Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Imbalanced Nutrtion
Загружено:
Mhil Ishan Margate0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
38 просмотров2 страницы,k
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документ,k
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
38 просмотров2 страницыImbalanced Nutrtion
Загружено:
Mhil Ishan Margate,k
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
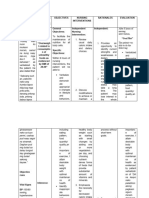
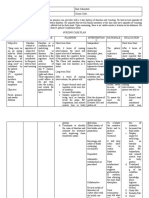
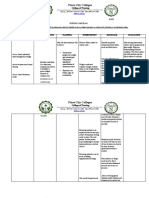
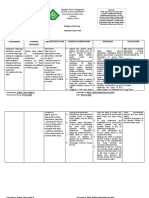
ASSESSMENT NURSING SCIENTIFIC GOALS NURSING RATIONALE EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS RATIONALE INTERVENTIONS
SUBJECTIVE Imbalanced One reason for enteral After 8 hours of INDEPENDENT: After 8 hours of
Nutrition: Less than 1. Assess general health 1. To be able to know
CUES: feeding is dysphagia or nursing nursing
Body Requirements condition what nursing
“Dire naman ini hiya related to inability to difficulty in swallowing. interventions, the interventions to be interventions, the
ingest food secondary given.
nakakakaon hin puro Neurological damage patient will be able patient was able to:
to Tuberculous
nga pagkaon kay Meningitis as brought about by certain to: 2. Establish Rapport 2. To gain patient’s
evidenced by presence and SO’s trust
naka tubo naman disease causes dysphagia.
of Nasogastric Tube
hya ada naagi it iya Tuberculosis meningitis To maintain 3. Observe and record 3. Monitors caloric To maintain
client’s food intake. intake or
pagkaon” as is a life-threatening or restore or restore
insufficient quality
verbalized by S.O infectious disease which nutritional of food nutritional
Consumption.
causes the cerebral cortex status status
“Dako na ini an iya to swell. Functions of the Demonstrate 4. Review nutritional 4. Identifies Demonstrate
history, including deficiencies and
gin gas’an tikang cerebral cortex includes stable stable
food preferences. suggests possible
han una.” As relay of impulses to weight or interventions. weight or
verbalized by S.O cranial nerves which progressive progressive
affect the weight gain 5. Determine child’s 5. Identifies individual weight gain
current nutritional nutritional needs
glossopharyngeal (CN toward goal. toward goal.
status using age- and provides
OBJECTIVE IX) nerve which is appropriate comparative
measurements, baseline.
CUES: responsible for
including weight and
swallowing reflex body build, strength,
activity level, and
Body weight: resulting to dysphagia.
sleep and rest cycles.
40.7 lb
6. Auscultate bowel 6. Provides
(Normal bpddy Nutrition is the most
sounds. Note information about
weight for age: basic aspect of our characteristics of digestion and bowel
stool, including color, function and may
62lbs.) body’s ability to function
amount, and affect choice and
timing of feeding..
Appears well. Enteral feeding is frequency of bowel
movements. .
lethargic often chosen by the
NGT tube noted physician maintain 7. Administer enteral 7. Ideal caloric intake
feeding as indicated per individual is
Muscle wasting dietary and metabolic
depending on the usually calculated
due to severe needs of client’s with nutritional needs of to estimate the
the client metabolic needs of
illness functional
the client.
Loss of gastrointestinal tract with
8. Always place client 8. Aids in preventing
subcutaneous fat inability to take enough
in high fowler’s aspiration.
Dry skin nutrition or dietary positon. Elevate the
head of the client
calories orally.
while feeding.
9. Ensure patency of the 9. Some enteral
enteral tube before formulas and some
and after feeding with medications may
Source: Medical-surgical water clog the tube
flushing it with
nursing: Reviews and
water will maintain
rationales by Mary Ann its patency.
Hogan
10.
10. Encourage or assist 11. Diminishes
with good oral bacterial
hygiene before and Growth,
after minimizing
Meals; use soft- possibility of
bristled toothbrush infection.
for gentle brushing.
Вам также может понравиться
- Essiac Nature's Cure For CancerДокумент14 страницEssiac Nature's Cure For CancerTrevanian2Оценок пока нет
- BIOPSY Oral SurgeryДокумент34 страницыBIOPSY Oral SurgeryNisha ChoudharyОценок пока нет
- NCP Fdar Fin.Документ8 страницNCP Fdar Fin.Bissette DomingoОценок пока нет
- Improved NutritionДокумент2 страницыImproved NutritionDaintyGarciaОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan For Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Req NCPДокумент4 страницыNursing Care Plan For Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Req NCPkarthi karthi50% (2)
- 23-Discharge Against Medical Advice (Dama)Документ3 страницы23-Discharge Against Medical Advice (Dama)akositabonОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan For Mother:: Sno Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation EvaluationДокумент4 страницыNursing Care Plan For Mother:: Sno Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Evaluationmishti100% (1)
- Label Nama Obat Di Rak ObatДокумент6 страницLabel Nama Obat Di Rak Obatanon_756054910Оценок пока нет
- Bed SoreДокумент16 страницBed SoreKim AquinoОценок пока нет
- Impaired Swallowing Related To Dysphagia Secondary To Dry Oral MucosaДокумент3 страницыImpaired Swallowing Related To Dysphagia Secondary To Dry Oral MucosaJUN JUN PALISOC100% (1)
- IV FluidsДокумент3 страницыIV FluidsEvangeline San Jose83% (6)
- Micromedex 360 Care Insights BrochureДокумент9 страницMicromedex 360 Care Insights BrochureSteve ArendОценок пока нет
- Atlas of Office Based Andrology PDFДокумент139 страницAtlas of Office Based Andrology PDFKoushik Sharma Amancharla100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan (Bowel Elemination)Документ8 страницNursing Care Plan (Bowel Elemination)Rijane Tabonoc Omlang100% (1)
- Life-members-Indian Medico-Legal & Ethics Association (Imlea) - Mix State & Mix DepartmentДокумент64 страницыLife-members-Indian Medico-Legal & Ethics Association (Imlea) - Mix State & Mix DepartmentKriti Kumari100% (1)
- Imbalance Nutrition Less Than Body RequirementsДокумент4 страницыImbalance Nutrition Less Than Body Requirementshatred heartОценок пока нет
- Afinidad, Jiezl A: Davao Doctors College Nursing ProgramДокумент4 страницыAfinidad, Jiezl A: Davao Doctors College Nursing ProgramJiezl Abellano AfinidadОценок пока нет
- Imbalanced Nutrition NCPДокумент2 страницыImbalanced Nutrition NCPChryst Louise Saavedra100% (1)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationДокумент2 страницыAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationHsintan HsuОценок пока нет
- Potential: Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationДокумент3 страницыPotential: Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationBasema HashhashОценок пока нет
- CHA NCPДокумент6 страницCHA NCPMonty_Legaspi_5664Оценок пока нет
- Ncp-Potential-Fernandez Hashhash Navarro PaitДокумент3 страницыNcp-Potential-Fernandez Hashhash Navarro PaitBasema HashhashОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan for Diabetic Patient with ConstipationДокумент3 страницыNursing Care Plan for Diabetic Patient with ConstipationRawan KОценок пока нет
- Case Scenario 2 NCP RevisedДокумент5 страницCase Scenario 2 NCP RevisedkdfhjfhfОценок пока нет
- Subjective Short Term Independent: Patient Is Conscious and CooperativeДокумент5 страницSubjective Short Term Independent: Patient Is Conscious and Cooperativeraven riveraОценок пока нет
- DIAGNOSIS OverweightДокумент7 страницDIAGNOSIS OverweightWappy WepwepОценок пока нет
- Ate Gabs Nyo Pagod NaДокумент3 страницыAte Gabs Nyo Pagod NaGabrielle EvangelistaОценок пока нет
- NCP FormatДокумент2 страницыNCP FormatellisequeenieОценок пока нет
- 88 FinalДокумент4 страницы88 FinalEshiebel OrganistaОценок пока нет
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Goal of Care Outcome Criteria Interventions and Rationale EvaluationДокумент2 страницыAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Goal of Care Outcome Criteria Interventions and Rationale EvaluationMariah Angela PonceОценок пока нет
- NCP Nutrition1Документ4 страницыNCP Nutrition1java_biscocho1229100% (1)
- Risk NCP - PESCADERO 4CДокумент1 страницаRisk NCP - PESCADERO 4COrlando VillanuevaОценок пока нет
- Hirsprung DseaseДокумент19 страницHirsprung DseaseKeepItSecretОценок пока нет
- NCP For Mobility IntoleranceДокумент2 страницыNCP For Mobility IntoleranceRenz Kier Lorenzo ComaОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Outcome Intervention Rationale EvaluationДокумент3 страницыNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Outcome Intervention Rationale EvaluationMarivic Yuson MalagarОценок пока нет
- Laboratory ExamsДокумент3 страницыLaboratory ExamsTolen TinoОценок пока нет
- To Gain Their Trust & Cooperation. For Baseline Data To Be Observed For Any DistressДокумент7 страницTo Gain Their Trust & Cooperation. For Baseline Data To Be Observed For Any DistressZhyraine Iraj D. CaluzaОценок пока нет
- PCC College of Nursing Care PlanДокумент4 страницыPCC College of Nursing Care PlanEspiridionОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan 2Документ4 страницыNursing Care Plan 2Carl Andre ReyesОценок пока нет
- Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements Diabetes NCP PDFДокумент5 страницImbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements Diabetes NCP PDFashamy acolОценок пока нет
- College of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanДокумент3 страницыCollege of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanPrince Juzzel Banag100% (1)
- Anorexia NervosaДокумент5 страницAnorexia NervosaPoonam RanaОценок пока нет
- Taberna Catherine T - ACUTE GOUTДокумент17 страницTaberna Catherine T - ACUTE GOUTaaron tabernaОценок пока нет
- Goal Met As Evidenced byДокумент2 страницыGoal Met As Evidenced byFranz Earl Niño AlbesaОценок пока нет
- Ncp1 317rle Ronquillo BryanДокумент2 страницыNcp1 317rle Ronquillo BryanPaul AnteОценок пока нет
- NURSING CARE PLAN Imbalanced Nutrition (Less Than Body Requirement)Документ3 страницыNURSING CARE PLAN Imbalanced Nutrition (Less Than Body Requirement)nofa safitriОценок пока нет
- NURSING CARE PLAN Imbalanced Nutrition (Less Than Body Requirement)Документ3 страницыNURSING CARE PLAN Imbalanced Nutrition (Less Than Body Requirement)HERLIN HOBAYANОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan AmebiasisДокумент7 страницNursing Care Plan AmebiasisCarl Simon CalingacionОценок пока нет
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implement Evaluation: Name: K.A. Age: 58 Years Old College Department: CAIS Sex: MДокумент2 страницыAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implement Evaluation: Name: K.A. Age: 58 Years Old College Department: CAIS Sex: MJulius Mathew EnopiaОценок пока нет
- Cues/Needs Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term Independent Short TermДокумент2 страницыCues/Needs Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term Independent Short TermLatrell GelacioОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan Patient's Name: AB: Henriette Jane de Leon Bn3A January 21, 2021Документ5 страницNursing Care Plan Patient's Name: AB: Henriette Jane de Leon Bn3A January 21, 2021Sbs Nhanxzkie Jountey MushroomxzОценок пока нет
- NCP Ovarian CancerДокумент6 страницNCP Ovarian Cancerwendy gaetosОценок пока нет
- Wesleyan Nursing Care PlanДокумент4 страницыWesleyan Nursing Care PlanPrince Juzzel BanagОценок пока нет
- NCP Nausea and VomitingДокумент4 страницыNCP Nausea and VomitingKingJayson Pacman06Оценок пока нет
- Nursing Care PlanДокумент4 страницыNursing Care PlanJobelyn TunayОценок пока нет
- Careplan AUBДокумент7 страницCareplan AUBSweta ManandharОценок пока нет
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveДокумент5 страницAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveGracia NievesОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan For Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCPДокумент3 страницыNursing Care Plan For Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCPLatrell Gelacio100% (1)
- Finalize Nursing CareplanДокумент20 страницFinalize Nursing Careplanglaizarosario8Оценок пока нет
- ASSESSMENT EXPLANATION OF THE OBJECTIVES NURSING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATIONДокумент5 страницASSESSMENT EXPLANATION OF THE OBJECTIVES NURSING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATIONRussel SantosОценок пока нет
- Nutrition Care Plan for Severe MalnutritionДокумент3 страницыNutrition Care Plan for Severe Malnutritioncharles estradaОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan for Malnutrition and DehydrationДокумент5 страницNursing Care Plan for Malnutrition and DehydrationJoy Mariel Isadora BurgosОценок пока нет
- Cavite State University Nursing Care Plan for Sleep Pattern DisturbanceДокумент2 страницыCavite State University Nursing Care Plan for Sleep Pattern DisturbanceLADY CLAIRE DOBLEОценок пока нет
- Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationДокумент6 страницAssessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationKRISTINE BULACANОценок пока нет
- VI. Nursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationДокумент3 страницыVI. Nursing Care Plan: Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationRyan AsistidoОценок пока нет
- NCP Uterine ProlapsedДокумент4 страницыNCP Uterine ProlapsedPrincessYnaRonquillo100% (1)
- Palawan Polytechnic College IncДокумент2 страницыPalawan Polytechnic College IncLord Pozak MillerОценок пока нет
- Education Provides Ample Information That The Client May Not Be Aware Of, Hence Leading To The Kind ofДокумент3 страницыEducation Provides Ample Information That The Client May Not Be Aware Of, Hence Leading To The Kind ofIrish Jane GalloОценок пока нет
- Intestinal Failure: Diagnosis, Management and TransplantationОт EverandIntestinal Failure: Diagnosis, Management and TransplantationAlan LangnasОценок пока нет
- Kaytlyn Marie Stephens: ObjectiveДокумент1 страницаKaytlyn Marie Stephens: Objectiveapi-268670617Оценок пока нет
- Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment in MumbaiДокумент7 страницDiabetic Retinopathy Treatment in MumbaiCharvi JainОценок пока нет
- A Healthy Dose of Humor: How Laughter Benefits Mind and BodyДокумент3 страницыA Healthy Dose of Humor: How Laughter Benefits Mind and BodyBen Hussa100% (2)
- Action Plan and Accomplishment Report (Indonesia)Документ4 страницыAction Plan and Accomplishment Report (Indonesia)Ezra Angeli Cariño JoaquinОценок пока нет
- Nurses: The Unsung Heroes of Patient CareДокумент4 страницыNurses: The Unsung Heroes of Patient CareJordan CruzОценок пока нет
- Summary Compassionate Use Remdesivir Gilead - enДокумент43 страницыSummary Compassionate Use Remdesivir Gilead - enlelaniaОценок пока нет
- GBS IntroДокумент2 страницыGBS IntroEula Angelica OcoОценок пока нет
- Burn WoundsДокумент14 страницBurn WoundsRuxandra BadiuОценок пока нет
- D&C Procedure ExplainedДокумент4 страницыD&C Procedure ExplainedCjay HernandezОценок пока нет
- Diseases of The ExternalДокумент34 страницыDiseases of The ExternalAaron Nicole Rivera100% (1)
- 31-10-19, Mrs. SY, 33 Y.O. Fraktur Blow Out+Fraktur Maxilla Le Fort I+Fr. Nasal. Dr. Saktrio D Subarno, Sp. BP-REДокумент28 страниц31-10-19, Mrs. SY, 33 Y.O. Fraktur Blow Out+Fraktur Maxilla Le Fort I+Fr. Nasal. Dr. Saktrio D Subarno, Sp. BP-REanon_893244902Оценок пока нет
- Infection Prevention and Control ProgramsДокумент2 страницыInfection Prevention and Control ProgramsAnonymous HSZMNq4100% (1)
- Drug Name Indication Mode of Action Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsДокумент3 страницыDrug Name Indication Mode of Action Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsAlyssa RodriguezОценок пока нет
- What Is Biliary Atresia?Документ6 страницWhat Is Biliary Atresia?echi_maniezz8719Оценок пока нет
- Discipline Relationship With Surgical Nurse PerformanceДокумент16 страницDiscipline Relationship With Surgical Nurse PerformanceDewi Nur Puspita SariОценок пока нет
- BANSUANRDRECORDДокумент4 страницыBANSUANRDRECORDclint xavier odangoОценок пока нет
- NIV and HFNCДокумент16 страницNIV and HFNCMarceline GarciaОценок пока нет
- Apollo Munich Health-Wallet-Brochure - NEW - 8x8 PDFДокумент9 страницApollo Munich Health-Wallet-Brochure - NEW - 8x8 PDFRajat GuptaОценок пока нет
- Teaching Project Summary PaperДокумент11 страницTeaching Project Summary Paperapi-630699625Оценок пока нет
- Clinical Case Reports - 2023 - Lee - Reactivated Herpetic Gingivostomatitis With Secondary Herpes Associated ErythemaДокумент7 страницClinical Case Reports - 2023 - Lee - Reactivated Herpetic Gingivostomatitis With Secondary Herpes Associated ErythemaAhmad AbrorОценок пока нет
- Cancer IntroДокумент29 страницCancer Intromara5140Оценок пока нет