Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Getformin Tab Leaflet Pakistan
Загружено:
Muhammad Vaqar HussainАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Getformin Tab Leaflet Pakistan
Загружено:
Muhammad Vaqar HussainАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
1mg+500mg
2mg+500mg
Tablets
DESCRIPTION oxidative biotransformati on into two main metabolites, a hydroxy
GETFORMIN combines glimepiride and metformin hydrochloride,two derivative and a carboxy derivative.
antihyperglycemic agents with complementary mechanisms of action, The half-life after multiple doses is about 9 hours. Approximately
to improve glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. 60% of dose is eliminated in the urine and 40% in the feces.
Chemically glimepiride is known as 1-[[p-[2-(3-ethyl-4-methyl-2-oxo-
3-pyrroline-1-carboxamido)ethyl]phenyl]-sulfonyl]-3-(trans-4- Metformin HCl:
methylcyclohexyl) urea having a molecular f ormula of C24H34N4O5S Metformin hydrochloride is slowly and incompletely absorbed from
and a structural formula of: the gastrointestinal tract. The absolute bioavailability of a single
500mg dose is reported to be about 50% to 60%, although this is
H 3C O reduced somewhat if taken with food. Once absorbed plasma protein
O H CH3
N C binding is negligible. It is excreted unchanged in urine. The plasma
H3 C–CH2 O NH CH2 CH2 SO 2 NH C NH H elimination half-life is reported to range from about 2-6 hours after
oral doses. Metformin crosses the placenta and is distributed into
Glimepiride breast milk in small amounts.
Chemically metformin HCl is known as 1,1-dimethyl biguanide Special Populations
hydrochloride having a molecular formula of C4H11 N5.HCl and a Renal Impairment
structural formula of: Glimepiride
CH3 Glimepiride serum levels decreased as renal function decreased.
I H However, metabolites serum levels (mean AUC values) increased.
N N NH 2 The apparent terminal half-life (T1/2) for glimepiride did not change,
H3C • HCI while the half-lives for metabolites increased as renal function
NH NH decreased. Mean urinary excretion of metabolites as percent of
dose, however, decreased.
Metformin HCl
Metformin HCl
QUALITATIVE & QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION In patients with impaired renal function, renal clearance is decreased
GETFORMIN (Glimepiride + Metformin HCl) is available for oral in proportion to that of cre atinine and thus the e limination half-life
administration as: is prolonged, leading to increased levels of metformin in plasma.
THERAPEUTIC INDICATIONS
1. GETFORMIN Tablets 1mg+500mg
GETFORMIN (Glimepiride + Metformin HCl) is indicated as an
Each film-coated tablet contains:
adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in patients
Glimepiride USP…1mg
with type 2 diabetes who se diabetes is not adequately controlled
Metformin HCl USP... 500mg
with glimepiride or metformin HCl alone, or for those patients w ho
have initially responded to glimepiride or metformin HCl alone and
2. GETFORMIN Tablets 2mg+500mg
require additional glycemic control.
Each film-coated tablet contains:
Glimepiride USP... 2mg DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
Metformin HCl USP... 500mg Dosage must be individualized on the basis of both effectiveness
and tolerance, while not exceeding the maximum recommended
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY dose. The maximum daily dose of metformin is 2000mg and of
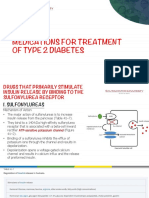
Mechanism of Action glimepiride is 8mg. The tablets should be swallowed whole and not
Glimepiride: crushed or chewed. The tablet is tak en once daily with meals t o a
Glimepiride is a third generation sulphonylurea. The primary maximum of 4 tablets/day or as directed by the physician.
mechanism of action of glimepiride appears to be dependent on
stimulating the release of insulin from functioni ng pancreatic b eta ADVERSE REACTIONS
cells. Diarrhea, vomiting, metallic taste, rash, isolated transaminase
In addition, extrapancreatic effects (e.g. reduction of basal hepatic elevations, cholestatic jaundice, allergic skin reactions, photosensitivity
glucose production and increased peripheral tissue sensitivity to reactions, leukopenia, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia, hemolytic
insulin and glucose uptake) may also play role in the activity of anemia, aplastic anemia, pancytopenia and blurred vision.
glimepiride. Glimepiride appears to be associated with a low incidence of
hypoglycemia. It has also been found to have low propensity
Metformin HCl: to cause adverse cardio vascular effects. Impaired gastrointestinal
Metformin hydrochloride is a biguanide anti-diabetic, which improves absorption of vitamin B12 and folic acid has been associated with
glucose tolerance in patients with type 2 diabetes, lowering both long term metformin therapy. Rarely, metformin administration has
basal and postprandial plasma glucose. Its mode of action is thought resulted in lactic acidosis.
to be multifactoral and includes delayed uptake of glucose from the
intestinal tract, increased peripheral glucose utilization mediated by CONTRAINDICATIONS
increased insulin sensitivity and inhibition of increased hepatic and Glimepiride + Metformin HCl combination is contraindicated in:
renal gluconeogenesis. − Patients with known hypersensitivity to sulfonylurea or biguanide
or any component of the drug.
Sulfonylureas and biguanides act complementary to each other.
− Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.
Both compounds have an additive anti-hyperglycemic effect without
− Renal or hepatic failure.
increasing the adverse effects of either pharmacological class.
− Alcoholism.
− NIDDM complicated by severe ketosis and acidosis.
Pharmacokinetics
− Diabetic pre-coma and coma.
Glimepiride:
− Patients undergoing surgery, after severe trauma or during
After oral administration glimepiride is completely absorbed from the
infections.
GI tract. The oral bioavailability is approximately 100%. Peak plasma
− Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
concentrations occur in 2-3 hours. More than 99% of the drug is
− Coronary heart disease, cardiac failure.
bound to plasma proteins. Glimepiride is completely metabolized by
− Peripheral vascular disease. risk of lactic acidosis. Metformin should be discontinued prior to,
− Pregnancy and lactation. or at the time of the test and not reinstituted untill 48 hours
afterwards and onl y after renal function has been re-evaluated
PRECAUTIONS and found to be normal.
General
− Hypoglycemia may occur if the patient's dietary intake is reduced OVERDOSE
or after accidental or deliberate overdose or after severe exercise, Glimepiride:
trauma and stress. Hypoglycemic symptoms can be reduced by An overdosage of Glimepiride can produce severe hypoglycemia.
prescribing a diabetic meal plan. Immediate intervention should Mild episodes of hypoglycemia can be treated with oral glucose.
be done if signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia occur. Severe hypoglycemic reactions constitute medical emergencies
Adjust dose of drug according to blood and urinary glucose levels requiring immediate treatment. Severe hypoglycemia with coma,
during the first few months. seizure or neurological impairment can be treated with glucagon or
− The patient’s fasting blood glucose and HbA1c must be measured intravenous glucose. Continued observation and additional
periodically to determine the minimum effective dose for the
carbohydrate intake may be necessary because hypoglycemia may
patient. After an initial period of effectiveness glycosylated
recur after apparent clinical recovery.
hemoglobin levels should be performed to monitor the patient’s
response to therapy.
Metformin HCl:
Lactic acidosis A large overdose of Metformin HCl may lead to lactic acidosis.
Lactic acidosis is rare, but serious metabolic complication that can Hemodialysis may be useful for removal of accumulated Metformin HCl
occur due to metformin accumulation. The incidence of lactic acidosis from patients in whom Metformin HCl overdosage is suspected.
can and should be reduced by assessing also other associated risk
factors such as poorly controlled diabetes, ketosis, prolonged fasting,
STORAGE
excessive alcohol intake, hepatic insufficien cy and any condition
Store at 25°C (Excursions permitted between 15°C-30°C).
associated with hypoxia.
Protect from sunlight and moisture.
Renal function
As metformin is excreted by the kidney, serum creatinine levels The expiration date refers to the product correctly stored at the
should be determined before initiating treatment and regularly required conditions.
thereafter.
HOW SUPPLIED
Pediatric use GETFORMIN (Glimepiride + Metformin HCl) Tablets 1mg+500mg
Safety and effectiveness of the drug in children have not been are available in blister pack of 30’s.
established.
GETFORMIN (Glimepiride + Metformin HCl) Tablets 2mg+500mg
Drug Interactions are available in blister pack of 30’s.
Glimepiride:
− The hypoglycemic action of sulfonylureas may be potentiated by Keep out of reach of children.
certain drugs, including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and
other drugs that a re highly protein bound, such as salicylates, To be sold on prescription of a registered medical practitioner
sulfonamides, chloramphenicol, coumarins, probenecid, only.
monoamine oxidase inhibitors and beta adrenergic blocking
agents. When these drugs are administered to a patient receiving
glimepiride, the patient should be observed closely for Please read the contents carefully before use.
hypoglycemia. This package insert is contin ually updated from time to t ime.
− Certain drugs tend to produce hyperglycemia an d may lead to
loss of control. These drugs include the thiazides and other
diuretics, corticosteroids, phenothiazines, thyroid products,
estrogens, oral contraceptives, phenytoin, nicotinic acid,
sympathomimetics and isoniazid. When these drugs are
administered to a patient receiving glimepiride, the patient should
be closely observed for loss of control.
− Glimepiride is metabolised by cytochrome P450 2C9 (CYP2C9).
This should be taken into account when glimepiride is
coadministered with inducers, inhibitors or substrates of CYP2C9
(e.g. rifampicin, fluconazole, amiodarone, tolbutamide, diclofenac,
ibuprofen, naproxen).
− H2 receptor antagonists, beta-blockers, clonidine and reserpine
may lead to either potentiation or weakening of the blood-glucose-
lowering effect.
− Acute and chronic alcohol intake may either potentiate or attenuate
the activity of glimepiride in an unpredictable fashion.
Metformin HCl:
− Drug interactions of metformin is seen with phenprocoumon,
hyperglycemic agent (e.g. - thiazides, corticosteroids,
phenothiazines, thyroid products, estrogens, oral contraceptives,
phenytoin, nicotinic acid, sympathomimetics, cal cium channel
blocking drugs and isoniazid), alcohol, furosemide, nifedipine
and cationic drugs (amiloride, digoxin, morphine, procainamide,
quinidine, quinine, ranitidine, triamterene, trimethoprim and Manufactured by:
cimetidine, vancomycin). The absorption of metformin may be
reduced by acarbose and guar gum.
− Intravascular administration of iodinated contrast agents may
lead to renal failure, resulting in metformin accumulation and a 200007821
Вам также может понравиться
- Hypoglycemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsОт EverandHypoglycemia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsОценок пока нет
- GLIMITAB M-1/GLIMITAB M-2 Tablets: CompositionДокумент6 страницGLIMITAB M-1/GLIMITAB M-2 Tablets: Compositiongaurav7augОценок пока нет
- Name Accession Number Type Groups Description: Show EntriesДокумент14 страницName Accession Number Type Groups Description: Show EntriesIndrayansah SiahaanОценок пока нет
- Oral Management of Diabetes Type IIДокумент34 страницыOral Management of Diabetes Type IIYasser Gebril100% (1)
- Unit 5 Part 2 InsulinДокумент61 страницаUnit 5 Part 2 InsulinKhairunnisa LoqmanОценок пока нет
- GlimepirideДокумент12 страницGlimepirideMobahil AhmadОценок пока нет
- Endo Pharma ElhДокумент14 страницEndo Pharma Elhodiodi57Оценок пока нет
- Oral Diabetes Mellitus MedicationsДокумент43 страницыOral Diabetes Mellitus MedicationsSanjeev Harry BudhooramОценок пока нет
- Zolid Tab Leaflet PakistanДокумент2 страницыZolid Tab Leaflet PakistanKhawaja Sajjad SaeedОценок пока нет
- Pi GlucophageДокумент35 страницPi GlucophageJennyLapitanОценок пока нет
- Zoliget 15mg 2mg Zoliget 30mg 2mgДокумент2 страницыZoliget 15mg 2mg Zoliget 30mg 2mgAZIZ UR RAHMANОценок пока нет
- Vilda MetДокумент28 страницVilda Metnaeem186Оценок пока нет
- Anti Diabetic DrugДокумент45 страницAnti Diabetic DrugRahul LokhandeОценок пока нет
- Amaryl M PI - May 2018marylДокумент11 страницAmaryl M PI - May 2018marylvicky upretiОценок пока нет
- Terapi DMДокумент65 страницTerapi DMditaОценок пока нет
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Документ42 страницыDiabetes Mellitus Type 2alexandrajane2007Оценок пока нет
- PamarylДокумент14 страницPamarylPharmacist ipsОценок пока нет
- Review of Pharmacology (PGMEE) Paperback - 2018 (PDFDrive)Документ1 страницаReview of Pharmacology (PGMEE) Paperback - 2018 (PDFDrive)Muez AlkeblawiОценок пока нет
- 4 Oral Hypoglycaemic DrugsДокумент10 страниц4 Oral Hypoglycaemic DrugsNashat SaadiОценок пока нет
- Metformin HCLДокумент3 страницыMetformin HCLAusaf AhmadОценок пока нет
- Actosmet+e+pi 20120405Документ44 страницыActosmet+e+pi 20120405Eva BanjarnahorОценок пока нет
- Drugs in Type 2 DMДокумент18 страницDrugs in Type 2 DMhussain AltaherОценок пока нет
- Pharmacotherapy of Diabetes MellitusДокумент32 страницыPharmacotherapy of Diabetes MellitusGhilli Jaya PrakashОценок пока нет
- PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY - AntihistaminesДокумент283 страницыPHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY - AntihistaminesGianniОценок пока нет
- Farmakoterapi DMДокумент49 страницFarmakoterapi DMTri Aji PujoОценок пока нет
- ANTI-DIABETIC AGENTS (OHAs)Документ42 страницыANTI-DIABETIC AGENTS (OHAs)Prajwal Rao KОценок пока нет
- Merged 3rd ShiftДокумент166 страницMerged 3rd Shiftreag0megaОценок пока нет
- Glipita MДокумент4 страницыGlipita M2019-1-55-003Оценок пока нет
- Pharmaceuticals 03 03005Документ16 страницPharmaceuticals 03 03005vigneshkumar.r3850Оценок пока нет
- Treatment of Diabetes MellitusДокумент31 страницаTreatment of Diabetes MellitusIrfan IdealistОценок пока нет
- PamarylДокумент9 страницPamarylPharmacist ipsОценок пока нет
- AntiDiabetic Drugs 2 BДокумент50 страницAntiDiabetic Drugs 2 BAvinash RajОценок пока нет
- Mefenamic AcidДокумент6 страницMefenamic AcidArisa VijungcoОценок пока нет
- Metformina y DiabetesДокумент21 страницаMetformina y DiabetesBetty Isabel GarcíaОценок пока нет
- Diabetes Type 2 HassanДокумент26 страницDiabetes Type 2 Hassanyash_acharya007100% (1)
- Drug Interaction DMT2Документ12 страницDrug Interaction DMT2Dhonat FlashОценок пока нет
- Icjpir-15-103 9-14Документ6 страницIcjpir-15-103 9-14Sriram NagarajanОценок пока нет
- Oral HypoglycemicДокумент5 страницOral HypoglycemicDavid HosamОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент13 страницDrug StudyAllan DiazОценок пока нет
- Pharmacological Principles Used in Patient Monitoring With Type 2 DiabetesДокумент6 страницPharmacological Principles Used in Patient Monitoring With Type 2 DiabetesCristian-Catalin GavatОценок пока нет
- DR - Mohammed Qasim 2017-2018 4 GradeДокумент60 страницDR - Mohammed Qasim 2017-2018 4 GradeFarah Bashar Al-RawachyОценок пока нет
- Oral HypoglycemicsДокумент50 страницOral HypoglycemicsSudhakar LakavathОценок пока нет
- MPT2081Документ11 страницMPT2081debkantha gopeОценок пока нет
- Amaryl 1mg Tablets - (eMC) Print Friendly PDFДокумент9 страницAmaryl 1mg Tablets - (eMC) Print Friendly PDFrakeshОценок пока нет
- Diabetes MedicationДокумент17 страницDiabetes MedicationTaj lamajedОценок пока нет
- ADO1 Agst 2013Документ48 страницADO1 Agst 2013blackjackОценок пока нет
- What Is Diabetes, Its Types, Role of Insulin and Hypoglycemic Agents, Mode of Action, Side Effects, Pharmacodynamics and PharmacokineticsДокумент9 страницWhat Is Diabetes, Its Types, Role of Insulin and Hypoglycemic Agents, Mode of Action, Side Effects, Pharmacodynamics and PharmacokineticsIshaani GargОценок пока нет
- Insulin and Antidiabetic Drugs: BSC Nursing Online and Offline Lecture SeriesДокумент27 страницInsulin and Antidiabetic Drugs: BSC Nursing Online and Offline Lecture SeriesSayan ChatterjeeОценок пока нет
- MetFormin Generic Health TabДокумент9 страницMetFormin Generic Health TabNur Ekayani SyamОценок пока нет
- MetforminДокумент5 страницMetforminAyeshaОценок пока нет
- Oral Anti Diabetic (OAD) : Indwiani Astuti Dept Pharmacology & Therapy Fac of Medicine Universitas Gadjah MadaДокумент34 страницыOral Anti Diabetic (OAD) : Indwiani Astuti Dept Pharmacology & Therapy Fac of Medicine Universitas Gadjah MadakikiaprilianiОценок пока нет
- Antidiabetic DrugsДокумент68 страницAntidiabetic DrugsninetysevenccОценок пока нет
- Shock Acute Myocardial Infarction Septicemia Precautions Diabetic KetoacidosisДокумент3 страницыShock Acute Myocardial Infarction Septicemia Precautions Diabetic KetoacidosisArienne_Mae_A__6554Оценок пока нет
- Drug Index Patient 2203Документ3 страницыDrug Index Patient 2203Arienne_Mae_A__6554Оценок пока нет
- The Side Effects of Metformin A ReviewДокумент7 страницThe Side Effects of Metformin A ReviewAlberto LiaoОценок пока нет
- Update On Diabetes Treatment - 2018Документ33 страницыUpdate On Diabetes Treatment - 2018Nanda SalmasОценок пока нет
- Treviamet Tab Leaflet PakistanДокумент2 страницыTreviamet Tab Leaflet PakistanAmir IntizarОценок пока нет
- Endocrine 1677476082Документ36 страницEndocrine 1677476082Winhtut ThantОценок пока нет
- Pancreatic Hormones Antidiabetic Drugs Part 2Документ24 страницыPancreatic Hormones Antidiabetic Drugs Part 2jenet soleilОценок пока нет
- Aronson, JK. Sulonylurea. Meyler's Side Effects of Drugs (Sixteenth Edition)Документ19 страницAronson, JK. Sulonylurea. Meyler's Side Effects of Drugs (Sixteenth Edition)SupriОценок пока нет
- PatientReportPDF 15Документ1 страницаPatientReportPDF 15Muhammad Vaqar HussainОценок пока нет
- Nagarmotha PDFДокумент17 страницNagarmotha PDFMuhammad Vaqar HussainОценок пока нет
- Nagarmotha PDFДокумент17 страницNagarmotha PDFMuhammad Vaqar HussainОценок пока нет
- Nagarmotha PDFДокумент17 страницNagarmotha PDFMuhammad Vaqar HussainОценок пока нет
- International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Chemistry: Phytochemical and Antimicrobial Studies OnДокумент4 страницыInternational Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Chemistry: Phytochemical and Antimicrobial Studies OnMuhammad Vaqar HussainОценок пока нет
- Serious Fungal Infections in PakistanДокумент8 страницSerious Fungal Infections in PakistanMuhammad Vaqar HussainОценок пока нет
- Cambridge Recognition Brochure PakistanДокумент10 страницCambridge Recognition Brochure PakistanMuhammad Vaqar HussainОценок пока нет
- PT 1 Midterm RubricДокумент3 страницыPT 1 Midterm RubricJohann Sebastian CruzОценок пока нет
- NIH Document Production Cover Letter 2021.10.20 McMorris RodgersДокумент2 страницыNIH Document Production Cover Letter 2021.10.20 McMorris RodgersAl StatiliusОценок пока нет
- Advanced Herd Health Management, Sanitation and HygieneДокумент28 страницAdvanced Herd Health Management, Sanitation and Hygienejane entunaОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Soya BeanДокумент6 страницIntroduction To Soya BeanMisbah FatimahОценок пока нет
- Lesson 5: Tabata TrainingДокумент31 страницаLesson 5: Tabata TrainingAshley Keith RamiloОценок пока нет
- Acute PancreatitisДокумент40 страницAcute PancreatitisAbdulsalam DostОценок пока нет
- Bdda2948944613921 1Документ2 страницыBdda2948944613921 1info.worldwideimmigration.comОценок пока нет
- Major Haemorrhage ProtocolДокумент2 страницыMajor Haemorrhage ProtocollaurenОценок пока нет
- Research Essay Final DraftДокумент14 страницResearch Essay Final Draftapi-558668635Оценок пока нет
- Sem 2 M.pharm PresentationДокумент16 страницSem 2 M.pharm PresentationPriya ShahОценок пока нет
- Integrative Cell Therapy Program EBrochureДокумент16 страницIntegrative Cell Therapy Program EBrochureAnonymous 5X7ELhpE100% (1)
- Webinar Lung CancerДокумент53 страницыWebinar Lung CancerJose Flores FernandezОценок пока нет
- Ijshr0038 PDFДокумент9 страницIjshr0038 PDFNilakshi Barik MandalОценок пока нет
- Ventilation Health Guide COVID 19Документ25 страницVentilation Health Guide COVID 19Carlos Valle TurciosОценок пока нет
- Revision Sistematica Preparacion A La Practica Dental 2018Документ9 страницRevision Sistematica Preparacion A La Practica Dental 2018Chris MartinОценок пока нет
- Learning Plan Nursing PregradДокумент3 страницыLearning Plan Nursing Pregradapi-25180064033% (3)
- InfluenzaДокумент7 страницInfluenzaGionne Carlo GomezОценок пока нет
- 00 - Introduction To PharmacologyДокумент19 страниц00 - Introduction To PharmacologyChipego NyirendaОценок пока нет
- Mrs. Garima Chauhan - TechnostressДокумент68 страницMrs. Garima Chauhan - TechnostressMukesh ChauhanОценок пока нет
- Roche ProductДокумент6 страницRoche ProductAndika Wira BangsawanОценок пока нет
- The Newcastle Upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Asepsis PolicyДокумент10 страницThe Newcastle Upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Asepsis Policyyousrazeidan1979Оценок пока нет
- Vlaar2021 Article TransfusionStrategiesInBleedinДокумент25 страницVlaar2021 Article TransfusionStrategiesInBleedinRaul DoctoОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER 1-Public Health (Environmental Pollution and Control)Документ18 страницCHAPTER 1-Public Health (Environmental Pollution and Control)muhdakmaladnan100% (4)
- The Concept of Powerlessness in Patient Treatment Nursing EssayДокумент38 страницThe Concept of Powerlessness in Patient Treatment Nursing EssayreginesulibОценок пока нет
- Gubra DIO Mouse Data FlyerДокумент2 страницыGubra DIO Mouse Data FlyerGabrielaMirelaAlexeОценок пока нет
- Ranjit Kumar-Research Methodology A Step-by-Step G-25-26Документ2 страницыRanjit Kumar-Research Methodology A Step-by-Step G-25-26Trendy NewsОценок пока нет
- Homoeopathic Management of Diabetes Mellitus Among Post-Menopausal Women by Helonias Dioica: A Case SeriesДокумент7 страницHomoeopathic Management of Diabetes Mellitus Among Post-Menopausal Women by Helonias Dioica: A Case SeriesAghosh B PrasadОценок пока нет
- Fistula NCPДокумент1 страницаFistula NCPHasna LisnaОценок пока нет
- Effect of Probiotics As A Complement To Non Surgical Periodontal Therapy in Chronic Periodontitis A Systematic RevieДокумент7 страницEffect of Probiotics As A Complement To Non Surgical Periodontal Therapy in Chronic Periodontitis A Systematic RevieMohammedОценок пока нет
- Outpatients Unit - Guideline Section - International Health Facility GuidelinesДокумент23 страницыOutpatients Unit - Guideline Section - International Health Facility GuidelinesSebastian laierОценок пока нет