Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Ninja - Antihyperlipidemics PDF
Загружено:
Erica Hyeyeon LeeОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Ninja - Antihyperlipidemics PDF
Загружено:
Erica Hyeyeon LeeАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
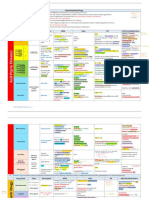
Antihyperlipidemic
Drugs
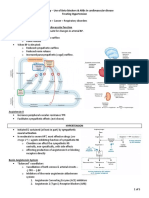
→ Hyperlipidemia: ↑cholesterol and/or ↑TAGs, or ↓HDL
→ ↑risk of cardiovascular mortality linked to ↑LDL and ↓HDL; ↑TAG!independent risk factor & can cause acute pancreatitis
→ Other risk factors for cardiovascular diseases!smoking, HTN, obesity, and diabetes
→ Disorders are detected by measuring serum lipids after a 10 hr. fast!TAGs, cholesterol(TC) and HDL measured directly; LDL= TC- (HDL+TG/5) when TAGs are <400mg/dL and pts are fasting
→ Statins=Lipid-lowering agents of first choice; adjunct to diet, exercise, smoking cessation; can reduce the risk of first cardiovascular events and death in pts with risk factors
Primary (Familial) Hyperlipidemia Secondary Hyperlipidemia
→ Causes: monogenetic disease, genetic polymorphisms, gene-environment interactions → MCC: sedentary lifestyle with XS dietary intake of saturated fat, cholesterol, and trans FAs
→ Most common cause of dyslipidemia in children → Most common cause of dyslipidemia in adults
→ Fredrickson Classification of Lipid Disorder: → Excess alcohol!↑VLDL production
Disease Lipid Profile Etiology → Hypertriglyceridemia in Type II DM d/t ↑VLDL synthesis and ↓chylomicron/VLDL catabolism
Type I o Insulin resistance!increased VLDL production since insulin normally inhibits VLDLs
↑Chylomicrons Deficiency in LPL or apoCII (Rare)
Familial Hyperchylomicronemia
Type IIA
o Insulin resistance!increased apoCII!↓chylomicron/VLDL catabolism
Familial Hypercholesterolemia
↑LDL ↓/non-fxnal LDL receptor
Type IIB Overproduction of VLDL by liver Hypertriglyceridemia ( VLDL) Hypercholesterolemia ( LDL)
↑LDL, ↑VLDL
Familial Combined hyperlipidemia (relatively common) Diabetes Mellitus Hypothyroidism
Type III Chronic renal failure Nephrotic syndrome
↑IDL Abnormal ApoE
Familial dysbetalipoproteinemia
Overproduction/impaired
Hypothyroidism Obstructive liver disease
Type IV Alcohol excess glucocorticoids
↑VLDL catabolism of VLDL (relatively
Familial Hypertriglyceridemia
common) Contraceptives
Type V ↑production/↓clearance of VLDL β-blockers
↑Chylomicrons, ↑VLDL
Familial mixed hypertriglyceridemia &chylomicrons
Glucocorticoids
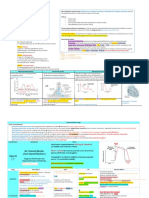
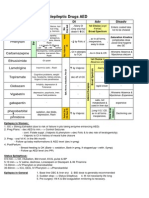
Drug Class Description MOA Uses Adverse Effects
Analogs of 3-OH-3-methylglutarate measure:
• baseline
(HMG) ↑aminotransferases (must be monitored) • 1-2 mo
Rosuvastatin • every 6-12 mo
Atorvastatin Lovastatin and simvastatin are Myopathy and rhabdomyolysis (measure CK) measure:
Competitively inhibit HMG-CoA reductase (RLE • baseline
Simvastatin prodrugs!inactivate lactones !myoglobinuria!renal injury • if symptomatic
HMG-CoA for de novo cholesterol synthesis) !↓
Lovastatin DOC for ↓LDL - discontinue
equal
reductase hydrolyzed in GI!active β- intracellular cholesterol!↑HMG-CoA reductase
Pravastatin Patients who are homozygous for familial
potency
inhibitors hydroxyl derivatives & ↑LDL receptors!↑LDL clearance
Fluvastatin ↓cardiovascular hypercholesterolemia benefit less from this TXT
Homozygous
mortality d/t lack of fxnal LDL-r
“Statins” ↓LDL, ↓TAG, small ↑HDL Best when used in combo with resins, niacin or type 2a: no LDLR
*in order of most
↑endothelial fxn ezetimibe
potent to least Contraindicated in women who are
↓platelet aggregation
potent pregnant/lactating/want to be pregnant!
↓inflammation
Category X
↓plasma CRP
Intense cutaneous flush after each dose (PG-
mediated so it can be blocked by aspirin)
Activate Gi !↓adenylyl cyclase! ↓cAMP & DOC for ↑HDL
↓PKA!inhibit HSL!↓FA transport!↓TAG
Pruritus, rashes, dry skin, and acanthosis nigricans
synthesis!↓VLDL production/release Useful in patients
with combined (LDL/VLDL)
type 2B
↑HDL significantly
Niacin Gi Nausea and abdominal discomfort
Niacin ↓VLDL, ↓LDL, and ↓Lp(a) ↑LPL activity!↑chylomicron & VLDL clearance hyperlipidemia and
(Nicotinic Acid)
Only one to ↓Lp(a) ↓HDL levels Rare:
[vitamin B3]
Hepatotoxicity!↑transaminases • atrial arrythmia
↓HDL catabolism!↑HDL
Insulin resistance!hyperglycemia
• toxic amblyopia
(lazy eye)
Adjunct therapy with
(Caution in pts with diabetes)
• toxic maculopathy
↓fibrinogen, ↑t-PA!reverse endothelial dysfxn statins
↑uric acid!gout
↓TAG (best one) Activate PPAR-α (peroxisome proliferator
Mild GI disturbances
↑HDL activated receptor α) expressed in liver and DOC for severe
Myositis fenofibrate less AE:
Gemfibrozil brown adipose tissue hypertriglyceridemia • does not inhibit hepatic statin uptake
Rhabdomyolysis
hepatic
Fibrates
Fenofibrate Gemfibrozil inhibits uptake of type 4 (LDL)
Cholelithiasis d/t ↑cholesterol excretion
statins!↑concentration of both ↓TAG d/t ↑LPL, ↓apoC-III & ↑hepatic oxidation
Avoid in pts with hepatic/renal dysfxn
drugs!↑rhabdomyolysis of FA
increased dietary C --> gallstones
Antihyperlipidemic Drugs Continued
Drug Class Description MOA Uses Adverse Effects
ion trapping at GIT Little effect on pts with dysfxn LDL-r Type 2a
homozygous
H20 insoluble, ↑MW, polymeric Binds to anionic bile acids in
anion exchange resins!NOT Used with statins/niacin Bloating, cramping & constipation
intestine!prevents
Cholestyramine Bile Acid- absorbed or metabolized! 100% to ↑LDL reduction (Colesevelam is better tolerated than others)
reabsorption!↑production in liver!↓
Colestipol Binding excretion in feces
intracellular cholesterol!upreg LDL-r!↓LDL
Colesevelam Resins DOC for children and Contraindicated in pts. w/ very high LDL
(partially offset by ↑cholesterol synthesis)
Useful only in pregnant Contraindicated in hyperTAGemia: will ^ VLDL
isolated
Modest ↑HDL liver senses decreased C:
hypolipoproteinemia’s with ↑LDL increases LDL expression Cholestyramine & Colestipol interfere with fat soluble
vitamins
(Type 2a only) absorption of other drugs and Vit. ADEK
Selectively inhibit NPC1L1 in jejunal
dietary
enterocytes!↓ cholesterol!↑cholesterol Reversible impaired hepatic fxn
Inhibits absorption of cholesterol Combo with statin in pts.
Cholesterol synthesis & upreg of LDL-r! ↓LDL
and phytosterols! ↓LDL who can’t reach their LDL
Ezetimibe absorption Myositis :risk if combined with statins
goal
inhibitors Effective even in absence of cholesterol b/c it
Complimentary actions to statins
inhibits reabsorption of cholesterol excreted in Absorption inhibited by bile acid sequestrants
bile :compensatory increase in HMG-CoA reductase
EPA Fish oils that ↓TAG in a dose
DHA dependent way ↑LDL-C Adjunct to
↓TAG synthesis and ↑FA oxidation in the liver
Lovaza ω-3 Fatty Contains both EPA and DHA diet in adults
May ↑ total LDL as they ↓TAG
Acids ↓TAG with very
impact on HDL varies
Vascepa Ethyl ester of EPA without high TAG
when TAG≥400 mg/dL
↑LDL
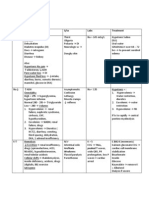
SUGGESTED DRUG THERAPY FOR DYSLIPIDEMIAS
Lipid Profile Initial Drug Additions
Niacin, Resin,
Elevated LDL Statin
Ezetimibe
Niacin, Fibrate,
Elevated LDL and TG Statin
ω-3 Fatty acid
Isolated low HDL Statin Niacin
Isolated severe Fibrate (or Niacin
Statin
hypertriglyceridemia or ω-3 Fatty acid)
80
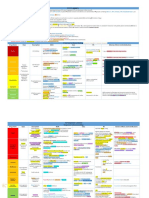
Effects of Antihyperlipidemics ANTIHYPERLIPIDEMIC DRUGS IN PREGNANCY
Drug Effect on LDL Effect on HDL Effect on TG • Statins: absolutely contraindicated in pregnancy.
Category X.
Statins ↓25%–60% ↑5%–15% ↓10%-40% • Fibrates: Category C.
Fibrates ↓ or ↑ ↑10%–30% ↓30%–60%
best drug
vs TAGs
• Niacin: Category C.
• Ezetimibe: Category C.
Resins ↓15%–30% ↑3%–5% ↑5%
• Cholestyramine & colestipol: might interfere
Ezetimibe ↓15%–20% ↑1%-2% ↓5% -10% with absorption of nutrients. Category C.
best drug
• Colesevelam: Category B. Should be used during
Niacin ↓10%–30% ↑20%–35% ↓30%–50% for HDL pregnancy only if clearly needed.
best drug vs
ω-3 Fatty acids ↑5%–10% ↑5%–10% ↓20%–50%78 only TAGs
81
Вам также может понравиться
- Hyper-coagulation, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОт EverandHyper-coagulation, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОценок пока нет
- Ninja - Antianginal Drugs PDFДокумент2 страницыNinja - Antianginal Drugs PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeОценок пока нет
- Ninja - Anemias PDFДокумент1 страницаNinja - Anemias PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeОценок пока нет
- GI Drugs PDFДокумент6 страницGI Drugs PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (1)
- Differentials For Finals: - Pleuritic Chest Pain - Pulmonary Embolism - Pneumothorax PneumoniaДокумент9 страницDifferentials For Finals: - Pleuritic Chest Pain - Pulmonary Embolism - Pneumothorax PneumoniaOlivia MoranОценок пока нет
- ECG Interpretations GoodДокумент104 страницыECG Interpretations GoodaymenОценок пока нет
- 0.5. ANS Quicksheet PDFДокумент1 страница0.5. ANS Quicksheet PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeОценок пока нет
- Heart FailureДокумент1 страницаHeart FailureTrisha VergaraОценок пока нет
- Internal Medicine #1Документ167 страницInternal Medicine #1Nikhil RayarakulaОценок пока нет
- Ninja - Antiarrhythmic Drugs PDFДокумент7 страницNinja - Antiarrhythmic Drugs PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (1)
- Pharm Fall Cardiovascular Pharmacology Study Guide-106Документ47 страницPharm Fall Cardiovascular Pharmacology Study Guide-106sean liyanageОценок пока нет
- Renal Guide and Charts: AlbuminДокумент16 страницRenal Guide and Charts: AlbuminYaima JimenezОценок пока нет
- Sphere: These DiarrheaДокумент3 страницыSphere: These Diarrheamed testОценок пока нет
- Pharm Expansion 17 NDFДокумент1 страницаPharm Expansion 17 NDFNokz M. Raki-inОценок пока нет
- ANS DrugsДокумент2 страницыANS Drugsmed testОценок пока нет
- Acid BaseДокумент89 страницAcid BaseEdouinaОценок пока нет
- Https:Jetmapp - orbundsis.com:Einstein-freshair:Videos::102793DigitalDownload LabValues NurseInTheMaking 2pagesДокумент5 страницHttps:Jetmapp - orbundsis.com:Einstein-freshair:Videos::102793DigitalDownload LabValues NurseInTheMaking 2pagesamazonian005100% (1)
- Antibiotics Chart 1Документ7 страницAntibiotics Chart 1Vee MendОценок пока нет
- Spinal Cord CompressionДокумент4 страницыSpinal Cord Compressionian3yeung-2Оценок пока нет
- Electrolyte ImbalanceДокумент3 страницыElectrolyte ImbalancemewilkinОценок пока нет
- Ninja - Anti-Coagulants PDFДокумент3 страницыNinja - Anti-Coagulants PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (1)
- Pain 2. Pallor Poikylothermia Parasthesia Pulselessness Factor V Leiden (Activated Protein C Resistance)Документ3 страницыPain 2. Pallor Poikylothermia Parasthesia Pulselessness Factor V Leiden (Activated Protein C Resistance)Ryan TurnerОценок пока нет
- CardionotesДокумент5 страницCardionotesNichole Coletta100% (1)
- CVPR Prototype Drugs TableДокумент27 страницCVPR Prototype Drugs TablethommyvaОценок пока нет
- Antihypotensive Drugs: Roger Joseph Ii Ramos Jecino, RN, M.DДокумент28 страницAntihypotensive Drugs: Roger Joseph Ii Ramos Jecino, RN, M.DFranz Earl Niño AlbesaОценок пока нет
- Ninja - Anti-HTN PDFДокумент6 страницNinja - Anti-HTN PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (2)
- Amboss Hemolytic AnemiaДокумент16 страницAmboss Hemolytic AnemiaAhmed Ali100% (2)
- Labs Electrolyte ChartДокумент1 страницаLabs Electrolyte ChartmdcmepОценок пока нет
- Pharmacology Main DrugsДокумент14 страницPharmacology Main DrugsSabir KhanОценок пока нет
- Clinical KardexДокумент2 страницыClinical KardexJackie Frey100% (2)
- Antibiotics Chart 2Документ10 страницAntibiotics Chart 2Vee MendОценок пока нет
- Renal Chart 2Документ21 страницаRenal Chart 2fortheloveofmedicineОценок пока нет
- Electrolyte Imbalance Cause Signs and Symptoms Intervention ConnectionДокумент6 страницElectrolyte Imbalance Cause Signs and Symptoms Intervention ConnectionmkninnyОценок пока нет
- Musculoskeletal PharmacologyДокумент18 страницMusculoskeletal PharmacologyBLEEMAGE100% (2)
- Internal Medicine Table SummaryДокумент31 страницаInternal Medicine Table SummaryShazaan Nadeem100% (1)
- Genetic Conditions For USMLEДокумент2 страницыGenetic Conditions For USMLEkcxieОценок пока нет
- Cardiac Drugs HypertensionДокумент5 страницCardiac Drugs HypertensionEciOwnsMeОценок пока нет
- Pharmacology - Use of Beta-Blockers & Arbs in Cardiovascular Disease Treating HypertensionДокумент5 страницPharmacology - Use of Beta-Blockers & Arbs in Cardiovascular Disease Treating HypertensionDana20SОценок пока нет
- Rhythm Interpretation and Its ManagementДокумент6 страницRhythm Interpretation and Its Managementjh_ajjОценок пока нет
- Antiepileptic Drugs AED: D' DI Disadv SE AdvДокумент1 страницаAntiepileptic Drugs AED: D' DI Disadv SE Advrayooona88Оценок пока нет
- Comprehensive Nclex Notes Easy To Read PDFДокумент97 страницComprehensive Nclex Notes Easy To Read PDFKenia GeorgesОценок пока нет
- Antiseizure, Sedative & HypnoticsДокумент8 страницAntiseizure, Sedative & HypnoticsThulasi tootsieОценок пока нет
- 1) Misc: Neuro HY PearlsДокумент2 страницы1) Misc: Neuro HY Pearlsdsfan86Оценок пока нет
- Immunopharmacology PDFДокумент2 страницыImmunopharmacology PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeОценок пока нет
- Antianginal DrugsДокумент3 страницыAntianginal DrugsyukariОценок пока нет
- Cardiovascular Drug IntroductionДокумент3 страницыCardiovascular Drug IntroductionSamah Khan100% (1)
- Bam Slam Drug CardДокумент4 страницыBam Slam Drug CardLeticia GonzalezОценок пока нет
- Gastro MnemonicsДокумент8 страницGastro MnemonicsRufina SoomroОценок пока нет
- GI Signs and SymptomsДокумент40 страницGI Signs and SymptomsJohnny BeeОценок пока нет
- SyncopeДокумент3 страницыSyncopeanishdОценок пока нет
- MS Myasthenia Gravis Gillian-Barre Syndrome Parkinson's: Ascending Reversible ParalysisДокумент5 страницMS Myasthenia Gravis Gillian-Barre Syndrome Parkinson's: Ascending Reversible ParalysishaxxxessОценок пока нет
- Acid Base Handout RevisedДокумент3 страницыAcid Base Handout RevisedKaren HutchinsonОценок пока нет
- Lab Values and Vital SignsДокумент4 страницыLab Values and Vital SignsWole Olaluwoye100% (1)
- Heart Rhythms S SДокумент3 страницыHeart Rhythms S SGloryJane100% (1)
- Notes ImДокумент5 страницNotes Imsharmee sarmientaОценок пока нет
- Hierarchy of O2 Delivery SystemsДокумент1 страницаHierarchy of O2 Delivery SystemsRevОценок пока нет
- 3 Treatment of HypertensionДокумент7 страниц3 Treatment of HypertensiontiaraОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 Compatible ModeДокумент93 страницыChapter 1 Compatible ModeJyha KhariОценок пока нет
- Opioids PDFДокумент2 страницыOpioids PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeОценок пока нет
- Immunopharmacology PDFДокумент2 страницыImmunopharmacology PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeОценок пока нет
- Asthma - Respiratory PDFДокумент1 страницаAsthma - Respiratory PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee0% (1)
- Ninja - Anti-Coagulants PDFДокумент3 страницыNinja - Anti-Coagulants PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (1)
- Ninja - Antiarrhythmic Drugs PDFДокумент7 страницNinja - Antiarrhythmic Drugs PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (1)
- Ninja - Autacoids PDFДокумент3 страницыNinja - Autacoids PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeОценок пока нет
- Ninja - Anti-HTN PDFДокумент6 страницNinja - Anti-HTN PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (2)
- Ninja - Cholinergic Drugs PDFДокумент4 страницыNinja - Cholinergic Drugs PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (2)
- 0.5. ANS Quicksheet PDFДокумент1 страница0.5. ANS Quicksheet PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeОценок пока нет
- Written Report Coronary Heart DiseaseДокумент5 страницWritten Report Coronary Heart DiseaseJade WushuОценок пока нет
- The Cholesterol Time BombДокумент464 страницыThe Cholesterol Time BombSophia NadalОценок пока нет
- PATHOLOGY Mendelian DisordersДокумент8 страницPATHOLOGY Mendelian DisordersAmna BaigОценок пока нет
- Bios Life Slim On PDRДокумент1 страницаBios Life Slim On PDRTemitayo BewajiОценок пока нет
- Guidelines For The Diagnosis and Management of Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia PDFДокумент14 страницGuidelines For The Diagnosis and Management of Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia PDFai_tОценок пока нет
- Meta-Analyses of Statin Therapy For Primary Prevention Do Not Answer Key Questions: An Empirical Appraisal of 5 Years of Statin Meta-AnalysesДокумент8 страницMeta-Analyses of Statin Therapy For Primary Prevention Do Not Answer Key Questions: An Empirical Appraisal of 5 Years of Statin Meta-AnalysesJulio JuarezОценок пока нет
- Becker Red Yeast Rice 2009Документ13 страницBecker Red Yeast Rice 2009Miin ChanОценок пока нет
- How Cholesterol WorksДокумент7 страницHow Cholesterol WorksVishal Kumar ShawОценок пока нет
- Reabilitare Dupa AvcДокумент91 страницаReabilitare Dupa AvcDiana StancaОценок пока нет
- Pengaruh Pemberian Sari Tebu Terhadap Kadar Kolesterol Darah Pada MencitДокумент7 страницPengaruh Pemberian Sari Tebu Terhadap Kadar Kolesterol Darah Pada MencitGaluhFahmiОценок пока нет
- Kanukula 2019Документ7 страницKanukula 2019Dianne GalangОценок пока нет
- 33 Side Effects of FoodsДокумент13 страниц33 Side Effects of FoodsFrankDicksonОценок пока нет
- Liver TransplantДокумент16 страницLiver TransplantNephrology On-DemandОценок пока нет
- RX - Citicoline, Kalium, Ketosteril, Methycobal, Myonal, Lipolin GelДокумент6 страницRX - Citicoline, Kalium, Ketosteril, Methycobal, Myonal, Lipolin GelntootОценок пока нет
- Cwe Nephrotic SnydromeДокумент12 страницCwe Nephrotic SnydromeFariezuan HamidОценок пока нет
- Heart AttackДокумент12 страницHeart AttackPaul NeedhamОценок пока нет
- Midterms Group 5Документ25 страницMidterms Group 5Karina MadriagaОценок пока нет
- DSS - Bridging The Gaps Tackling Inequalities in Cardiovascular DiseaseДокумент19 страницDSS - Bridging The Gaps Tackling Inequalities in Cardiovascular DiseaseEduard MoraruОценок пока нет
- Drug Study CHFДокумент13 страницDrug Study CHFALIANA KIMBERLY MALQUESTOОценок пока нет
- Annotated BibliographyДокумент4 страницыAnnotated Bibliographyapi-348925782Оценок пока нет
- 2-Unicity Balance PDFДокумент17 страниц2-Unicity Balance PDFLuis A Gil PantojaОценок пока нет
- Dislipidemia Lancet Durrington PDFДокумент15 страницDislipidemia Lancet Durrington PDFAlphaJulissa JuarezОценок пока нет
- Medical Hazards of Obesity: Ann Intern Med. 1993 119 (7 PT 2) :655-660Документ6 страницMedical Hazards of Obesity: Ann Intern Med. 1993 119 (7 PT 2) :655-660David WheelerОценок пока нет
- BIOS LIFE - Cleveland Clinic Trial by Dr. Dennis SprecherДокумент5 страницBIOS LIFE - Cleveland Clinic Trial by Dr. Dennis SprecherHisWellnessОценок пока нет
- Statin Drug StudyДокумент3 страницыStatin Drug StudyNikael Patun-ogОценок пока нет
- Bandana Chatterjee Et Al.Документ4 страницыBandana Chatterjee Et Al.International Journal of Clinical and Biomedical Research (IJCBR)Оценок пока нет
- Cholesterol TCM PDFДокумент6 страницCholesterol TCM PDFMartijn JohanОценок пока нет
- Health7 4TH Quarter ModuleДокумент20 страницHealth7 4TH Quarter Modulearmand bayoranОценок пока нет
- Malunggay MonographДокумент9 страницMalunggay Monographkiara4decenaОценок пока нет
- Biologia Celular y Moleculas - TallerДокумент2 страницыBiologia Celular y Moleculas - TallerJulieth Karina Mendoza AcostaОценок пока нет