Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Fnsacc507a Management Accounting Assessment 2 Question and Answer Booklet 2014 v1
Загружено:
Ian Paolo Española MeladАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Fnsacc507a Management Accounting Assessment 2 Question and Answer Booklet 2014 v1
Загружено:
Ian Paolo Española MeladАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
FNSACC507A
Provide Management Accounting Information
ASSESSMENT TASK – QUESTION & ANSWER BOOKLET
UNIT CODE: FNSACC507A UNIT NAME: Provide Management
Accounting Information
ASSESSMENT EVENT: 2 of 2 ASSESSMENT DATE: Flexible
STUDENT NUMBER: STUDENT NAME:
Performance measurement:
* For this unit, results will be reported as either competent or not yet competent.
* Students will be required to show competency in each element of the unit which means that questions
addressing each of the core elements within the assessment have to be attempted and 61% or more has to be
achieved for each.
Assessment conditions / instructions to students:
* Please write your answer to each question (either A, B, C or D) in the grid provided on PAGE 3.
* All questions must be attempted.
* You may use a calculator.
* Please make sure your writing is legible - answers that cannot be read won’t be marked.
* Please submit only PAGE 1, 2 and 3 of this assessment.
* Please SCAN and UPLOAD your completed assessment (i.e. pages 1, 2 and 3) via the SAKAI site for marking
as one file in either WORD or PDF format. Multiple files will not be
accepted.
Document1
Page 1 of 18 | Last revised: 6/02/2014
FNSACC507A
Provide Management Accounting Information
ASSESSMENT TASK – QUESTION & ANSWER BOOKLET
Question Marks Allocated Marks Achieved
Q1: Matching activity 5
Q2: Manufacturing statement 20
Q3: High-low analysis 15
Q4: Factory overhead allocation 20
Q5: Overhead variance analysis 20
Q6: Cost-Volume-Profit analysis 20
Total 100
SATISFACTORY UNSATISFACTORY
PLAGIARISM DECLARATION:
I have read the Student Services Guide under Student Responsibilities to “…not engage in plagiarism, collusion
or cheating in any assessment event or examination”.
Please note: Your assessment will not be marked until you have signed
Student Signature:__________________________________________
Document1
Page 2 of 18 | Last revised: 6/02/2014
FNSACC507A
Provide Management Accounting Information
ASSESSMENT TASK – QUESTION & ANSWER BOOKLET
Question 1: Management Accounting Concepts
You are required to match each word or phrase in ‘column A’ with its corresponding description in ‘column
B’. Next to each word or phrase in ‘column A’, you need to write the corresponding letter from ‘column B’ in
the ‘ANSWER’ column.
COLUMN A ANSWER COLUMN B
1. Spending variance A. Is the result of production being below Normal Manufacturing
Capacity which results in fixed costs being under-absorbed (or under-
applied).
2. Unfavourable B. Refers to the sales volume or activity level at which the profit
capacity variance generated is equal to zero.
3. Favourable capacity C. Is the result of having spent more or less than was budgeted at the
variance activity level worked.
4. Operating leverage D. Is about providing information to users external to the organisation
e.g. gov’t authorities.
5. Break-even point E. Is used to disclose the cost of goods manufactured.
6. Management F. In the context of factory overhead, it refers to the activity that
Accounting causes overhead costs to be incurred. For example, the cost of running
a cafeteria may be allocated to the different departments within a
company based on the number of employees working in each
department.
7. Financial Accounting G. Includes wages earned for the period as well as any allowances (e.g.
overtime) and incentives (e.g. commission).
8. Cost driver H. Is the result of production being above Normal Manufacturing
Capacity which results in fixed costs being over-absorbed (or over-
applied).
9. Manufacturing I. Is about providing information to users within the organisation e.g.
statement Operations Manager.
10. Gross wages J. Refers to the percentage of fixed costs in an organisation’s total cost
structure. The higher this fixed cost percentage, the more the
organisation’s income will be affected by fluctuations in sales volume.
Document1
Page 3 of 18 | Last revised: 6/02/2014
FNSACC507A
Provide Management Accounting Information
ASSESSMENT TASK – QUESTION & ANSWER BOOKLET
Question 2: Manufacturing & Trading Statements
The following information has been extracted from the accounting records of Jefferson Manufacturing. The
company accounts for all inventory using a periodic inventory system. Extracts from the accounting records
for the business for the six (6) months to 31 December 2012 show:
Balances on 1 July 2012: $
Inventories: - Raw materials (direct) 5,000 DR
- Factory supplies 11,000 DR
- Finished goods 25,000 DR
- Work-in-progress 14,000 DR
Prepayments: - Factory overhead 5,000 DR
Accruals: - Direct labour 5,000 CR
- Wages (general office staff) 3,000 CR
Balances on 31 December 2012: $
Factory land 100,000 DR
Factory buildings 240,000 DR
Accumulated depreciation – Factory buildngs 24,000 CR
(depreciation method: straight line; rate 5% per year)
Factory plant 360,000 DR
Accumulated depreciation – Factory plant 52,000 CR
(depreciation method: straight line; rate 10% per year)
Purchases: - Raw materials (direct) 255,000 DR
- Factory supplies 27,000 DR
- Finished goods 80,000 DR
Wages & salaries expense: - Direct wages 215,000 DR
- Indirect wages 50,000 DR
- Salaries paid to sales staff 75,000 DR
- Salary paid to factory manager 20,000 DR
Factory overhead expense 112,000 DR
Document1
Page 4 of 18 | Last revised: 6/02/2014
FNSACC507A
Provide Management Accounting Information
ASSESSMENT TASK – QUESTION & ANSWER BOOKLET
Balances on 31 December 2012: (continued) $
Inventories: - Raw materials (direct) 48,000 DR
- Factory supplies 14,000 DR
- Finished goods 27,000 DR
- Work-in-progress 18,000 DR
Prepayments: - Factory overhead 3,000 DR
Accruals: - Direct labour 4,000 CR
REQUIRED:
Prepare a properly formatted manufacturing statement for the six (6) months ended 31 December 2012.
Document1
Page 5 of 18 | Last revised: 6/02/2014
FNSACC507A
Provide Management Accounting Information
ASSESSMENT TASK – QUESTION & ANSWER BOOKLET
Jefferson Manufacturing
Manufacturing Statement for the six (6) months ended 31 December 2012
Document1
Page 6 of 18 | Last revised: 6/02/2014
FNSACC507A
Provide Management Accounting Information
ASSESSMENT TASK – QUESTION & ANSWER BOOKLET
Question 3: High-Low Analysis
The Lawson Distribution and Manufacturing Group makes and sells diagnostic medical equipment. For the
x-ray machine, it is reviewing the cost behaviour patterns of its indirect manufacturing costs in relation to
the number of units produced. Each x-ray machine requires 80 direct labour hours to manufacture.
Production volume and the associated indirect manufacturing cost for the past six (6) months are as follows:
Month Units Produced Overhead ($)
October 20 10,000
November 40 15,000
December 100 26,600
January 180 40,000
February 120 30,800
March 60 18,300
REQUIRED:
(a) Use the high-low method to calculate the variable cost per direct labour hour
(b) Use the high-low method to calculate the fixed cost per month.
(c) If in the coming month the firm has budgeted for total output equal to 3,600 direct labour hours,
what will be the estimate for indirect manufacturing costs. Please show estimates for fixed and
variable costs separately by using the cost equation (cost estimation formula).
Document1
Page 7 of 18 | Last revised: 6/02/2014
FNSACC507A
Provide Management Accounting Information
ASSESSMENT TASK – QUESTION & ANSWER BOOKLET
Part ( a ) : (5 marks)
Document1
Page 8 of 18 | Last revised: 6/02/2014
FNSACC507A
Provide Management Accounting Information
ASSESSMENT TASK – QUESTION & ANSWER BOOKLET
Part ( b ) : (6 marks)
Part ( c ): (4 marks)
Document1
Page 9 of 18 | Last revised: 6/02/2014
FNSACC507A
Provide Management Accounting Information
ASSESSMENT TASK – QUESTION & ANSWER BOOKLET
Question 4: Overhead Allocation
Jester Ltd is developing overhead factory overhead rates for the coming year. Budgeted overhead costs for
its four (4) factory departments are as follows:
Department Cost ($) Cost Driver
Production Dept. 1: 180,000 Machine hours
Cutting
Production Dept. 2: 138,000 Direct labour hours
Assembly
Service Dept. 1: 50,000 Machine hours
Maintenance
Service Dept 2: 32,000 Requisitions
Factory stores
Total $400,000
You are also provided with the following operating statistics for this year:
Cutting Assembly Maintenance Factory stores Total
Plant values $135,000 $40,000 $15,000 $10,000 $200,000
Floor space
(square metres) 500 300 100 200 1,100
Requisitions 60 40 100
No. of employees 45 35 15 5 100
Direct labour
hours 7,835 8,165 16,000
Machine hours 15,000 5,000 20,000
Document1
Page 10 of 18 | Last revised: 6/02/2014
FNSACC507A
Provide Management Accounting Information
ASSESSMENT TASK – QUESTION & ANSWER BOOKLET
REQUIRED:
(a) Calculate a plant-wide overhead rate based on direct labour hours.
(b) Calculate departmental overhead rates (i.e. a separate overhead recovery rate for each
PRODUCTION DEPARTMENT) assuming support department costs are allocated to production
departments using the direct method. Use the table provided to allocate budgeted overhead costs to
service & production departments and re-distribute service department costs to producing
departments before working out a departmental overhead rate for each production department.
Part ( a ) : Plant-wide overhead recovery rate: (3 marks)
Part ( b ) : Departmental overhead recovery rates: (11 marks)
Total Cutting Assembly Maintenance Factory stores
Budgeted
costs
Maintenance
Factory stores
Total
Document1
Page 11 of 18 | Last revised: 6/02/2014
FNSACC507A
Provide Management Accounting Information
ASSESSMENT TASK – QUESTION & ANSWER BOOKLET
Departmental overhead rate for CUTTING department: (3 marks) (round to 2 decimal places)
Departmental overhead rate for ASSEMBLY department: (3 marks) (round to 2 decimal places)
Document1
Page 12 of 18 | Last revised: 6/02/2014
FNSACC507A
Provide Management Accounting Information
ASSESSMENT TASK – QUESTION & ANSWER BOOKLET
Question 5: Overhead Variance Analysis
Jigsaw Ltd manufactres and sells jigsaw puzzles. For its best-selling puzzle, you have been provided with the
following factory overhead cost and production data for the year ended 30 June 2012:
Budget Actual
Variable factory overhead cost $84,000
Fixed factory overhead cost $99,000
Total factory overhead cost $183,000 $175,000
Production (units) 30,000 units 29,000 units
Other information:
1. The factory overhead budget was based on a normal production capacity of 30,000 units.
2. Budgeted rates are used to apply factory overhead to production.
3. Factory overhead is applied to production using a predetermined rate based on units produced as the cost
driver.
REQUIRED:
For the year ended 30 June 2012;
(a) Calculate the total predetermined factory overhead recovery rate.
(b) Calculate the variable predetermined factory overhead recovery rate.
(c) Determine the amount of over or under-applied overhead. Your answer must clearly state whether
the calculated amount is over or under-applied.
(d) Further analyse the over- or under- applied overhead into a spending variance and a capacity
variance. Your answer must also clearly state whether each variance is either favourable or
unfavourable.
Document1
Page 13 of 18 | Last revised: 6/02/2014
FNSACC507A
Provide Management Accounting Information
ASSESSMENT TASK – QUESTION & ANSWER BOOKLET
Part ( a ) : (2.5 marks)
Part ( b ) : (2.5 marks)
Part ( c ) : (5 marks)
Document1
Page 14 of 18 | Last revised: 6/02/2014
FNSACC507A
Provide Management Accounting Information
ASSESSMENT TASK – QUESTION & ANSWER BOOKLET
Part ( d ) : (10 marks)
Document1
Page 15 of 18 | Last revised: 6/02/2014
FNSACC507A
Provide Management Accounting Information
ASSESSMENT TASK – QUESTION & ANSWER BOOKLET
Question 6: Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis
Deep Ocean Ltd specialises in sourcing, producing and selling a special type of glass used to make only very
large aquariums. You are provided with the following budgeted financial data for the year ended
31 December 2012:
Selling price per unit $750.00
Variable cost per unit $350.00
Annual fixed costs $1,100,000
REQUIRED:
(a) Calculate the sales (in units) required to:
i) break-even. (3 marks)
ii) earn a net profit before tax of $600,000. (3 marks)
iii) earn a net return of 15% on sales revenue. (6 marks)
(b) Calculate the sales (in units) required to break-even if the variable cost per unit decreased by 10%
(assuming no changes in total fixed costs). (5 marks)
(c) Calculate the margin of safety ratio if Deep Ocean Ltd sold 10,000 units (expressed as a
percentage). (3 marks) (do not round your answer)
Document1
Page 16 of 18 | Last revised: 6/02/2014
FNSACC507A
Provide Management Accounting Information
ASSESSMENT TASK – QUESTION & ANSWER BOOKLET
Part ( a ) (i) : (3 marks)
Part ( a ) (ii) : (3 marks)
Part ( a ) (iii) : (6 marks)
Document1
Page 17 of 18 | Last revised: 6/02/2014
FNSACC507A
Provide Management Accounting Information
ASSESSMENT TASK – QUESTION & ANSWER BOOKLET
Part ( b ) : (5 marks)
Part ( c ) : (3 marks)
* * END OF ASSESSMENT 2 * *
Document1
Page 18 of 18 | Last revised: 6/02/2014
Вам также может понравиться
- Mock Assesmentba2Документ54 страницыMock Assesmentba2Bokang Junior KgariОценок пока нет
- Session-16-17-18-CVP AnalysisДокумент78 страницSession-16-17-18-CVP Analysis020Abhisek KhadangaОценок пока нет
- Bcom 5 Sem Cost Accounting 1 22100106 Jan 2022Документ4 страницыBcom 5 Sem Cost Accounting 1 22100106 Jan 2022Internet 223Оценок пока нет
- Man Acct Exam 2018S1 PDBTAДокумент6 страницMan Acct Exam 2018S1 PDBTAkwameОценок пока нет
- CH 5 Flexible Budget-7Документ23 страницыCH 5 Flexible Budget-7ed tuОценок пока нет
- CH 5 Flexible BudgetДокумент23 страницыCH 5 Flexible Budgettamirat tadeseОценок пока нет
- Cma Ii CH 1Документ18 страницCma Ii CH 1Mubarik HedrОценок пока нет
- 107-W7-8-Variable cost-chp05-STДокумент48 страниц107-W7-8-Variable cost-chp05-STmargaret mariaОценок пока нет
- Accounts CompilerДокумент827 страницAccounts CompilerKarthik RamОценок пока нет
- CLO 3 - LGE 3503 Accounting For ManagersДокумент25 страницCLO 3 - LGE 3503 Accounting For ManagersHello WorldОценок пока нет
- RESPONSIBILITY ACCOUNTING - A System of Accounting Wherein Performance, Based OnДокумент8 страницRESPONSIBILITY ACCOUNTING - A System of Accounting Wherein Performance, Based OnHarvey AguilarОценок пока нет
- Regression Analysis Method: It Is A StatisticalДокумент9 страницRegression Analysis Method: It Is A StatisticalMiccah Jade CastilloОценок пока нет
- Module 1 ch.12Документ2 страницыModule 1 ch.12Melody DidiОценок пока нет
- Quiz 2 PermansysДокумент10 страницQuiz 2 PermansysKristen StewartОценок пока нет
- Ch5 LimitingFactorsДокумент19 страницCh5 LimitingFactorsali202101Оценок пока нет
- FMA Assgnments - EX 2022Документ12 страницFMA Assgnments - EX 2022Natnael BelayОценок пока нет
- Integrated Accounting SystemsДокумент15 страницIntegrated Accounting SystemsSanjeev JayaratnaОценок пока нет
- A. Calculate The Break-Even Dollar Sales For The MonthДокумент25 страницA. Calculate The Break-Even Dollar Sales For The MonthPriyankaОценок пока нет
- Which Type of Benchmarking Is The Company Using?Документ20 страницWhich Type of Benchmarking Is The Company Using?Aslam SiddiqОценок пока нет
- Assignment - DCM2103 - Costing - BCom - Sem III - Set1 and 2 Sept 23Документ19 страницAssignment - DCM2103 - Costing - BCom - Sem III - Set1 and 2 Sept 23arinkalsotra19042003Оценок пока нет
- Farah Choudhary - Ehsan Ul HaqДокумент35 страницFarah Choudhary - Ehsan Ul HaqfarahchОценок пока нет
- Cost 2 ch3Документ10 страницCost 2 ch3Eid AwilОценок пока нет
- Financial Analysis For Product Management - Nikunj - RohanДокумент27 страницFinancial Analysis For Product Management - Nikunj - Rohanniks2409100% (5)
- Full Download Test Bank For Horngrens Accounting The Managerial Chapters 12Th Edition 12Th Edition PDFДокумент140 страницFull Download Test Bank For Horngrens Accounting The Managerial Chapters 12Th Edition 12Th Edition PDFalice.maxam777100% (9)
- Chapter 12: Strategy, Balanced Scorecard, and Strategic Profitability AnalysisДокумент3 страницыChapter 12: Strategy, Balanced Scorecard, and Strategic Profitability AnalysisMichelle Galapon LagunaОценок пока нет
- PM Sect B Test 7Документ5 страницPM Sect B Test 7FarahAin Fain0% (1)
- William Wenceslao - BA 202 Topic 6 Assignment - BY WILLДокумент4 страницыWilliam Wenceslao - BA 202 Topic 6 Assignment - BY WILLWiLliamLoquiroWencesLaoОценок пока нет
- Test Bank PerformanceДокумент4 страницыTest Bank PerformanceLeneth AngtiampoОценок пока нет
- 04 Absorption & Variable Costing With Pricing DecisionsДокумент6 страниц04 Absorption & Variable Costing With Pricing Decisionsrandomlungs121223Оценок пока нет
- 7 2010 Jun QДокумент8 страниц7 2010 Jun QWeezy360Оценок пока нет
- Advanced Management Accounting RTPДокумент25 страницAdvanced Management Accounting RTPSamir Raihan ChowdhuryОценок пока нет
- MAC3 Lecture 01. Responsibility Accounting Segment Evaluation and Transfer PricingДокумент4 страницыMAC3 Lecture 01. Responsibility Accounting Segment Evaluation and Transfer PricingAlliahData100% (1)
- Cost AccountingДокумент15 страницCost AccountingmeskiОценок пока нет
- Time: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Note: Attempt Any Five Questions. All Questions Carry Equal Marks. Use of Calculators Is AllowedДокумент4 страницыTime: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Note: Attempt Any Five Questions. All Questions Carry Equal Marks. Use of Calculators Is AllowedashishvasekarОценок пока нет
- Math Problem Chapter 1 (L 1 & 2)Документ7 страницMath Problem Chapter 1 (L 1 & 2)rajeshaisdu009Оценок пока нет
- MBA 7001 Accounting For Decision Makers AssignmentДокумент8 страницMBA 7001 Accounting For Decision Makers AssignmentSupun25% (4)
- Acc308 Prelim Exam Name: - Date: - Score: - Permit No. - I. True/FalseДокумент3 страницыAcc308 Prelim Exam Name: - Date: - Score: - Permit No. - I. True/FalseJamhel MarquezОценок пока нет
- Prelim/Advisory Exam: ACC 311 Managerial Accounting 1Документ3 страницыPrelim/Advisory Exam: ACC 311 Managerial Accounting 1Dexter Joseph CuevasОценок пока нет
- Managerial Accounting 15th Edition Garrison Solutions ManualДокумент54 страницыManagerial Accounting 15th Edition Garrison Solutions Manualcamcaic54l100% (28)
- Management Programme Term-End Examination: December, 2017 Ms-004: Accounting and Finance For ManagersДокумент3 страницыManagement Programme Term-End Examination: December, 2017 Ms-004: Accounting and Finance For ManagersreliableplacementОценок пока нет
- MA2 Mock 1-Qs - 2023-24Документ11 страницMA2 Mock 1-Qs - 2023-24daniel.maina2005Оценок пока нет
- MCS SumsДокумент29 страницMCS SumsRahul GargОценок пока нет
- Cost and Management AccountingДокумент5 страницCost and Management AccountingSolve AssignmentОценок пока нет
- Management Advisory Services: Responsibility Accounting & Transfer PricingДокумент9 страницManagement Advisory Services: Responsibility Accounting & Transfer PricingVanessa Arizo ValenciaОценок пока нет
- P 1 May 2008Документ35 страницP 1 May 2008sajid newaz khanОценок пока нет
- Sample MAS (Absorption & Variable Costing With Pricing Decision)Документ6 страницSample MAS (Absorption & Variable Costing With Pricing Decision)Gwyneth CartallaОценок пока нет
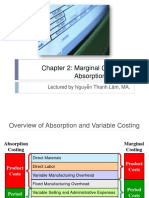
- Chapter 2 Marginal CostingДокумент21 страницаChapter 2 Marginal CostingLan Nhi NguyenОценок пока нет
- ABC CostingДокумент3 страницыABC CostingDae BakОценок пока нет
- Activity Based Costing: Unit-Level Activities Batch-Level Activities Product-Level Activities Facility-Level ActivitiesДокумент3 страницыActivity Based Costing: Unit-Level Activities Batch-Level Activities Product-Level Activities Facility-Level ActivitiesPrincess Corine BurgosОценок пока нет
- Inter-Paper-1 RTPS, MTPs and Past PapersДокумент276 страницInter-Paper-1 RTPS, MTPs and Past PapersPruthil MonpariyaОценок пока нет
- Managerial Accounting and Cost ConceptsДокумент10 страницManagerial Accounting and Cost ConceptsJessa BallonОценок пока нет
- BSBMGT605B - Assessment Task 2Документ7 страницBSBMGT605B - Assessment Task 2Ghie MoralesОценок пока нет
- MS-04 (Absorption & Variable Costing With Pricing Decisions)Документ6 страницMS-04 (Absorption & Variable Costing With Pricing Decisions)yshizamОценок пока нет
- SITXFIN003 Helpful For AssignmentДокумент15 страницSITXFIN003 Helpful For AssignmentTikaram Ghimire100% (1)
- ACCT 2102: Principles of Management AccountingДокумент64 страницыACCT 2102: Principles of Management AccountingJingxuan LuoОценок пока нет
- T2 Budgeting Behaviour (A)Документ3 страницыT2 Budgeting Behaviour (A)JIN FEN SOOОценок пока нет
- Paper12 Syl22 Dec23 Set2Документ6 страницPaper12 Syl22 Dec23 Set2Question BankОценок пока нет
- Topic 2 - Budgetary ControlДокумент28 страницTopic 2 - Budgetary Controlmarlina rahmatОценок пока нет
- P1 Solution CMA June 2019Документ7 страницP1 Solution CMA June 2019Awal ShekОценок пока нет
- Wiley CMAexcel Learning System Exam Review 2017: Part 1, Financial Reporting, Planning, Performance, and Control (1-year access)От EverandWiley CMAexcel Learning System Exam Review 2017: Part 1, Financial Reporting, Planning, Performance, and Control (1-year access)Оценок пока нет
- Gr10 - Questionnaire - To Be PrintedДокумент6 страницGr10 - Questionnaire - To Be PrintedIan Paolo Española MeladОценок пока нет
- Ethics: Lawrence Kohlberg - American Psychologist - Stages of Moral DevelopmentДокумент2 страницыEthics: Lawrence Kohlberg - American Psychologist - Stages of Moral DevelopmentIan Paolo Española MeladОценок пока нет
- Virtual Organizations: An Overview: IFIP International Federation For Information Processing September 2008Документ7 страницVirtual Organizations: An Overview: IFIP International Federation For Information Processing September 2008Ian Paolo Española MeladОценок пока нет
- NBA 2k21Документ102 страницыNBA 2k21Ian Paolo Española MeladОценок пока нет
- Melad, Ian Paolo E. BSAIS 3A: Creates ReputationДокумент3 страницыMelad, Ian Paolo E. BSAIS 3A: Creates ReputationIan Paolo Española MeladОценок пока нет
- Melad, Ian Paolo E. BSAIS 3A: Creates ReputationДокумент3 страницыMelad, Ian Paolo E. BSAIS 3A: Creates ReputationIan Paolo Española MeladОценок пока нет
- Physical Education 4 Team SportsДокумент10 страницPhysical Education 4 Team SportsIan Paolo Española MeladОценок пока нет
- Pestel and SwotДокумент2 страницыPestel and SwotIan Paolo Española MeladОценок пока нет
- The Physical Functions of ArtДокумент2 страницыThe Physical Functions of ArtIan Paolo Española MeladОценок пока нет
- How Does Fear of Death Play in The Part of Creating Culture?Документ1 страницаHow Does Fear of Death Play in The Part of Creating Culture?Ian Paolo Española MeladОценок пока нет
- Types of Consumer ProductsДокумент21 страницаTypes of Consumer ProductsIan Paolo Española MeladОценок пока нет
- Strategic Business AnalysisДокумент51 страницаStrategic Business AnalysisIan Paolo Española Melad80% (5)
- I. Percentage, Base and Rate A. PercentageДокумент12 страницI. Percentage, Base and Rate A. PercentageIan Paolo Española Melad100% (1)
- ProtagorasДокумент29 страницProtagorasIan Paolo Española MeladОценок пока нет
- ReviewerДокумент1 страницаReviewerIan Paolo Española MeladОценок пока нет
- PDFДокумент15 страницPDFIan Paolo Española MeladОценок пока нет
- 06 Chapter 2Документ36 страниц06 Chapter 2IahcОценок пока нет
- UTS CompleteДокумент46 страницUTS CompleteIan Paolo Española MeladОценок пока нет
- ReviewerДокумент1 страницаReviewerIan Paolo Española MeladОценок пока нет
- Mimo Express Org. Chart 1Документ1 страницаMimo Express Org. Chart 1Ian Paolo Española MeladОценок пока нет
- 5.3 Joserizals Travel Second Trip From HongkongДокумент46 страниц5.3 Joserizals Travel Second Trip From HongkongIan Paolo Española MeladОценок пока нет
- PDFДокумент15 страницPDFIan Paolo Española MeladОценок пока нет
- ITДокумент4 страницыITIan Paolo Española MeladОценок пока нет
- SSSForm Funeral ClaimДокумент2 страницыSSSForm Funeral ClaimRenmar John Abagat0% (1)
- CH 11Документ27 страницCH 11Nikki GarciaОценок пока нет
- SFPERFДокумент2 страницыSFPERFIan Paolo Española MeladОценок пока нет
- Mailings & References: Microsoft WordДокумент8 страницMailings & References: Microsoft WordJanine UbinaОценок пока нет
- Bev TemplateДокумент2 страницыBev TemplateIan Paolo Española MeladОценок пока нет
- ReviewerДокумент1 страницаReviewerIan Paolo Española MeladОценок пока нет
- Academic: Implementing Rules and Regulation in The Conduct of Jpia Day and NIGHT 2019 EventsДокумент7 страницAcademic: Implementing Rules and Regulation in The Conduct of Jpia Day and NIGHT 2019 EventsIan Paolo Española MeladОценок пока нет
- Final Exam Review-VrettaДокумент4 страницыFinal Exam Review-VrettaAna Cláudia de Souza0% (2)
- 02 Drillmec HH SeriesДокумент13 страниц02 Drillmec HH Seriessaysamajo100% (2)
- Group 6 & 7Документ11 страницGroup 6 & 7Apurv BijawatОценок пока нет
- Draft Notice Agenda and Notes - 1st Board Meeting Through VCДокумент2 страницыDraft Notice Agenda and Notes - 1st Board Meeting Through VCCA Tanmay JaiminiОценок пока нет
- Development CommunicationДокумент15 страницDevelopment CommunicationJanbaz RahylОценок пока нет
- CV-JM Van StraatenДокумент5 страницCV-JM Van StraatenJovan Van StraatenОценок пока нет
- Market DistortionsДокумент14 страницMarket DistortionsSmriti SalhotraОценок пока нет
- Business Proposal StructureДокумент2 страницыBusiness Proposal StructureGreyОценок пока нет
- Project Management, Tools, Process, Plans and Project Planning TipsДокумент16 страницProject Management, Tools, Process, Plans and Project Planning TipsChuma Khan100% (1)
- Employee Service RegulationДокумент173 страницыEmployee Service RegulationKrishan Kumar Sharma50% (2)
- Location Planning and AnalysisДокумент1 страницаLocation Planning and AnalysisRoseanne Binayao LontianОценок пока нет
- Presentation detailingto3DdetailingforRCDetailing PDFДокумент39 страницPresentation detailingto3DdetailingforRCDetailing PDFErnie ErnieОценок пока нет
- Tsu Note G.R. No. 181218Документ5 страницTsu Note G.R. No. 181218Anonymous BYeqWt8FHy0% (1)
- Actuate BIRT Report Designer ProfessionalДокумент2 страницыActuate BIRT Report Designer ProfessionalPınar GöçebeОценок пока нет
- Tugas 2 - MKWI4201 - Bahasa Inggris - 044905467 - DesyanaДокумент5 страницTugas 2 - MKWI4201 - Bahasa Inggris - 044905467 - Desyanahelena dwi novitaОценок пока нет
- Quality Assurance ManualДокумент25 страницQuality Assurance ManualArman RajuОценок пока нет
- Procurement KPIs - NCTДокумент22 страницыProcurement KPIs - NCTMohamed ElnagdyОценок пока нет
- BIR-1905 Updated1Документ3 страницыBIR-1905 Updated1Kevin CordovizОценок пока нет
- Choon's Design v. LaRose Industries Et. Al.Документ9 страницChoon's Design v. LaRose Industries Et. Al.PriorSmartОценок пока нет
- Projected Frequency and Severity and Cost-Benefit Analysis-Capital BudgetingДокумент23 страницыProjected Frequency and Severity and Cost-Benefit Analysis-Capital BudgetingLJ Eugenio RosanesОценок пока нет
- Employment Application Form - Ver2 (1) .0Документ7 страницEmployment Application Form - Ver2 (1) .0ranjithsutariОценок пока нет
- Focus Group Discussion On Perception About Food Delivery Apps, Swiggy Vs Uber EatsДокумент3 страницыFocus Group Discussion On Perception About Food Delivery Apps, Swiggy Vs Uber EatsSwarnim BarmeraОценок пока нет
- Urban Clap 1Документ3 страницыUrban Clap 1naughty ajayОценок пока нет
- Connected Party Declaration FormДокумент1 страницаConnected Party Declaration FormSyakir AfifiОценок пока нет
- Essay Test 2021 (Practice Test)Документ3 страницыEssay Test 2021 (Practice Test)Philani HadebeОценок пока нет
- QUIZ Group 1 Answer KeyДокумент3 страницыQUIZ Group 1 Answer KeyJames MercadoОценок пока нет
- Paul Sonkin Investment StrategyДокумент20 страницPaul Sonkin Investment StrategyCanadianValueОценок пока нет
- Formulation of Strategy For EbusinessДокумент11 страницFormulation of Strategy For Ebusinessarun.vasu8412100% (2)
- Repco Micro Finance Limited: Corporate Office, Chennai-35Документ4 страницыRepco Micro Finance Limited: Corporate Office, Chennai-35Abaraj IthanОценок пока нет
- Shamsher Kataria V Honda Siel & OrsДокумент215 страницShamsher Kataria V Honda Siel & OrsBar & BenchОценок пока нет