Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Nursing Care Plan: St. Anthony's College San Jose, Antique Nursing Department Name: M.L.H
Загружено:
Nicolne LorraineОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Nursing Care Plan: St. Anthony's College San Jose, Antique Nursing Department Name: M.L.H
Загружено:
Nicolne LorraineАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
St.
Anthony’s College
San Jose, Antique
Nursing Department
NAME:M.L.H.
AGE:55 years old
Dr.: Dr. Baria
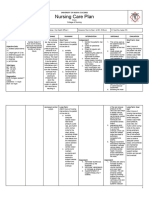
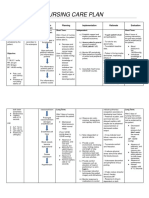
CC: NURSING CARE PLAN
CUES NURSING RATIONALE PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS
SUBJECTIVE: Inadequate blood GENERAL: After 8 INDEPENDENT:
“Nagataas akon BP.” As pumped by the heart hours of Nursing Review clients at risk as noted Persons with acute or chronic Goals patially met.
verbalized by the patient. Risk for decrease to meet metabolic intervention, the in Related Factors as well as conditions may compromise
demands of the body. patient will be able to individuals with conditions that circulation and place
cardiac output. maintain BP within stress the heart. excessive demands on the
individually heart.
acceptable range.
Check laboratory data (cardiac To identify contributing
OBJECTIVE: markers, complete blood cell factors.
Bp: 150/90 count, electrolytes, ABGs, blood
PR: 119bpm urea nitrogen and creatinine,
RR: 15 cardiac enzymes, and cultures,
such as blood, wound or
secretions).
Monitor and record BP. Comparison of pressures
Measure in both arms and thighs provides a more complete
three times, 3–5 min apart while picture of vascular
SPECIFIC: patient is at rest, then sitting, involvement or scope of
After 2 hours, the then standing for initial problem. Severe hypertension
patient will be able to evaluation. Use correct cuff size is classified in the adult as a
participate in and accurate technique. diastolic pressure elevation to
activities that reduce 110 mmHg; progressive
BP/cardiac workload. diastolic readings above 120
mmHg are considered first
accelerated, then malignant
(very severe). Systolic
hypertension also is an
established risk factor for
cerebrovascular disease and
ischemic heart disease, when
diastolic pressure is elevated.
Note presence, quality of central Bounding carotid, jugular,
and peripheral pulses. radial, and femoral pulses may
be observed and palpated.
Pulses in the legs and feet may
be diminished, reflecting
effects of vasoconstriction
(increased systemic vascular
resistance [SVR]) and venous
congestion.
DEPENDENT: Beta-Blockers may be ordered
Alpha, beta, or centrally instead of diuretics for patients
acting adrenergic with ischemic heart disease;
antagonists: doxazosin obese patients
(Cardura); propranolol (Inderal); with cardiogenic hypertension;
acebutolol (Sectral); metoprolol and patients with concurrent
(Lopressor), labetalol supraventricular
(Normodyne); atenolol arrhythmias, angina, or
(Tenormin); nadolol hypertensive cardiomyopathy.
(Corgard), carvedilol (Coreg); Specific actions of these drugs
methyldopa vary, but they generally
(Aldomet); clonidine (Catapres); reduce BP through the
prazosin (Minipress); terazosin combined effect of decreased
(Hytrin); pindolol (Visken); total peripheral resistance,
reduced cardiac output,
inhibited sympathetic activity,
and suppression of renin
release. Note: Patients
with diabetes should use
Corgard and Visken with
caution because they can
prolong and mask the
hypoglycemic effects
of insulin. The elderly may
require smaller doses because
of the potential for
bradycardia and hypotension.
African-American patients
tend to be less responsive to
beta-blockers in general and
may require increased dosage
or use of another drug
(monotherapy with a diuretic).
Вам также может понравиться
- Readiness For Enhanced Health ManagementДокумент6 страницReadiness For Enhanced Health ManagementJIMENEZ, TRISHA MARIE D.Оценок пока нет
- High Blood Pressure: Safe alternatives without drugsОт EverandHigh Blood Pressure: Safe alternatives without drugsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- NCP KateDor NewДокумент6 страницNCP KateDor NewSteffi GolezОценок пока нет
- Central Venous Pressure: Its Clinical Use and Role in Cardiovascular DynamicsОт EverandCentral Venous Pressure: Its Clinical Use and Role in Cardiovascular DynamicsОценок пока нет
- Joval TanДокумент2 страницыJoval TanJoval TanОценок пока нет
- Anticoagulation TherapyОт EverandAnticoagulation TherapyJoe F. LauОценок пока нет
- Patient's Says (The Worst So Far: Ssessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions RationaleДокумент1 страницаPatient's Says (The Worst So Far: Ssessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions RationaleDl Al-azizОценок пока нет
- NCP PPHДокумент2 страницыNCP PPHMark Joseph Christian100% (1)
- CT 11 - HPNДокумент12 страницCT 11 - HPNLycah RotoneОценок пока нет
- NCP 1Документ1 страницаNCP 1hsiriaОценок пока нет
- Handbook of Inpatient CardiologyОт EverandHandbook of Inpatient CardiologyBryan J. WellsОценок пока нет
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Expected Outcome Interventions Rationale EvaluationДокумент2 страницыAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Expected Outcome Interventions Rationale EvaluationQueenzee AsuncionОценок пока нет
- NCP-DP NCM112LecДокумент4 страницыNCP-DP NCM112LecShane CabucosОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan HypertensionДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan Hypertensionderic98% (124)
- NCP #2Документ2 страницыNCP #2Faith CalimlimОценок пока нет
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related To Shortness of Breath Possible Evidence by CuesДокумент7 страницIneffective Breathing Pattern Related To Shortness of Breath Possible Evidence by CuesLouie ParillaОценок пока нет
- PositionДокумент23 страницыPositionCharlene RojasОценок пока нет
- Clinical Cases in Heart FailureОт EverandClinical Cases in Heart FailureRavi V. ShahОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan For Palliative Care Nursing NotesДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan For Palliative Care Nursing NotesblaireОценок пока нет
- Case-Based Device Therapy for Heart FailureОт EverandCase-Based Device Therapy for Heart FailureUlrika Birgersdotter-GreenОценок пока нет
- Acute GastroenteritisДокумент3 страницыAcute Gastroenteritisreejay123Оценок пока нет
- Adult Congenital Heart Disease in Clinical PracticeОт EverandAdult Congenital Heart Disease in Clinical PracticeDoreen DeFaria YehОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan On HypertensionДокумент5 страницNursing Care Plan On Hypertensionbhavana100% (1)
- Management of Cardiac ArrhythmiasОт EverandManagement of Cardiac ArrhythmiasGan-Xin YanОценок пока нет
- Linician Pdate: Echo-Doppler HemodynamicsДокумент5 страницLinician Pdate: Echo-Doppler HemodynamicsAlvy SyukrieОценок пока нет
- Decreased Cardiac OutputДокумент4 страницыDecreased Cardiac Outputaudreyann.acobОценок пока нет
- Pacemaker Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОт EverandPacemaker Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОценок пока нет
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals & Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationДокумент2 страницыCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals & Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationMiggy SikatОценок пока нет
- High Blood Pressure: Natural Self-help for Hypertension, including 60 recipesОт EverandHigh Blood Pressure: Natural Self-help for Hypertension, including 60 recipesОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan For HypertensionДокумент4 страницыNursing Care Plan For HypertensionKathleen Dimacali100% (2)
- Case Study RleДокумент25 страницCase Study Rlelea jumawanОценок пока нет
- Beating with Precision: The Science of Cardiology: Understand the Intricacies of the Human HeartОт EverandBeating with Precision: The Science of Cardiology: Understand the Intricacies of the Human HeartОценок пока нет
- Risk For Decreased Cardiac Output: Nursing DiagnosisДокумент4 страницыRisk For Decreased Cardiac Output: Nursing DiagnosisRiska RamadaniОценок пока нет
- Compendium on Cardiomyopathies - Basics, Therapeutics, and PerspectivesОт EverandCompendium on Cardiomyopathies - Basics, Therapeutics, and PerspectivesОценок пока нет
- DrugStudy Ruaya Sophia T.Документ4 страницыDrugStudy Ruaya Sophia T.Hannah JanuhanОценок пока нет
- Actual NCP Eclampsia - PESCADERO 4CДокумент1 страницаActual NCP Eclampsia - PESCADERO 4COrlando VillanuevaОценок пока нет
- BSNURSE: NCP - HypertensionДокумент3 страницыBSNURSE: NCP - Hypertensionmickey_beeОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan. HypertensionДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan. HypertensionKiara Shanelle Posadas AbrioОценок пока нет
- Icu 4Документ7 страницIcu 4GemilleDaphneAndradaОценок пока нет
- HT SampleДокумент4 страницыHT SampleElla YuОценок пока нет
- Decreased Cardiac OutputДокумент3 страницыDecreased Cardiac OutputRizalyn QuindipanОценок пока нет
- Angiography (Cardiac Catherization) : Patient Teaching/preparationДокумент2 страницыAngiography (Cardiac Catherization) : Patient Teaching/preparationpsyОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan For HELLP SyndromeДокумент17 страницNursing Care Plan For HELLP SyndromeRosemarie Carpio75% (4)
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Decreased Cardiac OutputДокумент2 страницыNURSING CARE PLAN - Decreased Cardiac OutputDaniel Andre S. SomorayОценок пока нет
- NCP Risk For Decreased CO 1 PDFДокумент2 страницыNCP Risk For Decreased CO 1 PDFdubsОценок пока нет
- Congestive Heart Failure NCPДокумент6 страницCongestive Heart Failure NCPShaira Ann Calamba100% (1)
- Problem List: Vital SignsДокумент13 страницProblem List: Vital SignsRey Jean GarciaОценок пока нет
- Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationДокумент9 страницAssessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Interventio N Rationale Evaluationjosh100% (1)
- Activity 5Документ4 страницыActivity 5AngieОценок пока нет
- Road Safety QuestionnaireДокумент4 страницыRoad Safety QuestionnaireNicolne LorraineОценок пока нет
- Background and RationaleДокумент9 страницBackground and RationaleNicolne LorraineОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan: Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Obstructed AirwayДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan: Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Obstructed AirwayNicolne LorraineОценок пока нет
- Generic Name: Classification: IndicationДокумент2 страницыGeneric Name: Classification: IndicationNicolne LorraineОценок пока нет
- Breezeway Flower ShopДокумент11 страницBreezeway Flower ShopNicolne LorraineОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan: Impaired Urinary EliminationДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan: Impaired Urinary EliminationNicolne LorraineОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan: Age: 5 Years Old DR.: Dr. Tanchuan CC: Hypogastric PainДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan: Age: 5 Years Old DR.: Dr. Tanchuan CC: Hypogastric PainNicolne LorraineОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of HCVDДокумент5 страницPathophysiology of HCVDNicolne Lorraine100% (1)
- Actual Delivery In: St. Anthony'S CollegeДокумент2 страницыActual Delivery In: St. Anthony'S CollegeNicolne LorraineОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care PlanДокумент5 страницNursing Care PlanNicolne LorraineОценок пока нет
- Analisis Cost of Illness Penyakit Hipertensi Di Rumah Sakit Umum Daerah Praya, NTBДокумент8 страницAnalisis Cost of Illness Penyakit Hipertensi Di Rumah Sakit Umum Daerah Praya, NTBabdulОценок пока нет
- 18-Main Arteries & Veins of NeckДокумент43 страницы18-Main Arteries & Veins of NeckAbishek JОценок пока нет
- Hubungan Rasio Trigliserida/High Density Lipoprotein-Cholesterol (TG/HDL-C) Dengan Kejadian Infark Miokard Akut Di RSUP Prof. Dr. R. D. Kandou ManadoДокумент5 страницHubungan Rasio Trigliserida/High Density Lipoprotein-Cholesterol (TG/HDL-C) Dengan Kejadian Infark Miokard Akut Di RSUP Prof. Dr. R. D. Kandou ManadoIvanna NdoenОценок пока нет
- Coronary Heart Disease: Angina Pectoris: Assistant Professor Department of Internal Medicine #1Документ48 страницCoronary Heart Disease: Angina Pectoris: Assistant Professor Department of Internal Medicine #1nadhirahfauzi100% (1)
- Lesson Plan: Class: Subject: Topic: Submitted byДокумент10 страницLesson Plan: Class: Subject: Topic: Submitted bysimonjosan67% (3)
- Dr. Firman Leksmono SP - JP Basic ECG Interpretation For StudentДокумент54 страницыDr. Firman Leksmono SP - JP Basic ECG Interpretation For Studentacha kyungsooОценок пока нет
- Evaluation of The R One Robotic System For Percutaneous Coronary Intervention THДокумент11 страницEvaluation of The R One Robotic System For Percutaneous Coronary Intervention THNeranga SamaratungeОценок пока нет
- Lesson 1: Prepared By: Mark Christian N. LunaДокумент28 страницLesson 1: Prepared By: Mark Christian N. LunaJohn Mark CelosaОценок пока нет
- Hinmans+Atlas+of+UroSurgical+Anatomy Nodrm PDFДокумент381 страницаHinmans+Atlas+of+UroSurgical+Anatomy Nodrm PDFMariya Lyashevych100% (1)
- Heart DiseaseДокумент4 страницыHeart DiseasefidaauddinОценок пока нет
- DVT and TestsДокумент4 страницыDVT and TestsvishwanathОценок пока нет
- Initial Assessment and Management of Acute StrokeДокумент49 страницInitial Assessment and Management of Acute StrokeIrina DuceacОценок пока нет
- Estoya, Gen Paulo C. - Deep Vein Thrombosis NCP - NCM 112 LecДокумент2 страницыEstoya, Gen Paulo C. - Deep Vein Thrombosis NCP - NCM 112 LecGen Paulo EstoyaОценок пока нет
- Grade-9 Lesson PlanДокумент9 страницGrade-9 Lesson PlanPristine Aila RoblesОценок пока нет
- Medmastery Handbook - Echo Masterclass - The ValvesДокумент136 страницMedmastery Handbook - Echo Masterclass - The ValvesVladlena Cucoș-CaraimanОценок пока нет
- Biochemical Markers For Clinical Monitoring of Tissue PerfusionДокумент14 страницBiochemical Markers For Clinical Monitoring of Tissue PerfusionTrọng MPОценок пока нет
- (Reference Series in Biomedical Engineering) Wolfgang Holnthoner, Andrea Banfi, James Kirkpatrick, Heinz Redl (Eds.) - Vascularization For Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine-Springer InternaДокумент231 страница(Reference Series in Biomedical Engineering) Wolfgang Holnthoner, Andrea Banfi, James Kirkpatrick, Heinz Redl (Eds.) - Vascularization For Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine-Springer InternaIsidoro OlveraОценок пока нет
- Nursing Seminar 1 SAS Session 21Документ9 страницNursing Seminar 1 SAS Session 21ZiaОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease: Chest Pain Muscle Weakness Shortness of BreathДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology of Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease: Chest Pain Muscle Weakness Shortness of BreathCyril Jane Caanyagan AcutОценок пока нет
- Norepinephrine For Spinal Hypotension During Cesarean DeliveryДокумент3 страницыNorepinephrine For Spinal Hypotension During Cesarean DeliveryANGELICAОценок пока нет
- Life Process Part 2 2Документ32 страницыLife Process Part 2 2Anin BertОценок пока нет
- Abd AortaДокумент48 страницAbd AortaSanjib NepramОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of The HeartДокумент8 страницAnatomy of The HeartAbigail BrillantesОценок пока нет
- Lec 7Документ27 страницLec 7helenyakhyОценок пока нет
- Conceito de Pré Carga e Pós Carga em CardiologiaДокумент9 страницConceito de Pré Carga e Pós Carga em CardiologiarmesquitajrОценок пока нет
- SyncopeДокумент28 страницSyncopeDurgesh PushkarОценок пока нет
- Heart Gcse Qs OnlyДокумент6 страницHeart Gcse Qs OnlygriggansОценок пока нет
- Cardiovascular DrugsДокумент6 страницCardiovascular DrugsSilvio PerezОценок пока нет
- Anatomy NstemiДокумент3 страницыAnatomy NstemiSheana Tmpl100% (1)
- Circulatory SystemДокумент6 страницCirculatory SystemchelliОценок пока нет