Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Specialised Cell
Загружено:
Anonymous C3BD7OdОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Specialised Cell
Загружено:
Anonymous C3BD7OdАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
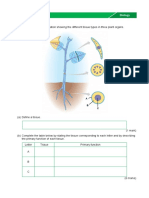
Cells and their specialisms
Task 1
Match the description of each cell organelle.
Place within cells where aerobic respiration takes place
cytoplasm to release energy.
An organelle in the cell in which protein synthesis takes
nucleus place.
Thin layer around the cell that controls everything that
ribosome enters and leaves the cell.
Material in a cell but not the material in the nucleus.
mitochondria Most chemical processes take place here, controlled by
enzymes.
Filled with cell sap and helps to keep cell turgid depending on
cell membrane the amount of water in cell. Can store water, minerals and
even toxins.
cell wall The control centre of the cell. Contains genetic material.
permanent vacuole Characteristic of plant cells. Made from cellulose.
Task 2
Match each diagram to the correct cell name.
guard cells root hair cell white blood cells palisade cells
ciliated cells sperm cells red blood cells
© www.teachitscience.co.uk 2014 19669 Page 1 of 5
Cells and their specialisms
Task 3
Match each specialised cell with its function.
Allows gas exchange in leaves. They control the
palisade cell size of the stomatal pores on the underside of
leaves. Controls water loss in leaves.
Adapted so water and mineral ions are easily
red blood cell
absorbed from the soil.
Plant cell found in mesophyll layer of leaf.
sperm cell
Absorbs light energy for photosynthesis.
Found in respiratory system and moves mucus
white blood cell
out of the way.
Contains half the DNA needed to fertilise an
root hair cell
egg.
Engulf bacteria. May release antibodies and
ciliated cell
antitoxins.
Transports oxygen in the blood from lungs to all
guard cell
cells in body.
© www.teachitscience.co.uk 2014 19669 Page 2 of 5
Cells and their specialisms
Task 4
Cut up the statements and match the adaptations with the correct cell. The numbers in
brackets show the number of statements for each cell.
palisade cell white blood cell sperm cell neurone
(4) (2) (3) (2)
red blood cell ciliated cell root hair cell guard cell
(3) (2) (2) (2)
Lots of mitochondria to provide energy Shape helps it move smoothly along
for movement. blood capillaries.
Contains many chloroplasts Regular and thin shape so they can be
packed together.
Adapted to engulf and digest ‘foreign’ Produce antibodies to help fight foreign
cells. antigens.
No nucleus but lots of room for Positioned near top of leaf.
haemoglobin to which oxygen attaches.
Many cilia that move in unison. Branched endings to connect with other
cells.
Provides a large surface area for the Long tail and streamlined head to help it
absorption of water. swim towards the egg.
Very long to allow nerve impulses to Contains many mitochondria to provide
travel to other parts of the body. cilia with energy.
Concave shape to increase surface area Shape allows it to grow between soil
for oxygen absorption. particles.
Kidney shape with thin outer walls and Long shape to provide greater surface
thick inner walls. area for absorbing carbon dioxide.
Enzymes in head digest through the Amount of water absorbed affects their
egg’s cell membrane. shape.
© www.teachitscience.co.uk 2014 19669 Page 3 of 5
Cells and their specialisms
Teaching notes and answers
For the first three tasks students could be asked to cut and paste or simply draw a line to
match up the correct statements.
Task 1
Material in a cell but not the material in the nucleus. Most chemical processes take
cytoplasm place here, controlled by enzymes.
nucleus The control centre of the cell. Contains genetic material.
ribosome An organelle in the cell in which protein synthesis takes place.
mitochondria Place within cells where aerobic respiration takes place to release energy.
cell membrane Thin layer around the cell that controls everything that enters and leaves the cell.
cell wall Characteristic of plant cells. Made from cellulose.
permanent Filled with cell sap and helps to keep cell turgid depending on the amount of water
vacuole in cell. Can store water, minerals and even toxins.
Task 2
guard cells ciliated cell white blood cells root hair cell
red blood cells palisade cells sperm cell
Task 3
palisade cell Plant cell found in mesophyll layer of leaf. Absorbs light energy for photosynthesis.
red blood cell Transports oxygen in the blood from lungs to all cells in body.
sperm cell Contains half the DNA needed to fertilise an egg.
© www.teachitscience.co.uk 2014 19669 Page 4 of 5
Cells and their specialisms
white blood cell Engulf bacteria. May release antibodies and antitoxins.
root hair cell Adapted so water and mineral ions are easily absorbed from the soil.
ciliated cell Found in respiratory system and moves mucus out of the way.
Allows gas exchange in leaves. Controls the size of the stoma (pores) underneath
guard cell leaves. Controls water loss in leaves.
Task 4
Contains many chloroplasts.
Positioned near top of leaf.
palisade cell (4) Regular and thin shape so they can be packed together.
Long shape to provide greater surface area for absorbing carbon dioxide.
No nucleus but lots of room for haemoglobin to which oxygen attaches.
red blood cell (3) Concave shape to increase surface area for oxygen absorption.
Shape helps it move smoothly along blood capillaries.
Long tail and streamlined head to help it swim towards the egg.
sperm cell (3) Lots of mitochondria to provide energy for movement.
Enzymes in head digest through the egg’s cell membrane.
Adapted to engulf and digest ‘foreign’ cells.
white blood cell (2) Produce antibodies to help fight foreign antigens.
Provides a large surface area for the absorption of water.
root hair cell (2) Shape allows it to grow between soil particles.
Many cilia that move in unison.
ciliated cell (2) Contains many mitochondria to provide cilia with energy.
Kidney shape with thin outer walls and thick inner walls.
guard cell (2) Amount of water absorbed affects their shape.
Branched endings to connect with other cells.
neurone (2) Very long to allow nerve impulses to travel to other parts of the body.
© www.teachitscience.co.uk 2014 19669 Page 5 of 5
Вам также может понравиться
- Rhodia - TDS - RHODAPEX CO 436 - EN PDFДокумент1 страницаRhodia - TDS - RHODAPEX CO 436 - EN PDFAnonymous C3BD7OdОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- d3 2Документ8 страницd3 2Anonymous C3BD7OdОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Triton x-305 PDFДокумент2 страницыTriton x-305 PDFAnonymous C3BD7OdОценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- D 3Документ23 страницыD 3Anonymous C3BD7OdОценок пока нет
- HYDROPALAT R 875 EДокумент4 страницыHYDROPALAT R 875 EAnonymous C3BD7OdОценок пока нет
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- AaaaaДокумент3 страницыAaaaaAnonymous C3BD7OdОценок пока нет
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Starch Water ResistanceДокумент6 страницStarch Water ResistanceAnonymous C3BD7OdОценок пока нет
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Ielts Writing Task 2Документ23 страницыIelts Writing Task 2Anonymous C3BD7OdОценок пока нет
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Energy Forms Conversions PDFДокумент4 страницыEnergy Forms Conversions PDFAnonymous C3BD7Od50% (2)
- Nayakem: Product Data Sheet DBMДокумент1 страницаNayakem: Product Data Sheet DBMAnonymous C3BD7OdОценок пока нет
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Crosslinker Melamine FormaldehydeДокумент5 страницCrosslinker Melamine FormaldehydeAnonymous C3BD7OdОценок пока нет
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- United States Patent Office: of 125 C.P.SДокумент3 страницыUnited States Patent Office: of 125 C.P.SAnonymous C3BD7OdОценок пока нет
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Plants or Animals Contain Genetic Material That Has Been To Them From Another SpeciesДокумент1 страницаPlants or Animals Contain Genetic Material That Has Been To Them From Another SpeciesAnonymous C3BD7OdОценок пока нет
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- IELTS Speaking Part 2 (Lesson 1) : Two MinutesДокумент26 страницIELTS Speaking Part 2 (Lesson 1) : Two MinutesAnonymous C3BD7OdОценок пока нет
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- Polyvinyl Acetate and Polyvinyl AlcoholДокумент3 страницыPolyvinyl Acetate and Polyvinyl AlcoholAnonymous C3BD7OdОценок пока нет
- Polyvinyl Acetate and Polyvinyl AlcoholДокумент3 страницыPolyvinyl Acetate and Polyvinyl AlcoholAnonymous C3BD7OdОценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- 7th Grade Laws of MotionДокумент3 страницы7th Grade Laws of MotionAnonymous C3BD7Od100% (1)
- Area and Perimeter Compound ShapesДокумент2 страницыArea and Perimeter Compound ShapesAnonymous C3BD7OdОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 - 2h Transport in Flowering PlantsДокумент26 страницUnit 2 - 2h Transport in Flowering PlantsSKОценок пока нет
- Practice Pas Xi EnglishДокумент6 страницPractice Pas Xi EnglishNysa MuktikusumaОценок пока нет
- Caie Igcse Biology 0610 Theory v2Документ33 страницыCaie Igcse Biology 0610 Theory v2HibsОценок пока нет
- Respiration in PlantДокумент25 страницRespiration in PlantFatimah AzzahrahОценок пока нет
- Tolerance Test On Ruellia (Ruellia Brittoniana) Toward Different Salinity LevelsДокумент10 страницTolerance Test On Ruellia (Ruellia Brittoniana) Toward Different Salinity LevelsRizko KurniawanОценок пока нет
- Biology Project KBДокумент35 страницBiology Project KBHarshita ThakkarОценок пока нет
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Parenchyma PDFДокумент5 страницParenchyma PDFmanoj_rkl_07Оценок пока нет
- MYP5 Biology: Leaves and PhotosynthesisДокумент17 страницMYP5 Biology: Leaves and PhotosynthesisAref Dahabrah100% (1)
- Keenan Et Al, 2013Документ5 страницKeenan Et Al, 2013Marcela LúciaОценок пока нет
- Ncert Solutions Mar3 For Cbse Class 7 Science Chapter 1Документ5 страницNcert Solutions Mar3 For Cbse Class 7 Science Chapter 1ANIRUDH PRATAP SINGH CHANDELОценок пока нет
- Science Final X 1mcqДокумент51 страницаScience Final X 1mcqbhagyapatel9723Оценок пока нет
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Pharmacognostic Specifications of Eight Cultivars of Piper Betle From Eastern Region of IndiaДокумент8 страницPharmacognostic Specifications of Eight Cultivars of Piper Betle From Eastern Region of IndiaKicky ChacaОценок пока нет
- Year 10 Specialist Biology Assignment 5Документ10 страницYear 10 Specialist Biology Assignment 5Sahana MEENACHISUNDARAMОценок пока нет
- Ans PWB 1b eДокумент31 страницаAns PWB 1b eWilson PoonОценок пока нет
- HKCEE - Biology - 1993 - Paper I - AДокумент13 страницHKCEE - Biology - 1993 - Paper I - AChinlam210100% (1)
- Prove That 7 Is Irrational ?: 10th ClassДокумент11 страницProve That 7 Is Irrational ?: 10th ClassMahesh YadavОценок пока нет
- Theories of Stomatal Movement: 4 Theories (With Diagram) : Theory # 1. Theory of Photosynthesis in Guard CellsДокумент7 страницTheories of Stomatal Movement: 4 Theories (With Diagram) : Theory # 1. Theory of Photosynthesis in Guard CellsVAISHNAVI MANOHARANОценок пока нет
- A01 Short Answer QuestionsДокумент29 страницA01 Short Answer Questionsmsuria06Оценок пока нет
- Lakhmir Singh Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Nutrition - Download Free PDFДокумент31 страницаLakhmir Singh Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Nutrition - Download Free PDFBGTM 1988Оценок пока нет
- Photosynthesis Lessons Student NotesДокумент12 страницPhotosynthesis Lessons Student NoteslinaОценок пока нет
- Biology PDFДокумент33 страницыBiology PDFRavi RajanОценок пока нет
- Ans End of Chapter Biologi KimiaДокумент23 страницыAns End of Chapter Biologi KimiaDouble Diamond Art ChannelОценок пока нет
- 2 Nutrition and RespirationДокумент7 страниц2 Nutrition and RespirationVenant HakizimanaОценок пока нет
- Uk Quals Gce Biology As 8042 24970Документ44 страницыUk Quals Gce Biology As 8042 24970Mohammed BilalОценок пока нет
- Biology Folio Photosynthesis)Документ22 страницыBiology Folio Photosynthesis)Nursakinah Najwah100% (1)
- Transport in PlantsДокумент6 страницTransport in PlantsMarlvin PrimeОценок пока нет
- Approaches To Greenbelt DesignДокумент19 страницApproaches To Greenbelt DesignTarun jajuaОценок пока нет
- Transport in PlantsДокумент8 страницTransport in PlantsZainab AliОценок пока нет
- Bio Gyan Transport in PlantsДокумент9 страницBio Gyan Transport in PlantsAvnish BhasinОценок пока нет
- Summary Greenplants Upload 130926150505 Phpapp02Документ7 страницSummary Greenplants Upload 130926150505 Phpapp02Cathee DaffoОценок пока нет