Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual PDF
Загружено:
SmartFix agudeloОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual PDF
Загружено:
SmartFix agudeloАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance
Manual
Issue 01
Date 2014-04-03
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD.
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2014. All rights reserved.
No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior
written consent of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Trademarks and Permissions
and other Huawei trademarks are trademarks of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
All other trademarks and trade names mentioned in this document are the property of their respective
holders.
Notice
The purchased products, services and features are stipulated by the contract made between Huawei and
the customer. All or part of the products, services and features described in this document may not be
within the purchase scope or the usage scope. Unless otherwise specified in the contract, all statements,
information, and recommendations in this document are provided "AS IS" without warranties, guarantees or
representations of any kind, either express or implied.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Every effort has been made in the
preparation of this document to ensure accuracy of the contents, but all statements, information, and
recommendations in this document do not constitute a warranty of any kind, express or implied.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Address: Huawei Industrial Base
Bantian, Longgang
Shenzhen 518129
People's Republic of China
Website: http://www.huawei.com
Email: support@huawei.com
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential i
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual About This Document
About This Document
Author
Prepared by Chu Shuo Date 2014-03-15
Reviewed by Maintenance support team Date 2014-03-15
Approved by Service representative Date 2014-03-15
Change History
Date Version Description Author
2014-03-15 V1.0 Released the first issue. Chu Shuo
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential ii
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual Contents
Contents
About This Document .................................................................................................................... ii
1 Overview......................................................................................................................................... 1
1.1 Applicable Scope .............................................................................................................................................. 1
1.2 Brief Introduction ............................................................................................................................................. 1
1.3 How to Obtain Product and Repair Information .............................................................................................. 1
2 Product Overview ......................................................................................................................... 2
2.1 Appearance ....................................................................................................................................................... 2
2.2 Phone Working Principles ................................................................................................................................ 2
2.3 PCBA Functions ............................................................................................................................................... 4
3 Components on the PCBA and BOM ........................................................................................ 7
4 Maintenance Tools ...................................................................................................................... 11
5 Troubleshooting .......................................................................................................................... 13
5.1 Integrated Device Maintenance Workflow ..................................................................................................... 13
5.2 Upgrading the Upgrade&Load Software........................................................................................................ 14
5.2.1 Upgrade Environment Requirements .................................................................................................... 15
5.2.2 Upgrade Files ........................................................................................................................................ 15
5.2.3 Multi-Download .................................................................................................................................... 15
5.2.4 Closing a Program................................................................................................................................. 19
5.2.5 Log File ................................................................................................................................................. 19
5.3 Software Upgrade ........................................................................................................................................... 19
5.3.1 Upgrade Preparation ............................................................................................................................. 19
5.3.2 Using the microSD Card for Upgrade ................................................................................................... 20
5.3.3 Using a USB for an Upgrade ................................................................................................................ 23
5.3.4 Troubleshooting Upgrade Failures ........................................................................................................ 28
5.4 Changing the EMMC ..................................................................................................................................... 29
5.5 Writing the Board Bar Code and Work Station Information .......................................................................... 29
5.6 Conducting the CBT....................................................................................................................................... 30
5.7 Preparing Information Reworking Files ......................................................................................................... 31
5.7.1 Determining the Rework Type .............................................................................................................. 31
5.7.2 Filling in a Rework Excel File for CDMA Phones ............................................................................... 32
5.7.3 Filling in a Rework Excel File for UMTS Phones ................................................................................ 33
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential iii
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual Contents
5.7.4 Rewriting Country and Vendor Information ......................................................................................... 33
5.8 Rewriting Physical Numbers and Customization Information ....................................................................... 34
5.8.2 Starting the Rework Tool ...................................................................................................................... 34
5.8.3 Specifying the Product Type and the Data Import Mode ...................................................................... 36
5.8.4 Clearing the DAP Time ......................................................................................................................... 37
5.8.5 Erasing the Software Version Restriction .............................................................................................. 37
5.8.6 Rewriting Vendor and Country Information ......................................................................................... 37
5.8.7 Rewriting Physical Numbers ................................................................................................................ 37
5.8.8 Modifying PLMN Settings .................................................................................................................... 38
5.8.9 Locking the Giag Interface ................................................................................................................... 39
5.8.10 Other Remarks .................................................................................................................................... 39
5.8.11 Uploading the Rework Information .................................................................................................... 40
5.9 Querying the Unlock Code ............................................................................................................................. 41
6 Troubleshooting Common Faults ............................................................................................ 42
6.1 Startup Failure ................................................................................................................................................ 42
6.1.1 No Current (DC Power Supply) ............................................................................................................ 42
6.1.2 Weak Current (DC Power Supply) ........................................................................................................ 44
6.1.3 Excessive Current (DC Power Supply) ................................................................................................. 47
6.2 Restart Fault ................................................................................................................................................... 50
6.3 Automatic Power-off ...................................................................................................................................... 52
6.4 No Ringtone ................................................................................................................................................... 52
6.5 No Voice Coming In ....................................................................................................................................... 54
6.6 Weak or No Transmission .............................................................................................................................. 55
6.7 Vibration Failure ............................................................................................................................................ 56
6.8 Weak or No Reception ................................................................................................................................... 57
6.9 SIM Card Detection Failure ........................................................................................................................... 57
6.10 Charging Failure ........................................................................................................................................... 58
6.11 Connection Failure Between the Phone and Computer ................................................................................ 60
6.12 Camera Failure ............................................................................................................................................. 61
6.13 LCD Display or Backlight Failure ............................................................................................................... 62
6.14 Touchscreen Failure ..................................................................................................................................... 62
6.15 GPS Signal Reception Failure ...................................................................................................................... 64
6.16 T-Flash Card Detection Failure .................................................................................................................... 65
6.17 Call Receiving Failure .................................................................................................................................. 65
6.18 Key Failure ................................................................................................................................................... 66
6.19 Reception Failure ......................................................................................................................................... 66
6.20 Transmission Failure .................................................................................................................................... 68
7 Solder Points on the PCB and BGA Chips ............................................................................. 70
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential iv
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 1 Overview
1 Overview
1.1 Applicable Scope
The G6-L11 Maintenance Manual is available in the simplified and advanced versions. The
two versions are respectively applicable to common service centers and advanced service
centers authorized by Huawei. This document provides repair instructions for technicians at
advanced service centers to conduct maintenance service of level 3. For maintenance services
of level 1 and level 2, see the G6-L11 Simplified Maintenance Manual. Being Huawei
proprietary, this document is accessible only for authorized service centers. Although every
effort was made to ensure the accuracy of the document, errors may still exist. If you find any
errors or have any suggestions, please report them through ComPartner.
1.2 Brief Introduction
This document introduces the product's working principles, functions of PCBA components,
maintenance workflow, and common troubleshooting methods. You will be able to clear
common faults of the product after you learn this document.
1.3 How to Obtain Product and Repair Information
To obtain product and maintenance information, visit Huawei service website. You are
recommended to install the Huawei service platform software ComPartner.
To obtain the ComPartner installation package, log in to
http://support.huaweidevice.com/service/, search for ComPartner. You will find the
installation package.
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 1
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 2 Product Overview
2 Product Overview
2.1 Appearance
Figure 2-1 shows the appearance of the HUAWEI G6-L11 mobile phone (G6-L11 for short).
Figure 2-1 G6-L11
2.2 Phone Working Principles
The G6-L11 is a bar-type mobile phone, consisting of the boards, battery, and other
mechanical parts. The boards contain the PCBA (M), proximity sensor FPC (LS), volume key
FPC (V), speaker FPC (SP), headset connector FPC (TL), TP, LCD module, 8M rear camera
module, mechanical parts, and antennas.
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 2
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 2 Product Overview
GPS WCN BT/WL Earphone
Receiver
Ant 3660 Ant jack
Proximixty&
Main 24 PIN BTB 8 PIN ZIF Ambient
SPK
cam 5M Connector Sensor
R/G/B LED 8 PIN ZIF Touch Panel
pmic emmc
G-sensor
msm8 Pop 24 PIN BTB LCD 5.0
926 ddr2 Connector QHD
Vibrator
wcd9302 4 PIN Volume
Battery Battery Connector Power Key
2000mah Connector WTR
Second
Micaro- USB mic
USB Connector
Main Main
mic Ant
The PCBA is the core part of the phone, which controls the baseband, RF, and other boards.
MSM8926 is a baseband processor chip that processes input and output signals such as video,
audio, or radio frequency (RF) signals. Baseband interfaces include the interfaces for the
keyboard, LCD, microSD card, Bluetooth, camera, and microphone.
PM8926 provides the analog multi-way switch, real time clock (RTC) circuit, temperature
compensated crystal oscillator (TCXO), motor drive circuit, and programmable current source.
WTR2605 is an RF signal processor that implements conversion of uplink and downlink RF
signals. The PCBs can be divided into four logical subsystems, that is, the baseband, RF
transceiver, power management unit, and user interface.
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 3
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 2 Product Overview
2.3 PCBA Functions
By function, the PCBA can be divided into four subsystems: baseband, RF, power, and user
interface subsystems.
Table 2-1 lists the modules and units of each subsystem.
Table 2-1 Modules and units of each subsystem
Subsyste
Module Unit Function
m
As a modem processor, the 2 x QDSP6 v. 5 is up to
700 MHz, performing the modulation and
demodulation of LTE, CDMA, WCDMA, GPS, and
Modem system
GSM. The subsystem includes the ARM9 processor,
modem DSP, modem AHB bus, interruption
controller, and sleep controller.
Quad ARM Cotex-A7 up to 1.2 GHz processor
Application
supports microSD card, EBI2, UART/USIM, I2C,
subsystem
GPIO, clock, and other functional modules.
MSM8926
Camera interface, PCM interface, broadband
CODEC, Vocoder, RF interface, HKADC, LCD
User interface
interface, microSD card interface, USB interface,
processing unit
UART interface, USIM card interface, SBI interface,
GPIO, JTAG/ETM interface, and keypad interface
The multimedia and game engine runs MPEG and
Multimedia and JPEG hardware engines and game engines, JAVA
Baseband game engine accelerator, and provides MP3/MMS/MIDI
subsystem functions.
Power supply Lists monitoring targets, such as external power
voltage input, Li-ion battery, button battery, VDD-phone,
monitoring and important LDO.
Temperature Temperature of the battery and power amplifier
PM8926
monitoring (PA).
Used to differentiate batteries of different
Battery ID manufacturers and discharge and discharge
algorithms.
NAND feature,
power
eMMC Stores programs and NV items, 8 GB
consumption, file
system support
POP encapsulated
LPDDR2RAM RAM for program running, 8 GB (256 MB x 32)
on the MSM8926
GpsOne Gen8 engine with GNSS
RF
GPS GPS receiver Receives and processes GPS signals
subsystem
Includes RTRLTN and the peripheral circuits.
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 4
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 2 Product Overview
Implements baseband functions of Bluetooth and
Bluetooth transmits and receives RF signals. Includes the
BT module
(BT)interface Bluetooth module of WCN3660 and peripheral
circuits.
Implements Wi-Fi baseband functions and transmits
and receives RF signals.
Wi-Fi interface Wi-Fi module
Includes the Wi-Fi module of WCN3660 and
peripheral circuits.
Crystal oscillator VCTCXO and
Provides high precision 19.2 MHz local clock
and frequency MSM control
TCXVCO.
synthesizer circuit
External antenna,
Provides built-in antenna for communication. The
internal interface
Antenna antennas include the main antenna, Wi-Fi/Bluetooth
component,
antenna, and GPS antenna.
antenna protection
Couples part of the output power to the RTRLTN
Coupler Power coupler
chip for power test.
The UART interface in MSM8926 subsystem is used
UART Interface
for Bluetooth.
Indicates the peripheral circuit of USB interface in
Driver, protection MSM8926 subsystem, and unit circuits such as
circuit, output protection circuit and interface connectors It is the
USB interface
interface major data service channel for the engineering
component sample, and can be used to debug and test devices
during product development.
Power supply,
protection circuit, Mainly includes the SIM card holder and related
SIM card interfaces
and SIM card connection circuits.
holder
Keypad driver
User circuit, external Performs interruption monitoring on volume keys
Keypad and
interface keypad, backlight using GPIO. Provides three side backlight LEDs.
backlight
subsystem LED control The backlight is on when a key is pressed.
circuit
LCD driver,
Color LCD and interface mode, The main LCD is of 1600 M color, 480 x 800. LDC
backlight and backlight backlight brightness is controlled by CABC function.
control
Power supply,
protection circuit, Mainly includes microSD card connector and related
microSD card
interface circuit.
Connectors
The power of the speaker that plays polyphonic
Driver mode,
ringtones when there is an incoming call can be 500
connection mode,
Test the speakers. mW(Class AB). Their frequency response is good
speaker
enough to playback 20 Hz to 20 kHz ringtones
component
smoothly. They can also play mono-audio MP3 files.
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 5
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 2 Product Overview
Driver mode, The power of the receiver for calls must be less than
connection mode, 70 mW
Receiver
receiver
component
Interface circuit,
connection mode, Built-in MIC using single microphone noise
Microphone
microphone reduction.
component
Earphone, headset
The phone provides a headset jack to output audio or
interface circuit,
Headset MP3 files. The microphone on the headset cable
microphone
picks up audio.
interface circuit
Driver mode,
Vibration motor When there is an incoming call, the motor vibrates to
connection mode,
interface notify the user of the call.
motor
I2C interface
Accelerometer Senses acceleration to help realize game functions.
control
Li-ion battery, standard output is 3.8 V/2000 mAh. It
Li-ion battery, is required that the charge/discharge lifecycle is over
Internal backup
interface 500 times. The battery should pass the following
battery
component authentication: GB18287 safety requirements (Li-ion
battery)
The charger can be used in China, Europe, the USA,
and Australia: 90–240 V, 45–55 Hz, AC input. The
model differs with different markets. The output
External power Adapter and
voltage of the charger is 5±0.25 V. The charger must
supply (travel interface
pass CE and CCC authentication. The charger's
charger) component
output current shall be adequate to charge the battery
and supply power to the phone for normal operation
at the same time.
Power
subsystem Power distribution Includes filtering networks and cabling for the power
network supply.
Backup battery It manages battery charging and discharging,
management, overcharging and over-discharging protection, and
charge circuit, also charges the capacitance used for RTC current
Power distribution charge mode, maintenance.
network and power charge protection
management
Mainly indicates LDO which manages power supply
Board circuit
flexibly. Based on the service status, protocol
power
requirements and power-saving analysis, the board
management
software manages power supply to unit circuits on
(power-on/off
the board to reduce power consumption. 32.768 KHz
analysis)
sleep clock is provided.
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 6
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 3 Components on the PCBA and BOM
3 Components on the PCBA and BOM
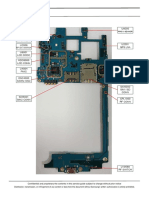
Figure 3-1 Layout of components and relevant failures A
J1502 USB
connector
U6001 3-in-1 Fault symptom:
chip USB failure
Fault symptom:
BT/WIFI/FM fault J1002 BTB connector U2201 gravity
Fault symptom: sensor D2404 tri- J2403 spring
Front camera fault Fault symptom: color indicator connector
Gravity sensor failure Fault Fault symptom:
symptom: Startup failure
U2801 NFC chip
Tri-color
Fault symptom:
NFC fault indicator failure
U1401 FLASH
Fault symptom:
Startup failure,
software fault
U701 CPU
U1402
Fault
symptom:
X201 19.2M Startup failure,
oscillator system down,
Fault symptom: RF fault
Startup failure, RF
fault
U201 PMU chip
Fault symptom:
Startup failure
U3701 RF PA
Fault symptom:
Transmission fault
U5601, U3301 Z4501
Z6602 transceiver
Fault symptom:
MIC1501 RF reception and
D2406PM chip
Fault symptom: transmission fault
Fault symptom:
Microphone fault
LED light fault
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 7
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 3 Components on the PCBA and BOM
Figure 3-2 Layout of components and relevant failures B
J2101 rear MIC1802Fault
camera symptom: J1602 BTB
connector Secondary connector
Fault symptom:
Fault symptom: microphone fault
Rear camera fault LCD display fault
J2503
connector
Fault
symptom:
TP fault
J1608 BTB
connector-
U1601 Fault
FEMALE-10
symptom:
Fault symptom:
Audio fault
Proximity sensor
fault
J2302 SD card
J4401 connector
antenna Fault symptom:
spring SD card fault
Fault
symptom:
Wi-Fi fault J2301 connector
Fault symptom:
Card detection
failure, SIM fault
J1501 battery
connector
Fault symptom: U2001 LCD
Startup failure backlight chip
Fault symptom:
LCD black screen
J2404 LCD connector
J6802 main Fault symptom:
antenna LCD fault
spring J2404 speaker FPC
Fault connector
symptom: Fault symptom: J1901 headset FPC
Reception/Tr No sound from the connector
ansmission speaker, no motor Fault symptom:
fault vibration Headset fault
Table 3-1 is provided for your reference only. It is subject to changes without notice. Obtain
the latest BOM information from Huawei TCS system. For details about how to query a BOM
code, see the simplified version.
Table 3-1 lists the BOM information about key components on the PCBA.
Table 3-1 BOM code list
Position BOM Description
Connectivity IC,2.4/5GHz WLAN/Bluetooth 4.0/FM
U6001 39210189
combo,WCN3660B,1.2~2.9V,79B WLNSP,Terminal Dedicated
U2201 38140098 Semiconductor Sensor,Accelerometer,LGA,3axis,Terminal Dedicated
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 8
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 3 Components on the PCBA and BOM
Position BOM Description
IO Connector,Micro_B Type Female,5pins,Side Plugging Type,SMT,4
J1502 14240656
Dip,above PCB,Terminal Dedicated
LED,0.0126cd/0.05cd/0.01cd, R(632)G(518)B(468)nm,2mA,SMD,Common
D2404 15020254
Anode,Teminal Dedicated
Card Socket,Spring Contact,4PIN,Horizontal,Center Line Spacing 1.6mm,Pin
J2403 14240778
Tail Length 0.4mm,SMT,Terminal Dedicated
NAND FLASH,8GB EMMC
U1401 40060516
V4.5/4.41a,200MHz,3.3V/1.8V,FBGA153(Pb-Free),Terminal Dedicated
Terminal Baseband process IC,LTE/WCDMA/TDSCDMA/GSM Multimode
U701 39200588 BASEBAND PROCESSOR MSM8926-1.2V/1.8V/2.85V/5V,12x12mm
POP,Terminal Dedicated
DDR2 DRAM,8Gb LPDDR2,533MHz,32bit,1.8V/1.2V,168BALL
U1402 40020240
FBGA(POP),Terminal Dedicated
U201 39200586 Terminal Baseband process IC,3.0~4.4V,172 WLNSP,Terminal Dedicated
Terminal Baseband process IC,1.225V/1.8V/2.1V,WLNSP164,Terminal
U5601 39200542
Dedicated
Duplexer,TX:1920~
Z4501 13080218
1980MHz/RX:2110~2170MHz,2.3dB.,2.8dB.,42dB.,2016,Terminal Dedicated
RF Switch,0.4-2.7GHz,MIPI SP12T
U3301 47140159
ASM,1.45dB,14dB,20dB.,3.2*2.5,Terminal Dedicated
Z6602 13010525 SAW Filter,2655MHz,3.0dB,1109,Terminal Dedicated
MIC1801,
22050099 Microphone,-42dB.,3.76*2.95*1.1mm,silicon
MIC1802
D2406 15020239 LED,0.045cd,White,2mA,0603,SMD,Teminal Dedicated
RF Multi-functional Component,MIPI MMMB
U3701 47150363
PA(6in8out),814~1980MHz,QFN,Terminal Dedicated
Crystal Unit,19.2MHz,7pF,+/-10ppm,70ohm,2.5*2.0*0.9mm,NTC
X201 12020215
internal,Terminal Dedicated
BTB Connector,BTBconnector,34PIN,0.4mm,0.8mm,SMT,female,Terminal
J2101 14240579
Dedicated
U1601 39200554 Terminal Baseband process IC,3.0~4.4V,55-WLNSP,Terminal Dedicated
J2302 14240840 Card Block Connector,Micro SD card,0.75mm,0.9mm,Terminal Dedicated
Card Connector,MicroSIM Card Connector,6PIN,Horizontal,2.54mm,hinge
J2301 14240686
type,Terminal Dedicated
Switching Regulators,2.7V,5.5V,0.2V,20mA,600KHz,QFN-6,1P10S LED
J2001 39110863
Driver,Terminal Dedicated
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 9
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 3 Components on the PCBA and BOM
Position BOM Description
J2404, J1901,
14240199 BTB Connector,Female,10Pin,0.4mm,SMT,0.9mm,Terminal Dedicated
J2503
J6802 51624989 Edge mini Groung Spring
J1501 14240576 Card Block Connector,BTF Connector,3*2,Female,1.3mm,Terminal Dedicated
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 10
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 4 Maintenance Tools
4 Maintenance Tools
Figure 4-1 Tools for advanced maintenance
Name: constant-temperature heat gun
Usage: to heat components
Name: constant-temperature heat gun
Usage: to heat components
Name: soldering iron
Usage: to solder components
Name: DC power supply
Usage: to supply DC power
Name: soldering table
Usage: to secure the PCBA
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 11
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 4 Maintenance Tools
Name: lead-free solder wire
Usage: soldering
Name: digital multimeter
Usage: to measure during repair
Name: toolkit
Usage: to assemble and disassemble terminal
products
Name: electric screwdriver
Usage: to fasten and remove screws
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 12
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 5 Troubleshooting
5 Troubleshooting
5.1 Integrated Device Maintenance Workflow
Figure 5-1 Repair workflow
Upload the
BOOT file using
JTAG tools (do
not erase the
flash data).
Step 1: Make the bin files.
Step 2: Modify the
physical numbers. Send the phone
Upgrade the Conduct the MMI Step 3: Write the
Software failure customization for quality check
software. test and MT.
information. (end).
Step 4: Upload the data
file.
Fault location and analysis
Erase the flash
data using
JTAG tools.
No fault found in
Fault
NFF (see the NFF
identification
process) Step 1: Upload the BOOT
file.
the version
Check the phone
software.
Upgrade
Step 2: Upgrade the
Replace the phone’s upgrade&load Conduct functions (conduct
flash chip. software. CBT. the MMI test and
Disposal Step 3: Write the board MT).
bar code using the SDK
tool.
Replace PAs
and RF ICs.
Hardware failure
Replace the
CPU.
Replace the faulty
part (such as the
headset,
microphone, LCD,
and touchscreen).
Table 5-1 Maintenance workflow
Step Description
Load the boot software using G6-L11 uses a USB to load the boot software. The upload tool is
a USB QPBLFBML01. For details, refer to the boot upload guide.
Upgrade the phone's version The version software is directly used by users. For details, see the simplified
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 13
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 5 Troubleshooting
Step Description
software. version.
Upload the phone's The upgrade&load software is used in the production line for RF calibration
upgrade&load software. and the function test. The way to upgrade this software is the same as
upgrading the version software.
Conduct the MMI test. The MMI test is carried out by the self-check software provided with the
phone. The MMI test is used to check the phone functions. For details, see the
simplified version.
Conduct the MT. The MT is used to test the phone's signal transmission. For details, see
section5.6 "Conducting the CBT."
Make the bin files. Make the bin files of the IMEI, SN, and PLMN information.
Modify the physical Modify the IMEI, SN, BT, Wi-Fi information. Refer to the local service policy
numbers. to determine whether to modify the IMEI. If IMEI modification is not required,
skip this step. For details, see section 5.8 "Rewriting Physical Numbers."
Write the customization Write the PLMN, country, and service provider (vendor) information. If there
information. is no such information on the phone, skip this step. For details, see section
5.8 "Rewriting Physical Numbers and Customization Information."
Upload the data file. After you modify the IMEI or PLMN information, a new data file will be
generated. Upload the new data file to ComPartner.
Write board bar code and Use the SDK tool to write the board bar code and work station information. For
work station information details, see section "5.5 Writing the Board Bar Code and Work Station
using the SDK tool. Information."
Conduct the CBT. RF calibration optimizes the RF performance of the phone. The RF function
test tells whether the RF indicators are qualified. For details, see section
5.6 "Conducting the CBT."
PCBA maintenance workflow:
To repair only the PCBA, refer to this workflow. However, MT is not required.
5.2 Upgrading the Upgrade&Load Software
G6-L11 uses a USB to load the boot software and the upload tool is QPBLFBML01. The
method is as follows:
When the board is empty or in other Download mode scenarios, Qualcomm driver must be
installed; in this case, after the board is connected to the PC, a Qualcomm port information
should be displayed as follows.
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 14
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 5 Troubleshooting
The board is in FASTBOOT port mode.
Note: In case of multi-downloading, all phones must use the same type of port.
5.2.1 Upgrade Environment Requirements
The Qualcomm driver must be installed.
The Android platform USB driver must be installed.
5.2.2 Upgrade Files
File Name
Upgrade File
Configuration File XML file
5.2.3 Multi-Download
1. Use a USB cable to connect the board to the PC. Then, a Qualcomm HS-USB QDLoader
port is displayed.
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 15
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 5 Troubleshooting
2. Install the software (QPBLFBML01Ver1000.exe installation package).
3. Run the software QPBLFT01.
4. Select an application area. If you select Manufacture, you need to enter a password; if
you select Service and RD, you do not need to enter a password,
5. Select the configuration file.
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 16
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 5 Troubleshooting
6. Click Next to navigate to the download page.
7. Click the ScanDownload button to start port searching. The port searching will persist
until the port is found; then, software downloading will start from port FASTBOOT.
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 17
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 5 Troubleshooting
8. After the downloading is complete, the following page is displayed.
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 18
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 5 Troubleshooting
5.2.4 Closing a Program
After the loading is complete, click Stop&remove to disable the program.
5.2.5 Log File
After the loading is complete, a log file will be generated in the PC
directory :C:\QPBLFBML01.
5.3 Software Upgrade
5.3.1 Upgrade Preparation
Table 5-2 lists the items to be prepared for a software upgrade.
Table 5-2 Items to be prepared
Item Description Remarks
Upgrade Computer Operating system (OS): Windows XP or Windows
environment 7
microSD card Available memory space larger than 2 GB
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 19
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 5 Troubleshooting
Item Description Remarks
Battery With at least 35% power remaining
USB cable Standard USB cable (BOM code: 02450768)
USB upgrade Handset WinDriver
driver
Upgrade tool Software tool that supports multiple upgrades
simultaneously (The tool's name subjects to that on
the ComPartner.)
Upgrade file UPDATE.APP Use the latest version for upgrade.
Upgrade Using the Normal upgrade
method microSD card
Forcible upgrade
Using the USB Normal upgrade
cable
Forcible upgrade
Before the upgrade, ensure that:
You have backed up important data on the phone because software upgrade will erase all user data.
Check the phone's software version because the software upgrade aims for upgrading lower versions
to higher versions only.
The power remaining of the battery is more than 50%.
Do not remove its battery during the upgrade.
About backing up important user data:
To back up contact information, text messages, and third-party applications installed, insert a
microSD card, and use the backup software on the phone (All Backup, for example) to back up all
the information to the microSD card.
To back up photos, videos, music, and personal files, manually back them up to the microSD card.
5.3.2 Using the microSD Card for Upgrade
To upgrade the phone using a microSD card:
Step 1 Format the microSD card using FAT32.
Step 2 Create a dload folder in the microSD card's root directory.
Figure 5-2 shows the dload folder under the root directory.
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 20
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 5 Troubleshooting
Figure 5-2 dload folder under the microSD card's root directory
Step 3 Copy the upgrade file UPDATE.APP to the dload folder.
Step 4 Insert the microSD card into the phone, power on the phone, and enter *#*#2846579#*#* on
the dialing screen. Touch ProjectMenu > Upgrade > SD card upgrade > Confirm.
Figure 5-3 Operation procedure
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 21
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 5 Troubleshooting
The upgrade progress is displayed on the phone screen, as shown in Figure 5-4.
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 22
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 5 Troubleshooting
Figure 5-4 Upgrade process
After the upgrade is complete, restore the phone to its factory settings and check whether the
software version is correct.
If the phone cannot be powered on, use either of the following methods to perform a forcible
upgrade:
Install the battery to the phone (if the phone screen flashes, remove the battery from the phone
and install it again after 5 minutes). Press and hold the volume up and down keys, and then
press the power key. The phone automatically starts a forcible upgrade. The upgrade process
displayed on the phone screen is the same as that shown in Figure 5-3.
Remove the battery from the phone. Press and hold the volume up and down keys, and
connect the charger to the phone. The phone automatically starts a forcible upgrade. The
upgrade process displayed on the phone screen is the same as that shown in Figure 5-3.
5.3.3 Using a USB for an Upgrade
Hardware Connection
Figure 5-5 shows the hardware connection.
Figure 5-5 Hardware connection
USB cable
便携机
Computer
PC
1
U6
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 23
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 5 Troubleshooting
Installing the USB Upgrade Driver
To install the USB upgrade driver:
Step 1 Download Handset WinDriver from ComPartner or www.support.huawei.com. Double-click
the file to install it.
Step 2 After the driver is successfully installed, power on the phone, connect the phone to the
computer using a USB cable, and open Computer Management to check whether the Ports
information is correct. If the port to which the phone is connected is not shown, switch the
phone to manufacturing mode.
To switch the phone's USB port to manufacturing mode, enter *#*#2846579#*#* on the
dialing screen, and touch ProjectMenu > Backgrounds settings > USB ports settings.
Figure 5-6 Port information
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 24
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 5 Troubleshooting
----End
Upgrading the Phone Using the USB Cable
To upgrade the phone using a USB cable:
Step 1 Power on the phone, and use the USB cable to connect it to the computer used for the
upgrade.
Step 2 Obtain the upgrade tool WH62406270ML01Ver1008 from ComPartner or at
www.support.huawei.com.
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 25
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 5 Troubleshooting
When the WH62406270ML01Ver1008 is run, the following dialog box is displayed.
Step 3 Enter the password (initial password: Huawei) and click OK. The Select Bin File dialog box
is displayed.
In the Be cautious to select field, choose whether to use a watchdog to authenticate the phone
with the DIAG interface locked. Connect a product-specific watchdog to the USB port on the
PC if clicking Use Safedog To Authenticate Phone.
(1) If the DIAG interface of the phone is locked, enter the password to unlock the DIAG
interface in the project menu before further operations. Alternatively, you can click Use
Safedog To Authenticate Phone and connect a product-specific watchdog to the USB port on
the PC so that the DIAG interface will be automatically unlocked in the following upgrade
procedure.
(2) A message will be displayed to remind you to connect a watchdog if you click Use
Safedog To Authenticate Phone but do not connect a product-specific watchdog.
Step 4 Click Not use safedog if you upgrade the G6 software.
You can use Huawei Multi-Upgrade Software - WH62406270ML01_Ver1008 to upgrade
the host software.
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 26
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 5 Troubleshooting
Step 5 Click Firmware and select the UPDATE.APP file from the upgrade software.
Step 6 Click Please Choose The Configuration File and select the
AndroidPhoneMultiUpgradeCfg_PCUI file.
Step 7 Click Next.
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 27
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 5 Troubleshooting
Step 8 Click Scan && Download. (Enter *#*#2846579#*#* on the phone dialer, and choose
ProjectMenu > Background Settings > UsbSetting > Manufacture mode.)
Step 9 Double-click on your computer, and use the authorized account to log in to the
platform. Select G6-U10 and double-click Upgrade Tool.
The phone automatically restarts when the upgrade succeeds.
If the phone cannot be started, use the following method to perform a forcible upgrade:
Use a USB cable to connect the phone to the PC, press and hold the volume up and down
keys to drive the phone to enter the forcible upgrade mode. Then perform the steps as you
conduct a normal upgrade.
5.3.4 Troubleshooting Upgrade Failures
Table 5-3 Upgrade failures and solutions
Failure Solution
(Computer) Failed to Check whether there is any other driver conflicting with the USB
detect the phone's upgrade driver.
presence Check whether the USB upgrade driver has been installed
properly.
Check whether the USB cable has been properly connected.
Check whether the serial port settings are correct.
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 28
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 5 Troubleshooting
Failure Solution
Failed to upgrade the Check whether the USB cable has been properly connected.
phone using the USB Check whether the target firmware version is higher than the
cable. original one.
Perform the upgrade again.
Fail to upgrade the Check whether the upgrade file is correct.
phone using the Check whether the upgrade method is correct.
microSD card.
Check whether the microSD card functions properly.
Perform the upgrade again.
5.4 Changing the EMMC
Return to Huawei for repair.
5.5 Writing the Board Bar Code and Work Station
Information
To write the board bar code and work station information into the phone using the SDK tool:
Step 1 Power on the phone, connect it to the computer, and check if the COM port to which the
phone is connected is correctly displayed.
Step 2 On the SDK tool window, enter the port number of the phone into USB port and click Diag
Unlock.
Step 3 Enter the bar code and click write barcode. Set set DT, set MT, set LT, set MMI, and set
PT to PASS. Click 正常模式.
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 29
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 5 Troubleshooting
----End
5.6 Conducting the CBT
Step 1 Prepare for CBT test. For details, refer to CBT Test Environment Setup Guide (CBT Test
Guide).
Step 2 Install CBT test service equipment SH76XX MS02.exe (PDM archive code is 00625935).
Step 3 Log in to MobileStudio platform, select CDMA2000 in Type, and select SH76XX MS02 in
engineering.
Step 4 Select TPS.
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 30
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 5 Troubleshooting
Step 5 Select the configuration file [MSM8926_G6-L75][Normal][CT].
Step 6 Input the password huawei to enter property page, and start the test after the configuration.
Step 7 Refer to the preceding parameter settings when you conduct BT tests (CT, CBL, and CBU)
and MT tests.
----End
5.7 Preparing Information Reworking Files
This section describes how to fill in information reworking excel files.
5.7.1 Determining the Rework Type
CDMA phones support the following types of reworking:
SmartPhone_CDMA_PhyNum: to modify physical numbers
SmartPhone_CDMA_PLMN: to modify the PLMN
UMTS phones support the following types of reworking:
SmartPhone_PhyNum: to modify physical numbers
SmartPhone_PLMN: to modify the PLMN
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 31
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 5 Troubleshooting
CDMA and UMTS phones support the same method of rewriting the country and vendor
information:
SmartPhone_Country_Vendor: to modify the vendor information
5.7.2 Filling in a Rework Excel File for CDMA Phones
In the SmartPhone_CDMA_PhyNum sheet, you can write the following information: MEID,
Bluetooth address, Wi-Fi addresses, IMEI1, and IMEI0 (secondary physical number for a
main international card).
An excel filling example is as follows.
Write the MEID of the main SD card in the first column.
Write the Bluetooth address in the second column.
Write the Wi-Fi address in the third column.
Write the SN in the fourth column.
Write the IMEI of the secondary SIM card in the fifth column (not for single-card
phones).
Write the secondary IMEI of the main SIM card in the sixth column (not for phones
without international cards).
In the SmartPhone_CDMA_PLMN sheet, you can change the PLMN information. A PLMN
change example is as follows.
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 32
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 5 Troubleshooting
5.7.3 Filling in a Rework Excel File for UMTS Phones
In the SmartPhone-PhyNum sheet, you can enter the following information: IMEI,
Bluetooth address, Wi-Fi addresses, and Sub IMEI (optional).
An excel filling example is as follows.
Write the MEID in the first column.
Write the Bluetooth address in the second column.
Write the Wi-Fi address in the third column.
Write the SN in the fourth column.
Write the IMEI of the secondary SIM card in the fifth column (not for single-card
phones).
In the SmartPhone_PLMN sheet, you can change the PLMN information. A PLMN change
example is as follows.
Write the PLMNNW in the first column.
Write the PLMNNS in the second column.
Write the PLMNSP in the third column. Fill in contents according to the customization
information.
5.7.4 Rewriting Country and Vendor Information
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 33
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 5 Troubleshooting
Enter the country in the first column and the vendor in the second column.
5.8 Rewriting Physical Numbers and Customization
Information
The rework tool for G6 is WPSPRW01.
Interface Status
After the phone is connected to a computer, the interface status is displayed and the interface
in the red block needs to be modified, as shown in the following figure.
5.8.2 Starting the Rework Tool
Log in to the ComPartner platform and start the rework tool (you can normally use the tool
only after login authentication succeeds). The following page is displayed.
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 34
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 5 Troubleshooting
Figure 5-7 Default page upon a login
Select CDMA. The following page is displayed.
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 35
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 5 Troubleshooting
When the primary card is an international card and the corresponding IMEI needs to be input, select
IMEI2 and set IMEI1 to the IMEI of the secondary card.
5.8.3 Specifying the Product Type and the Data Import Mode
Specify the data import mode based on the data sources to be reworked. Properly select the
product type and corresponding rework types.
From excel file: All rework types are supported, as shown in Figure 1. It is recommended that
you select From excel file.
Input: Only Vendor&Country and Physical Numbers are supported, as shown in Figure 3.
You need to manually input data.
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 36
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 5 Troubleshooting
Figure 5-8 Input tab
5.8.4 Clearing the DAP Time
Select Clear DAP Time. The DAP time is cleared. This function takes effect on phones that
support clearing DAP time only.
5.8.5 Erasing the Software Version Restriction
Select Erase Version and tick Erase customized version. The universal version can be used.
This function applies to cancel the upgrade restriction between customized versions.
Select Erase Version and tick Erase restricted version. The current version can be
downgraded to an earlier version. This operation can cancel the downgrade restriction
between later and earlier versions.
5.8.6 Rewriting Vendor and Country Information
Select Rewrite Vendor and Country and import the corresponding EXCEL or BIN file. The
vendor and country information of the phone can be modified. If you select the Input mode,
enter the vendor and country information in text boxes based on actual customization.
5.8.7 Rewriting Physical Numbers
Select Rewrite Physical Numbers, tick desired sub-items, and import the corresponding
EXCEL or BIN file. The IMEI/IMEI, BT MAC, WIFI MAC, SN, and Sub-IMEI information
of the phone can be modified, among which, IMEI/IMEI is mandatory by default and others
are optional. If you select the Input mode, enter the data in corresponding text boxes.
NCK data and corresponding password of the phone retain after physical numbers are
rewritten. If you select Cloud Account or Widevine, new cloud account and widevine will be
automatically generated, and then written into the board, uploaded to the server, and saved in
the rework result file (in the directory QualcommModifyInfoLog).
Connect only one phone when rewriting physical numbers. Enter the target IMEI or IMEI in Target
PSID (If you select the Input mode, do not enter the target physical number in Target PSID.)
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 37
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 5 Troubleshooting
Figure 5-9 Rewriting physical numbers
5.8.8 Modifying PLMN Settings
Select Rewrite PLMN and import the corresponding EXCEL file. Network parameters of the
phone can be modified. PLMN parameters are key data for customization. Incorrect PLMN
parameters result in network lock or a network registration failure for the phone. Carefully
confirm PLMN settings before modification.
Feature Inds and DCK Count Max vary with customizations, so specify the two parameters
in compliance with the customization file. If DCK Count Max is set to 0, the subscription
may fail. (This configuration is updated with PLMN information.)
NCK data and corresponding password of the phone change after PLMN settings are
modified, and related encrypted data is uploaded to the server and saved in the rework result
file. If you select Cloud Account or Widevine, a new cloud account and widevine will be
automatically read and saved in the rework result file (in the directory
QualcommModifyInfoLog).
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 38
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 5 Troubleshooting
Figure 5-10 Modifying PLMN settings
5.8.9 Locking the Giag Interface
Select Lock Diag. The Diag interface is locked. Lock solutions vary with products. For
phones using the 8930 platform, the password and PLMN settings are separate and you can
only lock the Diag interface only; for phones not using the 8930 platform, the Diag password
and PLMB settings must be modified together. When modifying PLMN settings, if Lock
Diag is not selected, the default password is 16 zeros.
5.8.10 Other Remarks
Process multiple rework types simultaneously.
You can select one or more rework types and click Search&Write. All selected items are
processed simultaneously and no other manual operations are required.
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 39
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 5 Troubleshooting
Figure 5-11 Simultaneously processing multiple rework types
Operate multiple phones simultaneously.
Start the rework tool and click Search&Write. A maximum of 8 connected phones can be
operated simultaneously. However, only one phone can be connected when you select Rewrite
Physical Numbers to modify physical numbers.
5.8.11 Uploading the Rework Information
After be rewritten, the customization information will be automatically uploaded to the server.
To check such a file, access C:\SmartPhoneModifyInfoLog\Report on your computer.
To upload the data file to ComPartner:
Step 1 Log in to ComPartner, click Upload unlock code.
Step 2 On the displayed dialog box, specify the path of the data file to upload.
Step 3 Click Upload.
The system will show you whether the file is successfully uploaded.
----End
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 40
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 5 Troubleshooting
5.9 Querying the Unlock Code
To query the unlock code:
Step 1 Log in to ComPartner and click Query unlock code.
Step 2 On the displayed dialog box, enter the physical number to query. Select your region and click
Query. In the Result area, select a lock code
type.
---End
Querying the unlock code requires you to have the permission. Contact the local Huawei technical
support to apply for the permission.
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 41
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 6 Troubleshooting Common Faults
6 Troubleshooting Common Faults
Before performing maintenance and repair, ensure that the failure is not caused by
environmental factors and incorrect phone settings. It is advisable to back up customer
information before restoring the factory settings for troubleshooting.
6.1 Startup Failure
To troubleshoot the power-on failure, firstly check whether the battery connector is damaged.
If not, use a DC regulated power supply to power the phone and test the current of the phone.
The methods to troubleshooting the power-on failures, see the following sections.
Power-on failures are divided into the following types:
No current: After you connect the phone to the DC power supply and power on the
phone, the reading on the power supply ranges from 0 mA to 5 mA.
Weak current: After you connect the phone to the DC power supply and power on the
phone, the reading on the power supply ranges from 5 mA to 100 mA.
Excessive current: After you connect the phone to the DC power supply and power on
the phone, the reading on the power supply exceeds 300 mA.
If the G6-L11 fails to be powered on, observe the power-on current reading on the DC
power supply to identify the fault.
6.1.1 No Current (DC Power Supply)
Generally speaking, there are three reasons for no current in the phone:
The battery port is not completely soldered.
The power key is damaged.
The circuit of the power key or the power management chip is damaged.
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 42
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 6 Troubleshooting Common Faults
Figure 6-1 Troubleshooting startup failures with no current
Power-on failure
Y
Check whether the power key FPC is
Replace the power key
damaged and whether the connector
FPC or fasten the power
pins are in good contact.
key FPC connector
N
Provide power to the phone
(3.8–4 V) and press the power
key to check the current
No current
Check whether there is Solder the battery connector.
open soldering in the
battery connector
N
Check whether Vbat network is Solder the
connected (check whether the parts parts Powe
on Vbat is intact and whether the red
network ports are connected by on?
using a multi-meter).
N
Y Y
Y
Check whether the phone End
can power on after
soldering PMU U201
Y
Check whether the
phone powers on
after changing U201
Replace the PBCA
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 43
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 6 Troubleshooting Common Faults
Figure 6-2 Component positions
6.1.2 Weak Current (DC Power Supply)
Generally, weak current (15–80 MA) may be caused by the following reasons:
Software faults (upgrading or reloading the software may solve the problem.
The PM output chip is damaged, leading to incomplete voltage output.
CPU or FLASH is damaged.
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 44
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 6 Troubleshooting Common Faults
Figure 6-3 Power-on/power-off sequence
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 45
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 6 Troubleshooting Common Faults
Figure 6-4 Troubleshooting startup failures with weak current
Startup failure – low
current
End
Problem solved upon
a software upgrade?
Problem solved after End
the BOOT software
is loaded using a
USB?
N
Replace the U201
Is the PM output voltage
normal?
Problem solved after the End
EMMC U1401 is replaced?
N
Y
Problem solved after the End
CPU U701 is replaced?
Return to Huawei for
repair.
Table 6-1 PM voltage output table
Signal Reference output value Test Point
VREG_S3_1P3 1.3 V L503
VREG_L3_1P15 1.15 V C621
VREG_S1_1P15 1.15 V L501
VREG_S4_2P1 2.1 V L504
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 46
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 6 Troubleshooting Common Faults
Signal Reference output value Test Point
VREG_L10_1P8 1.8V C608
6.1.3 Excessive Current (DC Power Supply)
Excessive current is caused by:
Excessive current generated after you press the power key: The PM is damaged or
short-circuited.
When it has been powered off (greater than 500MA): The battery VBAT or VPH-PWR
circuit is short-circuited.
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 47
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 6 Troubleshooting Common Faults
Figure 6-5 Troubleshooting startup failures with excessive current
Startup failure –
extreme current
N
Check the output
Check whether
circuits of the
VBAT is short-
VPH_PWR and the PM
circuited to the
ground
Y
Y
Check whether the Replace the
battery connector faulty component.
J1501 is short-
circuited
Replace the Y End
PM U201
Return to Huawei
for repair
Figure 6-6 Battery connector
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 48
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 6 Troubleshooting Common Faults
Figure 6-7 PM
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 49
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 6 Troubleshooting Common Faults
6.2 Restart Fault
Figure 6-8 Troubleshooting restart faults
Restart
Problem solved End
upon a software
upgrade?
N
Y
Problem solved End
after the BOOT
software is loaded
using a USB?
Y
Is the power key DOM pin Replace the power
or clip J2403 is short- key or its clip
circuited?
N
Is the ps_hold (test point
C208) or pm_resin_n (test Replace the PM
point R2402) voltage is 1.8 U201
V?
N
Return to Huawei for
repair
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 50
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 6 Troubleshooting Common Faults
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 51
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 6 Troubleshooting Common Faults
6.3 Automatic Power-off
Check that the power-off is not caused by low battery level. Automatic power-off may be
caused by application errors or compatibility issues of third-party applications. You can try to
solve such problem by restoring the phone to its factory settings or upgrading the phone to a
latest software version. If the problem persists, change the PCBA or return the phone to
Huawei for repair.
6.4 No Ringtone
Figure 6-9 Troubleshooting no ringtone
No ringtone
N
Check whether Replace the
the speaker is speaker
functional
N Check whether
Check whether the L203
speaker signal circuit is and L204
normal .are properly
soldered.
Y
Replace the PCBA
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 52
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 6 Troubleshooting Common Faults
Figure 6-10 Speaker circuit
Figure 6-11 L203 and L204 positions
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 53
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 6 Troubleshooting Common Faults
6.5 No Voice Coming In
Figure 6-12 Troubleshooting no voice coming in
No voice coming in
N
Check whether the End
receiver volume setting
is correct
Y
Y
Check whether a headset has Replace the
been inserted headset connector
Y
Problem solved after
End
the receiver is
replaced?
N Check whether
Check whether the L1803 and L1804
receiver signal circuit are properly
is normal soldered
Replace the 1601
Figure 6-13 Receiver circuit
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 54
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 6 Troubleshooting Common Faults
Figure 6-14 L1803 and L1804 positions
6.6 Weak or No Transmission
Figure 6-15 Troubleshooting weak or no call transmission
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 55
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 6 Troubleshooting Common Faults
6.7 Vibration Failure
Figure 6-16 Troubleshooting vibration failures
No vibration
Y
Is the problem
solved af ter you re-
load the phone End
sof tware?
N
Y
Is the problem solved
af ter you replace the End
motor?
Y
Is the VIB_DRV_N
Replace the
voltage equal to
D2407
the battery voltage?
Replace the U201
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 56
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 6 Troubleshooting Common Faults
6.8 Weak or No Reception
Figure 6-17 Troubleshooting weak or no reception
No reception
Is the problem solved Y Advise the
after you replace the SIM customer to use a
card? standard SIM card
Y Replace the
Is the problem solved after
main antenna
you replace the antenna?
Replace the
PCBA
6.9 SIM Card Detection Failure
Figure 6-18 Troubleshooting a SIM card detection failure
SIM card detection failure
N
Check whether the SIM card Replace the SIM
slot is normal card slot
N
Check whether the power supply Replace the
VREG_L22_UIM1 for the SIM card PCBA
is normal
N
Check whether the SIM Resolder or
card channel and other replace the
signal channels are component
normal
Y
Replace the PCBA
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 57
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 6 Troubleshooting Common Faults
6.10 Charging Failure
Failure analysis: Charging failure may occur in the following ways:
The charger is connected to the phone, but the phone does not respond.
The phone displays the charging icon, but the phone is not being charged.
To troubleshoot charging failure, firstly check whether the battery connector is damaged.
Figure 6-19 Troubleshooting a charging failure
Charging failure
Y
Check whether Replace the J1502
J1502 is poorly
soldered, deformed,
or damaged
N
Y
Test whether the voltage of
Replace the
J1502 pin 1 is about 5 V
J1502
Test whether the fuse Replace the
N
LB1501 is conductive LB1501
Return to Huawei for
repair
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 58
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 6 Troubleshooting Common Faults
Figure 6-20 USB connector circuit
Figure 6-21 J1502
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 59
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 6 Troubleshooting Common Faults
6.11 Connection Failure Between the Phone and Computer
Figure 6-22 Troubleshooting connection failures between the phone and computer
Connection failure between
the phone and computer
Y
Is the problem solved after End
you replace the USB cable?
Is the 5-pin mini USB connector Y
poorly soldered?
Resolder the
USB connector
Y
Is the problem solved
End
after you reload the
phone software?
Y
Is there voltage at
VCHG? Replace the U201
Replace the LB1501
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 60
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 6 Troubleshooting Common Faults
6.12 Camera Failure
Figure 6-23 Troubleshooting camera failures
Camera failure
Is the problem solved
End
after you restore the
phone factory settings?
Y
Check whether the BTB Resolder or replace
connector J2101/J2102 is the connector
damaged (pins are poorly
soldered or bent)
N
Is the problem
End
solved after you
replace the camera
module?
N
Return to Huawei for
repair
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 61
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 6 Troubleshooting Common Faults
6.13 LCD Display or Backlight Failure
Figure 6-24 Troubleshooting LCD display or backlight failures
No LCD display or backlight
Is the problem solved after Y
End
you reload the phone
software?
N
Check whether the LCD BTB Replace the
connector is normal connector
Y Y
Is the problem solved after End
you replace the LCD?
Test whether Y
N the resistance Replace the faulty
of T2001/T2002/T2003 to the component
ground is normal
Y
Is the backlight fault End
rectified after you replace
the D2001?
Replace the U701
6.14 Touchscreen Failure
The touchscreen fault mainly be reflected as touchscreen unlocking failure while the LCD
display is normal. The touchscreen components have great independence and multiplex power
supply and communication interfaces with other circuits; therefore, you can replace the front
shell to identify whether it is a touchscreen fault or PCBA-related circuit fault.
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 62
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 6 Troubleshooting Common Faults
Figure 6-25 Troubleshooting a touchscreen failure
Touchscreen failure
Is the problem solved after Y
End
you reload the phone
software?
N
Is the TP BTB connector Replace the
normal? connector
Y Y
Is the problem solved after End
you replace the touchscreen?
Y
Are small components are Resolder or replace
N soldered?
properly the component
Replace the U701
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 63
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 6 Troubleshooting Common Faults
6.15 GPS Signal Reception Failure
Figure 6-26 Troubleshooting GPS signal reception failures
GPSsignal reception
failure
Is the GPS
N Replace the GPS
antenna in good
contact with pins antenna or pin
J6805/J6806?
Y
Re-solder or
Is the GPS channel
replace the faulty
poorly soldered?
component
Re-load the
phone software
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 64
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 6 Troubleshooting Common Faults
6.16 T-Flash Card Detection Failure
Figure 6-27 Troubleshooting T-Flash card detection failures
T-Flash card detection failure
Y
Is the problem solved
after you replace the End
T-Flash card?
Y
Check whether the Z2301 is
poorly soldered Resolder the
Z2301
Replace the
Z2301
6.17 Call Receiving Failure
Figure 6-28 Troubleshooting call receiving failures
No sound received after a call
is set up
N
Check whether the End
receiver volume
setting is correct
Y
Is the problem solved after End
you replace the headset?
Y
Check whether Replace the
any signal is headset connector
output
Replace the
U1601
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 65
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 6 Troubleshooting Common Faults
6.18 Key Failure
Figure 6-29 Troubleshooting key failures
Key failure
N
Are the key dome Clean or
pins in good replace the
contact? key dome
sheets
Y
Y
Is the problem
solved after you
replace the key End
FPC?
Re-load the
phone
software
6.19 Reception Failure
This section describes the troubleshooting procedure for G850 reception failures as an
example.
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 66
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 6 Troubleshooting Common Faults
Figure 6-30 Troubleshooting reception failures
G850 reception failure
Check the J3305 with
no RF cable inserted
N
Are pin 1 of J3305 and Check the J3305
the middle pin are
conductive?
Y N
Check the Z3301
Check whether Z3301 is
conductive
Y
N
Check whether pin 1 of U3301 is Check the U3301
normal (with an insertion loss not
more than 2.5 dB)
N
Check whether Z3302 is Check the Z3302
normal
Check the U5601
Check whether the IQ signal of
U5601 is normal and the
power voltage is normal
Check the U701
End
For GSM1900, only replace the check procedure of Z3302 with that of the Z3901.
For a B8/GSM900 reception exception, check the Z4601 instead of Z3302 by using the
same method.
For B1 reception failures, only replace the check procedure of the Z3302 with that of the
Z4501.
For L3/GSM1800, only replace the check procedure of the Z3302 with that of the Z4701.
For an L20 reception exception, follow the same troubleshooting procedure but replace
the Z3302 detection with Z4001 detection.
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 67
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 6 Troubleshooting Common Faults
For an L7 reception exception, follow the same troubleshooting procedure but replace
the Z3302 detection with Z4101 detection.
6.20 Transmission Failure
For G6-L1 B1/B8/GSM/L3/L20, generally check whether the PA U3701 and U3301 are
normal.
For G6-L1 L7, generally check whether the PA U4101 and U3301 are normal.
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 68
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 6 Troubleshooting Common Faults
Figure 6-31 Troubleshooting transmission failures
W2100 transmission failure
Check the J3305 with
no RF cable inserted
N
Are pin 2 of J3305 and Check the J3305
the middle pin are
conductive?
Y N
Check the Z3301
Check whether Z3301 is
conductive
Y
N
Check whether U3301 is normal Check the U3301
N
Check whether the control Check the U3701
voltage and power supply
of U3701 is normal
Check the U5601
Check whether the IQ signal of
U5601 is normal and the
power voltage is normal
Check the U701
End
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 69
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 7 Solder Points on the PCB and BGA Chips
7 Solder Points on the PCB and BGA Chips
Red (R: 255, G: 0, B: 0) : vacant point; Green (R: 0, G: 255, B: 0) : ground point;
Blue (R: 0, G: 0, B: 255) : solder point
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 70
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 7 Solder Points on the PCB and BGA Chips
Figure 7-1 Solder points on PCB side A
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 71
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 7 Solder Points on the PCB and BGA Chips
Figure 7-2 Solder points on PCB side B
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 72
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 7 Solder Points on the PCB and BGA Chips
Figure 7-3 U701/U1402
Figure 7-4 U1401
Figure 7-5 U201
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 73
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual 7 Solder Points on the PCB and BGA Chips
Figure 7-6 U5601
Figure 7-7 U6001
Figure 7-8 U1601
Issue 01 (2014-04-03) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential 74
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd..
Вам также может понравиться
- Bts3900b GSM User Guide - (v600r009 - 01)Документ30 страницBts3900b GSM User Guide - (v600r009 - 01)Serkan KılınçarslanОценок пока нет
- Intel-Nokia AllianceДокумент18 страницIntel-Nokia AllianceTedtenorОценок пока нет
- Paxstore Features v10Документ11 страницPaxstore Features v10ashraf mhmadОценок пока нет
- Raid PPTДокумент29 страницRaid PPTArchana DhanasekaranОценок пока нет
- Wight Paper DpiДокумент17 страницWight Paper DpiradislamyОценок пока нет
- Journal of Physics Conference Series paper on adapting physics apps for blind studentsДокумент6 страницJournal of Physics Conference Series paper on adapting physics apps for blind studentsRo RohadiОценок пока нет
- Smart Phone Cum App Testingcourse CTS ITI SyllabusДокумент32 страницыSmart Phone Cum App Testingcourse CTS ITI SyllabusS RajaОценок пока нет
- PM AssДокумент16 страницPM AssSAADОценок пока нет
- Product Manual: Version: AДокумент101 страницаProduct Manual: Version: AGuilherme Ribeiro BarbosaОценок пока нет
- CEI44: Network and Hardware Support Lab 1: Network Creation Planning StageДокумент11 страницCEI44: Network and Hardware Support Lab 1: Network Creation Planning StageSvetlanaОценок пока нет
- WondercubeДокумент19 страницWondercubeapi-35523690760% (5)
- VICTORY ProposalДокумент18 страницVICTORY ProposalVictory technology100% (1)
- Pre Integration Check ListДокумент10 страницPre Integration Check ListChristopher SmithОценок пока нет
- Nokia's Strategies for Dominating the Indian Mobile MarketДокумент8 страницNokia's Strategies for Dominating the Indian Mobile Market2011ankitОценок пока нет
- Huawei Enterprise BusinessДокумент32 страницыHuawei Enterprise Businessukan2006Оценок пока нет
- Proposal For 3CX IP-PBX Solutions To: Karuturi Telecom PVT LimitedДокумент8 страницProposal For 3CX IP-PBX Solutions To: Karuturi Telecom PVT LimitedSantosh VarunОценок пока нет
- Wireless Deployment Guide For Wireless Service Providers 105493ae PDFДокумент20 страницWireless Deployment Guide For Wireless Service Providers 105493ae PDFFaise JanОценок пока нет
- Analysis of Business Failure Occurred To "Abc PLC-"Документ12 страницAnalysis of Business Failure Occurred To "Abc PLC-"Mohamed NidhalОценок пока нет
- RTN 950 V100R007C00 Commissioning Guide 02Документ213 страницRTN 950 V100R007C00 Commissioning Guide 02Nielsen KaezerОценок пока нет
- Team PowerBank WP8000 EDM enДокумент4 страницыTeam PowerBank WP8000 EDM enSofiane ChenОценок пока нет
- 01-8 Configuring Mobility ManagementДокумент43 страницы01-8 Configuring Mobility ManagementFrensel PetronaОценок пока нет
- Vodafone MarketingДокумент27 страницVodafone Marketingvai_d100% (1)
- Pre-ATP Checklist (Final) 6561Документ4 страницыPre-ATP Checklist (Final) 6561Azfar ShabbirОценок пока нет
- Product Description PDFДокумент148 страницProduct Description PDFCoachArun MishraОценок пока нет
- Asterisk Wakeup CodeДокумент2 страницыAsterisk Wakeup CodespiceboyzОценок пока нет
- Attendance Monitoring SystemДокумент2 страницыAttendance Monitoring Systemjeffreyian100% (2)
- Mobile TV SeminarДокумент24 страницыMobile TV SeminarRamlal Chavan0% (1)
- ZTE's Strategies for Iran Telecom MarketДокумент15 страницZTE's Strategies for Iran Telecom MarketSubarn Dev PantОценок пока нет
- Tethering and Portable HotspotДокумент22 страницыTethering and Portable HotspotSan Rawat0% (1)
- International Accounting & FinanceДокумент18 страницInternational Accounting & FinanceShaji Viswanathan. Mcom, MBA (U.K)Оценок пока нет
- Why Should You Consider Refurbished Smartphones?Документ2 страницыWhy Should You Consider Refurbished Smartphones?mobigarageseoОценок пока нет
- PPIF0552-002 Payshield 9000 Decommissioning GuideДокумент12 страницPPIF0552-002 Payshield 9000 Decommissioning GuideSudipto100919100% (1)
- What Is Technology AbsorptionДокумент5 страницWhat Is Technology Absorptionunidentified02100% (1)
- Assignment 1Документ15 страницAssignment 1Vignesh VishwanathОценок пока нет
- TSAPIДокумент2 страницыTSAPIVijay BandaruОценок пока нет
- Mobile Handset IndustryДокумент24 страницыMobile Handset IndustryNikhil NandanwarОценок пока нет
- Avaya IP Office Contact Center OverviewДокумент35 страницAvaya IP Office Contact Center OverviewMarthaGutnaraОценок пока нет
- Complete OS-notes PDFДокумент198 страницComplete OS-notes PDFAnoop PutturОценок пока нет
- Free Laptops & PC's Schematic Diagram and BIOS DownloadДокумент8 страницFree Laptops & PC's Schematic Diagram and BIOS DownloadLutfi Aziz100% (1)
- GoGlobal Installation DocumentДокумент5 страницGoGlobal Installation Documentganeshbabu123Оценок пока нет
- IP470 Installation User GuideДокумент39 страницIP470 Installation User GuideVodafone Business SurveillanceОценок пока нет
- VoIP Hosted PBX SolutionДокумент17 страницVoIP Hosted PBX SolutionSoji AbolarinОценок пока нет
- Base Transceiver StationДокумент2 страницыBase Transceiver StationArslan Ali100% (1)
- Calix MDU ONT DatasheetДокумент4 страницыCalix MDU ONT DatasheetChris MОценок пока нет
- VARTA - Powerpack 10.400: Order No.: 57961 101 401Документ1 страницаVARTA - Powerpack 10.400: Order No.: 57961 101 401Michael WallsОценок пока нет
- CDD reduces interference in cellular systems by less than 40 charactersДокумент19 страницCDD reduces interference in cellular systems by less than 40 charactersNitin SakpalОценок пока нет
- Extron FW Loader v5x1Документ17 страницExtron FW Loader v5x1Imthiyas AhmedОценок пока нет
- SouДокумент3 страницыSouSmita Chavan KhairnarОценок пока нет
- PortalsДокумент160 страницPortalsapi-26037880100% (1)
- ZTEsoft Profile & ExperienceДокумент33 страницыZTEsoft Profile & Experiencesunny709Оценок пока нет
- Block Diagram of A ComputerДокумент20 страницBlock Diagram of A ComputerXandra LeeОценок пока нет
- Procedure For Testing of Antenna and Feeder Cable System - Bird TopДокумент11 страницProcedure For Testing of Antenna and Feeder Cable System - Bird TopEber Fernando Escorcia MontoyaОценок пока нет
- Customer Support ServicesДокумент12 страницCustomer Support ServicesWilliamОценок пока нет
- Plant Communication System Catalogue4 PDFДокумент15 страницPlant Communication System Catalogue4 PDFpankajОценок пока нет
- 10 Hospitality Trends To Look Out ForДокумент3 страницы10 Hospitality Trends To Look Out ForErl DrizОценок пока нет
- Huawei Smart Retailing Solution PresentationДокумент25 страницHuawei Smart Retailing Solution PresentationReem YouОценок пока нет
- Proposal HWДокумент7 страницProposal HWTadesse GuadsieОценок пока нет
- SonyДокумент21 страницаSonyNeha UpadhyayОценок пока нет
- RF Acceptance Document (GP-Huawei) - Modified - 290410Документ22 страницыRF Acceptance Document (GP-Huawei) - Modified - 290410Raju_RNO EnggОценок пока нет
- G630-U10 Advanced Maintenance ManualДокумент71 страницаG630-U10 Advanced Maintenance ManualwebpcnetlinkОценок пока нет
- Asus Bitmap PasswordДокумент1 страницаAsus Bitmap PasswordSmartFix agudeloОценок пока нет
- BQ24728 Datasheet PDFДокумент42 страницыBQ24728 Datasheet PDFMiguel Sierra50% (2)
- Vietmobile - VN: Hl1Aevam Ver.D Silkscreen TopДокумент2 страницыVietmobile - VN: Hl1Aevam Ver.D Silkscreen TopSmartFix agudeloОценок пока нет
- Main Esquemático Xt1922 Moto g6 PlayДокумент38 страницMain Esquemático Xt1922 Moto g6 Playjeison hernandezОценок пока нет
- ART FILM ADT DOCUMENT VERSION HISTORYДокумент2 страницыART FILM ADT DOCUMENT VERSION HISTORYSmartFix agudeloОценок пока нет
- Samsung Level 3 Repair Guide - Fix Device Issues and Replace ComponentsДокумент40 страницSamsung Level 3 Repair Guide - Fix Device Issues and Replace ComponentsGak Tahu69% (13)
- MODEM Schematic Baseband Schematic: Huawei Tech Co.,LtdДокумент60 страницMODEM Schematic Baseband Schematic: Huawei Tech Co.,LtdSmartFix agudeloОценок пока нет
- Vietmobile - VN: Hl1Uevam Ver.D Silkscreen Top Spell Mode:1X2Документ2 страницыVietmobile - VN: Hl1Uevam Ver.D Silkscreen Top Spell Mode:1X2SmartFix agudeloОценок пока нет
- Schematic g6 PlusДокумент46 страницSchematic g6 PlusMicroelectronica Servitekcel100% (6)
- 08-SM-A107 Tshoo 7 PDFДокумент20 страниц08-SM-A107 Tshoo 7 PDFSmartFix agudeloОценок пока нет
- ZE550ML/ZE551ML Troubleshooting GuideДокумент7 страницZE550ML/ZE551ML Troubleshooting GuideDimaz HanggoroОценок пока нет
- Block DiagramДокумент1 страницаBlock DiagramDimaz Hanggoro0% (2)
- 华为4X维修原理图 PDFДокумент67 страниц华为4X维修原理图 PDFSmartFix agudelo0% (1)
- Level 2 Repair GuideДокумент98 страницLevel 2 Repair GuideSmartFix agudelo100% (1)
- G6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual PDFДокумент79 страницG6-L11 Advanced Maintenance Manual PDFSmartFix agudeloОценок пока нет
- 华为4X维修原理图 PDFДокумент67 страниц华为4X维修原理图 PDFSmartFix agudelo0% (1)
- Sony Xperia C3 PDFДокумент128 страницSony Xperia C3 PDFSmartFix agudeloОценок пока нет
- Level 2 Repair GuideДокумент98 страницLevel 2 Repair GuideSmartFix agudelo100% (1)
- Moto G5 Plus XT1680 - 7 Anibal Garcia PDFДокумент58 страницMoto G5 Plus XT1680 - 7 Anibal Garcia PDFSmartFix agudelo100% (3)
- SCL AL00线路图 (4A) PDFДокумент69 страницSCL AL00线路图 (4A) PDFSmartFix agudeloОценок пока нет
- Motorola Moto E5 Plus - Schematic Diagarm PDFДокумент32 страницыMotorola Moto E5 Plus - Schematic Diagarm PDFSmartFix agudelo0% (1)
- Level 3 Component LayoutДокумент42 страницыLevel 3 Component LayoutSmartFix agudelo100% (1)
- Схема acer aspire 4410t 4810t, 4810tg, 4810tz - service - guideДокумент157 страницСхема acer aspire 4410t 4810t, 4810tg, 4810tz - service - guideЮра ИвановОценок пока нет
- SoMachine Basic - Release NoteДокумент21 страницаSoMachine Basic - Release NoteHamza AgaplexОценок пока нет
- VCX-PLUS Introduction ReviseДокумент3 страницыVCX-PLUS Introduction ReviseDuc ThangОценок пока нет
- Upload Obstacle AvoidingДокумент40 страницUpload Obstacle AvoidinglesaОценок пока нет
- McAfee DLPe Device Control Best PracticesДокумент15 страницMcAfee DLPe Device Control Best Practicescontact2smtsОценок пока нет
- Test Device Technical Notes Nemo Outdoor 8.61 April 2020Документ28 страницTest Device Technical Notes Nemo Outdoor 8.61 April 2020adamasow1989Оценок пока нет
- DSE86xx PC Software ManualДокумент166 страницDSE86xx PC Software ManualbrawijayaОценок пока нет
- kvs3065cl Series PDFДокумент266 страницkvs3065cl Series PDFGroza Alexandru ClaudiuОценок пока нет
- Adms-15 FTM-200D Im Eng 2211-BДокумент35 страницAdms-15 FTM-200D Im Eng 2211-Bsoporte tecnico muleyОценок пока нет
- TLC5000 Dynamic ECG Systems User Manual TLC5000 CONTEC MEDICAL SYSTEMS CO., LTDДокумент65 страницTLC5000 Dynamic ECG Systems User Manual TLC5000 CONTEC MEDICAL SYSTEMS CO., LTDmilan100% (2)
- F20 1 Series Hatch 5door PricelistДокумент12 страницF20 1 Series Hatch 5door PricelistAdam LinОценок пока нет
- Canon WebCam Utility Instructions Win Official11Документ14 страницCanon WebCam Utility Instructions Win Official11Fajar ZeeОценок пока нет
- Safecom Go Ricoh Administrators Manual 60703-20Документ60 страницSafecom Go Ricoh Administrators Manual 60703-20Arturo García MolinaОценок пока нет
- 79FAA Alcatel Lucent IP Desktop SoftPhone SD Ed01Документ3 страницы79FAA Alcatel Lucent IP Desktop SoftPhone SD Ed01dlandiОценок пока нет
- Easylog Data Logger El Wifi THДокумент3 страницыEasylog Data Logger El Wifi THRohitОценок пока нет
- M2MS BP209ManualДокумент174 страницыM2MS BP209ManualSK Abdul Hai BashaОценок пока нет
- Ad4430r SimplifiedДокумент2 страницыAd4430r SimplifiedM.fakhrur raziОценок пока нет
- Polyvision TS SeriesДокумент2 страницыPolyvision TS SeriesElectronic Whiteboards WarehouseОценок пока нет
- Uface 402: Multi-Biometric Time Attendance and Access Control TerminalДокумент2 страницыUface 402: Multi-Biometric Time Attendance and Access Control Terminaleng_adelОценок пока нет
- Asus X751LK ManualДокумент104 страницыAsus X751LK ManualmentoriaОценок пока нет
- Deep Sea Electronics PLC: DSEL400 & DSEL401 Operator ManualДокумент83 страницыDeep Sea Electronics PLC: DSEL400 & DSEL401 Operator ManualMostafa ShannaОценок пока нет
- QUART Product Catalog 2019 Eng OpenДокумент40 страницQUART Product Catalog 2019 Eng OpenŁukasz Paweł KurkowskiОценок пока нет
- Vostro 15 3510 Setup Specs en UsДокумент24 страницыVostro 15 3510 Setup Specs en UsFederico GiannuzziОценок пока нет
- Man Leak Detector Pce LDC 15 en - 230627 - 070750Документ20 страницMan Leak Detector Pce LDC 15 en - 230627 - 070750hrstgaОценок пока нет
- 3M Digital Projector: FeaturesДокумент4 страницы3M Digital Projector: FeaturesValentin MihaiОценок пока нет
- Inside A Computer CabinetДокумент80 страницInside A Computer CabinetbiizayОценок пока нет
- Acard Technology 2033L (E)Документ88 страницAcard Technology 2033L (E)Alfredo De San SalvadorОценок пока нет
- MPC6515HardwareManual PDFДокумент37 страницMPC6515HardwareManual PDFgarimaniusОценок пока нет
- PIC LAB ManualДокумент13 страницPIC LAB ManualxyzzyzОценок пока нет
- Android USB Connections Explained - MTP, PTP, and USB Mass StorageДокумент4 страницыAndroid USB Connections Explained - MTP, PTP, and USB Mass StorageAyus TradeNiagaОценок пока нет