Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Shift (FSK) : Explain Keying Technique Wirh Relevant
Загружено:
Jerry SinghОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Shift (FSK) : Explain Keying Technique Wirh Relevant
Загружено:
Jerry SinghАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
31. a.
Explain Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) technique wirh relevant
constellation diagram.
diagrams, tuth table,
b. Explain the transmission and detecrion B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION,
signal with necessary block diagram. MAy 2017
"!"o?t" Third / Fourth Semester
52. a. Describe the following
(i) GSM I5EC252 _ PRINCIPLES OF COMMTINICATION SYSTEMS
(iD GPRS (For the candidates admitted during the academic year
Note:
20r s -
2016 onwards)
(i) Part - A should be answered in oMR sheet within first 45
over to hall invigilator at the end of 45fi minute_
minutes and oMR sheet should be handed
b. aid of a diagram, discuss uuout lou.X)optical communication
)vith-an system. Also mention (ii) Part - B and Part - C should be answered in answer
its advantages. booklet.
Time: Three Hours
Max. Marks: 100
*****
PART-A(20x1=20Marks)
Answer ALL euestions
l. In
AM technique the various of modulation index should be for recovery of
base band signal without distortion
(A) Infinity (B) Less than unity
(C) Greater than unity (D) Less than infinity
2. In an amplitude modulated system, if the power in carrier
is 400 W, modulation index is
unity. Then the total transmitted power is
(A) 600 w (B) 800 w
(c) 1200w (D) 1600 w
a,)-
is an indirect method of FM generation
(A) Foster seeley (B) Armstrong
(C) Varactor diode (D) phase shift
4. Which one of the following technique has more noise immunity?
(A) AM-DSBFC (B) AM_DSBSC
(c) FM rol prur
5. Master oscillator in a receiver generates
(A) Message signal (B) Sub harmonic of message signal
(C) Carrier signal (D) Sub harmonic of carrier signal
6. Intermediate frequency value in FM broadcast receiver is
(A) as5 KHz (B) 4ss KHz
(C) 10.7 KHz (D) 10.7 MHz
7. oontrols the amplitude fluctuations in FM receivers
=_______
(A) Pre-emphasis (B) Limiter
(C) Harmonic generator iO) ne_emphasis
8. The frequency range for commercial AM broad cast is
(A) 53s-l60sKLIz (B) 535-1605 MHz
(C) 88-108 KHz (D) 88-108 MHz
Page 4 of4
271\[13/4158C252 Page 1of4
z7NG3/4tsEc252
9. In PPM
- system, the transmitted pulses have PART-B(5x4=20Marks)
ial cr*t""t
amplirude, varying width (B) Constant amplitude, constanr width Answer ANY FM Questions
Conslant wiith, varyingu-ptit
iCj rd" (D) Varying width' varying amplitude
for AM system?
zl. Define modulation index. what is the range of modulation index
10. Which of the following modulation is digital in nature?
(A) PAM (B) PPM index for FM modulator with
(D) PCM 22. Determine the peak frequency deviation and modulation
(c) PwM deviation sensitivity SXllzN and modulating signal 3 cos(2zr
1000 0'
11. standardizes the intemet activites in receivers?
(B) IrU-r 23. What is image frequency? How can we reject the image signal
(A) IEEE
(c) ISo (D) IAB
24. Compare various pulse modulation techniques'
12. technique detects 99.9% of alltransmission errors
(B) vRC 25. Write short note 0n EBCDIC code.
(A) Check sum
(c) LRC (D) cRC
26. ForaQPSKsystemoperatingwithaninformationbitraleofZ|Kbps.Determine
some times referred to as On-Off keying?
(0
Baud
13. Which of the following technique is (ii)
Minimum Bandwidth
(A) ASK (B) FSK
(c) PSK (D) QPSK
27. What is cell splitting and hand-ofl?
to
14. The input titrate of 4000 bps for a QPSK modu.lator has a band equal PART-C(5x 12:60Marks)
(A) tboo tps @) 2ooo bPs Answer ALL Questions
icj
+ooo upr @) sooo bPs
and maximum
The possible number of output conditions with 'N' input bits can be expressed as 2g.a. For an AM DSBFC modulator with a carrier frequency fc=100KHz
I 5.
(1r) (B) M-2N+r modulating signal f*-10KHz '
u:LoG2N Determine
(C) M_2N @\ v-LOGzN+l
(i) Frequency limits for upper and lower side bands
(ii) Bandwidth
16. has more bandwidth efficiencY (iii) OutPut frequencY spectrum
(A) (B) QPSK 'for a carrier signal amplitude of 20 v and message signal
BPSK
(D) (iv) trloauution index
(c) 8-PSK BFSK -
amplitudeof5V.Alsowritetheexpressionformodulationwave
17. Microwaves are generallY described ad electromagnetic waves
with frequencies that range (oR)
from b.ExplainindirectmethodofFMgenerationwithneatdiagram.
(A) 400 KHz-1600 KHz (B) 500 KHz-300 MHz
(C) 800 MHz-300 GHz (D) 88-108 MIIz
29. a Explain AM superheterodyne receiver with neat block diagram'
18. The optical fibre uses portion of EM sPectrum (oR)
(A) rR (B) VHF discrimination circuit'
(D) rrF b. Explain the demodulation of FM signal using Foster Seeley
(c) uI{F
diagram'
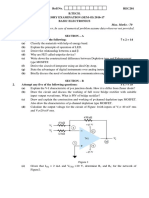
30. a. Explain tire generation and demodulation of PAM signal with relevant
1g. The minimum frequency Re-use distarrce D can be obtained fi'om
(A) d -3k.R (B) a -Jx.n (oR)
(c) (D) P=l6rn
a -^,[-ltc.n b.i. Explain enor correction techniques.
20. GSM is based on ii. Explain VRC, LRC error detection techniques with an example'
(A) FDMA (B) TDI\4A
(c) CDMA (D) SDI\4A
zT[,83/4t58C252
271\tI3l415ECZ5Z Page 3 of4
Prge 2ofa
Вам также может понравиться
- (Or) o Offive.: Examination, MayДокумент2 страницы(Or) o Offive.: Examination, MayDeepak MisraОценок пока нет
- Paper 1Документ2 страницыPaper 1subhaОценок пока нет
- Strucrure - L Srings: Worrd, Toot) - O, CДокумент2 страницыStrucrure - L Srings: Worrd, Toot) - O, CUday SinhaОценок пока нет
- Pps End Semester Papers (Combined)Документ18 страницPps End Semester Papers (Combined)S.SRI KRISHNA (RA2111026020166)Оценок пока нет
- ME1035 - 6 - Sem (1) 2018RДокумент2 страницыME1035 - 6 - Sem (1) 2018RDeepak MisraОценок пока нет
- Obtain title and Kirchhoff's equationsДокумент2 страницыObtain title and Kirchhoff's equationsPrashant VyasОценок пока нет
- 15EE207 3 SemДокумент2 страницы15EE207 3 SemSarvesh SinghОценок пока нет
- (Id (I) (Id O: May - B. LVDRДокумент2 страницы(Id (I) (Id O: May - B. LVDRSarvesh SinghОценок пока нет
- Tos Math 7 1st Quarter Test 2023-2024 FinalДокумент3 страницыTos Math 7 1st Quarter Test 2023-2024 FinalMarrie Anne Buena-Agua MercaОценок пока нет
- B. List - : Will (Or) How TwoДокумент2 страницыB. List - : Will (Or) How TwoSarvesh SinghОценок пока нет
- 15EC203J 4 SemДокумент2 страницы15EC203J 4 SemUttam NeelapureddyОценок пока нет
- 10EC/TE61: Answer Any FIVE Full Questions, Selecting at Least TWO Questions From Each PartДокумент2 страницы10EC/TE61: Answer Any FIVE Full Questions, Selecting at Least TWO Questions From Each PartdonyarmstrongОценок пока нет
- Dte (22320)Документ71 страницаDte (22320)kolipratham1Оценок пока нет
- Digital Techniques Model Answer BreakdownДокумент26 страницDigital Techniques Model Answer Breakdownrishi sahuОценок пока нет
- 5032 April - 2018Документ2 страницы5032 April - 2018Muneef NОценок пока нет
- DAA - Paper - CT Exam - 2022-2023 - K.kaushikДокумент2 страницыDAA - Paper - CT Exam - 2022-2023 - K.kaushikshiv.2125csit1121Оценок пока нет
- FGDHДокумент21 страницаFGDHkishorshinde75Оценок пока нет
- De 5Документ2 страницыDe 5PADMANABAN SОценок пока нет
- Flat End Sem PaperДокумент1 страницаFlat End Sem Paperritiksaraf24Оценок пока нет
- Diploma Examination Engineering/Technology/Management/Commercial Practice April 2018 - Engineering MetrologyДокумент2 страницыDiploma Examination Engineering/Technology/Management/Commercial Practice April 2018 - Engineering MetrologyGokul KrishnanОценок пока нет
- College: Diploma Management/CommercialДокумент3 страницыCollege: Diploma Management/CommercialMercyОценок пока нет
- Computer Networks Prev Papers-LazysrmiteДокумент4 страницыComputer Networks Prev Papers-LazysrmiteChalla RohitОценок пока нет
- (Ii) (Iid (Iv) : V/Ith FollowingДокумент2 страницы(Ii) (Iid (Iv) : V/Ith FollowingPADMANABAN SОценок пока нет
- Microwave Theory and Techniques Ques PaperДокумент2 страницыMicrowave Theory and Techniques Ques PaperABHISHEK JHAОценок пока нет
- B. Tech. IV Year I Semester MID-I Examinations, August 2019: Radar SystemsДокумент1 страницаB. Tech. IV Year I Semester MID-I Examinations, August 2019: Radar SystemsrajiОценок пока нет
- 6042 April-2019Документ2 страницы6042 April-2019vinayak jithОценок пока нет
- Paper Id (80213) : Roll No. Total No. of Questions: 7L Ltotal No. of Pages: 02Документ2 страницыPaper Id (80213) : Roll No. Total No. of Questions: 7L Ltotal No. of Pages: 02Jazz VirakОценок пока нет
- DIPLOMA EXAMINATION IN ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGYДокумент2 страницыDIPLOMA EXAMINATION IN ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGYMuneef NОценок пока нет
- FLRX If (C) V RR (B) : ExaminationДокумент2 страницыFLRX If (C) V RR (B) : ExaminationJerry SinghОценок пока нет
- Test convergence of series using comparison and Cauchy's criterionДокумент2 страницыTest convergence of series using comparison and Cauchy's criterionHariharan VetrivelОценок пока нет
- 15A04601 Microprocessors & MicrocontrollersДокумент1 страница15A04601 Microprocessors & Microcontrollers17BF1A04L7 kalyanОценок пока нет
- 2022-23 Microwave and Radar Engineering 7th SemДокумент2 страницы2022-23 Microwave and Radar Engineering 7th SemPulkit GoelОценок пока нет
- NR 311901 Digital Systems DesignДокумент5 страницNR 311901 Digital Systems DesignSrinivasa Rao GОценок пока нет
- 2018 Winter Model Answer PaperДокумент16 страниц2018 Winter Model Answer PaperEr Amarsinh RОценок пока нет
- S&S Previous Question PapersДокумент75 страницS&S Previous Question PapersAllanki Sanyasi RaoОценок пока нет
- Be - Electrical Engineering - Semester 5 - 2018 - November - Power Electronics Pe Pattern 2015Документ3 страницыBe - Electrical Engineering - Semester 5 - 2018 - November - Power Electronics Pe Pattern 2015sahish pandavОценок пока нет
- Facilitating Business Process ReengineeringДокумент12 страницFacilitating Business Process ReengineeringSriharsha SKОценок пока нет
- Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: Be Precise in Your Answer. in Case of Numerical Problem Assume Data Wherever Not ProvidedДокумент2 страницыTime: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: Be Precise in Your Answer. in Case of Numerical Problem Assume Data Wherever Not Providedpcjoshi02Оценок пока нет
- ContentWeightages NTDCДокумент40 страницContentWeightages NTDCHamza AsifОценок пока нет
- ,R, L: (L-,', (,t:,li: - R R .. LLL (R) - +..... :-1'.2'3',6 lllr-2Документ2 страницы,R, L: (L-,', (,t:,li: - R R .. LLL (R) - +..... :-1'.2'3',6 lllr-2SUMAN SAGARОценок пока нет
- Control Systems ExamДокумент3 страницыControl Systems ExamDankanVGowdaОценок пока нет
- Analog Communication April 2019Документ5 страницAnalog Communication April 2019Rameshchandra K ECEОценок пока нет
- National Transmission & Despatch Company LTDДокумент49 страницNational Transmission & Despatch Company LTDextra loginОценок пока нет
- Psa 1Документ4 страницыPsa 1Sanjana DulangeОценок пока нет
- 18EVE322Документ2 страницы18EVE322Vinay JavalkarОценок пока нет
- Question Paper CSE 3RD SEMДокумент10 страницQuestion Paper CSE 3RD SEMrocky madarОценок пока нет
- DSBSC Modulation:: Demodulation of AM SignalsДокумент4 страницыDSBSC Modulation:: Demodulation of AM SignalsSalman AhmadОценок пока нет
- VR17 17EC3502: Siddhartha Engineering CollegeДокумент2 страницыVR17 17EC3502: Siddhartha Engineering CollegeMmk ReddyОценок пока нет
- Least Learned q3 Revised Kra 4 Obj 11 Item Analysis LLC For Mso 2003 2Документ37 страницLeast Learned q3 Revised Kra 4 Obj 11 Item Analysis LLC For Mso 2003 2Perl NamuagОценок пока нет
- Jntuk 2-2 Ece June 2015 PDFДокумент33 страницыJntuk 2-2 Ece June 2015 PDFMurali KrishnaОценок пока нет
- DCN EC-3028 Mid Semester Autumn 2022 Question PaperДокумент2 страницыDCN EC-3028 Mid Semester Autumn 2022 Question PaperSk sarkarОценок пока нет
- Punjab Technical University: B.Tech. (Sem. - 3) Computer ArchitectureДокумент2 страницыPunjab Technical University: B.Tech. (Sem. - 3) Computer ArchitecturesandeepaprОценок пока нет
- 6183 Apr-19Документ2 страницы6183 Apr-19Shibli ThangalОценок пока нет
- Nov Dec 2018Документ2 страницыNov Dec 2018Karan Babar (22EE244)Оценок пока нет
- Satellite Communications Exam QuestionsДокумент2 страницыSatellite Communications Exam QuestionsParminder BoparaiОценок пока нет
- ONE Full Question From Each Module.: (08 Marks) (08 Marks)Документ2 страницыONE Full Question From Each Module.: (08 Marks) (08 Marks)NingammaОценок пока нет
- Electronic Circuit Analysis PDFДокумент5 страницElectronic Circuit Analysis PDFNookaraju SnrОценок пока нет
- Time: 3 Hours Total Marks: 100: Printed Pages: 02 Sub Code: NEC 801Документ2 страницыTime: 3 Hours Total Marks: 100: Printed Pages: 02 Sub Code: NEC 801Prabhakar DubeyОценок пока нет
- March 201965Документ2 страницыMarch 201965pecoxor808Оценок пока нет
- Laplace Transform MathematicsДокумент53 страницыLaplace Transform MathematicsJerry SinghОценок пока нет
- Complex Integration MCQ Notes PDFДокумент33 страницыComplex Integration MCQ Notes PDFJerry SinghОценок пока нет
- 1543313257phpfJfGH6 PDFДокумент11 страниц1543313257phpfJfGH6 PDFJerry SinghОценок пока нет
- 15 Ma 201Документ2 страницы15 Ma 201Jerry SinghОценок пока нет
- Of (I) (Ii) : Bills. For MAYДокумент2 страницыOf (I) (Ii) : Bills. For MAYJerry SinghОценок пока нет
- Stat For KnowledgeДокумент20 страницStat For KnowledgeAyush MishraОценок пока нет
- FLRX If (C) V RR (B) : ExaminationДокумент2 страницыFLRX If (C) V RR (B) : ExaminationJerry SinghОценок пока нет
- Book EV Charging Stations Near YouДокумент22 страницыBook EV Charging Stations Near YouJerry SinghОценок пока нет
- Report EV InfraДокумент11 страницReport EV InfraSanthoshОценок пока нет
- EC6512 Communication System Lab ManualДокумент52 страницыEC6512 Communication System Lab ManualSalai Kishwar JahanОценок пока нет
- Arduino TEA5767 FM Radio ReceiverДокумент25 страницArduino TEA5767 FM Radio ReceiverjovicaradОценок пока нет
- Broadcast FM Radio Tuner For Portable Applications: Description FeaturesДокумент3 страницыBroadcast FM Radio Tuner For Portable Applications: Description FeaturesdemostenessОценок пока нет
- BK4802N - IC Radio PDFДокумент19 страницBK4802N - IC Radio PDFpatolin_123Оценок пока нет
- Transmission For PP For E.SДокумент484 страницыTransmission For PP For E.SEngrMuhammadZaidiОценок пока нет
- Pioneer - VSX 1023 K - VSX 43 - VSX 823 K - rrv4419Документ171 страницаPioneer - VSX 1023 K - VSX 43 - VSX 823 K - rrv4419Daniel MajorОценок пока нет
- 11 November 1992Документ116 страниц11 November 1992Monitoring TimesОценок пока нет
- JP 1Документ90 страницJP 1yashОценок пока нет
- 25W FM Transmitter Technical ManualДокумент67 страниц25W FM Transmitter Technical ManualRaul Angel Perez AbadОценок пока нет
- Viva Questions - CS LabДокумент2 страницыViva Questions - CS LabpoornimaОценок пока нет
- Biomedical Telemetry and Telemedicine PDFДокумент12 страницBiomedical Telemetry and Telemedicine PDFninja_12340% (1)
- Radar 2009 A - 11 Waveforms and Pulse CompressionДокумент58 страницRadar 2009 A - 11 Waveforms and Pulse Compressionkamal__singhОценок пока нет
- Sony Mex-Bt3800u Bt38uw Bt3807u Bt3850u PDFДокумент25 страницSony Mex-Bt3800u Bt38uw Bt3807u Bt3850u PDFGuille FrutosОценок пока нет
- Icm 506Документ45 страницIcm 506AhmedОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Radar System and Component TestsДокумент29 страницIntroduction To Radar System and Component TestsTuuli Hark100% (1)
- Dornier 328Jet-CommunicationsДокумент49 страницDornier 328Jet-CommunicationsRicardo zafraОценок пока нет
- Moseley PCL6000 ManualДокумент278 страницMoseley PCL6000 ManualJuan PerezОценок пока нет
- ReferencesДокумент5 страницReferencesdavidОценок пока нет
- Wireless Communication Fundamentals ExplainedДокумент25 страницWireless Communication Fundamentals ExplainedAbirami ManiОценок пока нет
- IQ ModulationДокумент3 страницыIQ ModulationBenjamin DoverОценок пока нет
- 12hrs Marathon Session UPSC Prelims 2022 Notes Part 01Документ142 страницы12hrs Marathon Session UPSC Prelims 2022 Notes Part 01vineeth ravooriОценок пока нет
- Noise in Analog Modulation: Assoc Prof. Dr. Ho Van Khuong Tele. Dept., HCMUT Email: AДокумент48 страницNoise in Analog Modulation: Assoc Prof. Dr. Ho Van Khuong Tele. Dept., HCMUT Email: AUy đzОценок пока нет
- Communication Systems With SolutionsДокумент109 страницCommunication Systems With SolutionsChindam Hari Prasad50% (2)
- Basic: Analog Communication Systems (Gate - 2018) - ReportsДокумент15 страницBasic: Analog Communication Systems (Gate - 2018) - ReportsAnirban SahaОценок пока нет
- Dvor 900 PDFДокумент17 страницDvor 900 PDFAgnelo Mapande100% (1)
- 180ies - 1-Communication Systems PDFДокумент110 страниц180ies - 1-Communication Systems PDFDlishaОценок пока нет
- 2 Marks Question BankДокумент7 страниц2 Marks Question BankThiru DaaОценок пока нет
- Service-Manual Wouxun Kguvd1Документ43 страницыService-Manual Wouxun Kguvd1VITTAYA_SCRIBD50% (2)
- 16Документ220 страниц16indrajeetОценок пока нет
- Instruction Manual: Communications ReceiverДокумент64 страницыInstruction Manual: Communications ReceiverghtrytrytrytrytrytryОценок пока нет