Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Chapter 2
Загружено:
Atta Ur RahmanАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chapter 2
Загружено:
Atta Ur RahmanАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Unit 11 Homeostasis Class 10th
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
1. Organisms have the ability to change and modify their internal
conditions to the environment through:
All of the above
2. All of the following are the adaptation of xerophytes except:
Large number of stomata
3. The loss of water from the plants in the form of small droplets is:
Guttation
4. From a nephron, waste enters into the:
Collecting tubules
5. The tube the kidney and urinary bladder is the:
Ureter
6. Waste products excreted by the kidneys are:
Urea, water and salts
7. Secretion of urea in sweat makes skin a:
Excretory organ
8. The two main functions of sweat are to:
Remove waste products and to cool the body
9. Which is NOT present in the filtrate entering the Bowman’s capsule of a
nephron?
Blood cells
10. Liver also plays a role in excretion. It makes urea from:
Amino acids
11. Regulation of the amount of water in body fluids is called
Osmoregulation
12. Plants which take salts from water are called
Halophytes
13. The structural and functional unit of kidneys is called
Nephron
Class 10th Biology Page 1
Unit 11 Homeostasis Class 10th
14. Plants which do not contain root hairs in their roots are called
Hydrophytes
15. The loss of water from the leaves in liquid form is called
Guttation
16. The loss of water from the leaves in the form of water vapours is:
Transpiration
17. Rubber plant excretes their waste in the form of:
Latex
18. Acacia plant (keekar) excretes their waste in the form of:
Gums
19. Coniferous tree excretes their waste in the form of:
Resins
20. Ladyfinger (benddi) excretes their waste in the form of:
Mucilage
21. Which animal hang their tongue outside their body for cooling effect:
Dog
22. A tube which carry urine from the urinary bladder to the outside
Urethra
23. Human kidney is about………cm long
10
24. Human kidney is about……..cm wide
5
25. Human kidney is about………cm thick
4
26. During each heartbeat, about………% of the blood is received by the
kidneys
20
27. On concave side of the kidney there is a small depression called as:
Hilus
Class 10th Biology Page 2
Unit 11 Homeostasis Class 10th
28. Renal pyramids are present in………..of the kidney
Renal medulla
29. Urinary bladder can store………..ml urine
300-400
30. Calcium oxalate type stones are……..% of all kidney stones
70
31. Lithotripsy works best with stones between…………. In diameter
4mm-2cm
32. Which vitamins may also cause kidney stone formation?
Vitamin C and D
33. Abdul Qasim Al-Zahrawi is known in the west as:
Abulcasis
34. When kidneys are not able to perform their function, the condition is:
Kidney failure
35. About……. % of the kidney stones are calcium phosphate stones
15
36. About……. % of the kidney stones are uric acid stones
10
37. The removal of nitrogenous waste from the blood by artificial mean is:
Dialysis
38. A type of dialysis which takes place inside the body of the patient is:
Peritoneal dialysis
39. The dialysis in which the patient’s blood is pumped out:
Haemodialysis
40. Melanocytes are found in
Skin
41. Filtration unit of the nephron is:
Renal Corpuscle
Class 10th Biology Page 3
Unit 11 Homeostasis Class 10th
Short Questions
1. Define homeostasis and Osmoregulation.
Answer:
Homeostasis:
Homo……means same/constant
Stasis……means condition
Definition: The ability of living organisms to maintain their internal
condition constant OR the ability of living organisms to adjust itself with
the changing external environment is called Homeostasis.
Osmoregulation:
Osmo………….means osmosis (water)
Regulation….means keeping constant
Definition: A type of homeostasis in which living organisms maintain the
amount of water and dissolve solutes inside their body at constant level is
called Osmoregulation.
2. Differentiate between the adaptations of hydrophytes and xerophytes
for Osmoregulation.
Answer:
Hydrophytes:
Hydro….means water
Phyte…..means plants
Definition: All those plants which completely or partially living inside
water are called hydrophytes.
Types: There are two types of hydrophytes:
1. Sub-merged: those hydrophytes which are completely embedded in
water are called Sub-merged.
2. Emerged: those hydrophytes which are half inside water and half in air
are called Emerged.
Adaptations: following adaptation are made by hydrophytes
o They have larger size leaves
o Their leaves have large number of stomata
o Stomata are found on the upper surface of the leaves
o Their root system is short
Class 10th Biology Page 4
Unit 11 Homeostasis Class 10th
o They have no root hairs
Xerophytes:
Xero………means hot and dry
Phytes…..means plants
Definition: those plants which grow in an area where temperature is high
and water is low are called hydrophytes.
Adaptations: Xerophytes have the following adaptations
o These plants have long root system
o Their roots contain many root hairs
o Their leaves are small in size with thick cuticle layer
o Some leaves have modified to spines
o Leaves have less stomata
o Stomata are sunken in nature
o Store water in their stem and root.
3. Briefly discuss how kidneys control the composition of blood?
Answer:
Blood: blood is a connective tissue which circulates throughout the body
and distributes food, water, minerals etc among cells.
Composition of blood: Human blood contain following components
1. Red blood cells
2. White blood cells
3. Platelets
4. Plasma (90% water)
5. Proteins
6. Enzymes and hormones
7. Sugars, amino acids, fatty acids etc
Kidneys: Kidneys are bean shaped organs; consist of small units called
Nephron. Each nephron is consists of two components i.e. Renal corpuscle
and Renal tubule. These components are responsible for controlling the
blood composition.
Control of Blood composition: When blood reaches the renal corpuscle,
its pressure is very high. Due to high pressure, blood is filtered and most of
its components like plasma water, proteins, enzymes, sugars, and amino
Class 10th Biology Page 5
Unit 11 Homeostasis Class 10th
acids are filtered out. Thus only blood cells are left due to their larger size.
Blood becomes empty.
In order to maintain the blood composition, most of the components are re-
absorbed in the renal tubules and added to the blood.
4. Enlist materials in our diet which are more likely to cause kidney
stones.
Answer:
Materials which cause kidney stone: following materials of our diet can
cause kidney stone:
o Calcium oxalate (present in tomato)
o Calcium phosphate (present in green vegetables)
o Ammonium phosphate (present in fats & Dairy product)
o Extra amount of vitamin C & D (present in fruits and vegetables)
5. Define lithotripsy.
Answer:
Litho……means stone
Tripsy….means breaking
Definition: The non-surgical removal of stone present in the kidney, Ureter
or urinary bladder with the help of high frequency radiations (shock wave)
is called Lithotripsy.
Mechanism: Stone is hit by highly energetic rays like α-rays, produced by a
machine called lithotripter, which break the stone into small pieces. These
pieces are then pass out of the body in urine.
5. What is the role of skin in thermoregulation?
Answer:
Thermoregulation:
Thermo……..means heat
Regulation…means keeping constant
Definition: A type of homeostasis in which living organisms maintain their
internal body temperature at a constant level is called Thermoregulation.
Role of skin in thermoregulation:
Class 10th Biology Page 6
Unit 11 Homeostasis Class 10th
In cold condition: During cold, muscles attach to the skin’s hairs contracts.
As a result hairs stay erect, does not allow body heat to go out.
In warm condition: During warm, sweat glands of the skin produce sweat
which absorb heat and comes out, thus decrease body heat.
6. Which term is used for the disease when one or both kidneys do not
perform their function?
Answer:
When one or both kidneys fail to perform their function, the term “Kidney
failure” is used for the diseased.
7. Define dialysis
Answer:
Filtering the blood of a kidney patient by artificial means to remove extra
water and nitrogenous waste is called dialysis.
8. Differentiate between Haemodialysis and Peritoneal dialysis.
Answer:
Haemodialysis: Haem….means blood. That type of dialysis in which blood
is pumped out of the body and pass through a machine (Dialyzer) is called
Haemodialysis. Inside the machine, blood is filter with a semi-permeable
membrane and return back to the body.
Peritoneal dialysis: The space around the digestive organ is called
peritoneal cavity. This cavity is surrounded by a membrane called
peritoneum. In this type of dialysis, the peritoneal cavity is filled with a
liquid which filter the blood inside the body.
9. What is meant by kidney transplantation?
Answer:
Kidney transplantation: A medical process in which a healthy kidney
from a donor is grafted in the body of a patient whose both kidneys are no
longer working is called kidney transplantation.
10. Define Kidney stones.
Answer: Hard substances which are made up of calcium, phosphate and
uric acid and block the nephron are called kidney stone.
Class 10th Biology Page 7
Unit 11 Homeostasis Class 10th
11. Explain that lungs are homeostatic organ.
Answer:
Lungs as homeostatic organ: During respiration CO2 produces. CO2 if
dissolve in blood water, it can form carbonic acid (H2CO3) and decrease pH
of the blood. Therefore it must be removed just after formation. Here lungs
acts as homeostatic organ, remove CO2 from the body and maintain blood
pH at a constant level (7.4).
12. Differentiate between Guttation and Transpiration.
Answer:
Guttation: The loss of water from the leaf apex in the form of liquid drops
is called Guttation. It occurs in grasses like wheat plants.
Transpiration: The loss of water from the arial parts of the plants in the
form of water vapours is called transpiration. It occurs in trees like mango.
13. Describe the contribution of Abul-Qasim in the field of science.
Answer:
He was a well known surgeon of the Muslim world during 10th century. He
was famous for the removal of bladder stone throughout the world. He
famous Medical encyclopedia is called Al-Tasrif which is composed of 30
volumes. In this encyclopedia, he mentioned his observation during
surgery, dissection of animals and throat surgery.
13. Explain the contribution of Al-Farabi.
Answer:
He was a Turkish philosopher. He wrote many books on the diseases of
human kidney like kidney stone formation and their removal.
Class 10th Biology Page 8
Unit 11 Homeostasis Class 10th
Long Questions
1. Describe the structure of kidneys in human beings.
Answer:
Human kidneys:
Shape: Kidneys are bean shape structure. One side is convex and other one
is concave, contain a small depression called Hilus.
Number: They are two in number in every individual.
Position: human kidneys are located below the diaphragm, in the
abdominal cavity, on each side of the vertebral column. Right kidney is
slightly lower than the left kidney because lobe of liver is placed over it.
Color: They are dark brown in color.
Size: each kidney is about 10cm in length, 5cm in width and 4cm in
thickness.
Weight: each kidney is about 150 grams.
Protection: Kidneys are protected by a tough membrane called
Peritoneum.
Internal Structure: When a human kidney is cut down lengthwise, it
shows two distinct regions:
1. Renal cortex: it is the outermost light region
2. Renal medulla: it is the inner dark region; contain many triangular
structures called renal pyramids. Center of the renal medulla has a cavity
called renal pelvis. Renal artery, renal vein and Ureter communicate to the
kidney through pelvis.
Structural and functional unit: Each kidney consists of about one millions
structural and functional units called Nephron.
Structure of nephron: each nephron is consists of two portions
1. Renal corpuscle: Renal corpuscle is made up of Glomerulus and Bowman
capsule. Glomerulus filters the blood and Bowman capsule collect the
filtrate.
2. Renal tubules: renal tubules are made up of proximal convoluted tubule,
loop of henle and distal convoluted tubule. All these segments return
important substances back to blood and remove nitrogenous waste.
Class 10th Biology Page 9
Unit 11 Homeostasis Class 10th
2. Why do plants excrete? What are the different mechanisms through
which plants excretes different substances?
Answer:
Excretion: The removal of un-necessary, metabolic waste products from
the body of living organisms is called Excretion.
Excretion in plants: Plants are living organisms. They perform different
metabolic activities. As a result of metabolism, large numbers of different
waste materials are produced. These materials cause a disturbance in the
internal environment of the plants so they must be eliminated to maintain a
constant internal environment. Therefore, plants excrete wastes.
Examples: Plants produce following metabolic waste materials:
CO2: Produced during respiration
O2: Produced during photosynthesis
Water: Produced during photosynthesis
Latex: Produced by rubber plant
Resin: Produced by Pinus
Gum: Produced by Acacia
Mechanism of excretion:
1. Carbon dioxide and oxygen: During day time, CO2 produced in
respiration is used by photosynthesis, while O2 produced by
photosynthesis, is used by respiration. During night, CO2 is released
through stomata.
2. Water: If plant have extra amount of water then it is excreted either in
vapours form from stomata through transpiration or in liquid form from
leaf apex through leaf apex.
3. Latex, Resin and Gum: these types of waste products are excreted
through the special cracks present in the stem called Lenticels.
Class 10th Biology Page 10
Unit 11 Homeostasis Class 10th
3. What are kidney stones and how are they formed? Suggest ways in
which these stones can be removed from the body?
Answer:
Kidney stones: Hard substances which are made up of chemicals like
calcium, phosphate, oxalate and uric acid and block the nephron are called
kidney stone.
Formation of kidney stones: Kidneys are filter plant of the body. They
filter the blood and remove toxic substances from it. Sometimes the filtrate
contains highly reactive chemicals like calcium, oxalate, phosphates and
uric acid. These chemicals react with one another and make solid
compounds like calcium oxalate and calcium phosphate which store in the
kidneys and block them.
Removal of kidney stones:
1. Drinking of water: if the kidney stones are small in size (1-2mm), they
can be removed in urine by drinking plenty of water. Because water
increases the blood volume which then dilates the nephron.
2 Lithotripsy: The non-surgical removal of stone present in the kidney,
Ureter or urinary bladder with the help of high frequency radiations (shock
wave) is called Lithotripsy. If the stone size ranges between 4mm-2cm, this
technique is applied.
Stone is hit by highly energetic rays like α-rays, produced by a machine
called lithotripter, which break the stone into small pieces. These pieces are
then pass out of the body in urine.
3. Surgery: If the stones are larger in size (above 2cm), it is removed by
surgery.
4. Define haemodialysis. How it is performed?
Haemodialysis: Haem….means blood. That type of dialysis in which blood
is pumped out of the body and pass through a machine (Dialyzer) is called
Haemodialysis.
Structure of Dialyzer machine: The dialyzer machine is made up of many
small tubes. The walls of these tubes are consist of semi-permeable
membrane. Outside the tubes, there is a liquid called dialyzing solution
which filled all the spaces present between tubes.
Mechanism of haemodialysis: Patient’s blood is pumped out and directed
towards the tubes of the dialyzer. As blood flows inside the tubes, their
Class 10th Biology Page 11
Unit 11 Homeostasis Class 10th
nitrogenous waste are filter through the semi-permeable wall and
absorbed by the dialyzing solution. After sometimes, the used dialyzing
solution is replaced with fresh one. This process is repeated several times
and finally the purified blood is return back to the body.
5. How does a dialyzer works? Relate the function of a dialyzer with that
of the kidney.
Answer:
Work of the dialyzer: The dialyzer machine is made up of many small
tubes. The walls of these tubes are consist of semi-permeable membrane.
Outside the tubes, there is a liquid called dialyzing solution which filled all
the spaces present between the tubes.
Patient’s blood is pumped out and directed towards the tubes of the
dialyzer. As blood flows inside the tubes, their nitrogenous waste are filter
through the semi-permeable wall and absorbed by the dialyzing solution.
After sometimes, the used dialyzing solution is replaced with fresh one.
This process is repeated several times and finally the purified blood is
return back to the body.
Relation between the function of dialyzer and kidney:
Kidneys: Each kidney consists of about one millions structural and
functional units called Nephron. Each nephron is consists of two portions:
1. Renal corpuscle: Renal corpuscle is made up of Glomerulus and Bowman
capsule. Glomerulus is a bunch of capillaries that filters the blood and
Bowman capsule is a cup shape structure which collects the filtrate.
2. Renal tubules: renal tubules are made up of proximal convoluted tubule,
loop of henle and distal convoluted tubule. All these segments absorb
essential components like water, minerals, vitamins, hormones, enzymes
from the filtrate and return back to blood while remove the remaining
nitrogenous waste. Kidneys maintain the blood composition just according
to the body needs.
Dialyzer: function of dialyzer is based on simple diffusion process. Blood
flows in semi-permeable tubes which diffuse the waste into the fluid.
Dialyzer cannot maintain the blood composition properly.
Class 10th Biology Page 12
Unit 11 Homeostasis Class 10th
6. Write a note on urine the process of formation.
Answer:
Urine formation: During digestion protein are broken down into amino
acids. Amino group (NH2) is removed from each amino acid which reacts
with water and form urine. This urine must be eliminated from the blood
because it is toxic.
Elimination of urine: elimination of urine from the blood consists of the
following steps.
1. Pressure filtration: Blood comes in pressure and enters to the
Glomerulus. Due to high pressure, most of the components of the blood like
water, urea, salts, sugars, amino acids, enzymes, hormones are filter out
and collected by the Bowman capsule. These substances are called filtrate.
Class 10th Biology Page 13
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Aqa Byb1 W QP Jun07Документ12 страницAqa Byb1 W QP Jun07李超然Оценок пока нет
- Anhidrosis in EquineДокумент3 страницыAnhidrosis in EquineZain AsifОценок пока нет
- FCA (SA) - Part - II - Past - Papers 10Документ30 страницFCA (SA) - Part - II - Past - Papers 10matentenОценок пока нет
- NCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Документ4 страницыNCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Jessamine EnriquezОценок пока нет
- Neurological Complications in Lumbar Spine SurgeryДокумент9 страницNeurological Complications in Lumbar Spine SurgeryMimi SyakilaОценок пока нет
- Osmosis Diffusion Active - Transport+studentДокумент35 страницOsmosis Diffusion Active - Transport+studentMetaknight360 LiveОценок пока нет
- Fluid Volume DeficitДокумент2 страницыFluid Volume DeficitpeternohibiОценок пока нет
- Acute and Chronic PyelonephritisДокумент7 страницAcute and Chronic PyelonephritisMatthew Ryan100% (1)
- Hillside School: Biology For Grade 12 Note 2 Topic: The Structure and Function of Bacterial CellДокумент8 страницHillside School: Biology For Grade 12 Note 2 Topic: The Structure and Function of Bacterial Celloli JrОценок пока нет
- RECALLS - Key points from Preboard 2015 Clinical ChemistryДокумент2 страницыRECALLS - Key points from Preboard 2015 Clinical ChemistrySheanalene CastroОценок пока нет
- RECONSTRUCTION MAndibula 2Документ62 страницыRECONSTRUCTION MAndibula 2RadianNasution100% (1)
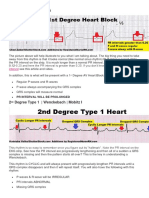
- Understanding 1st, 2nd and 3rd Degree Heart BlocksДокумент3 страницыUnderstanding 1st, 2nd and 3rd Degree Heart BlockslhenОценок пока нет
- NLS InfographicsДокумент6 страницNLS InfographicsMihai Ion GhioaldaОценок пока нет
- Vocal AnatomyДокумент8 страницVocal AnatomyfunktotumОценок пока нет
- Genetika PopulasiДокумент48 страницGenetika PopulasiRoy SinagaОценок пока нет
- Histological Characteristics of the Lingual FrenulumДокумент1 страницаHistological Characteristics of the Lingual FrenulumajudОценок пока нет
- Structure of BacteriaДокумент13 страницStructure of BacteriaRirin UtariОценок пока нет
- ELECTROPHRESISДокумент66 страницELECTROPHRESISM.PRASAD NAIDU100% (1)
- Blood Administration and Transfusion Reactions QuizДокумент5 страницBlood Administration and Transfusion Reactions Quizremooheshmat100% (1)
- 英文TG900series 8885 lowДокумент4 страницы英文TG900series 8885 lowJose L GuzCamОценок пока нет
- IndianJOralSci5278-1137123 030931Документ5 страницIndianJOralSci5278-1137123 030931Maqbul AlamОценок пока нет
- Phases of The Cell CycleДокумент9 страницPhases of The Cell CycleZia PhotostateОценок пока нет
- DecongestantsДокумент3 страницыDecongestantskОценок пока нет
- Abg Interpretation 2Документ1 страницаAbg Interpretation 2Barbara Casqueira100% (2)
- Pedia Pulmo 2 10.18.16Документ73 страницыPedia Pulmo 2 10.18.16Medisina101Оценок пока нет
- Learning Theories of PersonalityДокумент13 страницLearning Theories of Personalitypavitra_madhusudanОценок пока нет
- Chronic UrticariaДокумент40 страницChronic UrticariaeeeeewwwwwОценок пока нет
- Chapter 31 - Assessment and Management of Patients With Vascular DisordersДокумент7 страницChapter 31 - Assessment and Management of Patients With Vascular DisordersMichael Boado100% (1)
- Receptors IntroductionДокумент53 страницыReceptors IntroductionSunilОценок пока нет
- PTC MCQДокумент7 страницPTC MCQYevan HarryBrata0% (1)