Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Shallow Foundations PDF
Загружено:
LynzerОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Shallow Foundations PDF
Загружено:
LynzerАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION TO FOUNDATIONS
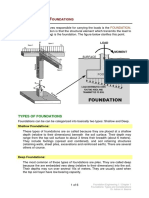
The soil beneath structures responsible for carrying the loads is the FOUNDATION.
The general misconception is that the structural element which transmits the load to
the soil (such as a footing) is the foundation. The figure below clarifies this point.
TYPES OF FOUNDATIONS
Foundations can be can be categorized into basically two types: Shallow and Deep.
Shallow Foundations:
These types of foundations are so called because they are placed at a shallow
depth (relative to their dimensions) beneath the soil surface. Their depth may
range from the top soil surface to about 3 times their breadth (about 6 meters).
They include footings (spread and combined), and soil retaining structures
(retaining walls, sheet piles, excavations and reinforced earth). There are several
others of course.
Deep Foundations:
The most common of these types of foundations are piles. They are called deep
because the are embedded very deep (relative to their dimensions) into the soil.
Their depths may run over several 10s of meters. They are usually used when
the top soil layer have low bearing capacity.
1 of 6 Foundation Engineering 1 / Chapter 1
Foundations: Types and Considerations
Dr. Adnan A. Basma
DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
To perform satisfactorily, foundations must carry the loads (and moments) and have
two main characteristics:
1. Be safe against overall shear failure (Bearing Capacity Failure).
2. Not undergo excessive displacement (Settlement).
These conditions will insure that the foundation i.e. the soil is safe and can carry the
loads without major problems. Therefore, when designing foundations, these two
characteristic must be satisfied.
In addition to satisfying the conditions for the foundation, the structural members
(concrete, steel and/or wood) must be able to transfer the load to the soil without
failing. In the case of concrete, two basic conditions must be satisfied:
1. No shear failure: This is satisfied by providing an adequate thickness of
concrete.
2. No tension failure: This is satisfied by providing adequate steel reinforcement.
This course covers the analysis and design (geotechnical and concrete design) of
the basic and most commonly used types of foundations including both shallow and
deep foundations. Other types of foundations are covered in the follow-up course,
"Foundation Engineering 2".
The following types of foundations will be covered in Foundation Engineering 1
FOOTINGS
(a) (b)
(c) (d)
Fig. 1 Spread Footings: (a) Square, (b) Rectangular, (c) Wall (Strip) and (d) Circular
2 of 6 Foundation Engineering 1 / Chapter 1
Foundations: Types and Considerations
Dr. Adnan A. Basma
Fig. 2 Rectangular Combined Footing
Fig. 8. Steel layout for a rectangular Fig. 9. Trench and steel layout for a wall
combined footing footing
3 of 6 Foundation Engineering 1 / Chapter 1
Foundations: Types and Considerations
Dr. Adnan A. Basma
EARTH RETAINING STRUCTURES
Fig. 3. Cantilever Retaining Wall Fig. 4. Gravity Retaining Wall
Fig. 5. Counter fort Retaining Wall
4 of 6 Foundation Engineering 1 / Chapter 1
Foundations: Types and Considerations
Dr. Adnan A. Basma
DEEP FOUNDATIONS: PILES
Fig. 6. Various types of concrete piles
Fig. 7. Layout of Piles in Groups
5 of 6 Foundation Engineering 1 / Chapter 1
Foundations: Types and Considerations
Dr. Adnan A. Basma
Table 1. Soil Types and Foundation Consideration
Soil Foundation
Type Type Reason(s) for use Trouble Areas
SAND Footings Easy to construct and Bearing capacity
economical may be a problem
but in most cases it
Retaining Structures Must be used since sand can is sufficient.
not support themselves
Excessive
Deep Foundations (Piles) Uses for friction resistance settlement in wet
but low in bearing capacity and loose deposits
Confining pressure
is usually low
CLAY Footings Economic but may have Low bearing
problem with bearing capacity capacity.
in saturated clays Generally low shear
Retaining Structures Clays are self-supportive up to strength when wet.
a certain height (critical). Must High consolidation in
be used if height increases soft clays
beyond the critical.
Swelling is possible
Deep Foundations (Piles) If bearing capacity is low, piles Over-consolidated
may be driven to rock. May clays may contain
change formation of clay. cracks and fissures.
Table 2. Possible Solutions to some Problems in Foundations
Soil Nature of problem Possible solution
Type
SAND Settlement Loose sands must be compacted
Lowering water table may result in sand densification.
Bearing Capacity Compaction increases c and and thus bearing capacity
Use deep foundations
Clay Consolidation Lowering water table
Pre-loading
Drive pile to rock
Bearing Capacity Compaction
Use deep foundations
Expansion or Swelling Treat or stabilize soil
Maintain constant water table
Alter soil nature (similar to stabilization)
Include swell pressure in design
6 of 6 Foundation Engineering 1 / Chapter 1
Foundations: Types and Considerations
Dr. Adnan A. Basma
University of Technology
Building and Construction Engineering
Department
Roads and Bridges Section
_________________________________________
FOUNDATION ENGINEERING COURSE
Subject:- Shallow foundation – Bearing capacity
Prepared by :- Prof. Dr. Kais Taha Shlash
__________________________________________________________
Course designa on : geo. 01
University of Technology
Building and Construction Engineering
Department
Roads and Bridges Section
_________________________________________
FOUNDATION ENGINEERING COURSE
Subject:- Shallow foundation – settlement
Prepared by :- Prof. Dr. Kais Taha Shlash
__________________________________________________________
Course designa on : geo. 01
University of Technology
Building and Construction Engineering
Department
Roads and Bridges Section
_________________________________________
FOUNDATION ENGINEERING COURSE
Subject:- Shallow foundation – Structural design
Prepared by :- Prof. Dr. Kais Taha Shlash
__________________________________________________________
Course designa on : geo. 01
Under preparation
Вам также может понравиться
- Advanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionОт EverandAdvanced Opensees Algorithms, Volume 1: Probability Analysis Of High Pier Cable-Stayed Bridge Under Multiple-Support Excitations, And LiquefactionОценок пока нет
- Beam Design 1Документ23 страницыBeam Design 1kanishkaОценок пока нет
- Celebrating Literacy in the Rwenzori Region: Lest We Forget: a Biographical Narrative of Uganda’S Youngest Member of Parliament, 1980-1985От EverandCelebrating Literacy in the Rwenzori Region: Lest We Forget: a Biographical Narrative of Uganda’S Youngest Member of Parliament, 1980-1985Оценок пока нет
- Appendix 5 Only For PresentationДокумент28 страницAppendix 5 Only For PresentationkanishkaОценок пока нет
- Application of Infrared Thermography Technique in Uilding Finish EvaluationДокумент9 страницApplication of Infrared Thermography Technique in Uilding Finish EvaluationNicolas De NadaiОценок пока нет
- Bridges - Initial DesignДокумент20 страницBridges - Initial Design2003655300% (1)
- ELS Sample Questions For 2010 HKPU T3 Top Up Course PDFДокумент2 страницыELS Sample Questions For 2010 HKPU T3 Top Up Course PDFYu chung yinОценок пока нет
- Consultancy Service For Detailed Engineering Design For Abu Hamad - Karima RoadДокумент28 страницConsultancy Service For Detailed Engineering Design For Abu Hamad - Karima RoadAfolabi OladunniОценок пока нет
- Alternative Methods of MeasurementДокумент24 страницыAlternative Methods of MeasurementMohamed A.HanafyОценок пока нет
- Pet Hi Ya God AДокумент10 страницPet Hi Ya God AShashika IreshОценок пока нет
- 1.1 Mat Foundation PPT Used in The Course PDFДокумент12 страниц1.1 Mat Foundation PPT Used in The Course PDFkissistvanОценок пока нет
- Load Path ConceptsДокумент39 страницLoad Path Conceptsmmp_ccs100% (2)
- 4icee-Stmf Goel PrenstДокумент18 страниц4icee-Stmf Goel PrenstKYINCОценок пока нет
- Table 60001 Concrete DurabilityДокумент1 страницаTable 60001 Concrete DurabilityZaid JamilОценок пока нет
- GSA Progressive Collapse Analysis and Design GuidelinesДокумент119 страницGSA Progressive Collapse Analysis and Design GuidelinesSimoHovariОценок пока нет
- Conduits, Pipes, and Culverts Associated With Dams and Levee SystemsДокумент404 страницыConduits, Pipes, and Culverts Associated With Dams and Levee SystemsRaveeОценок пока нет
- Vtu Civil June July 2019Документ140 страницVtu Civil June July 2019Anil GowdaОценок пока нет
- Building Construction CAP 123B PDFДокумент28 страницBuilding Construction CAP 123B PDFJustin NgОценок пока нет
- Ilya Titov PortfolioДокумент27 страницIlya Titov Portfoliollya TitovОценок пока нет
- Lecture 3Документ42 страницыLecture 3Harold Jackson MtyanaОценок пока нет
- Example Calculation To BC3-2013Документ23 страницыExample Calculation To BC3-2013Thiru KumananОценок пока нет
- Concrete Construction Article PDF - Estimating Reinforcing Bars PDFДокумент6 страницConcrete Construction Article PDF - Estimating Reinforcing Bars PDFCharilyn EcheverreОценок пока нет
- APC of RC Building by Non-Linear Static AnalysisДокумент46 страницAPC of RC Building by Non-Linear Static AnalysisMuhannad AbdulRaoufОценок пока нет
- Hares Seri Saujana PDFДокумент10 страницHares Seri Saujana PDFMat Joe JieОценок пока нет
- Specification For Highway Works UK - SERIES 1900Документ78 страницSpecification For Highway Works UK - SERIES 1900Kévin JacobОценок пока нет
- Cost-Effective Piled-Raft Foundation For High-Rise BuildingДокумент8 страницCost-Effective Piled-Raft Foundation For High-Rise Buildingxheurtaux100% (1)
- Sea Water ConcretingДокумент13 страницSea Water ConcretingChetan HavaragiОценок пока нет
- Engineering Guide For Development - 2005 - : Growing With PrideДокумент238 страницEngineering Guide For Development - 2005 - : Growing With PrideHari SinghОценок пока нет
- A Redesign of Eenhana Waste Stabilization Ponds in Namibia by Israel HaimbiliДокумент56 страницA Redesign of Eenhana Waste Stabilization Ponds in Namibia by Israel Haimbiliisrael haimbiliОценок пока нет
- Bre Sd12005 Scan Copypdf 3 PDF FreeДокумент68 страницBre Sd12005 Scan Copypdf 3 PDF FreeAhmed HeibaОценок пока нет
- Tutorial Letter 101/0/2019: SurveyingДокумент47 страницTutorial Letter 101/0/2019: SurveyingRachel Du PreezОценок пока нет
- Bearing Capacity Values of Different Types of SoilДокумент3 страницыBearing Capacity Values of Different Types of SoilRohn J JacksonОценок пока нет
- Resume Mariwan - Mirhaj 26-12-2016Документ4 страницыResume Mariwan - Mirhaj 26-12-2016Mariwan MirОценок пока нет
- Guide On BQ Preparation (South Africa)Документ21 страницаGuide On BQ Preparation (South Africa)hantu_limahОценок пока нет
- RC2 22873Документ2 страницыRC2 22873Henok AlemayehuОценок пока нет
- Final Report Corrected V.14 PDFДокумент61 страницаFinal Report Corrected V.14 PDFNuha SafiОценок пока нет
- WWW SefindiaДокумент11 страницWWW SefindiaSUSHANTBIJAMОценок пока нет
- ConfinedMasonryHouse 003 2013 31may PDFДокумент138 страницConfinedMasonryHouse 003 2013 31may PDFbojana_246941181Оценок пока нет
- Hotel Karada Golla Final-Layout4Документ1 страницаHotel Karada Golla Final-Layout4Nuwan AththanayakaОценок пока нет
- Stabilization of Weak Subgrade For Road Using Fly Ash and Rice Husk AshДокумент5 страницStabilization of Weak Subgrade For Road Using Fly Ash and Rice Husk Ashumi shakilaОценок пока нет
- Slope Brochure Tecco Spider en CH 72dpi 160617Документ12 страницSlope Brochure Tecco Spider en CH 72dpi 160617Mehmet Ilker GurhaniОценок пока нет
- Protadetails 2019 QSG enДокумент22 страницыProtadetails 2019 QSG enDoan PHongОценок пока нет
- Peak Flow Calculation-LunugalaДокумент3 страницыPeak Flow Calculation-LunugalakanishkaОценок пока нет
- Labor EstimateДокумент10 страницLabor Estimatecitristan02Оценок пока нет
- Civil II YearДокумент75 страницCivil II Yearsathya prakashОценок пока нет
- Structural PerformanceДокумент8 страницStructural PerformancevjtaanmОценок пока нет
- Bored Pile WallДокумент8 страницBored Pile WallSrilal SahabanduОценок пока нет
- iNDiS 2012 EngДокумент987 страницiNDiS 2012 Engslavijasrb3Оценок пока нет
- Final Year Project Chapter 2Документ7 страницFinal Year Project Chapter 2MohamadMuqhrisОценок пока нет
- Construction Cost in PakistanДокумент47 страницConstruction Cost in Pakistanzahid nawaz ajamОценок пока нет
- Types of FootingДокумент3 страницыTypes of FootingRonald DolorОценок пока нет
- Use of Mathcad As A Teaching and Learning Tool ForДокумент9 страницUse of Mathcad As A Teaching and Learning Tool ForTarek Ed EОценок пока нет
- JL-98-November-December Restraint Moments in Precast Prestressed Concrete Continuous BridgesДокумент18 страницJL-98-November-December Restraint Moments in Precast Prestressed Concrete Continuous Bridgesjrobert123321Оценок пока нет
- Design of Reinforced Concrete Rectangular TanksДокумент47 страницDesign of Reinforced Concrete Rectangular TanksKawan EngОценок пока нет
- Experience Gained During Construction of The First RCC Dam in Bolivia (Ortega & Gross, 2002)Документ12 страницExperience Gained During Construction of The First RCC Dam in Bolivia (Ortega & Gross, 2002)c_gs008010Оценок пока нет
- FoundationДокумент6 страницFoundationRodain NajjarОценок пока нет
- Shallow Foundations PDFДокумент55 страницShallow Foundations PDFyhpro100% (7)
- Trouble Areas Types Reason For Use: Soil Type FoundationДокумент6 страницTrouble Areas Types Reason For Use: Soil Type FoundationP S HARSHITAОценок пока нет
- Deep FoundationsДокумент6 страницDeep FoundationsMarielle G. CastilloОценок пока нет
- FD 1Документ38 страницFD 1DrSuman ManandharОценок пока нет
- GG PaperДокумент15 страницGG PaperLynzerОценок пока нет
- Highway and Transportation Engineering Review (May 2020)Документ2 страницыHighway and Transportation Engineering Review (May 2020)LynzerОценок пока нет
- AMCIS2013 GreenITandGreenISДокумент14 страницAMCIS2013 GreenITandGreenISLynzerОценок пока нет
- Concrete Pressure Analysis: Ref. 1. Concrete Properties:: Wall & Column Formwork AnalysisДокумент1 страницаConcrete Pressure Analysis: Ref. 1. Concrete Properties:: Wall & Column Formwork AnalysisLynzerОценок пока нет
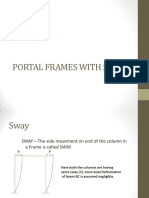
- Portal Frames With SwayДокумент9 страницPortal Frames With SwayLynzerОценок пока нет
- Structural Steel Design Project: Calculation SheetДокумент30 страницStructural Steel Design Project: Calculation SheetLynzerОценок пока нет
- Daylight YaynlanmДокумент16 страницDaylight YaynlanmLynzerОценок пока нет
- Macdonald 12Документ11 страницMacdonald 12LynzerОценок пока нет
- A Study O F House Paint Properties: National Research Council Canada Division of Bufl-Ding ResearchДокумент15 страницA Study O F House Paint Properties: National Research Council Canada Division of Bufl-Ding ResearchLynzerОценок пока нет
- Final Exam101Документ46 страницFinal Exam101LynzerОценок пока нет
- Lincoln Colorado Status Report 5.16.19Документ51 страницаLincoln Colorado Status Report 5.16.19LynzerОценок пока нет
- 22FI0002 Construction Schedule, S-Curve, Manpower & Eqpt Sched - R1Документ29 страниц22FI0002 Construction Schedule, S-Curve, Manpower & Eqpt Sched - R1Dennis SagaoОценок пока нет
- Boats From Ferro-Cement. (Utilization of Shipbuilding and Repair Facilities Series, No. 1) (04534.en)Документ145 страницBoats From Ferro-Cement. (Utilization of Shipbuilding and Repair Facilities Series, No. 1) (04534.en)Dábilla Adriana BehrendОценок пока нет
- Exit Gate Civil PartДокумент30 страницExit Gate Civil PartMATRIX ENGINEERSОценок пока нет
- Protastructure 2018 Whats New PDFДокумент57 страницProtastructure 2018 Whats New PDFDokan groupОценок пока нет
- NA To SS EN 1991-1-5-2009Документ16 страницNA To SS EN 1991-1-5-2009ominzhenОценок пока нет
- Region 1 - Concreting Works Materials Prices - PHILCON PRICESДокумент9 страницRegion 1 - Concreting Works Materials Prices - PHILCON PRICESMark Gregory RimandoОценок пока нет
- CDOT Bridge Design ManualДокумент216 страницCDOT Bridge Design ManualAbdul-azeez BelloОценок пока нет
- 6.6.5 TRUSSES: 6.6.5.1 Steel Truss ConstructionДокумент3 страницы6.6.5 TRUSSES: 6.6.5.1 Steel Truss ConstructionMalith De SilvaОценок пока нет
- Dog House Plans 12 - MetricДокумент4 страницыDog House Plans 12 - MetricDevika PrithiОценок пока нет
- Design of Road Bridges: Substructure Design (Pier Cap) : CE-651 Bridge EngineeringДокумент41 страницаDesign of Road Bridges: Substructure Design (Pier Cap) : CE-651 Bridge EngineeringAbhishek ChaurasiyaОценок пока нет
- Method of Statement For Foundation of P5, P11 69kvДокумент8 страницMethod of Statement For Foundation of P5, P11 69kvTwin Bulls100% (2)
- Item Description Qty. Unit Rate Civil Works: Section (A)Документ4 страницыItem Description Qty. Unit Rate Civil Works: Section (A)nirmalaОценок пока нет
- Cast-In Place ConcreteДокумент217 страницCast-In Place ConcreteFarid ObandoОценок пока нет
- Beam Column Joint GKMДокумент31 страницаBeam Column Joint GKMSathish Kumar CivilОценок пока нет
- Conto Aceh Selatancantilever Method-PciДокумент18 страницConto Aceh Selatancantilever Method-PcicoreteamОценок пока нет
- 3 - General NotesДокумент5 страниц3 - General Notesgaurav saxenaОценок пока нет
- State-Of-The-Art Report On Fiber Reinforced Concrete ACI 544-2002Документ66 страницState-Of-The-Art Report On Fiber Reinforced Concrete ACI 544-2002Attie761367% (3)
- Vernacular Terms in Philippine ConstructionДокумент3 страницыVernacular Terms in Philippine ConstructionCar Tejada69% (16)
- OutputДокумент78 страницOutputSAI ASSOCIATE100% (1)
- Limit State Design Method: Chapter: Three Design of Reinforced Concrete StructureДокумент8 страницLimit State Design Method: Chapter: Three Design of Reinforced Concrete StructureNabin Chandra SharmaОценок пока нет
- Plate GirdersДокумент22 страницыPlate GirdersM Kishore KumarОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 Plate GirderДокумент23 страницыChapter 6 Plate GirderolomuОценок пока нет
- AASHTO Standard Specifications For Highway Bridges 17th Ed - Errata OnlyДокумент56 страницAASHTO Standard Specifications For Highway Bridges 17th Ed - Errata Onlyjackcan501Оценок пока нет
- MiTek Engineered Building ProductsДокумент6 страницMiTek Engineered Building ProductsNiko TassigiannakisОценок пока нет
- Inspection Checklist For Installation of Interlocking Precast Concrete Pavers and KerbstonesДокумент1 страницаInspection Checklist For Installation of Interlocking Precast Concrete Pavers and KerbstonesDipin Nediya Parambath100% (3)
- United Cement (P) LTD Despatch Clinker Test ReportДокумент6 страницUnited Cement (P) LTD Despatch Clinker Test ReportVinod Kumar VermaОценок пока нет
- Concrete TechnologyДокумент100 страницConcrete TechnologyAnonymous 2UbC4s94M0100% (2)
- UGS2009 Assessment of CCL C824 Boulevard Siding Earth Retaining System and Proposal For Strengthening Works, 2009Документ8 страницUGS2009 Assessment of CCL C824 Boulevard Siding Earth Retaining System and Proposal For Strengthening Works, 2009freezefreezeОценок пока нет
- Construction Estimating Using Excel 3rd Edition Peterson Test BankДокумент8 страницConstruction Estimating Using Excel 3rd Edition Peterson Test BankChristianBrownxmstk100% (15)
- To Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignОт EverandTo Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (138)
- The Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda Cans (Father's Day Gift for Science and Engineering Curious Dads)От EverandThe Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda Cans (Father's Day Gift for Science and Engineering Curious Dads)Оценок пока нет
- Composite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsОт EverandComposite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsОценок пока нет
- The Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansОт EverandThe Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (21)
- Sodium Bicarbonate: Nature's Unique First Aid RemedyОт EverandSodium Bicarbonate: Nature's Unique First Aid RemedyРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (21)
- Guidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisОт EverandGuidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Well Control for Completions and InterventionsОт EverandWell Control for Completions and InterventionsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (10)
- Crossings: How Road Ecology Is Shaping the Future of Our PlanetОт EverandCrossings: How Road Ecology Is Shaping the Future of Our PlanetРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (10)
- The Great Bridge: The Epic Story of the Building of the Brooklyn BridgeОт EverandThe Great Bridge: The Epic Story of the Building of the Brooklyn BridgeРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (59)
- Geotechnical Engineering Calculations and Rules of ThumbОт EverandGeotechnical Engineering Calculations and Rules of ThumbРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (17)
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsОт EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsОценок пока нет
- Rocks and Minerals of The World: Geology for Kids - Minerology and SedimentologyОт EverandRocks and Minerals of The World: Geology for Kids - Minerology and SedimentologyРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (5)
- Process Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityОт EverandProcess Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- An Applied Guide to Water and Effluent Treatment Plant DesignОт EverandAn Applied Guide to Water and Effluent Treatment Plant DesignРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (4)
- The Perfumed Pages of History: A Textbook on Fragrance CreationОт EverandThe Perfumed Pages of History: A Textbook on Fragrance CreationРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Pulp and Paper Industry: Emerging Waste Water Treatment TechnologiesОт EverandPulp and Paper Industry: Emerging Waste Water Treatment TechnologiesРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)