Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Abustan, Advincula, Apollo, Atendido & Baculo: (Labile Cells - Cell Division)
Загружено:
Kim AtendidoИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Abustan, Advincula, Apollo, Atendido & Baculo: (Labile Cells - Cell Division)
Загружено:
Kim AtendidoАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
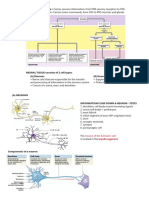
NERVOUS TISSUE o Axon collaterals – branches of axon; at right angles
- Multipolar cells (many processes: dendrites & axon) o Terminal buttons – bulblike structures at the branching ends of
- Basophilic (including cytoplasm: nissl bodies [basophilic blocks]) axons; contains vesicles w/ neurotransmitters
- Fish-eye nucleus ● Dendrites – afferent
- Has nerve processes o Shorter; more abundant
- Excitatory membrane o Presence of gemmules (dendritic spines; structural
modifications that increase the SA of dendrites)
NEURONS o Has primary, secondary, and tertiary branching
Function
- Receive info from environment/other nerve cells ORGANELLES AND INCLUSIONS
- Process information ● Neurofilaments – intermediate filaments
- Send information to other neurons/effector tissues ● Mitochondria – abundant in synaptic junction
- Manipulate information ● Centriole – useless in neurons permanent cells
Characteristics ● Golgi complex
- Permanent cells – no cell division (Labile cells – cell division) ● Nissl bodies – basophilic
- Abundant in euchromatin (light & active); heterochromatin, o Known as the rough ER
nucleolus - dark o Absent in axon
- 1.5 – 2 yrs old – neurons undergo apoptosis ● Lipofuscin – wear-and-tear pigment; more abundant than melanin
- Neuronal plasticity – neurons adjust ● Melanin – small number
Infants > adults
Some recover, some don’t AXONAL TRANSPORT BY MICROTUBULES (24 nm)
- > 40 yrs = neuron death accelerated abuse ● Anterograde/orthograde transport – fast (proteins) or slow
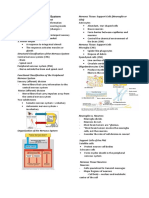
Nerve Processes (microfilaments) based on protein kinesin
Dendrite Axon o Cell body → terminal
Extensions of cell body Lacks Nissl body, from Axon Hillock
●Retrograde transport – driven by protein dynein
Shorter Longer
o Nerve → cell body
More abundant Fewer
o Passageway of viruses into the system (rabies virus,
More branching, near cell body Few branches, axon collaterals
Clostridium tetani)
Presence of gemmules No gemmules
- reach CNS multiply
Cellulipetal (towards neurons) Cellulifugal (extending away)
o Inject nerve growth factor
PARTS NEURON TYPE ACC. TO # OF PROCESSES
● Cell body (perikaryon) – processing site 1. Multipolar – most common; gray matter of spinal cord
● Axon hillock – clearing of nissl bodies - 1 axon, multiple dendrites
● Axon – cannot synthesize its own protein because of absence of 2. Bipolar – 1 axon, 1 dendrite
nissl bodies completely dependent on nerve cell body (only 1); - Special sensory organs
send information
PAGE Abustan, Advincula, Apollo, Atendido & Baculo
3. Pseudounipolar – 1 process is
both the axon and dendrite → dendraxon
JELLY ROLL
HYPOTHESIS
NEURON TYPE ACC. TO LENGTH OF
PROCESSES
1. Golgi cell type I – long process;
limbs (purkinje cell) [SC: gray m. to
SKM, brain]
2. Golgi cell type II – short
process; interneurons (granule - Myelin
cell) formation → concentrically
wrapped (schwann cell – PNS)
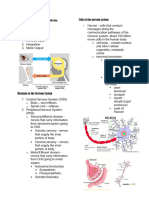
GANGLION CELLS (PNS) - axon will indent on the
DORSAL ROOT GANGLION AUTONOMIC GANGLION
schwann cell,
Sensory then the schwann Long
Cross-
Pseudounipolar Multipolar section
Section
cell will envelop
Fine nissl bodies uniformly Intermediate size of nissl bodies
the axon
dispersed in cytoplasm - Myelin (insulator)
Presence of amphicytes (satellite Few satellite cells Black →
cells) contains lipids
Myelinated (fast) Unmyelinated (slow)
which absorb
osmium
tetroxide
Source:
schwann
cells (1
schwann
cell: 1
internode); Saltatory
conductor
PAGE Abustan, Advincula, Apollo, Atendido & Baculo
● Node of ranvier (axolemma) – NERVE ENDINGS/RECEPTORS
area between myelin (transduction; stimulus nerve impulse)
● Myelin – bubbly, open ● Proprioceptors
appearance ○ information on orientation,
● Axolemma - covering of axon skeletal position, muscle
tension, and movement
● Endoneurium – outermost
○ neuromuscular spindle and
covering of axon; connective
Golgi tendon organs
tissue
● Exteroceptors
● Perineurium – connective tissue
○ Epithelium
surrounding the fascicles
■ Free nerve endings
● Epineurium – covers 1 nerve
(versatile; most for
fiber
pain, touch, thermal
sense, pressure)
■ Slowly adapting
(discriminatory touch
& pressure receptor)
○
○
SYNAPSE (20-30 nm in diameter; ○
Unidirectional)
○
- Axo-dendritic – most common
○
(axon-dendrite)
○
- Axosomatic – axon-cell body
junction; muscles ○
(neuromuscular junction) ○
- Axo-axonic – rare (axon-axon) ○
*post-synaptic web – dark (stain) ○
○
○
● Secondary synaptic cleft –
○
neuromuscular junction
○
o Invaginations in the
○
postsynaptic membrane
o Increases surface area ○
(more ACh binding) ○
● Myasthenia gravis – autoimmune ○
disease ○
of no receptors in postsynaptic ○
membrane ○
o form antibodies against Connective Tissue
receptors ■ Merkel cells
o block receptor ACh not
■ Meissner’s
bind
corpuscle
PAGE Abustan, Advincula, Apollo, Atendido & Baculo
■ Vater Pacinian o Flower spray – contractile area,
Merkel cells - slowly adapting; Meissner’s corpuscle - fast on the end of
for discriminatory touch and adapting; discriminatory the fiber
pressure receptors. touch and vibration (stretch
through
hammer)
Vater Pacinian corpuscle - fast Ruffini’s end organ - found in
*test: muscle spindle,
adapting for rapid vibration; deep skin and soles; detects
extrafusal, dorsal root,
onion-like tension
ventral root, efferent
End bulb of Krause - encapsulated receptor in oropharynx and nerves
conjunctiva
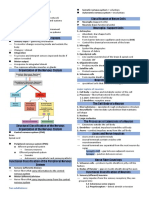
SPINAL CORD
Gray matter Whit
inner, basophilic) outer, n
Contains nerve cell bodies and My
proximal processes
Fibrous a
Protoplasmic astrocytes
oligo
Corpuscle
■ Ruffini’s end organ
■ End bulb of Krause
● Nociceptors
○ Pain
○ 2 Types of Pain Carriers
■ A delta fibers – fast
pain (myelinated)
■ C fibers – slow pain
(unmyelinated)
● Neuromuscular spindle – regulate
muscle tone
o extrafusal fibers
o “intrafusal fibers” -nuclear bag
(dilated portion) & nuclear chain;
for reflex actions
o Anulospiral – center of the
intrafusal fiber (stretch through
hammer)
PAGE Abustan, Advincula, Apollo, Atendido & Baculo
Вам также может понравиться
- Histo Mod1 NervesДокумент4 страницыHisto Mod1 Nervessayeda.raza24Оценок пока нет
- Physio Lec 6 Apr 2021Документ3 страницыPhysio Lec 6 Apr 2021Luis IbarrolaОценок пока нет
- Nervous System - HistologyДокумент8 страницNervous System - HistologyambercrisologoОценок пока нет
- Nervous Tissue: Nervous System Neuron - The Only Cell Type Capable of Generating and PropagatingДокумент5 страницNervous Tissue: Nervous System Neuron - The Only Cell Type Capable of Generating and PropagatingAlyssa AlferezОценок пока нет
- Sem 1 - 机能解剖学 (Chapter 2 - Histology of nervous tissue) 笔记Документ6 страницSem 1 - 机能解剖学 (Chapter 2 - Histology of nervous tissue) 笔记Cah YeeОценок пока нет
- Nervous TissueДокумент77 страницNervous Tissuemarjanggyamar7Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 - Structure and Functions For The Cells of The Nervous SystemДокумент14 страницChapter 2 - Structure and Functions For The Cells of The Nervous SystemLANCE GILL Tolentino100% (1)
- Note in Nervous TissueДокумент7 страницNote in Nervous TissueNo NameОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9-Nervous SystemДокумент2 страницыChapter 9-Nervous SystemLynОценок пока нет
- CNS PNS: Lipofuscin: Wear and TearДокумент10 страницCNS PNS: Lipofuscin: Wear and TearDr P N N ReddyОценок пока нет
- CNS PNS: Absent in AxonsДокумент6 страницCNS PNS: Absent in AxonsDr P N N ReddyОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 Human Histology - Nervous System PDFДокумент7 страницChapter 7 Human Histology - Nervous System PDFErica Ann IcalОценок пока нет
- Nervous Tissue (Histo)Документ8 страницNervous Tissue (Histo)BEATRIZ MITZI BEHAGAN BALINGITОценок пока нет
- Junquier's Histology Summary Nervous Tissue and The Nervous SystemДокумент7 страницJunquier's Histology Summary Nervous Tissue and The Nervous SystemJohn Michael CastroОценок пока нет
- 7 Control & CoordinationДокумент38 страниц7 Control & CoordinationSaifAkhtarОценок пока нет
- Nervous TissueДокумент2 страницыNervous TissueALEXIS MOIRAH CALIGAGANОценок пока нет
- Nerve Cell: Zy - Erds Depatment of Histology, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Sumatera Utara 2020Документ29 страницNerve Cell: Zy - Erds Depatment of Histology, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Sumatera Utara 2020Rhena Fitria KhairunnisaОценок пока нет
- NERVOUS TISSUE HandoutДокумент6 страницNERVOUS TISSUE HandoutAkemi100% (1)
- The Nervous SystemДокумент18 страницThe Nervous SystemSheyn Mahru ConomanОценок пока нет
- 5-Histology of Nervous TissueДокумент78 страниц5-Histology of Nervous Tissuevbh8222Оценок пока нет
- Histology of The CNSДокумент7 страницHistology of The CNStiiandiОценок пока нет
- Osmosis High-Yield Physiology - Medicalstudyzone - Com (Sürüklenen)Документ87 страницOsmosis High-Yield Physiology - Medicalstudyzone - Com (Sürüklenen)Dilay MercimekОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Ear PDFДокумент22 страницыAnatomy and Physiology of The Ear PDFannora daffaОценок пока нет
- The Nervous SystemДокумент9 страницThe Nervous SystemnixicoleОценок пока нет
- Neurons Nerve Fibers and Peripheral NervesДокумент20 страницNeurons Nerve Fibers and Peripheral NervesCJ GoОценок пока нет
- Nerve PhysiologyДокумент4 страницыNerve PhysiologyMalti SharmaОценок пока нет
- NEUROANATOMY IntroductionДокумент10 страницNEUROANATOMY IntroductionIshant SinghОценок пока нет
- Nervous Sytem 1Документ11 страницNervous Sytem 1Elaine Victoria ElizanОценок пока нет
- Sistem NervosumДокумент35 страницSistem NervosumRaniyah Az-zahraОценок пока нет
- PSYC - 1001 - Chapter 3Документ20 страницPSYC - 1001 - Chapter 3Alaina PalmaОценок пока нет
- Nervous System Part 1Документ11 страницNervous System Part 1Mariel AbatayoОценок пока нет
- CSE485 Lec3 Neurons SensationPerception M2021Документ30 страницCSE485 Lec3 Neurons SensationPerception M2021Monica PonnamОценок пока нет
- Nervous SystemДокумент12 страницNervous SystemSJane FeriaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 - Structure and Functions of CellsДокумент7 страницChapter 2 - Structure and Functions of Cellsmanilyn dacoОценок пока нет
- Anaphy Reviewer (Semi Finals)Документ5 страницAnaphy Reviewer (Semi Finals)Sophia Mae ClavecillaОценок пока нет
- Anaphy Reviewer (Semi Finals)Документ28 страницAnaphy Reviewer (Semi Finals)Sophia Mae ClavecillaОценок пока нет
- Nervous SystemДокумент3 страницыNervous SystemAly HannahОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 The Nervous System (ANAPHY)Документ7 страницChapter 7 The Nervous System (ANAPHY)Krisha AvorqueОценок пока нет
- Nervoussystem: Functions (Crime)Документ13 страницNervoussystem: Functions (Crime)Dave ChenОценок пока нет
- Physiobio ReviewerДокумент5 страницPhysiobio ReviewerGemma RossОценок пока нет
- Lesson 5 Nervous SystemДокумент52 страницыLesson 5 Nervous SystemPIALOGO RONA GIAОценок пока нет
- PhysiologicalДокумент32 страницыPhysiologicalElle QuizonОценок пока нет
- NEUROGLIAL ("White Matter") AstrocytesДокумент12 страницNEUROGLIAL ("White Matter") AstrocytesGabrielle MagdaraogОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 - Nervous SystemДокумент3 страницыChapter 7 - Nervous SystemRishelle Mae Miñoza PilonesОценок пока нет
- Nervous System Part 1Документ4 страницыNervous System Part 1Cyrill Denise CastañedaОценок пока нет
- Anaphy Nervous - SystemДокумент8 страницAnaphy Nervous - SystemArcher RiegoОценок пока нет
- ANAPHY - Nervous SystemДокумент5 страницANAPHY - Nervous SystemMA. ANDREA NICOLE DURANОценок пока нет
- Neurology 1Документ47 страницNeurology 1Sonu CanОценок пока нет
- The Nervous System First PartДокумент15 страницThe Nervous System First PartNicole NipasОценок пока нет
- Chapter 8 - Nervous SystemДокумент12 страницChapter 8 - Nervous SystemlalaОценок пока нет
- Abct2326 Nerve 2023Документ95 страницAbct2326 Nerve 2023Nga Man ChanОценок пока нет
- Nervous Tissue 4th Year 2020-2021 DR Mona1Документ40 страницNervous Tissue 4th Year 2020-2021 DR Mona1Atheer AltowairqiОценок пока нет
- What Is A Neuron? The Parts of A Neuron: - ! Cell Body or Soma! - ! - !Документ7 страницWhat Is A Neuron? The Parts of A Neuron: - ! Cell Body or Soma! - ! - !Bernadine SaladoОценок пока нет
- Histology Pt. IiДокумент3 страницыHistology Pt. Iimaxpein zein and aceОценок пока нет
- 03-Nervous System TheoryДокумент29 страниц03-Nervous System TheoryabhiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 12 Lecture Outline: Nerves Are VascularizedДокумент6 страницChapter 12 Lecture Outline: Nerves Are VascularizedBEATRIZ MITZI BEHAGAN BALINGITОценок пока нет
- Functional Classification of The Peripheral Nervous SystemДокумент20 страницFunctional Classification of The Peripheral Nervous SystemLapitan Jared Anne S.Оценок пока нет
- 神经生物学Документ58 страниц神经生物学jdskydtОценок пока нет
- Nervous System: Nissl Bodies-Sites of Protein Synthesis in NeuronsДокумент16 страницNervous System: Nissl Bodies-Sites of Protein Synthesis in NeuronsZella ViaОценок пока нет
- Excitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesОт EverandExcitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 Sense Organs Eyes Skin and TongueДокумент33 страницыUnit 2 Sense Organs Eyes Skin and TongueBONGISIPHO HLOPHEОценок пока нет
- KONJI KinesioTapingДокумент12 страницKONJI KinesioTapinggvozdenОценок пока нет
- Lect.3, Properties of ReceptorsДокумент21 страницаLect.3, Properties of ReceptorsAttiqaQureshi100% (2)
- (TRO) Human-Inspired Robotic Grasp Control With Tactile SensingДокумент13 страниц(TRO) Human-Inspired Robotic Grasp Control With Tactile SensingwsfОценок пока нет
- PresjurДокумент18 страницPresjurIhsanОценок пока нет
- How Many Nerve Endings Are in A FingerДокумент2 страницыHow Many Nerve Endings Are in A FingerJennifer Garcia EreseОценок пока нет
- Kinesiotaping TechniquesДокумент26 страницKinesiotaping TechniquesSuhana hidayat100% (1)
- Lower Extremity Perturbation Training.12Документ8 страницLower Extremity Perturbation Training.12Martiniano Vera EnriqueОценок пока нет
- OmrДокумент39 страницOmrabhijeetОценок пока нет
- Jurnal Meniskus Medial Dan Laterall FisioterapiДокумент6 страницJurnal Meniskus Medial Dan Laterall FisioterapiAstrid Nasna LarasatiОценок пока нет
- Thomas Fischer Weiss - Cellular Biophysics, Vol. 2 - Electrical Properties-A Bradford Book (1996)Документ300 страницThomas Fischer Weiss - Cellular Biophysics, Vol. 2 - Electrical Properties-A Bradford Book (1996)RhinometalI&CОценок пока нет
- Chapter 14 - The Somatic Nervous SystemДокумент55 страницChapter 14 - The Somatic Nervous SystemTH TОценок пока нет
- The Sensorimotor System Part I The Physiologic Basis of Functional Joint StablityДокумент9 страницThe Sensorimotor System Part I The Physiologic Basis of Functional Joint StablityMauro Esban Obreque QuianОценок пока нет
- Update On Proprioception: Considerations For Dance EducationДокумент8 страницUpdate On Proprioception: Considerations For Dance EducationAna Carolina PetrusОценок пока нет
- CH 17 SqsДокумент3 страницыCH 17 SqszalimchuhanОценок пока нет
- Gardner ELS2010 PDFДокумент12 страницGardner ELS2010 PDFEdna Odette Melo UscangaОценок пока нет
- Mechanical ComfortДокумент36 страницMechanical ComfortDr Muhammad Mushtaq MangatОценок пока нет
- 2003 Fascial Plasticity - A New Neurobiological Explanation - Part 1 and Part 2Документ22 страницы2003 Fascial Plasticity - A New Neurobiological Explanation - Part 1 and Part 21Rogerio100% (1)
- Sensory and Motor SystemДокумент12 страницSensory and Motor SystemrobertoОценок пока нет
- ROOD ApproachДокумент59 страницROOD Approachsridhar_physio75% (4)
- Anatomy and Physiology Foundations For The Health Professions 1st Edition Deborah Roiger Test Bank 1Документ36 страницAnatomy and Physiology Foundations For The Health Professions 1st Edition Deborah Roiger Test Bank 1stevenbrownxockdjatwe100% (23)
- Chapter 24. Sense Organs: ObjectivesДокумент25 страницChapter 24. Sense Organs: ObjectivesFrancisco GonzálezОценок пока нет
- Scapula Strengthening Exercises Evidence and Summary.Документ57 страницScapula Strengthening Exercises Evidence and Summary.ryankelsall100% (2)
- Anaphy Lec Special SensesДокумент6 страницAnaphy Lec Special SensesRyan Dave UmayamОценок пока нет
- Mechanosensation and Blood Supply of HmaДокумент4 страницыMechanosensation and Blood Supply of HmaJOHN HAROLD CABRADILLAОценок пока нет
- The Sensorimotor SystemДокумент8 страницThe Sensorimotor SystemAinisaОценок пока нет
- The Physiology of Bone Pain. How Much Do We Really Know?: Sara Nencini and Jason J. IvanusicДокумент15 страницThe Physiology of Bone Pain. How Much Do We Really Know?: Sara Nencini and Jason J. IvanusiczainurhafizОценок пока нет
- Plasticity FascialДокумент13 страницPlasticity FascialMichael DuranОценок пока нет
- Guyton Somatic SensesДокумент2 страницыGuyton Somatic SensesJamie Ong100% (1)
- 10.1177 1941738111429419Документ12 страниц10.1177 1941738111429419refniОценок пока нет