Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Crop Physiology - Unit 1
Загружено:
Nishchaya Narula0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
268 просмотров19 страницabout crops
Оригинальное название
Crop Physiology_Unit 1
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документabout crops
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
268 просмотров19 страницCrop Physiology - Unit 1
Загружено:
Nishchaya Narulaabout crops
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 19
UNIT – I
Introduction to crop physiology
Introduction
As primary producers, plants convert solar energy to
chemical energy.
Being non motile, plants must grow toward light, and
they must have efficient vascular systems for movement
of water, mineral nutrients, and photosynthetic products
throughout the plant body.
Green land plants must also have mechanisms for
avoiding dehydration.
Noggle and Fritz
(1983) described the
Plant Physiology as “the
science concerned
with processes and
functions, the response
of plants to changes in
environment and the
growth and
development that
results from responses.
Crop physiology is concerned with the
processes and functions of the crops at cellular,
sub-cellular and whole plant levels in response
to environmental variables and growth.
In short, physiology is the study of
functional aspects of crop plants.
Importance in Agriculture
In horticulture and agriculture along with food
science, plant physiology is an important topic
relating to fruits, vegetables, and other consumable
parts of plants.
Topics studied include: Climatic requirements, fruit
drop, nutrition, ripening, fruit set.
Production of food crops also based on the
study of plant physiology, covering topics
such as: optimal planting and harvesting
times and post harvest storage of plant
products for human consumption and the
production of secondary products like
drugs and cosmetics.
Superior varieties can be selected on the basis
of physiological traits (LAI, WUE, high
uptake efficiency, translocation efficiency
etc.) and can be incorporated in crop
improvement programme.
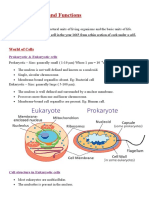
Cell
Plants are multicellular organisms composed of
millions of cells with specialized functions.
At maturity, such specialized cells may differ greatly
from one another in their structures.
However, all plant cells have the same basic
eukaryotic organization: They contain a nucleus, a
cytoplasm, and sub cellular organelles, and they are
enclosed in a membrane that defines their
boundaries.
Cell ultrastructure
Diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of molecules or atoms
from a region of high concentration to a region of
low concentration.
This is also referred to as the movement of a
substance down a concentration gradient.
Diffusion also refers to the process by which
molecules intermingle as a result of their
kinetic energy of random motion.
Importance of diffusion in plant life
It is an essential process in exchange of gases
(O2 and CO2) during respiration and
photosynthesis.
Uptake of minerals is also affected by the
process of diffusion.
It helps in removal of excess water by the
process of transpiration.
Cont…….
Translocation of organic solutes also takes
place by diffusion means.
Fragrance of flowers or sweet scent emitted
by flowers spread in air by diffusion means
attracts insects to materialize pollination.
Osmosis
Osmosis is the spontaneous net movement of
solvent molecules through a semi-permeable
membrane into a region of higher solute
concentration, in the direction that tends to
equalize the solute concentrations on the two
sides.
Importance of osmosis in plants
It is a mean by which plant cells maintain their
water content despite the loss of water to the
air that is constantly occurring.
It provides turgidity to the softer tissues and
is, therefore, essential for their mechanical
support.
It controls the absorption of water by root
hairs from the soil.
Cell to cell diffusion of water is also affected
by osmosis.
Conduction of water from xylem elements to
the neighboring cells is controlled by
osmosis.
Growing tips of roots remain turgid because
of osmosis and are, thus, able to penetrate
into the soil.
It controls opening and closing of stomata
during transpiration through its regulation of
the turgidity of guard cells.
Movement of plants and plant parts (e.g.,
movement of leaflets of the sensitive plant
Mimosa pudica) are controlled by cell turgor
which is induced by osmosis.
Thanks……….
Вам также может понравиться
- Environment Quiz - Climate Change and Global WarmingДокумент2 страницыEnvironment Quiz - Climate Change and Global Warmingbhingmeh yotal100% (2)
- Iec 61330-2005Документ10 страницIec 61330-2005pradyumnaukОценок пока нет
- Principles of Plant PathologyДокумент38 страницPrinciples of Plant PathologyPooja BhusalОценок пока нет
- IFOAM Training MAnualДокумент243 страницыIFOAM Training MAnualSampathkumar TharmarОценок пока нет
- Nematode Biology, Physiology & Ecology - Conversion GateДокумент42 страницыNematode Biology, Physiology & Ecology - Conversion GatePra YoudhaОценок пока нет
- Abiotic and Biotic Stresses in Soybean Production: Soybean Production Volume 1От EverandAbiotic and Biotic Stresses in Soybean Production: Soybean Production Volume 1Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- 7days Internship Report-20102068,72,75,115Документ11 страниц7days Internship Report-20102068,72,75,115ParthasarathiОценок пока нет
- 2 Stroke Diesel Engine Components-1Документ72 страницы2 Stroke Diesel Engine Components-1EdemОценок пока нет
- Applications of Tissue Culture To Plant Improvement: February 2017Документ42 страницыApplications of Tissue Culture To Plant Improvement: February 2017nareman hassanОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of HV Circuit-BreakersДокумент22 страницыFundamentals of HV Circuit-BreakersBastian OspinaОценок пока нет
- CCT Module 3 01 PDFДокумент35 страницCCT Module 3 01 PDFIecjs BwgiОценок пока нет
- 1 Plant NutritionДокумент35 страниц1 Plant NutritionAbbie UgotОценок пока нет
- ThermoДокумент25 страницThermoJerryco AlviarОценок пока нет
- General Microbiology Laboratory Manual: Biology 490Документ83 страницыGeneral Microbiology Laboratory Manual: Biology 490Ibnul MubarokОценок пока нет
- B38dbbaccfpractical - Ma Kharif 2 PDFДокумент66 страницB38dbbaccfpractical - Ma Kharif 2 PDFTejindarjit Kaur Gill BahgaОценок пока нет
- Bazam Company ProfileДокумент30 страницBazam Company ProfileIbrahimrashid Billow HusseinОценок пока нет
- Moisture Stress of PlantДокумент30 страницMoisture Stress of PlantHassen100% (1)
- Theory: Micropropagation Plant TissueДокумент17 страницTheory: Micropropagation Plant TissuekzrdurОценок пока нет
- Isolation and Characterization of Endophytic Microbiome From Indigenous Maize (Zee Mays) Variety of Manipur and Its Impact On Biological ControlДокумент7 страницIsolation and Characterization of Endophytic Microbiome From Indigenous Maize (Zee Mays) Variety of Manipur and Its Impact On Biological ControlInternational Journal of Human Genetics Medical Biotechnology & Microbiological StudiesОценок пока нет
- Hemp As Construction MaterialДокумент37 страницHemp As Construction MaterialAlex Imreh100% (5)
- Course Details: Course Details:: Course Coordinator: Email: Office Location: Other LecturersДокумент5 страницCourse Details: Course Details:: Course Coordinator: Email: Office Location: Other LecturersLokesh AhirwarОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 - MicropropagatioonДокумент104 страницыChapter 6 - MicropropagatioonDương Hà Trúc Tâm100% (1)
- LPG Co-MinglingДокумент17 страницLPG Co-MinglingderhgawenrahulОценок пока нет
- Their Potential PGPR ReviewДокумент19 страницTheir Potential PGPR ReviewMohammad Mosharraf HossainОценок пока нет
- PC14R-3 S/N F40003 and UpДокумент573 страницыPC14R-3 S/N F40003 and UpRAMON TEIXIDORОценок пока нет
- Plant Growth Promoting RhizobacteriaДокумент11 страницPlant Growth Promoting RhizobacteriaDiral SadriОценок пока нет
- Breeding For ResistanceДокумент6 страницBreeding For Resistancerifki faisal100% (1)
- Practical Manual 171Документ85 страницPractical Manual 171Souvik Roy Chowdhury100% (1)
- TomatoДокумент12 страницTomatoAileen MontuyaОценок пока нет
- Pollination: Name: Sheryl Bhatnagar Roll No: 2047 Sub: Reproductive Biology Course: Botany 2 YrДокумент27 страницPollination: Name: Sheryl Bhatnagar Roll No: 2047 Sub: Reproductive Biology Course: Botany 2 YrAnny LovibОценок пока нет
- Plant Responses To Abiotic StressДокумент303 страницыPlant Responses To Abiotic StresskamalОценок пока нет
- Introduction and History of HorticultureДокумент39 страницIntroduction and History of HorticulturejaganОценок пока нет
- Micro CH 6 BacteriaДокумент58 страницMicro CH 6 BacteriaBernadette Joyce PascualОценок пока нет
- Physiological Disorders in Fruit CropsДокумент8 страницPhysiological Disorders in Fruit CropsMohamed BahgatОценок пока нет
- Introductory Plant PathologyДокумент3 страницыIntroductory Plant PathologyKevin Oreko100% (1)
- Mass SelectionДокумент123 страницыMass SelectionYosef AndualemОценок пока нет
- 05 Introduction To Plant PathologyДокумент20 страниц05 Introduction To Plant PathologyirwanpaluОценок пока нет
- Agronomy of Seed Production and Agroclimatic ZonesДокумент46 страницAgronomy of Seed Production and Agroclimatic ZonesnabiОценок пока нет
- Plant Tissue CultureДокумент5 страницPlant Tissue CultureHewa HusenОценок пока нет
- How To Handle and Apply Pesticides SafelyДокумент15 страницHow To Handle and Apply Pesticides SafelycefaenglishОценок пока нет
- Seed Technology PDFДокумент30 страницSeed Technology PDFAnonymous f5gNPeZDC0% (1)
- CD 256 Neutral Disinfectant Cleaner MSDSДокумент2 страницыCD 256 Neutral Disinfectant Cleaner MSDSMurtaza SherwaniОценок пока нет
- Chapter 11 - Meristem Culture For Virus Free Plants - 2013 - Plant Tissue Cultur PDFДокумент8 страницChapter 11 - Meristem Culture For Virus Free Plants - 2013 - Plant Tissue Cultur PDFLuis BermudezОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 (Animal Cell Culture, Micropropagation, IVF, Cloning)Документ88 страницChapter 2 (Animal Cell Culture, Micropropagation, IVF, Cloning)Batul KhuzemaОценок пока нет
- Plant HormoneДокумент31 страницаPlant HormoneChristine De GuzmanОценок пока нет
- Plant PathologyДокумент7 страницPlant PathologyJon Verny Biaco0% (1)
- Seed Processing 4Документ36 страницSeed Processing 4Prima AgungОценок пока нет
- Botany Assignment 1Документ4 страницыBotany Assignment 1FrancineAntoinetteGonzales100% (1)
- CRP 101 Crop Physiology (2+1)Документ189 страницCRP 101 Crop Physiology (2+1)AnandKuttiyan100% (4)
- 1st Sem Syllabus For B.SC Agri For MPKVДокумент23 страницы1st Sem Syllabus For B.SC Agri For MPKVVIKRAM9350% (4)
- Questions and Answers About MycorrhizaДокумент8 страницQuestions and Answers About MycorrhizaEpiscia Atfal LintangОценок пока нет
- Soil Science Lec 11Документ3 страницыSoil Science Lec 11Thiyaneswaran KumarОценок пока нет
- Cell - Structure and Functions: World of CellsДокумент5 страницCell - Structure and Functions: World of CellsPriyanshu Priyadarshi MeherОценок пока нет
- Plant Symbionts InteractionДокумент13 страницPlant Symbionts InteractionIram TahirОценок пока нет
- PAT 401 Diseases of Horticultural Crops 2020-RevisedДокумент175 страницPAT 401 Diseases of Horticultural Crops 2020-RevisedAarzoo JainОценок пока нет
- How To Perform An Agricultural Experiment PDFДокумент30 страницHow To Perform An Agricultural Experiment PDFShane Hodge100% (1)
- Soil Water RelationshipДокумент34 страницыSoil Water RelationshipraghurmiОценок пока нет
- Microbial Nutrition and GrowthДокумент42 страницыMicrobial Nutrition and GrowthRPMahdanОценок пока нет
- Post Harvest Loss of FruitsДокумент14 страницPost Harvest Loss of FruitsUssama YasinОценок пока нет
- Plant Breeding NotesДокумент15 страницPlant Breeding Notesjack oumaОценок пока нет
- Use of Microbes in AgricultureДокумент4 страницыUse of Microbes in AgricultureAran MuthОценок пока нет
- Pest Management PDFДокумент34 страницыPest Management PDFyasir zebОценок пока нет
- Introduction of Cerel and PulsesДокумент2 страницыIntroduction of Cerel and Pulsesvikasbnsl1Оценок пока нет
- Effects of Storage Temperature On Post-Harvest of Potato by Bikash Khanal & Dipti UpretyДокумент7 страницEffects of Storage Temperature On Post-Harvest of Potato by Bikash Khanal & Dipti Upretyijr_journalОценок пока нет
- Weed Manegement Practical Manual SSR SKДокумент87 страницWeed Manegement Practical Manual SSR SKRex DullitОценок пока нет
- In Vitro Regeneration and Somatic Embryogenesis and Their Antimicrobial Studies in Selected Ornamental PlantsДокумент20 страницIn Vitro Regeneration and Somatic Embryogenesis and Their Antimicrobial Studies in Selected Ornamental Plantsbakru248326Оценок пока нет
- History of Plant Pathology LectureДокумент16 страницHistory of Plant Pathology LectureAmitesh ChouhanОценок пока нет
- A646408393 - 18758 - 14 - 2019 - Testing New k17Документ108 страницA646408393 - 18758 - 14 - 2019 - Testing New k17Nishchaya NarulaОценок пока нет
- Crop Physiology - Unit 1 PDFДокумент19 страницCrop Physiology - Unit 1 PDFNishchaya NarulaОценок пока нет
- Lecture1-2 - Fundamental Data StructureДокумент15 страницLecture1-2 - Fundamental Data StructureNishchaya NarulaОценок пока нет
- Digital Electronics Sample Chapter PDFДокумент106 страницDigital Electronics Sample Chapter PDFRokiniKumarasamyОценок пока нет
- Undertaking by The Applicant (For Opting Food Plan)Документ1 страницаUndertaking by The Applicant (For Opting Food Plan)Nishchaya NarulaОценок пока нет
- Technology Based Points1Документ1 страницаTechnology Based Points1Nishchaya NarulaОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Rural Sociology and Educational Psychology: Reading MaterialДокумент56 страницFundamentals of Rural Sociology and Educational Psychology: Reading MaterialVeera PandianОценок пока нет
- Photosynthesis and Transpiration PDFДокумент21 страницаPhotosynthesis and Transpiration PDFNishchaya NarulaОценок пока нет
- Eceunit2 PDFДокумент17 страницEceunit2 PDFNishchaya NarulaОценок пока нет
- SVAT Model IntroductionДокумент29 страницSVAT Model IntroductionChamila DiasОценок пока нет
- Whitepaper: Accelerated Lifetime-Test For Metallized Film CapacitorsДокумент24 страницыWhitepaper: Accelerated Lifetime-Test For Metallized Film CapacitorsccuevasarenasОценок пока нет
- Start Practice Exam Test Questions Part 1 of The SeriesДокумент155 страницStart Practice Exam Test Questions Part 1 of The SeriesNida Bagoyboy NatichoОценок пока нет
- CSB-F: Three-Phase Power Capacitor With Fuse ProtectionДокумент2 страницыCSB-F: Three-Phase Power Capacitor With Fuse ProtectionAbdul RafaeОценок пока нет
- Green Buildings, Energy EfficiencyДокумент7 страницGreen Buildings, Energy EfficiencyAbu Talha FarooqiОценок пока нет
- DLAB Centrifuges-Benchtop DM0636 ManualДокумент27 страницDLAB Centrifuges-Benchtop DM0636 ManualServicio AHSОценок пока нет
- EPA / CARB Locomotive Letter - Trade GroupsДокумент3 страницыEPA / CARB Locomotive Letter - Trade GroupsNick PopeОценок пока нет
- BSCH User ManualДокумент20 страницBSCH User Manualjo_eli_Оценок пока нет
- 27 Hilux (Cont. Next Page) : Engine Control (1GD-FTV)Документ8 страниц27 Hilux (Cont. Next Page) : Engine Control (1GD-FTV)autocomtrucksОценок пока нет
- Catalog - Regent RSV Ed 3Документ14 страницCatalog - Regent RSV Ed 3Nyu123456Оценок пока нет
- Test - Astm 1378 Rev2Документ16 страницTest - Astm 1378 Rev2Matthew KuttikadОценок пока нет
- Bearcat Bc80xlt ManualДокумент32 страницыBearcat Bc80xlt Manualjwyatt4155Оценок пока нет
- Training ReportДокумент21 страницаTraining ReportPiyush Khandait0% (1)
- Manual de Utilizare Uscator Beko 8 KGДокумент64 страницыManual de Utilizare Uscator Beko 8 KGPerfectreviewОценок пока нет
- Sustainability 09 02214Документ11 страницSustainability 09 02214dictussОценок пока нет
- Mechathon - High Pressure Pump ReportДокумент89 страницMechathon - High Pressure Pump ReportPrasad AdigaОценок пока нет
- KAT0815-0001-E Single Pole Insulated Conductor RailДокумент36 страницKAT0815-0001-E Single Pole Insulated Conductor RailirinaОценок пока нет
- ThermAsset 2 Low ResДокумент2 страницыThermAsset 2 Low ResThonny Barrera QuispeОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Marine MachineriesДокумент13 страницIntroduction To Marine MachineriessrcattozziОценок пока нет
- Ibc 2003Документ10 страницIbc 2003MIKHA2014Оценок пока нет
- Digital Liquid Meter: Owners Installation, Operation, and Safety ManualДокумент48 страницDigital Liquid Meter: Owners Installation, Operation, and Safety ManualJuarez FerdОценок пока нет