodegradable properties
Bionature can be gradually biodegraded through hydrolysis, where sufficient
water, temperature (warmth) and microorganisms exist, and finally produce
water and carbon dioxide. The rate of degradation is very slow and has no
adverse effect on the environment.
・ Inflammability
The amount of carbon dioxide generated from incineration of Bionature is
less than that of other fibers, and the heat of incineration is also less, that
means a lesser burden to the incinerator. No harmful substances has been
detected in the ash.
・ Physical properties
The heat stability of Bionature is high enough because its raw material is
polyester resin. Where the hydrolysis does not happen, no biodegradation
occurs, then, there is almost no degradation in practical use.
A lot of functional finishes will be developed in future in Japan, and Prof. Joukou
of Kyoto Women’s Univ. presented a classification of functional finishes at a
meeting of the Japan Dyers’ Association in Osaka in June 2005 (Figure-1).This
classification includes physically based technology and chemically based
technology, the former is the improvement of potential function by modification
of the inner part of the fiber, and the later is the settlement of additional
function by modification of the surface of the fiber5).
He explained that the former includes crease-resistant finish, wash-and-wear
finish, permanent-press finish, shape-stabilizing finish, shrink-proofing finish,
mercerizing, imitation-linen finish, hardening finish, softening finish, salt-
shrinking finish, weighting finish, deep-coloring treatment and weight-reducing
treatment, and later includes water-repellent finish, oil-repellent finish,
hydrophilic finish, soil-repellent and release finish, antistatic finish, stretching
finish, mothproofing finish, antimicrobial and smell-proofing finish, ultraviolet-
protection finish.
According to our investigation, the process of incorporating active chemicals into
the fiber in its manufacturing stage is increasing and the product obtained is
called “functional fiber”, but functional finishes (physical and chemical) are still
major at present.
Some famous textile finishers who are active in their operation have established
many kinds of basic finishing technology for the aftertreatment of polyester
fabrics to allow the customer to feel safety and comfort in the clothes.
One example is graft polymerization on the fiber surface to improve moisture
absorbency in order to give physiological comfort to the customer. For
improving sweat absorbency, surface polymerization and polymer coating of
fiber surfaces are employed.
For breathable waterproofing finish, a surface modification using porous film and
conjugated polymer is commercially produced. New technology of improving the
penetration of active chemicals into the fiber, combined with skillful utilization of
polymer film technology was established in order to promote the antimicrobial
and smell-proofing effect. For an effective antistatic finish, new surface
modification technology using grafted polymer film was also established. For
http://textileinfo.com/en/tech/21c/02.html (2 of 3)12/22/2006 6:12:56 PM
A forecast on the textile processing industry in 21C 2.Functional finish to ...xtile like human skin - IS Co., Ltd. Senshoku Keizai Shimbun textileinfo.com
making the fiber electro-conductive, some metals are skillfully adhered to the
fiber. This technology is also included in surface modification.
The purpose of the functional finish is to confer not only physiological comfort,
but also give safety and durability to the textiles.
To make fibers noninflammable and polyester fiber nonmeltable, a combination
of three basic technologies, those are thorough penetration into fiber, graft
polymerization and polymer film technology, is successfully employed. This
technology is characterized by the simultaneous effect of the modifications of
the inner structure and the surface of the fiber.
Most of those technologies are summarized as surface modification
technologies.
Other finishers also concentrate their activity on surface modification
technologies.
In Japan, functional finish using a photocatalyst is developing although this
technology is still under discussion. In these circumstances, major Japanese
textile processors utilize some surface modification technologies and have
applied for some patents concerning smell-proofing of synthetic fiber,
preventing the adsorption of smell and improving the durability of these effects
to washing.This technology is characterized by using a photocatalyst of the
visual light response type and preventing the dye and the fiber from
degradation.
Summary of physical and chemical modification of the fiber
As mentioned above, functional finishes are divided into two categories, named
physical finish and chemical finish. Prof. K. Joukou of Kyoto Women’s Univ.
explained at the Japan Dyers’ Association meeting held in June 20056) ; “The
nature of physical finishes is noncontact and nonaqueous treatment.At present,
physical modifications based on UV, laser and low temperature plasma attract
high attention, and are studied aggressively. One of the advantages of this
surface modification is that the modification is restricted only to the surface,
without influencing any fundamental properties of the fiber. These modification
effects come from chemical and/or physical reactions, but their classification is
difficult.”
Reference
5-6) Lecture meeting by K-Jouko at Japan Dyer’s Association meeting
Copyright (c) 1999-2006, IS Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved. net@textileinfo.com
No reproduction or republication without written permission.
http://textileinfo.com/en/tech/21c/02.html (3 of 3)12/22/2006 6:12:56 PM
A forecast on the textile processing industry in 21C 3.Design of fabrics for functional finishes - IS Co., Ltd. Senshoku Keizai Shimbun textileinfo.com
Search pages from texitileinfo Google Search
A forecast on the textile processing industry in 21C
Editor of textileinfo
Technology IS Co., Ltd.
Contents 3.Design of fabrics for functional finishes
A forecast on the
textile processing In Japan, it is considered to be important to optimize the relation between “
industry in 21C structure of woven or knitted fabric “ and “ functional finish “ in order to gain
1. Classification of effective functional finishes.
fiber surface
modification
Even though the same chemicals for water-repellent and oil-repellent finishes
technology
are used, the effect given by these chemicals varies depending on the fabrics to
2. Functional finish be treated or on the finishing mills. Whether the suitable structure of fabrics is
to make textile employed or not is especially important.
like human skin
3. Design of fabrics Recently, in the technical textile area, resin coatings are gradually changing
for functional from organic solvent types to aqueous types. With an advance in this change,
finishes the structure of fabrics to be coated and the selection of optimum coating
4. Functional finish machines are regarded as important. European literature said that fluorocarbon
and new chemicals are effective for improving soil-repellency. In Japan, there are a few
technology in opinions that specialized silicones may be major in the future.
future
Dr. Wakida (emeritus professor of Kyoto Institute of Technology) et al presented
new ideas of water repellency on the occasion of the annual meeting of The
Society of Fiber Science and Technology in Gifu (Japan) on June 2005. The
content of this discussion is the change of the fiber surface properties caused by
washing and heat treatment of water-repellent woven fabrics. Silk palace and
wool tropical were treated with zirconium based water-repellent finishes and
silicone resins by the pad-dry-cure process. KES, shear and bending properties
of these treated fabrics are measured. The water- repellency of these fabrics
decreases with washing but recovers through heat treatment. Mechanical
properties of zirconium-based water-repellent finishes were also explained in
detail7). Theoretical analysis on water-repellency will progress, and many
technical experts expect Dr Wakida to continue his work.
Mr. K. Nishi (Meisei Chemical, Japan) et al also presented on the related subject
“ Effect of washing and heat treatment on nylon 6 and triacetate fabrics treated
with hydrocarbon water-repellent finish “.
On the other hand, the presentation of Mr. Y. Yanai (Shinshu Univ. )et al, which
was the relation between liquid ammonia treatment conditions and the structure
change of cotton, drew much attention8). The summary of this presentation was
that a change of processing speed on the bulk liquid ammonia treatment
machine alters the degree of dryness and finally leads to changes in the
structures of both crystalline and amorphous parts. With the advance of drying,
the portion of type Ⅲ crystalline becomes higher. (Crystalline form of cotton
changes from type Ⅰ to type Ⅱor type Ⅲ by chemical treatment.) And with an
increase in the rate of drying, the portion of the amorphous part increases. The
http://textileinfo.com/en/tech/21c/03.html (1 of 2)12/22/2006 6:13:01 PM
A forecast on the textile processing industry in 21C 3.Design of fabrics for functional finishes - IS Co., Ltd. Senshoku Keizai Shimbun textileinfo.com
change of the amorphous part is very complex ; crease-resistant properties,
tensile strength and flex rigidity increase, but pore volume and moisture
retention decrease, with an increase the rate of drying. The moisture regain and
tensile strength increase at the beginning of drying, but above a certain point
they gradually decrease with the advance of drying. The exhaustion degree of
the dye also slightly increases with liquid ammonia treatment, but its relation to
the degree of drying is very complicated8). This result is expected to be applied
to bulk production.
Reference
7-8)From the annual meeting of The Society of Fiber Science and Technology,
Japan 2005.
Copyright (c) 1999-2006, IS Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved. net@textileinfo.com
No reproduction or republication without written permission.
http://textileinfo.com/en/tech/21c/03.html (2 of 2)12/22/2006 6:13:01 PM
A forecast on the textile processing industry in 21C 4.Functional finish and... technology in future - IS Co., Ltd. Senshoku Keizai Shimbun textileinfo.com
Search pages from texitileinfo Google Search
A forecast on the textile processing industry in 21C
Editor of textileinfo
Technology IS Co., Ltd.
Contents 4.Functional finish and new technology in future
A forecast on the
textile processing The purpose of functional finishes is to allow all the textiles including apparel
industry in 21C and technical for all end-use, high-grade functions. The utilization of so called
1. Classification of nanotechnology can not be ignored to secure further advantages.
fiber surface Nanotechnology is indispensable in the design of new products with specialized
modification features through the control of nano structures. Scientists expect that nano
technology structure will be used to build separate parts or to construct large particles or
2. Functional finish
fibers. It stimulates innovation in fiber, film and coating technology and may
to make textile help to make up large materials like building blocks.
like human skin
Recently, a Japanese textile processor has developed a new technology, which is
3. Design of fabrics
the coating of a very thin (nano level ) metal film on a sheet consisting of
for functional
finishes
woven, knitted or nonwoven fabric. This method does not use any adhesive
such as a binder, and the metal attaches to the sheet only by physical energy,
4. Functional finish that is, molecular or atomic attraction. By attaching the metal film on the
and new surface of the sheet, new performance of hydrophilic properties,
technology in
future
electromagnetic shielding and UV protection are attained. Further advantages
such as high heat insulation are also realized. Many creative nano technologies
will be released in the future market to differentiate the effects of functional
finishes. It is undeniable that functional finish is a technical bridge for
harmonization with the environment and production.
Copyright (c) 1999-2006, IS Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved. net@textileinfo.com
No reproduction or republication without written permission.
http://textileinfo.com/en/tech/21c/04.html12/22/2006 6:13:06 PM
Вам также может понравиться
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5795)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- SweetenersДокумент23 страницыSweetenersNur AfifahОценок пока нет
- Benefits of OTN in Transport SDNДокумент9 страницBenefits of OTN in Transport SDNGhallab AlsadehОценок пока нет
- ForewordДокумент96 страницForewordkkcmОценок пока нет
- 5 160 1 PBДокумент13 страниц5 160 1 PBLotkomoaidone Harahu TukambaОценок пока нет
- Feasibility Study On The Seaweed Kappaphycus Alvarezii Cultivation Site in Indari Waters ofДокумент9 страницFeasibility Study On The Seaweed Kappaphycus Alvarezii Cultivation Site in Indari Waters ofUsman MadubunОценок пока нет
- Head N Neck-MCQsДокумент57 страницHead N Neck-MCQsbhargavi pasagadaОценок пока нет
- LINEAR INDUCTION MOTOR 6981660.ppsxДокумент56 страницLINEAR INDUCTION MOTOR 6981660.ppsxFalley FasterОценок пока нет
- North Central Mindanao College: Maranding, Lala, Lanao Del NorteДокумент8 страницNorth Central Mindanao College: Maranding, Lala, Lanao Del NorteAnalyn FielОценок пока нет
- DSR Codes - 1Документ108 страницDSR Codes - 1lakkireddy seshireddyОценок пока нет
- Nitofloor NДокумент3 страницыNitofloor Nkiranmisale7Оценок пока нет
- Hyundai Forklift Catalog PTASДокумент15 страницHyundai Forklift Catalog PTASjack comboОценок пока нет
- Bsi MD Ivdr Conformity Assessment Routes Booklet Uk enДокумент15 страницBsi MD Ivdr Conformity Assessment Routes Booklet Uk enGuillaumeОценок пока нет
- A Collection of Ideas For The Chemistry Classroom by Jeff HepburnДокумент14 страницA Collection of Ideas For The Chemistry Classroom by Jeff HepburnPaul SchumannОценок пока нет
- Medical CodingДокумент5 страницMedical CodingBernard Paul GuintoОценок пока нет
- 11 - Morphology AlgorithmsДокумент60 страниц11 - Morphology AlgorithmsFahad MattooОценок пока нет
- AssignmentДокумент13 страницAssignmentSwakshar DebОценок пока нет
- Bomber JacketДокумент3 страницыBomber JacketLaura Carrascosa FusterОценок пока нет
- IMCI UpdatedДокумент5 страницIMCI UpdatedMalak RagehОценок пока нет
- Cho Gsas - Harvard 0084L 11462Документ503 страницыCho Gsas - Harvard 0084L 11462Claudemiro costaОценок пока нет
- Mechanism Design: A SeriesДокумент3 страницыMechanism Design: A Seriesamirmasood kholojiniОценок пока нет
- 基礎居合講座Документ33 страницы基礎居合講座任平生100% (1)
- Health Problems Vocabulary Esl Matching Exercise Worksheet For KidsДокумент2 страницыHealth Problems Vocabulary Esl Matching Exercise Worksheet For KidsTarisubhОценок пока нет
- 1704 Broschuere Metal-Coating en EinzelseitenДокумент8 страниц1704 Broschuere Metal-Coating en EinzelseiteninterponОценок пока нет
- Curso VII Lectura 2. New Rural Social MovementsДокумент12 страницCurso VII Lectura 2. New Rural Social MovementsFausto Inzunza100% (1)
- Osce05ans 110918053819 Phpapp01Документ20 страницOsce05ans 110918053819 Phpapp01masood alamОценок пока нет
- E Numbers Are Number Codes ForДокумент3 страницыE Numbers Are Number Codes ForaradhyaОценок пока нет
- Book 2 - Koning (COMPLETO)Документ100 страницBook 2 - Koning (COMPLETO)Kevin VianaОценок пока нет
- Anchor Chart-Describing Words-Descriptive Details of Setting and Character PDFДокумент2 страницыAnchor Chart-Describing Words-Descriptive Details of Setting and Character PDFdellindiaОценок пока нет
- Load Distribution Flow Chart For Bridge DesignДокумент1 страницаLoad Distribution Flow Chart For Bridge DesignBunkun15Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 5, Abdominal TraumaДокумент41 страницаChapter 5, Abdominal TraumaRandy HarrisОценок пока нет