Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Should Be All in V/R For Nodal.) : TH OC SC TH
Загружено:
Shu Ern0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
25 просмотров2 страницыcheat sheet for electrical science
Оригинальное название
Nodal Analysis
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документcheat sheet for electrical science
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
25 просмотров2 страницыShould Be All in V/R For Nodal.) : TH OC SC TH
Загружено:
Shu Erncheat sheet for electrical science
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
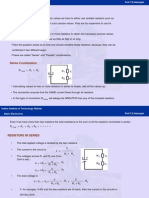
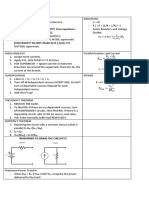
NODAL ANALYSIS EQUATIONS
1. Select 1 node as your ground reference. - V = IR
2. Assign Voltages. - R || R = (1/R + 1/R) ^-1
3. Apply KCL (FINDING CURRENT!!!! Your equations - Series Resistors and Voltage
should be all in V/R for nodal.) Divider.
𝑉
4. Use Ohm’s law, then solve equations. V1 = i x R1 = (𝑅 +𝑅 )𝑅1
1 2
5. FOR SUPERNODE -> Apply KVL INSIDE supernode.
(VOLTAGES!!! Do NOT divide by R.) Apply KCL
OUTSIDE supernode.
MESH ANALYSIS Parallel Resistors and Current
1. Assign mesh currents. 𝑅1 𝑥 𝑅2
𝑅𝑒𝑞 =
2. Apply KVL. (VOLTAGES!!! I X R) Solve. 𝑅1 + 𝑅2
3. FOR SUPERMESH -> Ignore currents in between
branches! Go around the supermesh, then KCL for the 𝑅2 ∗ 𝑖
𝑖1 =
current at the branch. 𝑅1 + 𝑅2
SUPERPOSITION POWER
1. Label VT = V1 + V2 / IT = I1 + I2
2. Turn off all independent sources EXCEPT ONE. Do NOT P = IV = I2R = V2/R
turn of dependent sources! Repeat for each 𝑉𝑡ℎ 2
independent source. 𝑃𝑚𝑎𝑥 =
4𝑅𝑡ℎ
3. Add the I/V up!
THEVENIN’S THEOREM
1. REMOVE THE LOAD.
2. To find Rth: if there are no dependent sources, turn
off INDEPENDENT circuits, then find Rth. If there is a
dependent circuit, add 1V OR 1A source, and solve.
3. Vth: Solve normally (with load REMOVED!)
NORTON’S THEOREM
1. Replacing the circuit with a scurrent source IN that is
parallel to RN. (RN = Rth)
2. IN = ISC,
3. VTH (VOC) = ISC X RTH
REMEMBER TO DRAW THE CIRCUITS!!
Maximum Power Transfer
- When RTH = RL. If RTH is NOT RL, compute the power
delivered to the load!
Вам также может понравиться
- The Power of AbstractionДокумент22 страницыThe Power of Abstractionlisa annОценок пока нет
- Oliveros - Edwin Jethro - Bsee2a - Laboratory 5Документ6 страницOliveros - Edwin Jethro - Bsee2a - Laboratory 5TheNinjaDragon gamingОценок пока нет
- 3.basic Electrical Engineering Lecture Part 3Документ45 страниц3.basic Electrical Engineering Lecture Part 3Cedric ZamoraОценок пока нет
- Circuit Analysis Study Guide - Cheat-SheetДокумент11 страницCircuit Analysis Study Guide - Cheat-SheetSimeonОценок пока нет
- DC Circuits: E IR P EIДокумент5 страницDC Circuits: E IR P EIMuhib RazaОценок пока нет
- DT DQ DQ DW DT DW: (Units: C/s Amps (A) ) (Units: J/C Volts (V) )Документ4 страницыDT DQ DQ DW DT DW: (Units: C/s Amps (A) ) (Units: J/C Volts (V) )Kyle BradwellОценок пока нет
- Final Review PDFДокумент19 страницFinal Review PDFurfriend_jjn05Оценок пока нет
- Circuit TheoryДокумент18 страницCircuit Theorygokulphd100% (1)
- BEE1 ChapterДокумент36 страницBEE1 ChapterpvpriyaОценок пока нет
- Cheat-Sheet Ebook 6thДокумент11 страницCheat-Sheet Ebook 6thNguyễn Bá HoàngОценок пока нет
- Lab Report 9 PDFДокумент4 страницыLab Report 9 PDFRajput JanjuaОценок пока нет
- Circuit Lab: Practice #11-Specialty Devices, Dependent Sources, Superposition, and Troubleshooting Mr. BurlesonДокумент20 страницCircuit Lab: Practice #11-Specialty Devices, Dependent Sources, Superposition, and Troubleshooting Mr. BurlesonJoe WangОценок пока нет
- EE236 - Chapter 2Документ141 страницаEE236 - Chapter 2S AlshОценок пока нет
- Lecture 15 Chapter 26 Part 1Документ19 страницLecture 15 Chapter 26 Part 1Mircea PanteaОценок пока нет
- Basic Elec 3Документ22 страницыBasic Elec 3Hari100% (2)
- Emailing AC - Exp - 04 - StudentДокумент4 страницыEmailing AC - Exp - 04 - StudentNafiul BariОценок пока нет
- Exp 1 Astable MVДокумент5 страницExp 1 Astable MVNavnoor kaurОценок пока нет
- Electricity - Part 2Документ22 страницыElectricity - Part 2Anonymous CommentatorОценок пока нет
- Superposition Method in Circuit Analysis Prepared by Engr. A.C.PatricioДокумент6 страницSuperposition Method in Circuit Analysis Prepared by Engr. A.C.PatricioChristian CalisinОценок пока нет
- Experiment No. 9: Resonance I. ObjectivesДокумент2 страницыExperiment No. 9: Resonance I. ObjectivesKenneth SinsonОценок пока нет
- Electric Circuit AnalysisДокумент17 страницElectric Circuit AnalysisMuhammad HasnainОценок пока нет
- For This WeekДокумент37 страницFor This WeekPlacido EarlОценок пока нет
- Physics Experiment 8 About ElectronicДокумент9 страницPhysics Experiment 8 About ElectronicFelixОценок пока нет
- EEE 102 - Expt 3 - KCLДокумент2 страницыEEE 102 - Expt 3 - KCLnushrat.khlОценок пока нет
- 1 Circuit TheoryДокумент44 страницы1 Circuit TheoryWinter NaiОценок пока нет
- 27U LCR Circuit W OscilloscopeДокумент9 страниц27U LCR Circuit W OscilloscopeValeria MendozaОценок пока нет
- Topic 2 - Basic LawsДокумент5 страницTopic 2 - Basic LawsUmakandan MuniandyОценок пока нет
- EE13001 2 Th&No TheoremsДокумент24 страницыEE13001 2 Th&No TheoremsMahindaОценок пока нет
- 1 Circuit TheoryДокумент44 страницы1 Circuit Theoryamirul aminnОценок пока нет
- Lecture # 06 Controlled RectifiersДокумент44 страницыLecture # 06 Controlled RectifiersSohira QaziОценок пока нет
- Robotics ReviewerДокумент5 страницRobotics ReviewerKyle Angelo SantiagoОценок пока нет
- Topic5 Electricity Part4Документ54 страницыTopic5 Electricity Part411. Feby CecilliaОценок пока нет
- Network Anal 2020Документ17 страницNetwork Anal 2020chuariwapoohОценок пока нет
- EEE - 122 - Exp1 (8 Files Merged)Документ5 страницEEE - 122 - Exp1 (8 Files Merged)SHAJEDA AKTHER 2102154Оценок пока нет
- Elec FormulasДокумент9 страницElec FormulaskazımОценок пока нет
- Lecture 3 Equivalent Resistance, Voltage and Current DividerДокумент20 страницLecture 3 Equivalent Resistance, Voltage and Current DividerM. Chughtai0% (1)
- Circuit LawsДокумент19 страницCircuit LawsWakahare PtahОценок пока нет
- 1.ee101 ContentsДокумент21 страница1.ee101 ContentsSJОценок пока нет
- Ee 211Документ37 страницEe 211Muhammad OsamaОценок пока нет
- EE301 Lesson 04 Parallel Elements, KCL, CDRДокумент13 страницEE301 Lesson 04 Parallel Elements, KCL, CDRMaalmalan KeekiyyaaОценок пока нет
- 1 - TransformersДокумент32 страницы1 - TransformersKeneth John Gadiano PadugaОценок пока нет
- Electrical Engineering FormulasДокумент15 страницElectrical Engineering Formulasajayyadav19100% (4)
- EE 306 ManualДокумент55 страницEE 306 Manualzain khuramОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ61 страницаChapter 2CHEAH HUI TING STUDENTОценок пока нет
- EE Lec 10Документ13 страницEE Lec 10adil11699611Оценок пока нет
- Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering: North South UniversityДокумент8 страницDepartment of Electrical & Computer Engineering: North South UniversityMD Shariful IslamОценок пока нет
- Beee PPT - 5Документ24 страницыBeee PPT - 5Girish Shankar MishraОценок пока нет
- TP 1: General TheoremsДокумент4 страницыTP 1: General TheoremsZiad FAwalОценок пока нет
- TransistorДокумент30 страницTransistorGnanaseharan Arunachalam100% (1)
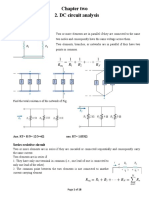
- Chapter Two 2. DC Circuit Analysis: Simple Resistive Circuit Parallel Resistive CircuitДокумент18 страницChapter Two 2. DC Circuit Analysis: Simple Resistive Circuit Parallel Resistive Circuitalemu assefaОценок пока нет
- 1 Circuit Theory - MZMДокумент47 страниц1 Circuit Theory - MZMSyahmi AkmalОценок пока нет
- Superposition PDFДокумент17 страницSuperposition PDFJlnamaez SerefineОценок пока нет
- Recall: Functioning Equations For Ideal ElementsДокумент29 страницRecall: Functioning Equations For Ideal ElementsppОценок пока нет
- SWR Meters Make You StupidДокумент38 страницSWR Meters Make You StupidnosajseveerОценок пока нет
- Passive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2От EverandPassive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2Оценок пока нет
- Endosymbiosis TheoryДокумент1 страницаEndosymbiosis TheoryShu ErnОценок пока нет
- Notes For QuantДокумент1 страницаNotes For QuantShu ErnОценок пока нет
- Should Be All in V/R For Nodal.) : TH OC SC THДокумент2 страницыShould Be All in V/R For Nodal.) : TH OC SC THShu ErnОценок пока нет
- Assignment 6 Time ReflectionДокумент1 страницаAssignment 6 Time ReflectionShu ErnОценок пока нет
- CH 9, 10, & 16 Alcohol, Tobacco, Drugs, and ViolenceДокумент5 страницCH 9, 10, & 16 Alcohol, Tobacco, Drugs, and ViolenceShu ErnОценок пока нет
- Gen Bio Final Study GuideДокумент7 страницGen Bio Final Study GuideShu ErnОценок пока нет
- 22 Ohm's Law TNДокумент4 страницы22 Ohm's Law TNShu ErnОценок пока нет
- Weekly Planner For The Week of - , - Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday SundayДокумент1 страницаWeekly Planner For The Week of - , - Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday SundayShu ErnОценок пока нет
- College of Math and Science Minors: Engineering PhysicsДокумент2 страницыCollege of Math and Science Minors: Engineering PhysicsShu ErnОценок пока нет
- CHEM 2621 Networking Assignment GenДокумент1 страницаCHEM 2621 Networking Assignment GenShu ErnОценок пока нет
- Weekly Planner For The Week of - September 18, 2016 - , - Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday SundayДокумент1 страницаWeekly Planner For The Week of - September 18, 2016 - , - Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday SundayShu ErnОценок пока нет
- Squirrel SummaryДокумент2 страницыSquirrel SummaryShu ErnОценок пока нет
- Organic Chem - Chapter 3.Документ3 страницыOrganic Chem - Chapter 3.Shu ErnОценок пока нет
- Organic Chem - Chapter 2Документ2 страницыOrganic Chem - Chapter 2Shu ErnОценок пока нет
- Blab Lab LaДокумент3 страницыBlab Lab LaShu ErnОценок пока нет
- IДокумент1 страницаIShu ErnОценок пока нет
- Script For Potato PeopleДокумент4 страницыScript For Potato PeopleShu ErnОценок пока нет
- ParisДокумент23 страницыParisShu ErnОценок пока нет
- Timetable For Form 1Документ1 страницаTimetable For Form 1Shu Ern50% (2)
- LyricsДокумент31 страницаLyricsShu ErnОценок пока нет
- Proud To Be MalaysianДокумент1 страницаProud To Be MalaysianShu ErnОценок пока нет
- Cebora Bravo 155 CombiДокумент3 страницыCebora Bravo 155 CombiAdiОценок пока нет
- Ultra ConductorsДокумент19 страницUltra ConductorsI79E1A0 4i6Оценок пока нет
- Physics Formulae For Grade 10Документ14 страницPhysics Formulae For Grade 10Umesh PrasadОценок пока нет
- Kinematics of Rigid Bodies: Prepared By: Engr. Dezirre PadillaДокумент13 страницKinematics of Rigid Bodies: Prepared By: Engr. Dezirre PadillaAndrew TorioОценок пока нет
- SPH 3u1Документ21 страницаSPH 3u1Adam JonesОценок пока нет
- Acoustic LevitationДокумент16 страницAcoustic LevitationMatt Stephens-Row100% (2)
- Lab Sheet Air Conditioning (Perfect Gas)Документ8 страницLab Sheet Air Conditioning (Perfect Gas)JIJENDERKUMAR A/L VIJAYAN MoeОценок пока нет
- Turbine Flow MeterДокумент33 страницыTurbine Flow MeterPandeyОценок пока нет
- Itr Ew 03b HV MV SwitchboardДокумент6 страницItr Ew 03b HV MV SwitchboardmatrengОценок пока нет
- Prediction of Transmission Line Overloading UsingДокумент23 страницыPrediction of Transmission Line Overloading UsingDevendra SharmaОценок пока нет
- IntermixДокумент2 страницыIntermixanttic2009Оценок пока нет
- MCQ PhysicsДокумент24 страницыMCQ PhysicsBhardwaj Rajinder SippyОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Fluid Mechanics Prof. Suman Chakraborty Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 39 Application of Bernoulli's Equation - Part - IIДокумент8 страницIntroduction To Fluid Mechanics Prof. Suman Chakraborty Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 39 Application of Bernoulli's Equation - Part - IIdjadja nakamayaОценок пока нет
- Distance Vs Time GraphsДокумент4 страницыDistance Vs Time GraphsMercedes DolendoОценок пока нет
- 3-And 4-Pole Switching in UPS Installation: White Paper SeriesДокумент7 страниц3-And 4-Pole Switching in UPS Installation: White Paper SeriesAlexandru-Mihnea RaduОценок пока нет
- 1.3 - Energy Basics, Fuel Supply and PricingДокумент36 страниц1.3 - Energy Basics, Fuel Supply and PricingKhaled QarraОценок пока нет
- Physics A-C 2nd 10Документ3 страницыPhysics A-C 2nd 10Debela mendaraОценок пока нет
- 03 Transmission of Heat Practice ProblemДокумент10 страниц03 Transmission of Heat Practice ProblemAkash GhoshОценок пока нет
- System of Particles NarayanaДокумент97 страницSystem of Particles NarayanaJanarthan SekarОценок пока нет
- Dielectric Withstanding Voltage Test AN-115: AN-115 Application Note v0418Документ4 страницыDielectric Withstanding Voltage Test AN-115: AN-115 Application Note v0418Galarce OrlandoОценок пока нет
- Microsoft Word - PZT Manual ABAQUS PDFДокумент9 страницMicrosoft Word - PZT Manual ABAQUS PDFHarshMahajan100% (1)
- DPP - PhysicsДокумент6 страницDPP - PhysicsdeepaĸОценок пока нет
- DC Motor Lecture 3Документ27 страницDC Motor Lecture 3Fira tubeОценок пока нет
- Pratica 2Документ14 страницPratica 2Eberton SantosОценок пока нет
- MV Substation DesignДокумент12 страницMV Substation DesignPEC E&I-2Оценок пока нет
- KapilДокумент69 страницKapilPraveen SrivastavaОценок пока нет
- Types of Insulation Used On Rotating Machines, Their Insulation Life, and Deterioration CausesДокумент14 страницTypes of Insulation Used On Rotating Machines, Their Insulation Life, and Deterioration CausessantoshkumarОценок пока нет
- Kinetic Theory of GasesДокумент22 страницыKinetic Theory of Gasesshan mackОценок пока нет
- Pspice IntroductionДокумент63 страницыPspice IntroductionNmg KumarОценок пока нет
- Copland Outdoor UnitsДокумент18 страницCopland Outdoor UnitsatiqОценок пока нет