Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
CE161P Soil Mechanics Homework on Permeability Testing
Загружено:
Myca QuizaОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CE161P Soil Mechanics Homework on Permeability Testing
Загружено:
Myca QuizaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Name: ______________________________________________________ CE161P GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING (SOIL MECHANICS)
Student Number: ___________________________________________ 2nd quarter | 2018-2019 | Engr. CHENNIE CARISSA A. CAJA
HOMEWORK 03
ONE-DIMENSIONAL FLOW OF WATER THROUGH SOILS
Answer the following problems. Write your solutions on short bond papers and box your final answer.
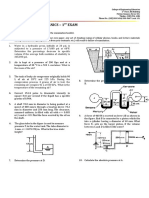
1. For a constant head permeability test in a 5. A sand layer of the cross-sectional area shown
sand, the following are given: in the figure has been determined to exist for
L = 300 mm a 800-m length of the levee. The hydraulic
A = 175 cm2 conductivity of the sand layer is 2.8 m/day.
H = 500 mm Determine the quantity of water which flows
water collected in 3 mins = 620 cm3 into the ditch in m3/min.
void ratio of sand = 0.58
Determine:
a. hydraulic conductivity, k (cm/s)
b. seepage velocity
2. In a constant head permeability test in the
laboratory, the following are given: L = 12 in,
and A = 15 in2. If the value of k = 0.006 in/s
and a flow rate of 450 in3/hr must be
maintained through the soil, what is the head
6. Find the flow rate in m3/sec/m length (at right
difference, h, across the specimen? Also
angles to the cross section shown) through the
determine the discharge velocity under the
permeable soil layer. Given H=5 m, H1=2.8 m,
test conditions.
h=3.1 m, L=60 m, 𝛼=5°, k=0.05 cm/sec.
3. For a falling head permeability test, the
following are given:
Length of soil specimen = 700 mm
Area of the soil specimen = 20 cm2
Area of the standpipe = 1.05 cm2
Head difference at time t=0 is 800 mm
Head difference at time t=8 min is 500
mm
Determine:
a. absolute permeability of the soil
b. head difference at time t = 6 min
Assume that the test was conducted at 20°C
and at 20°C, 𝛾𝑤 = 9.789 kN/m3 and 𝜂 =
1.005×10-3 N∙s/m2.
4. For a falling head permeability test, the
following are given: length of specimen = 380
mm; area of specimen = 6.5 cm2; k = 0.175
cm/min. What should be the area of the
standpipe for the head to drop from 650 to 300
cm in 8 min?
Name: ______________________________________________________ CE161P GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING (SOIL MECHANICS)
Student Number: ___________________________________________ 2nd quarter | 2018-2019 | Engr. CHENNIE CARISSA A. CAJA
HOMEWORK 03
EQUIVALENT COEFFICIENT OF PERMEABILITY IN STRATIFIED SOILS
Answer the following problems. Write your solutions on short bond papers and box your final answer.
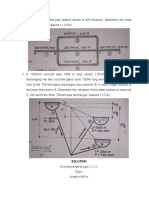
1. A layered soil is shown in the figure. Estimate a. Determine the total flow per meter.
the ratio of equivalent hydraulic conductivity b. Determine the equivalent coefficient of
kH(eq) / kV(eq). permeability.
3. A test is set-up as shown in the figure below.
A cylindrical mold, 4” in diameter is filled
with silt to a height H1=0.20 ft whose
coefficient of permeability is 6.10x10-4 ft/min.
A second coaxial mold, placed on top of the silt
inside the first mold, has an inside diameter of
1.50” and height H2=0.30 ft. Its thickness is
negligible. The inside of this second mold is
filled with the same silt, but the annular ring
outside is filled with sand whose coefficient of
permeability is 2.50x10-3 ft/min.
The test set-up is a permeameter of constant
head. Water is placed in the mold and
maintained at a level h=1.25 ft above the level
2. Given the stratified soil shown in the figure. of the outlet. It may be considered that the
The properties of each soil are as follows: system consists of a fictitious soil of thickness
H=H1+H2 and a coefficient of permeability kf.
Coefficient of permeability:
k1 = 6.50 cm/hr; k2 = 5.25 cm/hr; k3 = 3.50
cm/hr; k4 = 6.00 cm/hr; k5 = 8.80 cm/hr; k6 =
4.40 cm/hr
Thickness:
H = 1.50 m; H3 = 0.50 m; H4 = 0.60 m; H5 =
0.40 m
Length:
L1 = 1.0 m; L2 = 0.8 m; L3 = 1.5 m; L6 = 1.2 m
Determine:
a. the total amount of flow of water
through the soil.
b. the equivalent coefficient of
permeability of the system.
c. the total amount of flow that
percolated after 30 minutes.
Вам также может понравиться
- Hydraulics and Geotechnical Answer KeyДокумент2 страницыHydraulics and Geotechnical Answer KeyAngelica RomeroОценок пока нет
- Q P A Q 1600 4 (4) Q 100 Kpa: SolutionДокумент8 страницQ P A Q 1600 4 (4) Q 100 Kpa: SolutionFrancis John BuacОценок пока нет
- Gis Located Above B)Документ10 страницGis Located Above B)Apple AterradoОценок пока нет
- CE EVALUATION EXAM No. 7 - Soil Testing, Foundations, Retaining Wall (Answer Key)Документ6 страницCE EVALUATION EXAM No. 7 - Soil Testing, Foundations, Retaining Wall (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la CruzОценок пока нет
- Quiz Bowl: AUGUST 13, 2019Документ36 страницQuiz Bowl: AUGUST 13, 2019Armenion Mark AllenОценок пока нет
- Structural Engineering & ConstructionДокумент13 страницStructural Engineering & ConstructionREX AMPONGANОценок пока нет
- Mste 1Документ4 страницыMste 1Mingjaw MingmingОценок пока нет
- Ce 343L - Fluid Mechanics - 1 ExamДокумент2 страницыCe 343L - Fluid Mechanics - 1 ExamMichelle Daarol100% (1)
- Module 2 Analysis of Prestressed Concrete Beams Using Combined Load ApproachДокумент48 страницModule 2 Analysis of Prestressed Concrete Beams Using Combined Load ApproachVann AlfredОценок пока нет
- HF Using Manning Formula Sample Problems: Voice: Balase, Ann Maricar FДокумент11 страницHF Using Manning Formula Sample Problems: Voice: Balase, Ann Maricar FKyohai RinggoОценок пока нет
- Strength 4 May 2021Документ3 страницыStrength 4 May 2021Jon SnowОценок пока нет
- Agacita John PaulДокумент10 страницAgacita John PaulCarlo Dela CruzОценок пока нет
- Pipes Dia. Length Friction "F" 1 900 MM 1500 M 0.0208 2 600 MM 450 M 0.0168 3 450 MM 1200 M 0.0175Документ1 страницаPipes Dia. Length Friction "F" 1 900 MM 1500 M 0.0208 2 600 MM 450 M 0.0168 3 450 MM 1200 M 0.0175John Mortel AparicioОценок пока нет
- Pressure Variations and Pascal's LawДокумент18 страницPressure Variations and Pascal's LawBillie Ian. Salamante JrОценок пока нет
- Problem 7. Structural Design "CE Board Exam Nov. 1992Документ1 страницаProblem 7. Structural Design "CE Board Exam Nov. 1992AlvinОценок пока нет
- CE 010 Module 1.2-1.3Документ29 страницCE 010 Module 1.2-1.3NIÑO LEANDRO LEYESОценок пока нет
- CE EVALUATION EXAM No. 6 - Channels, Weir, Hydrodynamics, Soil Prop (Answer Key)Документ7 страницCE EVALUATION EXAM No. 6 - Channels, Weir, Hydrodynamics, Soil Prop (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la Cruz100% (1)
- Understanding Weirs: Formulas and ClassificationsДокумент4 страницыUnderstanding Weirs: Formulas and ClassificationsJovy AndoОценок пока нет
- Activity Sheet 4Документ3 страницыActivity Sheet 4Shiebastian ArietaОценок пока нет
- MATH Final PreboardДокумент8 страницMATH Final PreboardKristelle V. TorrealbaОценок пока нет
- M2 03 Constant and Falling Head TestДокумент13 страницM2 03 Constant and Falling Head TestPzynae FlorentinoОценок пока нет
- Shear ReinforcementДокумент7 страницShear ReinforcementJohn Saniel J. EstacionОценок пока нет
- Bolted Connection Design & Analysis MethodsДокумент3 страницыBolted Connection Design & Analysis MethodsJohn Philip NuñezОценок пока нет
- 14 Making and Curing Concrete Test Specimens in The FieldДокумент6 страниц14 Making and Curing Concrete Test Specimens in The FieldJohn MarkОценок пока нет
- Fluid Mech May 2021Документ5 страницFluid Mech May 2021Naigell SolomonОценок пока нет
- HGE#003-Hydraulics Engineering 3Документ3 страницыHGE#003-Hydraulics Engineering 3Kim Ryan PomarОценок пока нет
- Thermal Stresses: Mechanics of Deformable BodiesДокумент15 страницThermal Stresses: Mechanics of Deformable BodiesJake CanlasОценок пока нет
- Republic of The Philippines: Battery - 1Документ9 страницRepublic of The Philippines: Battery - 1Michael James ll BanawisОценок пока нет
- CIVIL ENGINEERING BOARD EXAMДокумент7 страницCIVIL ENGINEERING BOARD EXAMConan EdogawaОценок пока нет
- CE Review - Steel Design Problems SolvedДокумент3 страницыCE Review - Steel Design Problems SolvedLemuel TeopeОценок пока нет
- Determine Water Surface Elevation and Pipe Discharge PowerДокумент4 страницыDetermine Water Surface Elevation and Pipe Discharge PowerDiecon Irish ArboledaОценок пока нет
- Soil CompactionДокумент10 страницSoil CompactionBernie G. CatarigОценок пока нет
- Civil Engineering November 2020 Review Innovations Hydraulics ProblemsДокумент1 страницаCivil Engineering November 2020 Review Innovations Hydraulics ProblemsJustine Ejay MoscosaОценок пока нет
- Republic of The Philippines: Exam 2Документ4 страницыRepublic of The Philippines: Exam 2Jan Jan AnoОценок пока нет
- Policarpio 6 - Refresher SECДокумент2 страницыPolicarpio 6 - Refresher SECJohn RoaОценок пока нет
- Civil Engineering Board Exam Bridge ProblemsДокумент7 страницCivil Engineering Board Exam Bridge ProblemsRyan CagsawaОценок пока нет
- Soil Mechanics Problems and SolutionsДокумент18 страницSoil Mechanics Problems and SolutionsBemzar SamsonОценок пока нет
- CE HPGE 2023 Definition of Terms UnlockedДокумент21 страницаCE HPGE 2023 Definition of Terms UnlockedRichard ParedesОценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент19 страницUntitledRojane FloraОценок пока нет
- C-9104 Conventional Ultraviolet Flame Detector Issue 2.05Документ2 страницыC-9104 Conventional Ultraviolet Flame Detector Issue 2.05Seagull MarineОценок пока нет
- Hydraulics New ProblemsДокумент5 страницHydraulics New ProblemsEugine BalomagaОценок пока нет
- Principles of Geotechnical Engineering-149-151Документ3 страницыPrinciples of Geotechnical Engineering-149-151Andrea Arroba0% (1)
- Ce0061 Professional Course 4 - (Specialized 2) Ste Track: Prestressed Concrete DesignДокумент40 страницCe0061 Professional Course 4 - (Specialized 2) Ste Track: Prestressed Concrete DesignjerichoОценок пока нет
- 2023april Psad UnlockedДокумент6 страниц2023april Psad UnlockedKristelle V. TorrealbaОценок пока нет
- Subject 1 Algebra Trigonometry Plane Geometry Solid Geometry Analytic Geometry Probability PhysicsДокумент49 страницSubject 1 Algebra Trigonometry Plane Geometry Solid Geometry Analytic Geometry Probability PhysicsDani LubosОценок пока нет
- CE Board 2010 2023 Definition of TermsДокумент37 страницCE Board 2010 2023 Definition of TermsRichard ParedesОценок пока нет
- F2F Handouts (Stress Distribution & Shear Strength of Soil) - SOLUTIONS & ANSWERSДокумент5 страницF2F Handouts (Stress Distribution & Shear Strength of Soil) - SOLUTIONS & ANSWERSSelling AqwОценок пока нет
- RCE2018 math and geometry problems solutions under 40 charactersДокумент1 страницаRCE2018 math and geometry problems solutions under 40 charactersArwin VillegasОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3b - Analysis of Tension MembersДокумент56 страницChapter 3b - Analysis of Tension MembersRami DemachkiОценок пока нет
- Factor of Safety Against Sliding Refresher CourseДокумент3 страницыFactor of Safety Against Sliding Refresher CourseKim Ryan PomarОценок пока нет
- Refresher Module 16 (GH8) - Geotechnical Engineering and HydraulicsДокумент1 страницаRefresher Module 16 (GH8) - Geotechnical Engineering and HydraulicsMadelyn OronosОценок пока нет
- Flexural Analysis of BeamsДокумент50 страницFlexural Analysis of BeamsIsmail FarajpourОценок пока нет
- Ce Board Strength ReviewerДокумент1 страницаCe Board Strength ReviewerZherrinore RasayОценок пока нет
- Local Media3116916508017834053 2Документ7 страницLocal Media3116916508017834053 2Ben BenbenОценок пока нет
- Specific Gravity Determination Using U-Tube ManometerДокумент9 страницSpecific Gravity Determination Using U-Tube ManometerEly ReyesОценок пока нет
- Maximum Stresses On A Pole Subjected To Combined LoadingsДокумент2 страницыMaximum Stresses On A Pole Subjected To Combined LoadingsShiela GonzalesОценок пока нет
- Module 10 Pipes in Series and Parallel Reservoir ProblemsДокумент18 страницModule 10 Pipes in Series and Parallel Reservoir ProblemsAragones, Trisha Marie CОценок пока нет
- KIPPAP EDUCATION CE Exam 17 ReviewДокумент8 страницKIPPAP EDUCATION CE Exam 17 ReviewMichael MercadoОценок пока нет
- Soil Breakdown ProcessДокумент105 страницSoil Breakdown ProcessSigue Ramel HinayasОценок пока нет
- Guide to Straw Bale Construction Methods and Their BenefitsДокумент27 страницGuide to Straw Bale Construction Methods and Their Benefitsஆனந்த் கிருஷ்ணன்100% (1)
- Philippine Christian University: Subject: Managerial EconomicsДокумент3 страницыPhilippine Christian University: Subject: Managerial EconomicsMara AngeliОценок пока нет
- Welding Consumable Nominal Chemical Composition, Wt. Pct. Other Designation SystemsДокумент1 страницаWelding Consumable Nominal Chemical Composition, Wt. Pct. Other Designation SystemsLLОценок пока нет
- Bazam Company ProfileДокумент30 страницBazam Company ProfileIbrahimrashid Billow HusseinОценок пока нет
- SBB 2 Painting FinalДокумент14 страницSBB 2 Painting FinalNeilJohnОценок пока нет
- Refrigerant-Piping Design Guide-McquayДокумент91 страницаRefrigerant-Piping Design Guide-Mcquayapi-19789368100% (4)
- Compliance With NR-12 Requirements PetrobrasДокумент8 страницCompliance With NR-12 Requirements PetrobrascourarodrigoОценок пока нет
- CIVE1171 Lecture 1Документ33 страницыCIVE1171 Lecture 1JoshОценок пока нет
- Manual For Deflection of Beam ApparatusДокумент4 страницыManual For Deflection of Beam Apparatusramniwas123Оценок пока нет
- GB1516 Sac 240 CV SP 0003 - AДокумент31 страницаGB1516 Sac 240 CV SP 0003 - AkkkkОценок пока нет
- WJ-Series WJ-Series: Turbine Meter Instructions Turbine Meter InstructionsДокумент8 страницWJ-Series WJ-Series: Turbine Meter Instructions Turbine Meter InstructionsIndra SUdirmanОценок пока нет
- BILLING NO.2 - Daanlungsod-Calangahan DetailedДокумент1 страницаBILLING NO.2 - Daanlungsod-Calangahan Detailedanthony christian yangОценок пока нет
- Otr Product CatalogДокумент116 страницOtr Product CatalogIwan KurniawanОценок пока нет
- Facility Management of Smart BuildingsДокумент7 страницFacility Management of Smart BuildingsVie KaunangОценок пока нет
- Pump FoundationДокумент4 страницыPump FoundationbabuОценок пока нет
- Renovation, Alteration and Addition WordДокумент22 страницыRenovation, Alteration and Addition Word笨豬Оценок пока нет
- Bilaga 3 ReservdelsprislistaДокумент856 страницBilaga 3 ReservdelsprislistaMarlon OliveiraОценок пока нет
- Analisa Paving Block Teb. 6 CMДокумент20 страницAnalisa Paving Block Teb. 6 CMnixonОценок пока нет
- Metal Siding Deflection LimitДокумент1 страницаMetal Siding Deflection Limitwaweng22Оценок пока нет
- Cet201 Mos Module 1Документ27 страницCet201 Mos Module 1Sidhartha Krishna TОценок пока нет
- MTR-50, 90, 140 3-Position Swing Cylinders: Instruction & Repair Parts SheetДокумент28 страницMTR-50, 90, 140 3-Position Swing Cylinders: Instruction & Repair Parts SheetJesus D. Gutierrez G.Оценок пока нет
- Umbrella HouseДокумент6 страницUmbrella HouseGonzalo Agulló FernándezОценок пока нет
- Sheet 1A IE304 Material TechnologyДокумент5 страницSheet 1A IE304 Material TechnologyAhmedAhmedОценок пока нет
- RCC Box Drain SpecificationДокумент110 страницRCC Box Drain SpecificationMaulik RavalОценок пока нет
- Quarry & Stone PDFДокумент32 страницыQuarry & Stone PDFGary VinesОценок пока нет
- Precast Concrete Pile DesignДокумент2 страницыPrecast Concrete Pile DesignSamishiОценок пока нет
- Piping Fabrication What Is A Pipe?Документ9 страницPiping Fabrication What Is A Pipe?eduardo ramon giron lopezОценок пока нет
- Critical State Soil Mechanics LectureДокумент30 страницCritical State Soil Mechanics LecturevariablespiceОценок пока нет
- Aluform Work ChecklistДокумент2 страницыAluform Work ChecklistVeera SenthilОценок пока нет
- Annex F Notes and TablesДокумент10 страницAnnex F Notes and TablesasegotaОценок пока нет