Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
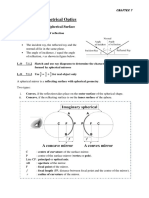
Reflection: Convex Mirror Nature of Image and Its Formation
Загружено:
NimendraИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Reflection: Convex Mirror Nature of Image and Its Formation
Загружено:
NimendraАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
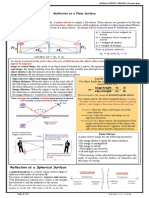
REFLECTION
When a light ray falls on smooth surface it
bounces back in same medium, it is called
reflection of light. Convex Mirror Nature of Image and its Formation
Whose reflecting surface is curved
outward. Also called diverging mirror Image
Focal length = positive Object ? Between F & P
Magnification (m) = positive i M ? Diminished
Laws of Reflection At 4 r
A ? Virtual and erect
? Incident ray, reflected ray and normal all lie in
A′
same plane at same point.
B
? Angle of incidence (∠i) = angle of reflection Object P B′ F C
(∠r). Spherical Mirror At any point
Whose reflecting surface is curved. between 4 & P
N
Object M Image
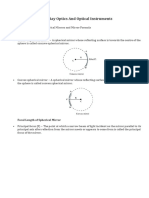
Mirror At 4 ? Virtual
It is a smooth reflecting surface whose one Concave Mirror ? Point sized
side is polished. Whose reflecting surface is curved ? Behind mirror
inward. P F
Also called converging mirror
Focal length = negative
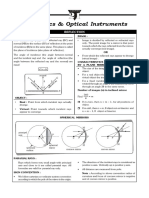
Plane Mirror Magnification (m) = – ve or + ve N
Whose reflecting surface is
plane.
Focal length = infinity (¥)
Nature of image
? Always forms virtual image
? Object distance (u) is always Nature of Image & its Formation
equal to the image distance
(v). M
Object (beyond C)
M M A D
Object (At C)
? Always erect image is formed A D A
i
Object (at 4)
behind the mirror. r B
B′ P B′ C P
? Magnification (m) of the plane P B F
mirror is +1, which means C F C F
A′ A′ E
the size of object is equal to
B N
size of image. N D N Image
Image Image
? Real, inverted
? Real, inverted ? Real, inverted
? At C
? At F ? Between C and F
? Same size
? Diminished ? Diminished
Image Formation
Flat mirror Where, M E Object (between F & P)
Object (between F & C) M E Object (at F)
(u = v) A′
A D M E
A D B
C C A
B′ P
P F
BF i
C F B r P B′
At infinity N
N
A′ Image Image
? Real, inverted ? Virtual, erect N
u v Image
? Real, inverted ? At infinity ? Behind mirror
? Beyond C ? Magnified ? Enlarged
? Enlarged
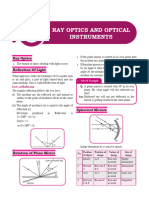
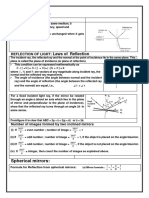
REFRACTION Laws of Refraction
When light rays travel from one medium to other, ? Incident ray, refracted ray and normal all lie in
either they bend towards the normal or away from the same plane, at a same point.
the normal, it is called refraction of light. ? Ratio of sine of angle i and sine of angle r is a
constant called refractive index.
i.e., sin i = constant = µ
sin r
? It is also called Snell's law . Concave Lens
Lens ? It is also called diverging lens.
A piece of glass or other transparent material with
curved sides for concentrating or dispersing light ? Focal length = – ve
rays, used single (in magnifying glass) or with ? Magnification (m) = + ve
other lens (in a telescope) is called lens.
Image Formation & its Nature
Object (at infinity) M Image
Sign Convention Convex Lens ? At focus
A ? It is also called converging ? Virtual, erect
Direction of lens. ? Point sized
Height upwards
incident light ? Focal length = + ve 2F1 F1 O
positive
? Magnification (m) = – ve
Distance towards or + ve
Distance towards right positive
B BN left negative N
XN X
P Object (any point between 4 and O)
Height downwards M
A Image
negative
? Between F1 and O
Mirror A′
? Virtual, erect
A′ ? Diminished
2F1 B F1 B′ O
Image Formation & its Nature Power of Lens (P)
If is defined as the reciprocal of
Object (4) Image focal length in metre.
Image
? Real
? Real, inverted
i.e. Power (P) = 1 (meter)
? At focus Object f
F 2F P ′ F 2F ? Beyond 2F SI unit of Power = dioptre (D)
P P P ′
2F′ F′ 2F ′ F′ Image
(Between F and 2F)
Image
? Real, inverted
? Between F & 2F Image For convex lens, For concave
Object F 2F Object F 2F ? Real, inverted P = + ve lens, P = – ve
Image P ′
P
(at F ′) 2F ′ F ′ P ′ ? At 4
Beyond 2F ′ F′
2F ′
Image
Object
2F
? Real, inverted Image
F 2F Image
F P ′ ? At 2F P ? Virtual, erect
P
2F ′ F′ Image 2F ′ F′ P′
(Between ? On same side
(at 2F)
F and O) of object
Вам также может понравиться
- All in One SCIENCE 10 - Mid Map - CH 9Документ2 страницыAll in One SCIENCE 10 - Mid Map - CH 9narasakuru79Оценок пока нет
- Light Reflection and Refraction (@StudyManiaStore)Документ18 страницLight Reflection and Refraction (@StudyManiaStore)GIRIDHARAN MURUGANОценок пока нет
- Ray Optics and Optical Instruments - Short Notes - Lakshya JEE 2024Документ4 страницыRay Optics and Optical Instruments - Short Notes - Lakshya JEE 2024bhaveshkumarbijaniОценок пока нет
- Light EnergyДокумент55 страницLight EnergygpfphysicsОценок пока нет
- Ray OpticsДокумент62 страницыRay OpticsmrdaddydaddaОценок пока нет
- Ray Diagramming and Mirror EquationДокумент54 страницыRay Diagramming and Mirror Equationnathanielstanaj.mОценок пока нет
- 筆記 2022年6月19日Документ6 страниц筆記 2022年6月19日小貓Оценок пока нет
- 77 Topper 21 101 2 4 62 Light Reflection and Refraction Up201807101458 1531214913 5575 PDFДокумент10 страниц77 Topper 21 101 2 4 62 Light Reflection and Refraction Up201807101458 1531214913 5575 PDFsudhaОценок пока нет
- Geometrical OpticsДокумент20 страницGeometrical OpticsPRIYAA A/P JAYASANKAR / UPMОценок пока нет
- LightДокумент3 страницыLightgm6mry8mrgОценок пока нет
- Light Reflection and Refraction: Shobhit Nirwan'SДокумент18 страницLight Reflection and Refraction: Shobhit Nirwan'S2erwrОценок пока нет
- Real Object: Use "Real-Is-Positive" For SignsДокумент1 страницаReal Object: Use "Real-Is-Positive" For SignskcОценок пока нет
- Light Class XДокумент109 страницLight Class XLekshmipriya PОценок пока нет
- Ray Optics & Optical Instrument Most WantedДокумент17 страницRay Optics & Optical Instrument Most Wantedramianx01Оценок пока нет
- Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Notes Physics Science3Документ13 страницLight Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Notes Physics Science3M S SHANKARОценок пока нет
- Light - Reflection and RefractionДокумент19 страницLight - Reflection and RefractionShalom LogosОценок пока нет
- LightДокумент18 страницLightAyush BarnwalОценок пока нет
- Physics Experiment 6Документ4 страницыPhysics Experiment 6ramkewat744Оценок пока нет
- Phy 214 - Optics and Acoustics: Jumarie E. Coreses, Rche, RCHT MST - ChemistryДокумент60 страницPhy 214 - Optics and Acoustics: Jumarie E. Coreses, Rche, RCHT MST - ChemistryjumarieОценок пока нет
- Ray OpticsДокумент41 страницаRay Opticssangitat082Оценок пока нет
- Light Presentation Class by M PrakashДокумент66 страницLight Presentation Class by M PrakashprakashОценок пока нет
- Spherical Mirror and LensesДокумент3 страницыSpherical Mirror and LensesNins SarmientoОценок пока нет
- Physics Class 10 CDFДокумент13 страницPhysics Class 10 CDFPuppala Vardhan50% (2)
- Light-Re Ection and Refraction: SyllabusДокумент7 страницLight-Re Ection and Refraction: SyllabusKumar AbhishantОценок пока нет
- Class Note 10 LightДокумент31 страницаClass Note 10 LightDiptimayee JenaОценок пока нет
- Light - Shobhit NirwanДокумент22 страницыLight - Shobhit NirwanAakash KumarОценок пока нет
- Ncjescoa 10Документ61 страницаNcjescoa 10ODDENSIGN 2007Оценок пока нет
- 5.1 Reflection of Light 2017Документ89 страниц5.1 Reflection of Light 2017MOHD FARHAN BIN MOHD NA'AIM MoeОценок пока нет
- Ari 12 CH 9 Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsДокумент54 страницыAri 12 CH 9 Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsCommandoОценок пока нет
- Cermin DatarДокумент26 страницCermin DatarOfik Mahesa ChannelОценок пока нет
- Science 10th PDFДокумент189 страницScience 10th PDFMD Moon100% (1)
- ZabateJaymarieC QuizNo4 Waves&OpticsLecДокумент8 страницZabateJaymarieC QuizNo4 Waves&OpticsLecJaymarie ZabateОценок пока нет
- Ray Optics: Physics 11Документ16 страницRay Optics: Physics 11Trishla VermaОценок пока нет
- Mirrors and LensesДокумент49 страницMirrors and LensesjosephrandalldeiparineОценок пока нет
- Q2 Module 3Документ34 страницыQ2 Module 3Ryza AcunaОценок пока нет
- Ray Optics FormulasДокумент8 страницRay Optics Formulassamueljoshuah2004Оценок пока нет
- Image Formationby LensДокумент7 страницImage Formationby LensSharmmeОценок пока нет
- Lenses and Mirrors Part1Документ38 страницLenses and Mirrors Part1Ian DibОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER 10 Light-Reflection and RefractionДокумент14 страницCHAPTER 10 Light-Reflection and RefractionMohammedОценок пока нет
- PowerPoint Presentation of Convex MirrorДокумент25 страницPowerPoint Presentation of Convex MirrorPanuncialman, Johanna Mary B.Оценок пока нет
- Light VerifiedДокумент12 страницLight VerifiedHIMNISH SHARMAОценок пока нет
- (86-112) 2A. Ray Optics FiДокумент27 страниц(86-112) 2A. Ray Optics FiMayuri chatpalliwarОценок пока нет
- Ray Optics Optical InstrumentsДокумент9 страницRay Optics Optical InstrumentsEternalChronosОценок пока нет
- Geometrical Optics: Curved MirrorДокумент61 страницаGeometrical Optics: Curved MirrorMr. XОценок пока нет
- 5.1 Reflection of LightДокумент16 страниц5.1 Reflection of LightJunaidah Mohamad RamliОценок пока нет
- Light Chapter Notes by Mustahmin Khan (V - 1.0) LightДокумент11 страницLight Chapter Notes by Mustahmin Khan (V - 1.0) LightJack KowmanОценок пока нет
- General Physics2 Lesson 6 PDFДокумент7 страницGeneral Physics2 Lesson 6 PDFJohn Renzo MolinarОценок пока нет
- Geometrical Optics: Velocity of ImageДокумент47 страницGeometrical Optics: Velocity of ImageMr. XОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9 Ray Optics by Prashanth RДокумент18 страницChapter 9 Ray Optics by Prashanth RRakshitha YadavОценок пока нет
- Chapter 34B - Reflection and Mirrors II (Analytical)Документ28 страницChapter 34B - Reflection and Mirrors II (Analytical)Heindrich Lloyd Mendoza BasiОценок пока нет
- CH 3 Light FullДокумент11 страницCH 3 Light Fullriwivoj527Оценок пока нет
- Spherical Mirrors PDFДокумент9 страницSpherical Mirrors PDFAditya SudhakarОценок пока нет
- 5.1 Reflection of Light by Curved MirrorДокумент13 страниц5.1 Reflection of Light by Curved MirrorMastura MohamadОценок пока нет
- Physics MIRRORS ProjectДокумент39 страницPhysics MIRRORS Projectaneesh.ubanОценок пока нет
- Lecture 36: Spherical Refracting Surfaces & Thin LensesДокумент7 страницLecture 36: Spherical Refracting Surfaces & Thin LensesparveezОценок пока нет
- LightДокумент5 страницLightpranav .gОценок пока нет
- RAY ConceptДокумент19 страницRAY ConceptMAHESWARA RAO ThotaОценок пока нет
- Phys4C Lecture45Документ29 страницPhys4C Lecture45tatinnnnn.diokno00Оценок пока нет
- Google Automatically Generates HTML Versions of Documents As We Crawl The WebДокумент2 страницыGoogle Automatically Generates HTML Versions of Documents As We Crawl The Websuchi ravaliaОценок пока нет
- Teuku Tahlil Prosiding38491Документ30 страницTeuku Tahlil Prosiding38491unosa unounoОценок пока нет
- General Health Questionnaire-28 GHQ-28Документ3 страницыGeneral Health Questionnaire-28 GHQ-28srajanОценок пока нет
- Kodak Case StudyДокумент8 страницKodak Case StudyRavi MishraОценок пока нет
- MOA Agri BaseДокумент6 страницMOA Agri BaseRodj Eli Mikael Viernes-IncognitoОценок пока нет
- Psc720-Comparative Politics 005 Political CultureДокумент19 страницPsc720-Comparative Politics 005 Political CultureGeorge ForcoșОценок пока нет
- Test Statistics Fact SheetДокумент4 страницыTest Statistics Fact SheetIra CervoОценок пока нет
- Multiple Linear RegressionДокумент26 страницMultiple Linear RegressionMarlene G Padigos100% (2)
- Chapter 12 NotesДокумент4 страницыChapter 12 NotesIvanTh3Great100% (6)
- Invitation 2023Документ10 страницInvitation 2023Joanna Marie Cruz FelipeОценок пока нет
- Grade 7 1ST Quarter ExamДокумент3 страницыGrade 7 1ST Quarter ExamJay Haryl PesalbonОценок пока нет
- Ielts Reading Whale CultureДокумент4 страницыIelts Reading Whale CultureTreesa VarugheseОценок пока нет
- Reported Speech Step by Step Step 7 Reported QuestionsДокумент4 страницыReported Speech Step by Step Step 7 Reported QuestionsDaniela TorresОценок пока нет
- Iso 20816 8 2018 en PDFДокумент11 страницIso 20816 8 2018 en PDFEdwin Bermejo75% (4)
- Dan 440 Dace Art Lesson PlanДокумент4 страницыDan 440 Dace Art Lesson Planapi-298381373Оценок пока нет
- Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & ReviewsДокумент3 страницыDiabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & ReviewspotatoОценок пока нет
- Thesis Statement VampiresДокумент6 страницThesis Statement Vampireslaurasmithdesmoines100% (2)
- CN and OS Lab ManualДокумент53 страницыCN and OS Lab Manualsudheer mangalampalliОценок пока нет
- Trigonometry Primer Problem Set Solns PDFДокумент80 страницTrigonometry Primer Problem Set Solns PDFderenz30Оценок пока нет
- Risteski Space and Boundaries Between The WorldsДокумент9 страницRisteski Space and Boundaries Between The WorldsakunjinОценок пока нет
- AMCAT All in ONEДокумент138 страницAMCAT All in ONEKuldip DeshmukhОценок пока нет
- Los Documentos de La Dictadura Que Entregó Estados Unidos (Parte 2)Документ375 страницLos Documentos de La Dictadura Que Entregó Estados Unidos (Parte 2)Todo NoticiasОценок пока нет
- How Is Extra-Musical Meaning Possible - Music As A Place and Space For Work - T. DeNora (1986)Документ12 страницHow Is Extra-Musical Meaning Possible - Music As A Place and Space For Work - T. DeNora (1986)vladvaidean100% (1)
- MPCДокумент193 страницыMPCpbaculimaОценок пока нет
- Workshop 02.1: Restart Controls: ANSYS Mechanical Basic Structural NonlinearitiesДокумент16 страницWorkshop 02.1: Restart Controls: ANSYS Mechanical Basic Structural NonlinearitiesSahil Jawa100% (1)
- Calcined Clays For Sustainable Concrete Karen Scrivener, AurÇlie Favier, 2015Документ552 страницыCalcined Clays For Sustainable Concrete Karen Scrivener, AurÇlie Favier, 2015Débora BretasОценок пока нет
- Sucesos de Las Islas Filipinas PPT Content - Carlos 1Документ2 страницыSucesos de Las Islas Filipinas PPT Content - Carlos 1A Mi YaОценок пока нет
- Errol PNP Chief AzurinДокумент8 страницErrol PNP Chief AzurinDarren Sean NavaОценок пока нет
- NetStumbler Guide2Документ3 страницыNetStumbler Guide2Maung Bay0% (1)
- CV Michael Naughton 2019Документ2 страницыCV Michael Naughton 2019api-380850234Оценок пока нет