Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Chem 101 Lecture
Загружено:
Karen Mae TingАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chem 101 Lecture
Загружено:
Karen Mae TingАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
TOLO, Christian Keanno D.
BMLS-1B
082719
CHEM 101-LEC
CHAPTER 2: COMPOUNDS AND CHEMICAL BONDS
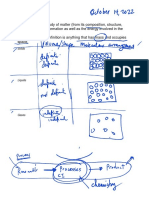
Classification and Properties of Matter
Two principal ways of classifying matter are according to its physical state (as a gas, liquid, or
solid) and according to its composition (as an element, compound, or mixture). A sample
of matter can be a gas, a liquid, or a solid. These three forms of matter are called the states
of matter.
All matter has physical and chemical properties. Physical properties are characteristics that
scientists can measure without changing the composition of the sample under study, such as
mass, color, and volume (the amount of space occupied by a sample). Chemical
properties describe the characteristic ability of a substance to react to form new substances;
they include its flammability and susceptibility to corrosion. Physical properties can be extensive
or intensive. Extensive properties vary with the amount of the substance and include mass,
weight, and volume. Intensive properties, in contrast, do not depend on the amount of the
substance; they include color, melting point, boiling point, electrical conductivity, and physical
state at a given temperature.
Ionic compound and bonding
Ionic compounds are compounds made up of ions. These ions are atoms that gain or lose
electrons, giving them a net positive or negative charge. Ionic bonding is the complete transfer
of valence electron(s) between atoms. It is a type of chemical bond that generates two
oppositely charged ions. In ionic bonds, the metal loses electrons to become a positively
charged cation, whereas the nonmetal accepts those electrons to become a negatively charged
anion.
Naming ions and ionic compounds
An ionic compound is named first by its cation and then by its anion. The cation has the
same name as its element. For example, K+1 is called the potassium ion, just as K is called the
potassium atom. The anion is named by taking the elemental name, removing the ending, and
adding “ide.”
Valence bonding and molecules
Valence bond theory is a chemical bonding theory that explains the bonding between two
atoms is caused by the overlap of half-filled atomic orbitals. The two atoms share each other's
unpaired electron to form a filled orbital to form a hybrid orbital and bond together.
TOLO, Christian Keanno D.
BMLS-1B
082719
Naming molecular compounds
1) Remove the ending of the second element and add “ide” just like in ionic compounds.
2) When naming molecular compounds prefixes are used to dictate the number of a given
element present in the compound. ” mono-” indicates one, “di-” indicates two, “tri-” is three,
“tetra-” is four, “penta-” is five, and “hexa-” is six, “hepta-” is seven, “octo-” is eight, “nona-” is
nine, and “deca” is ten.
3) If there is only one of the first element, you can drop the prefix. For example, CO is carbon
monoxide, not monocarbon monoxide.
4) If there are two vowels in a row that sound the same once the prefix is added (they
“conflict”), the extra vowel on the end of the prefix is removed. For example, one oxygen would
be monooxide, but instead it’s monoxide. The extra o is dropped.
Polyatomic Ions
Polyatomic ions are ions which consist of more than one atom. For example, nitrate ion, NO3-,
contains one nitrogen atom and three oxygen atoms. The atoms in a polyatomic ion are usually
covalently bonded to one another, and therefore stay together as a single, charged unit.
References:
https://wps.prenhall.com/wps/media/objects/165/169061/blb9ch0102.html
https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/General_Chemistry/Map%3A_Chemistry_-
_The_Central_Science_(Brown_et_al.)/01._Introduction%3A_Matter_and_Measurement/1.3%3
A_Properties_of_Matter
https://study.com/academy/lesson/what-are-ionic-reactions-definition-
examples.html#/targetText=Ionic%20compounds%20are%20compounds%20made,have%20a
%20net%20negative%20charge
https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Organic_Chemistry/Supplemental_Modules_(Organic_C
hemistry)/Fundamentals/Ionic_and_Covalent_Bonds
https://courses.lumenlearning.com/introchem/chapter/naming-ionic-
compounds/#targetText=An%20ionic%20compound%20is%20named,%2C%20and%20adding
%20%E2 80%9Cide%E2%80%9D
https://www.thoughtco.com/definition-of-valence-bond-theory-605771
https://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-chemistry/chapter/naming-
compounds/#targetText=When%20naming%20molecular%20compounds%20prefixes,and%20
%E2%80%9Cdeca%E2%80%9D%20is%20ten.
https://www.chem.purdue.edu/gchelp/nomenclature/poly_atom.htm#targetText=Polyatomic%
20ions%20are%20ions%20which,as%20a%20single%2C%20charged%20unit.
Вам также может понравиться
- Elements Compounds MixturesДокумент16 страницElements Compounds Mixturesmajji satishОценок пока нет
- Elements of ArtДокумент1 страницаElements of Artsamson8cindy8louОценок пока нет
- Ib History Command Term PostersДокумент6 страницIb History Command Term Postersapi-263601302100% (4)
- Preliminary Chemistry NotesДокумент33 страницыPreliminary Chemistry NotesStacey100% (1)
- How To Identify MQ Client Connections and Stop ThemДокумент26 страницHow To Identify MQ Client Connections and Stop ThemPurushotham100% (1)
- 4 Atoms and MoleculesДокумент14 страниц4 Atoms and Moleculesaustinfru7Оценок пока нет
- Roleplayer: The Accused Enchanted ItemsДокумент68 страницRoleplayer: The Accused Enchanted ItemsBarbie Turic100% (1)
- Turn Around Coordinator Job DescriptionДокумент2 страницыTurn Around Coordinator Job DescriptionMikeОценок пока нет
- Dalton's Atomic Theory: Key PointsДокумент32 страницыDalton's Atomic Theory: Key PointsLeo Radan100% (1)
- Hima OPC Server ManualДокумент36 страницHima OPC Server ManualAshkan Khajouie100% (3)
- Arens - Auditing and Assurance Services 15e-2Документ17 страницArens - Auditing and Assurance Services 15e-2Magdaline ChuaОценок пока нет
- Organization and Management Module 3: Quarter 1 - Week 3Документ15 страницOrganization and Management Module 3: Quarter 1 - Week 3juvelyn luegoОценок пока нет
- Atoms, Ions and MoleculesДокумент39 страницAtoms, Ions and MoleculesEvita Sandra PaculanangОценок пока нет
- 41GATE Material For Chemistry - OptДокумент70 страниц41GATE Material For Chemistry - OptSanthi SriОценок пока нет
- Jhoan Rhea L. Pizon, PHDДокумент59 страницJhoan Rhea L. Pizon, PHDRancell Vincent Gablines MorenoОценок пока нет
- Dalton's Atomic Theory: Cations Are Ions With A Net Positive ChargeДокумент2 страницыDalton's Atomic Theory: Cations Are Ions With A Net Positive ChargeJalaineLoisLatojaОценок пока нет
- Name: Terejoy A. Cocjin Grade and Section: 11-Max WeberДокумент6 страницName: Terejoy A. Cocjin Grade and Section: 11-Max Weberbro nawalibmatОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Inorganic Chemistry LectДокумент65 страницFundamentals of Inorganic Chemistry Lectgiuseppe galeottiОценок пока нет
- Ralf Neier, Christa Trojanowski and Rainer MattesДокумент8 страницRalf Neier, Christa Trojanowski and Rainer MattesjessicrmОценок пока нет
- ProportionsДокумент2 страницыProportionsJoeОценок пока нет
- Chem6A - F11 Hol - Chapter 2 - Part AДокумент12 страницChem6A - F11 Hol - Chapter 2 - Part AJZ8923Оценок пока нет
- Gen. Chem. 1 Module 1 HandoutДокумент4 страницыGen. Chem. 1 Module 1 HandoutMichellin QuerijeroОценок пока нет
- Reviewer 1Документ7 страницReviewer 1john.kerry.sanglay22Оценок пока нет
- ChemistrymidtermДокумент4 страницыChemistrymidtermapi-311220298Оценок пока нет
- GY 111 Lecture Note Series: Elemental ChemistryДокумент6 страницGY 111 Lecture Note Series: Elemental ChemistryKuldeepKaushikОценок пока нет
- Module 3 General ChemistryДокумент17 страницModule 3 General ChemistryIan ParoneОценок пока нет
- Atom, Molecul and IonДокумент62 страницыAtom, Molecul and IonChamilass YayaОценок пока нет
- Assignment 3 Azfatini & Zety LiyanaДокумент3 страницыAssignment 3 Azfatini & Zety LiyanaAzfa Teeniey NawiОценок пока нет
- John DaltonДокумент5 страницJohn DaltonTerraza de IbajayОценок пока нет
- Atomic Structure: How Did The Sub-Atomic Particles Discovered?Документ56 страницAtomic Structure: How Did The Sub-Atomic Particles Discovered?LycetteОценок пока нет
- Gen Chem 2Документ35 страницGen Chem 2jennierubyjane KimОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Gen ChemДокумент10 страницChapter 2 Gen ChemJennifer MalunaoОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Module 2 - Part 1Документ15 страницChemistry Module 2 - Part 1Francis RecocoОценок пока нет
- Properties of MatterДокумент24 страницыProperties of MatterVea AnadonОценок пока нет
- BSMT 1Документ4 страницыBSMT 1Kyle AsuncionОценок пока нет
- Alp 1Документ5 страницAlp 1niaziОценок пока нет
- CHEMДокумент31 страницаCHEMSheena Ann L. LLarenasОценок пока нет
- ChemДокумент13 страницChemAngelica Marie DiegoОценок пока нет
- II. ATOMS, MOLECULES and IONSДокумент18 страницII. ATOMS, MOLECULES and IONSHania ABDULОценок пока нет
- General Chemistry 1 Week 1.2Документ34 страницыGeneral Chemistry 1 Week 1.2Giovanni Gumahad Jr.Оценок пока нет
- 2.atomic StructureДокумент49 страниц2.atomic StructurehosifaОценок пока нет
- Lecture Note PDFДокумент91 страницаLecture Note PDFGamachis Mulugeta100% (1)
- Combinepdf 6Документ151 страницаCombinepdf 6DemiGodShuvoОценок пока нет
- Understanding The Concepts of Chemical ElementsДокумент10 страницUnderstanding The Concepts of Chemical ElementsChristine De San JoseОценок пока нет
- Atomic StructuresДокумент28 страницAtomic StructuresElaSharmaОценок пока нет
- Intro To Bonding WebsiteДокумент16 страницIntro To Bonding Websiteapi-110789702Оценок пока нет
- General Chemistry - DocsДокумент17 страницGeneral Chemistry - DocsJohn leeОценок пока нет
- Chemistry and Engineering: Big Stuff (Objects, Etc.)Документ27 страницChemistry and Engineering: Big Stuff (Objects, Etc.)Madhav MakkarОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of ChemistryДокумент71 страницаFundamentals of Chemistryrahuldev43Оценок пока нет
- Atoms and MoleculesДокумент10 страницAtoms and MoleculesAJ BrothersОценок пока нет
- Ch2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions 1Документ18 страницCh2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions 1Ariyandi PurnamaОценок пока нет
- John Dalton and Atomic TheoryДокумент1 страницаJohn Dalton and Atomic TheoryAlbert Josh MauyaoОценок пока нет
- CHM 101 - General Chemistry-1-Lecture Note - 2023Документ36 страницCHM 101 - General Chemistry-1-Lecture Note - 2023bangysmashiОценок пока нет
- Dalton's Atomic Theory: Part 1: All Matter Is Made of AtomsДокумент8 страницDalton's Atomic Theory: Part 1: All Matter Is Made of AtomsMargie OpayОценок пока нет
- Biochemical Principles: Atomic StructureДокумент4 страницыBiochemical Principles: Atomic StructureJona KoçiОценок пока нет
- Atomic Structure: N.C. Aparajitha 1020719BD015 Department of Physical ScienceДокумент47 страницAtomic Structure: N.C. Aparajitha 1020719BD015 Department of Physical Sciencelab chemistОценок пока нет
- Lesson 2A: Atoms, Molecules and Ions: Isotopes and Chemical Formula (Week 2) Competencies CoveredДокумент3 страницыLesson 2A: Atoms, Molecules and Ions: Isotopes and Chemical Formula (Week 2) Competencies CoveredChristine Gabuya CagasОценок пока нет
- John Dalton and The Atomic TheoryДокумент4 страницыJohn Dalton and The Atomic TheoryByPixel9mm NexusTMОценок пока нет
- Periodic Table Class 10 ICSE 2023 - 24Документ8 страницPeriodic Table Class 10 ICSE 2023 - 24Ramesh PatelОценок пока нет
- Atomic Theory - Part 1Документ13 страницAtomic Theory - Part 1satish_trivediОценок пока нет
- Atoms, Molecules, and IonsДокумент24 страницыAtoms, Molecules, and IonsUci HannaОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Inorganic Chemistry - SCH1101 - 2021Документ84 страницыFundamentals of Inorganic Chemistry - SCH1101 - 2021amoskipngetich87Оценок пока нет
- EMTL 250 Module 1 2018Документ57 страницEMTL 250 Module 1 2018Yeab MengistuОценок пока нет
- Module 1 Lecture Part 1Документ49 страницModule 1 Lecture Part 1Princess joy De RuedaОценок пока нет
- Week 10-13 (Handout)Документ10 страницWeek 10-13 (Handout)Mary Cris MovillaОценок пока нет
- Solution Manual For Chemistry A Molecular Approach Canadian 2nd Edition by Tro ISBN 013398656X 9780133986563Документ36 страницSolution Manual For Chemistry A Molecular Approach Canadian 2nd Edition by Tro ISBN 013398656X 9780133986563henryarmstrongypajbizoqe100% (22)
- ParasitesДокумент5 страницParasitesKaren Mae TingОценок пока нет
- Political SlefДокумент1 страницаPolitical SlefKaren Mae TingОценок пока нет
- Research TopicДокумент1 страницаResearch TopicKaren Mae TingОценок пока нет
- ReflectionДокумент2 страницыReflectionKaren Mae TingОценок пока нет
- Asian Regionalism FinalДокумент2 страницыAsian Regionalism FinalKaren Mae Ting100% (1)
- Roof Live LoadДокумент1 страницаRoof Live LoadKaren Mae TingОценок пока нет
- UTS Activity 3Документ3 страницыUTS Activity 3Karen Mae TingОценок пока нет
- Ltfl-Poth: 41i) Abo Yl) I (U Mo. LindoДокумент3 страницыLtfl-Poth: 41i) Abo Yl) I (U Mo. LindoKaren Mae TingОценок пока нет
- Assignment CE561Документ2 страницыAssignment CE561Karen Mae TingОценок пока нет
- 2 Floor, B&E Building Matina Campus, Davao City Telefax: (082) 296-1084 Phone No.: (082) 300-5456/300-0647 Local 133Документ1 страница2 Floor, B&E Building Matina Campus, Davao City Telefax: (082) 296-1084 Phone No.: (082) 300-5456/300-0647 Local 133Karen Mae TingОценок пока нет
- 2 Floor, B&E Building Matina Campus, Davao City: College of Engineering EducationДокумент5 страниц2 Floor, B&E Building Matina Campus, Davao City: College of Engineering EducationKaren Mae TingОценок пока нет
- Ass 2 Elec 4Документ27 страницAss 2 Elec 4Karen Mae TingОценок пока нет
- "Don't Set Limits On Your Unlimited Potential." AnonymousДокумент3 страницы"Don't Set Limits On Your Unlimited Potential." AnonymousKaren Mae TingОценок пока нет
- In A Nutshell (ULO-2b)Документ2 страницыIn A Nutshell (ULO-2b)Karen Mae TingОценок пока нет
- Millennials Spirituality 1. Millennials: Millennials in The Philippines Are Usually SeenДокумент5 страницMillennials Spirituality 1. Millennials: Millennials in The Philippines Are Usually SeenKaren Mae TingОценок пока нет
- Season Meaning Duration Civil Calendar Liturgical Color AdventДокумент2 страницыSeason Meaning Duration Civil Calendar Liturgical Color AdventKaren Mae TingОценок пока нет
- Sea Urchin (Hpo) Mammalian Blastula Frog (Lpo) Mammalian NeurulaДокумент1 страницаSea Urchin (Hpo) Mammalian Blastula Frog (Lpo) Mammalian NeurulaKaren Mae TingОценок пока нет
- Curves Design TABLEДокумент4 страницыCurves Design TABLEKaren Mae TingОценок пока нет
- Read While Being Blind.. Braille's Alphabet: Be Aware and Active !Документ3 страницыRead While Being Blind.. Braille's Alphabet: Be Aware and Active !bitermanОценок пока нет
- Working Capital in YamahaДокумент64 страницыWorking Capital in YamahaRenu Jindal50% (2)
- Dalasa Jibat MijenaДокумент24 страницыDalasa Jibat MijenaBelex ManОценок пока нет
- DP 2 Human IngenuityДокумент8 страницDP 2 Human Ingenuityamacodoudiouf02Оценок пока нет
- Stress-Strain Modelfor Grade275 Reinforcingsteel With Cyclic LoadingДокумент9 страницStress-Strain Modelfor Grade275 Reinforcingsteel With Cyclic LoadingRory Cristian Cordero RojoОценок пока нет
- Chapter13 PDFДокумент34 страницыChapter13 PDFAnastasia BulavinovОценок пока нет
- 2SB817 - 2SD1047 PDFДокумент4 страницы2SB817 - 2SD1047 PDFisaiasvaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 ClassnotesДокумент35 страницChapter 1 ClassnotesAllison CasoОценок пока нет
- Technology Management 1Документ38 страницTechnology Management 1Anu NileshОценок пока нет
- C - Amarjit Singh So Bhura SinghДокумент5 страницC - Amarjit Singh So Bhura SinghRohit JindalОценок пока нет
- Agco Serie 800 PDFДокумент24 страницыAgco Serie 800 PDFJohnny VargasОценок пока нет
- Equivalent Fractions Activity PlanДокумент6 страницEquivalent Fractions Activity Planapi-439333272Оценок пока нет
- Online Extra: "Economists Suffer From Physics Envy"Документ2 страницыOnline Extra: "Economists Suffer From Physics Envy"Bisto MasiloОценок пока нет
- Making Effective Powerpoint Presentations: October 2014Документ18 страницMaking Effective Powerpoint Presentations: October 2014Mariam TchkoidzeОценок пока нет
- Partes de La Fascia Opteva Y MODULOSДокумент182 страницыPartes de La Fascia Opteva Y MODULOSJuan De la RivaОценок пока нет
- AntibioticsДокумент36 страницAntibioticsBen Paolo Cecilia RabaraОценок пока нет
- Traveling Salesman ProblemДокумент11 страницTraveling Salesman ProblemdeardestinyОценок пока нет
- Rule 113 114Документ7 страницRule 113 114Shaila GonzalesОценок пока нет
- Hamstring - WikipediaДокумент21 страницаHamstring - WikipediaOmar MarwanОценок пока нет
- Financial Accounting 2 SummaryДокумент10 страницFinancial Accounting 2 SummaryChoong Xin WeiОценок пока нет
- Radiation Safety Densitometer Baker PDFДокумент4 страницыRadiation Safety Densitometer Baker PDFLenis CeronОценок пока нет
- UTP Student Industrial ReportДокумент50 страницUTP Student Industrial ReportAnwar HalimОценок пока нет